1. System startup process
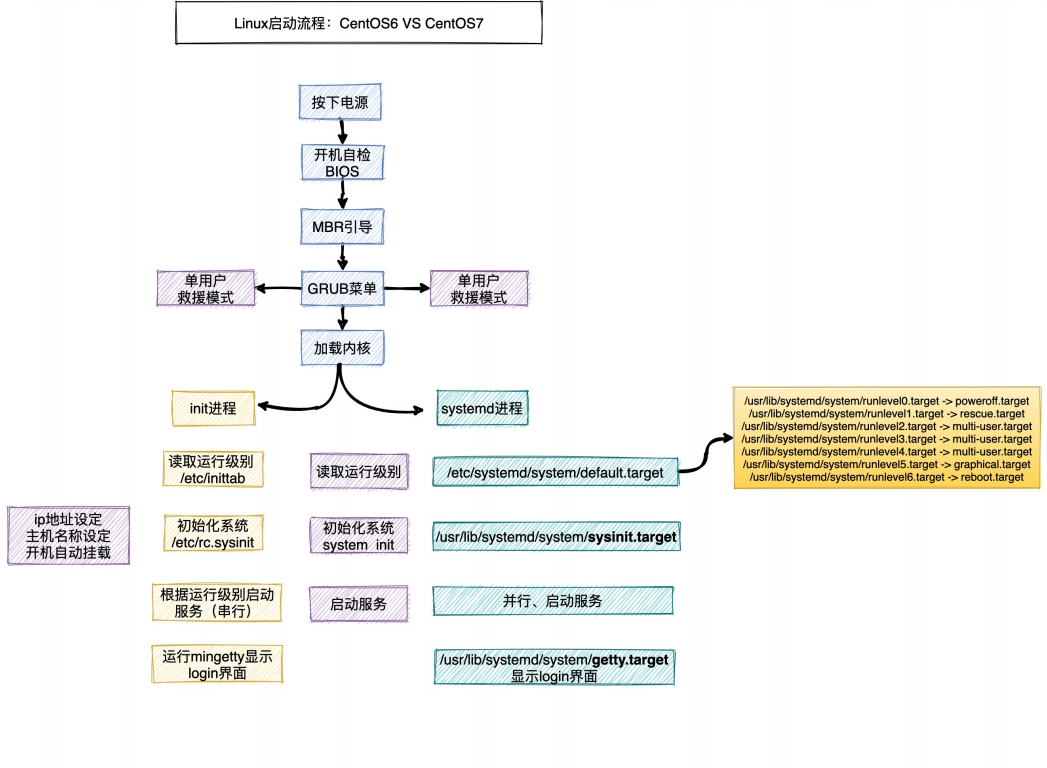
2. Start operation level
2.1 what is the operation level
Run level: refers to the functional level at which the operating system is running
| system V init run level | systemd target name | effect |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | runlevel0.target,poweroff.target | Shut down |
| 1 | runlevel1.target,rescue.target | Single user mode (change password) |
| 2 | runlevel2.target,multi-user.target | |
| 3 | runlevel3.target,multi-user.target | Character interface (maximum) |
| 4 | runlevel4.target,multi-user.target | |
| 5 | runlevel5.target,graphical.target | Graphical interface |
| 6 | runlevel6.target,reboot.target | restart |
2.2 adjust operation level
- systemd uses targets instead of runlevels. There are two
Main objectives:
. multi-user.target: similar to runlevel 3
. graph ical.target: similar to runlevel 5
1. View the default operation level of the system
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default multi-user.target
2. To set the default target, run
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl set-default TARGET.target # TARGET.target run target
3.systemd management
3.1 origin of SYSTEMd
- Linux has always adopted init process as its ancestor process, but
Yes, init has two disadvantages:
1. The system takes a long time to start. The init process is started serially and only
After the previous process is started, the next process will be started;
2. The startup script is complex. After initializing the system, many scripts will be loaded. The scripts will deal with their own situations, and there are many and miscellaneous scripts;
3. Write script; - systemd is the system daemon. systemd was born to solve the above problems
- The goal of systemd is to provide a complete solution for system startup and management;
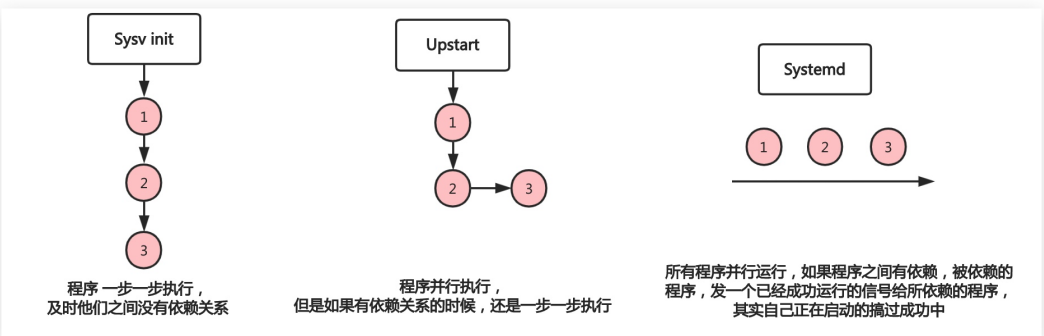
- Centos5 is slow to start, and the process of serial start, regardless of whether the processes depend on each other or not.
- The startup speed of Centos6 has been improved. Processes with dependencies are started in turn, while others without dependencies are started in parallel and synchronously.
- All processes in Centos7 are started in parallel whether they have dependencies or not (of course, most of the time, the process is not really started, but only a signal or mark, which will be really started when it is really used.)
3.2 advantages of SYSTEMd
- 1. The latest systems use systemd to manage RedHat7, CentOS7 and Ubuntu 15;
- 2. Centos7 supports parallel startup service, which significantly improves startup efficiency;
- 3. When Centos7 is shut down, only running services are shut down, while Centos6 is shut down once;
- 4. The start and stop of Centos7 services are not managed by scripts, that is, / etc / init There is no script under D;
- 5. Centos7 uses systemd to solve the defects of the original mode. For example, the original service will not close the subprocess generated by the program;
3.3 systemd related commands
- /usr/lib/systemd/system /: service startup and shutdown files. Start, stop and reload the files through systemctl command
| command | meaning |
|---|---|
| systemctl start crond | Start service |
| systemctl stop crond | Out of Service |
| systemctl restart crond | Restart service |
| systemctl reload crond | Overload service |
| systemctl enable crond | The service is set to start and run |
| systemctl disabled crond | The service is set to start and not run |
| systemctl daemon-reload crond | Creating a service startup file requires overloading the configuration |
| systemctl list-unit-files | View the startup and disabling of services at various levels |
| systemctl is-enabled crond.service | Check whether a specific service is self started |
| systemctl is-active crond | Check whether the service is running |
3.4 systemd management Nginx
1. Compiling nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.21.1]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx- 1.21.1.tar.gz [root@localhost nginx-1.21.1]# tar xf nginx-1.21.1.tar.gz [root@localhost nginx-1.21.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.21.1 --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --without-http [root@localhost nginx-1.21.1]# make && make install [root@localhost nginx-1.21.1]# ln -s /usr/local/nginx-1.21.1/ /usr/local/nginx
2. Conventional startup nginx mode
4. Rescue mode
4.1 scenario 1 - forget the super administrator password
- How to use single user mode to change system password? Take Centos7 system as an example:
. Step 1: when the Linux system host is restarted and the boot interface appears, press the e key on the keyboard to enter the kernel editing interface
. Step 2: add forcing = 0 init = / bin / bash after the line of Linux 16, and then press Ctrl + x to enter
. Step 3: enter the single user mode of the system, enter the following commands in sequence, restart the operating system and log in with a new password
1. mount -o rw,remount / default / partition read only,
Remount to read-write mode
2. echo "123" | passwd --stdin root: not
Interactive password modification
3. exec /sbin/init: reboot the system
4.2 scenario 2 - data backup required due to system damage
- When the system breaks down and can't log in to the system, but you need to copy the data inside, what should I do?
Step 1: Mount ISO image file, modify BIOS and adjust
The DVD disc is the first boot;
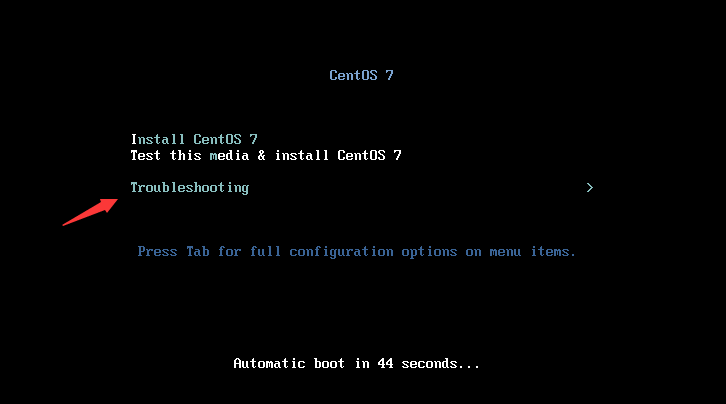
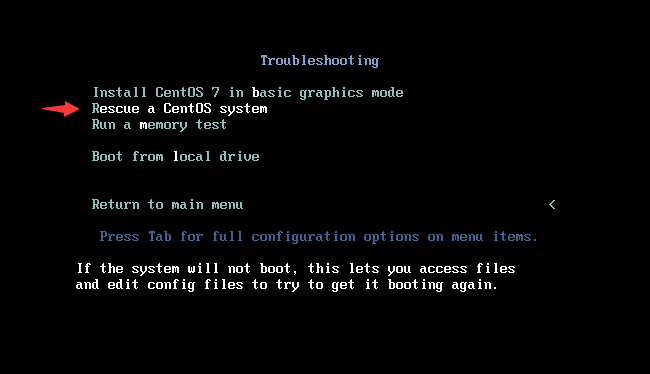
Step 2: select Troubleshooting and continue to select
Rescue a CentOS system rescue mode;
Step 3: enter 1, and then execute the command chroot /mnt/sysimage to mount the real system;
Step 4: back up the data files in the system to other disks;
4.3 scenario 3 - how to repair a grub file accidentally deleted by Centos
Step 1: simulate the false deletion fault RM -rf / boot / Grub2 & & reboot
Step 2: the system cannot be started normally (prompt grub cannot be found)
To)
Step 3: then enter the rescue mode according to the previous operation and execute
chroot /mnt/sysimage mounts the real operating system;
Step 4: use grub2 related commands to repair
Grub2 install / dev / SDA re add mbr boot
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Rebuild configuration
Enter exit
reboot again
ls /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
 After restart
After restart
5. System optimization
- cpu:
. 1. Virtualization support
. 2. cpu hyper threading - disk
. 1,SAS
. 2,SSD
5.1 adjusting the source
- The yum warehouse provided by the default installation system is a foreign site. You can modify the site to a domestic site to speed up the download of software packages
# base [root@oldxu ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos- 7.repo # epel [root@oldxu ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo # mysql, zabbix, elk packages
5.2 turn off the firewall
- By default, the firewall will be closed to avoid affecting the use of later services;
. Virtual machine: there are security group products provided by hardware to provide protection;
. Physical machine: generally, companies have hardware firewalls at the entrance level;
# firewalld [root@oldxu ~]# systemctl stop firewalld [root@oldxu ~]# systemctl disabled firewalld # selinux [root@oldxu ~]# setenforce 0 [root@oldxu ~]# sed -i '/^SELINUX=/c SELINUX=disabled' /etc/selinux/config
5.3 ulimit resource constraints
- The ulimit command can control system resources
. - u: Limit the maximum number of processes that ordinary users can open; (per user)
. - n: Limit the number of file descriptors that users can allocate;
5.3.1 limit the maximum number of processes
1. Limit the maximum number of open processes per user to 3
[root@localhost ~]# ulimit -u 500 #Temporarily effective, the current window switches users
5.3.2 limit the number of open files
1. Limit the maximum open file descriptor of the process to 10
[root@localhost ~]# ulimit -n 10 #Temporarily effective, the current window switches users
2. Write a python program to simulate opening multiple files
#!/usr/bin/env python
import time,os
from threading import Thread
print(os.getpid())
def new_file(n):
with open('%s.file' %n,mode='wt') as f1:
time.sleep(2000)
if __name__ == "__main__":
count=1
while True:
Thread(target=new_file,args= (count,)).start()
count+=1
3. After waiting for a period of time, the program will prompt when the open file exceeds the limit
Abnormal;
Exception in thread Thread-16128: Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/lib64/python2.7/threading.py", line 812, in __bootstrap_inner File "/usr/lib64/python2.7/threading.py", line 765, in run File "o.py", line 8, in new_file IOError: [Errno 24] Too many open files: '1.file'
5.3.3 adjusting ulimit limit parameters
- Adjusting the number of open files and processes through ulimit is a temporary operation, so it needs to be permanently configured
. Configuration file: / etc / security / limits conf
. Adjustment mode:
Soft: soft limit. If it exceeds, you will be prompted;
Hard: hard limit, if exceeded, stop;
[root@localhost ~]# tail /etc/security/limits.conf #ftp hard nproc 0 #@student - maxlogins 4 # End of file # max user processes * soft nproc 60000 * hard nproc 60000 # open files # * soft nofile 100000 #2 ^ 16-1 (the 16th power of 2 cuts 1) * hard nofile 100000 #2 ^ 16-1 (the 16th power of 2 cuts 1) # At the system level, add the following fields (only after adjusting the kernel can it take effect) [root@localhost ~]# tail -10 /etc/sysctl.conf # /usr/lib/sysctl.d/, /run/sysctl.d/, and /etc/sysctl.d/. # # Vendors settings live in /usr/lib/sysctl.d/. # To override a whole file, create a new file with the same in # /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. To override # only specific settings, add a file with a lexically later # name in /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. # # For more information, see sysctl.conf(5) and sysctl.d(5). fs.file-max = 100000