shell script
A shell script is a collection of commands
#!/bin/bash echo "The beginning of the file means that the file uses bash grammar"
1, Run sh file
Method 1: execute the current file sh file
# The file must contain x Execution Authority [Document assignment x jurisdiction: chmod u+x hello.sh] ./test.sh # The file can be empty x jurisdiction sh test.sh
Method 2: absolute path execution sh file
/home/test/test.sh ./home/test/test.sh sh /home/test.test.sh
View running process
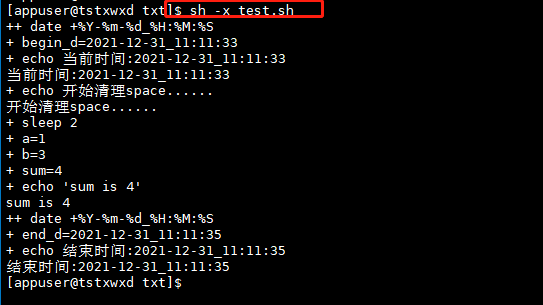
sh -x test.sh
Run Preview
2, Scripting
# function.sh file [~]$ sh test.sh
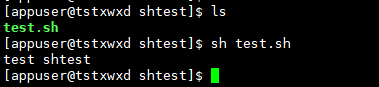
Example 1: output content to console
# test.sh content echo "test shtest"
Operation results
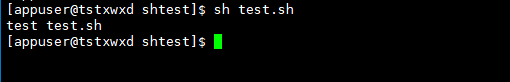
Example 2: variable format: "variable name = variable value". When referring to a variable in a script, you need to add the '$' symbol or "${variable}"
# variable var_name ;Reference variable $var_name var_name="test.sh" echo "test $var_name"
Execution results
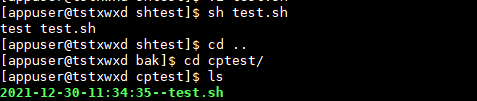
Example 3: copying files
# variable `date......` [`Not a single quote, but an inverse single quote] var_name="test.sh" echo "test $var_name" cp /home/appuser/ntest/$var_name /home/appuser/cptest/`date "+%Y-%m-%d-%H:%M:%S"`--$var_name
Execution results
Example 4: use the result of executing the command as variable output
# variable var_name="test.sh" var_para=$(ls) echo "test Output variables: $var_name" echo "test Output the result variable of executing the command: ${var_para}"
Execution results
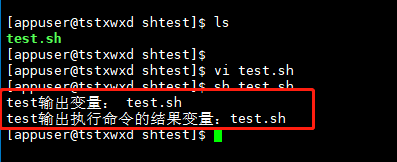
Example 5: user input , indicates in_ The value of the name variable needs to be entered by the user through the keyboard
# Writing method 1: read -p Similar options echo Role of read -p "Please enter your name:" in_name echo "The name you entered is:$in_name" # Writing method 2: there will be line feed input echo "Please enter your age:" read in_age echo "The age you entered is: $in_age"
Operation results
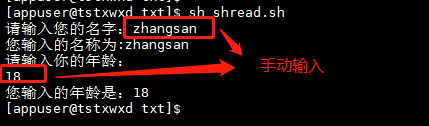
Example 6: create a file with the current time as a variable
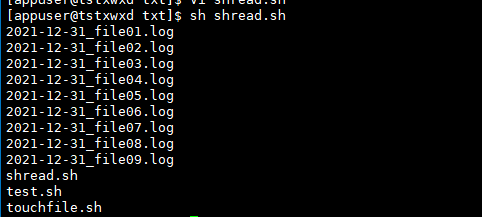
now_date=$(date "+%Y-%m-%d_%H:%M:%S") echo "current time :$now_date" # Batch create files touch file{01..03}_$now_date.log #touch ${now_date}_file{04..07}.log
# touchfile.sh Create file script filename="$(date +%Y-%m-%d)" echo "Start creating file......" touch ${filename}_file{01..09}.log echo "Created successfully" echo "$(ls)
Operation results
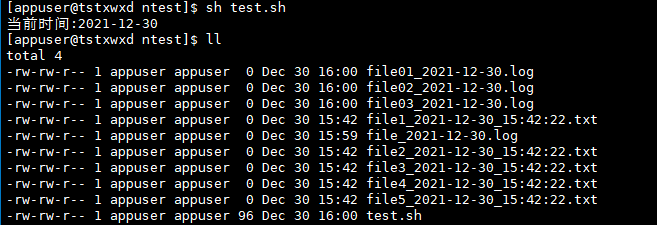
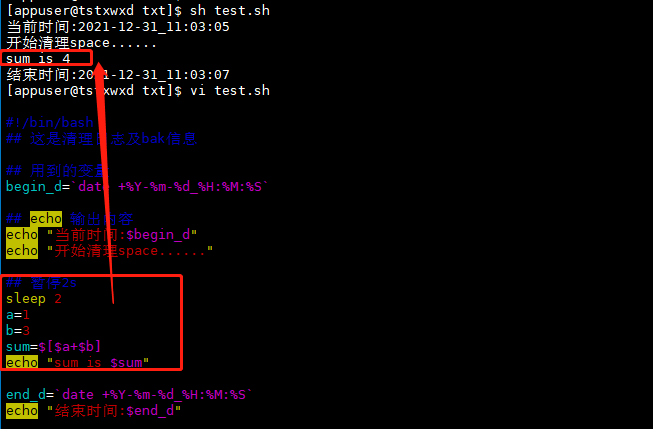
Example 7: the mathematical calculation should be enclosed by '[]' and a '$' should be taken outside
# Pause 2 s sleep 2 # variable a=1 b=3 # calculation a,b Sum of sum=$[$a+$b] echo "sum is $sum"
Operation results
Example 8: preset variables
# $1 The value of is 1 entered during execution, and $2 The value of is entered during execution $2 $0 Represents the file name echo "$0 $1 $2" sum=$[$1+$2] echo $sum
Operation results
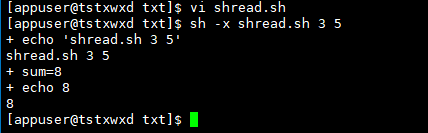
Example 9: logical judgment
if Judgment statement; then command elif Judgment statement;then command else command fi
# No else ((nums<20))Because.sh In, using a parenthesis or not will report an error read -p "Please enter a number:" nums if ((nums<20));then echo "Input cannot be less than 20" fi # belt else read -p "Please enter a number:" nums if ((nums<20));then echo "Input cannot be less than 20" else echo "congratulations" fi
# belt elif ;there && It means "and". Of course, you can also use it || Means "or" read -p "Please enter a number:" nums if ((nums<20));then echo "Input cannot be less than 20" elif ((nums>25))&&((nums<42));then echo "25==42" else echo "congratulations" fi
## Note: in addition to "(())", "[]" can also be used in if judgment. However, symbols such as >, <, = cannot be used. Use - lt (less than), - gt (greater than), - le (less than or equal), - ge (greater than or equal), - eq (equal to), - ne (not equal to) read -p "Please enter a number:" nums if [ $nums -lt 20 ];then echo "Input cannot be less than 20" elif [ $nums -gt 25 ] && [ $nums -lt 42 ];then echo "25==42" else echo "congratulations" fi
Operation results
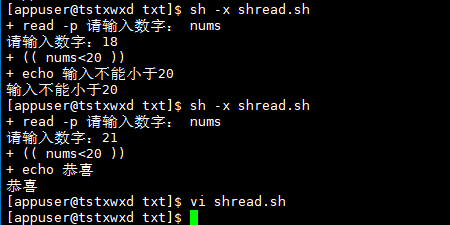
Example 10: judging document attributes
# The format is: if [ -e filename ] ; then # -e : Determine whether the file or directory exists if [ -e touchfile.sh ];then echo "touchfile.sh File exists" fi #-d : Determine whether it is a directory and whether it exists if [ -d touchfile.sh ];then echo "It's a directory" else echo "touchfile.sh Not a directory" fi #-f : Judge whether it is an ordinary file and exists if [ -f touchfile.sh ];then echo "touchfile.sh It's a normal file" fi #-r : Determine whether the document has read permission if [ -r touchfile.sh ];then echo "touchfile.sh Have read permission" fi #-w : Judge whether there is write permission if [ -w touchfile.sh ];then echo "touchfile.sh Have write permission" fi #-x : Determine whether it is executable if [ -x touchfile.sh ];then echo "touchfile.sh Is an executable" fi
Operation results
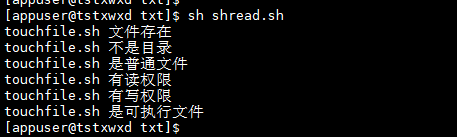
Example 11: logical judgment case; Unlimited number of value s (used to write startup scripts for system services)
case variable in value1) command ;; value2) command ;; value3) command ;; *) command ;; esac
read -p "For parity judgment, please enter a value:" nums r=$[$nums%2] case $r in 1) echo "Odd number" ;; 0) echo "even numbers" ;; esac
Operation results
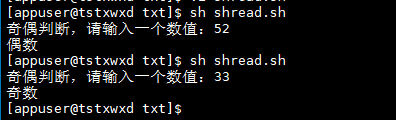
Example 12: for loop
for Variable name in Conditions of circulation; do command done
# In script seq 1 5 Represents a sequence from 1 to 5 for i in `seq 1 5`;do echo $i done
Operation results
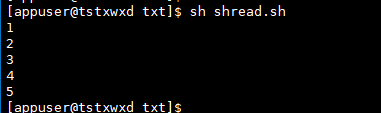
for i in `ls`; do echo $i; done #for i in `cat test.txt`; do echo $i; done
Operation results
Example 13: while loop
while condition; do command done
while :; do command done
a=7 while [ $a -ge 1];do echo "$a" a=$[$a-2] done
Operation results
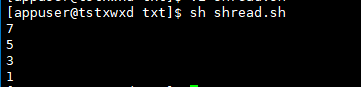
Example 14: function
# function function Function name() { command } # call Function name $1 $2 # implement sh shread.sh value1 value2
function sun(){ sum=$[$1 + $2] echo $sum } sun $1 $2
Operation results
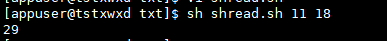
Example 15:
expand
Question 1: variable not found: test sh: line 2: var_ name: command not found
Problem reason: there can be no space between the variable name and value of the equal sign twice
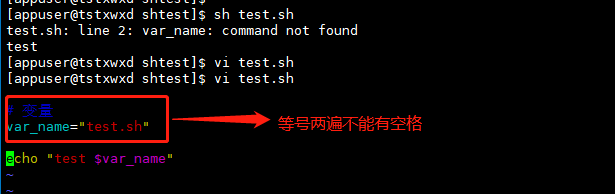
Knowledge points:
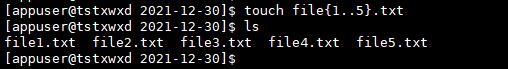
# batch create files
touch file{1..5}.txt
Operation results
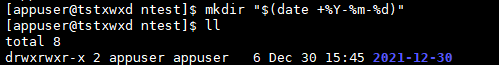
#Create a directory with the current date as the name
mkdir "$(date +%Y-%m-%d)"
Operation results
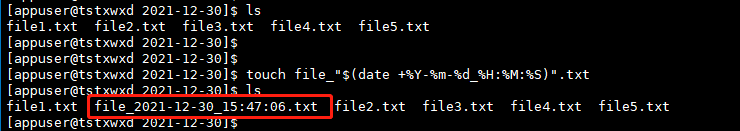
#Create a file with the current time as the name
touch file_"$(date +%Y-%m-%d_%H:%M:%S)".txt
Operation results
#Batch create files with the current time as the name
touch file{01..07}_"$(date +%Y-%m-%d_%H:%M:%S)".txt
Operation results
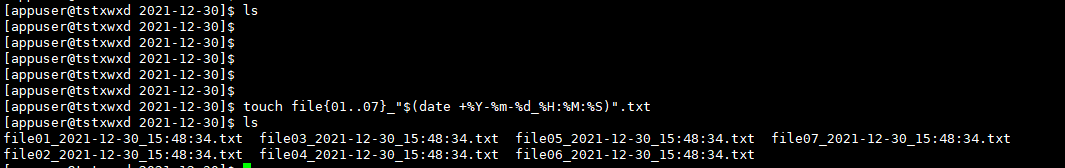
#Display the current year, month, day, hour, minute and second, horizontal bar - and colon: customizable [% Y represents year,% m represents month,% d represents date,% H represents hour,% m represents minute,% S represents second and w represents week]
date +%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S:
Operation results
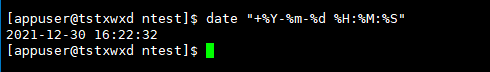
#Show week
date +%w
Operation results
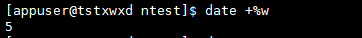
#The - d , option is also frequently used. It can print the date n days ago or n days later. Of course, it can also print the date n months / year ago or later.
date -d "+1 month" "+%Y-%m-%d" #date -d "-1 month" "+%Y-%m-%d"
Operation results
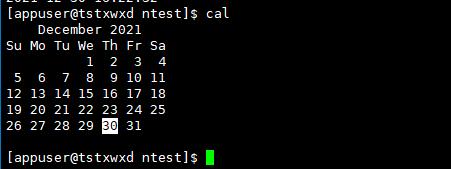
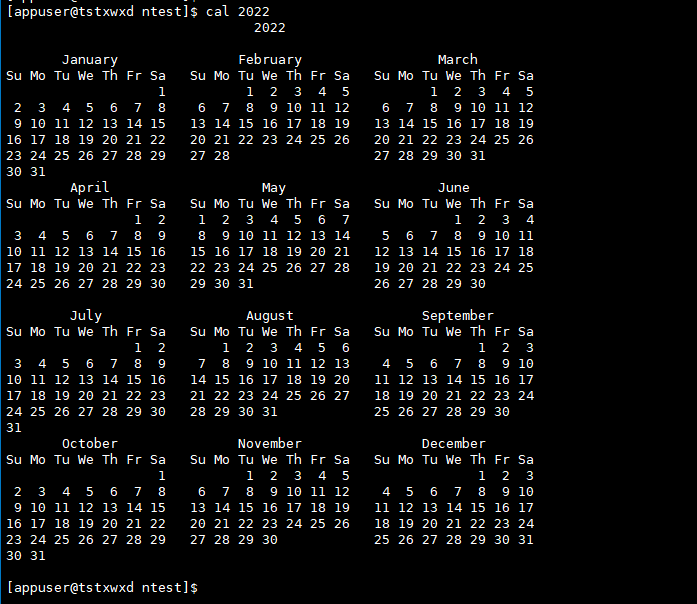
#View calendar
cal # View current month calendar cal 2022 # View year calendar
Operation results
#Enable the extglob function of bash (this function is used to delete files that do not include files in the number in the way of RM! (* JPG))
rm -f !(file10) # Delete all(Documents except parentheses) Keep single rm -rf !(test.sh|file1.log|file2.log) # Delete all(More than one file is reserved except for parentheses rm -rf !(file5|file6|file7).txt # Delete all.txt(More than one file is reserved except for parentheses.txt
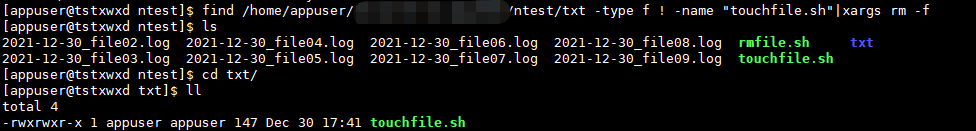
#Delete the txt directory except touchfile All files except sh files
# One pass xargs Pass parameter, one through find of-exec Execute command parameters to complete find /xxx/txt -type f ! -name "touchfile.sh"|xargs rm -f # find /xxx/txt -type f ! -name "touchfile.sh" -exec rm -f {} \;
Operation results
#Output redirection and append data
>: Output redirection writes the contents of one file to another in the form of overwrite >>: Append: append the contents of a file to the end of another file Syntax: ls -l >file Writes the contents of the list to a file(Overwrite original content) ls -al >>file Append the contents of the list to the end of the file cat File 1 > Document 2 Write the contents of file 1 to file 2(Overwrite the contents of the latter file) echo "content" >> file Append content to file