Experimental environment
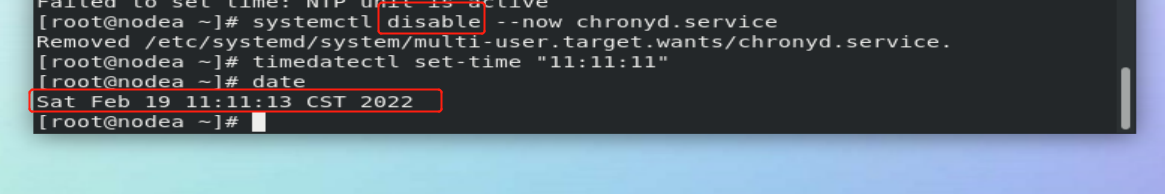
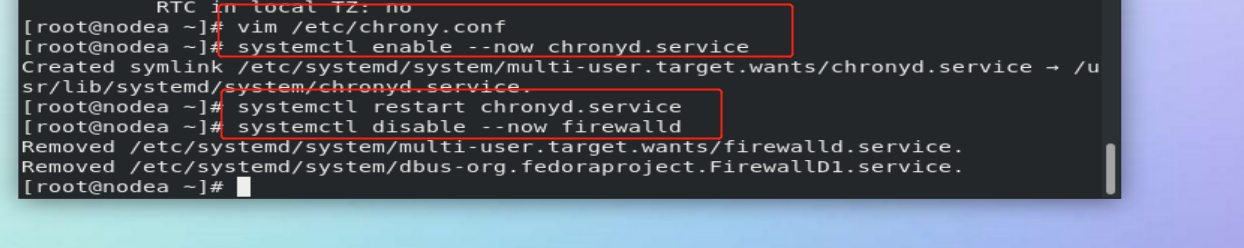
systemctl stop firewalld
1.journald
Service Name: SYSTEMd journal service
journalctl
Default log storage path: / run/log
Experiment 1 usage of journalctl command
journalctl
-n 3 ## latest 3 entries in log
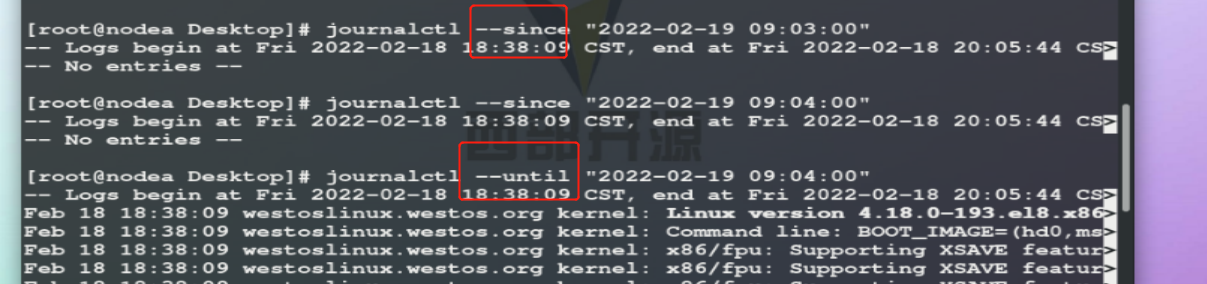
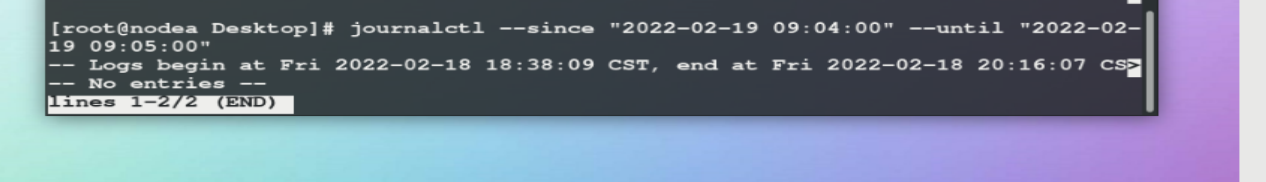
--since "2020-05-01 11:00:00" ## displays the log after 11:00
--until "2020-05-01 11:05:00" ## display log to 11:05
-o## set the display mode of log
Show log in short classic mode
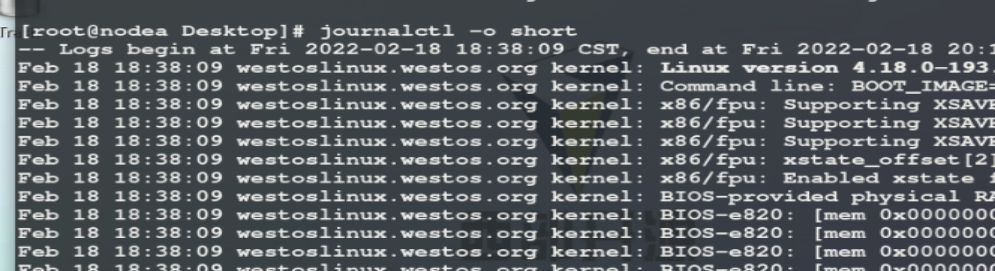
verbose displays all bytes of the log
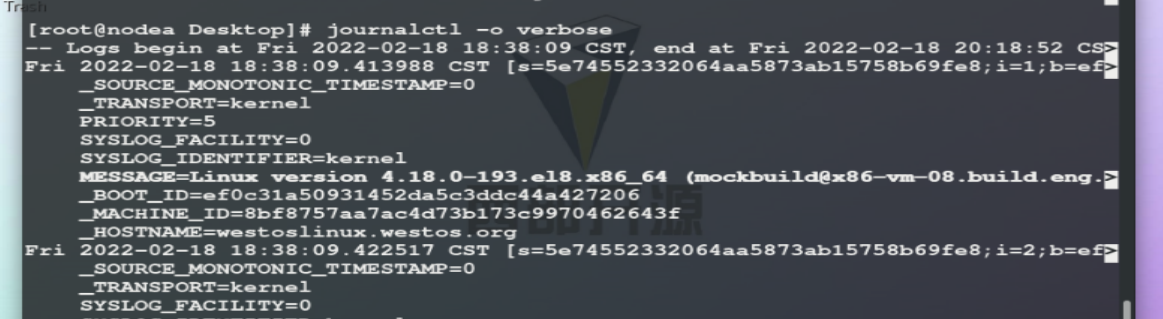
export binary format suitable for outgoing and backup
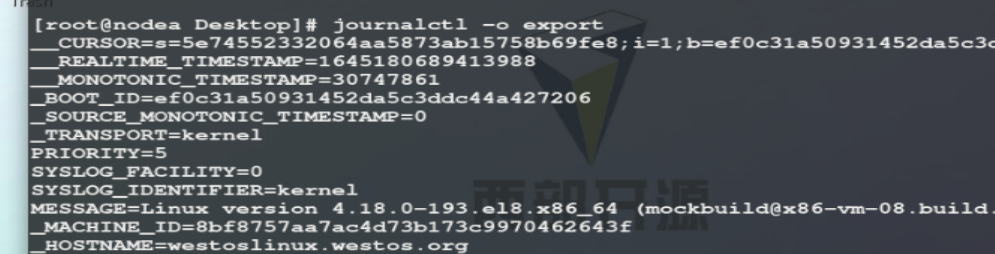
json js format display output
-p ##Displays the log at the specified level #Critical issue log for 0 emerg system #1. Information to be changed immediately in alert system #2. Crit severity level will cause the system software to not work normally #3 err program error #4 warning program warning #5 notice general log of important information #6 info general information #7. Error shooting information of debug program
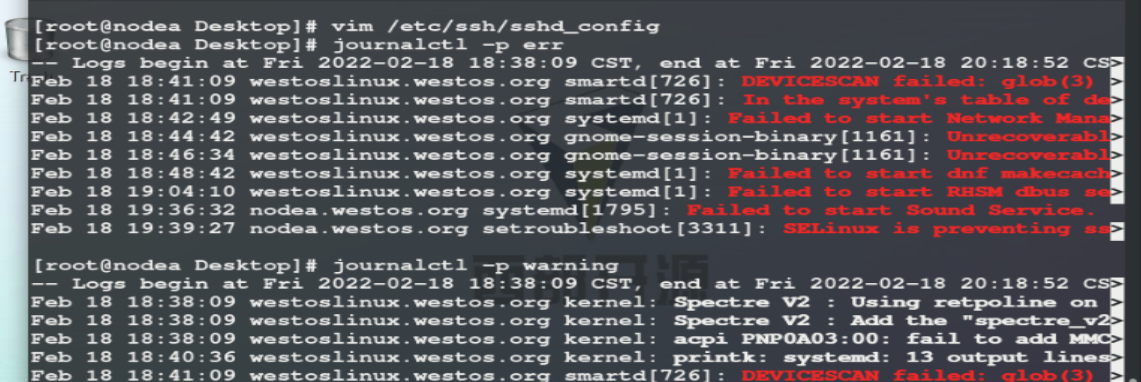
-F PRIORITY ## view controllable log level
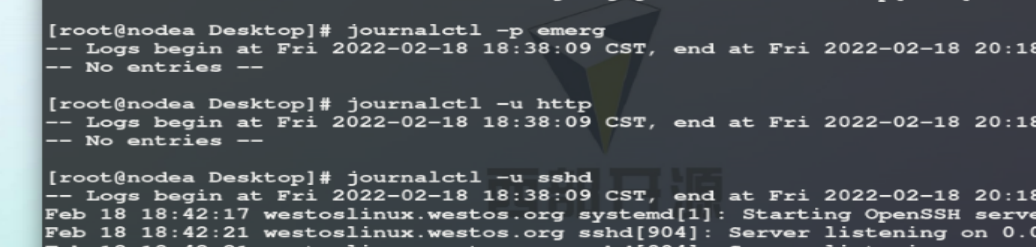
-u sshd ## specify viewing service
– disk usage ## view log size
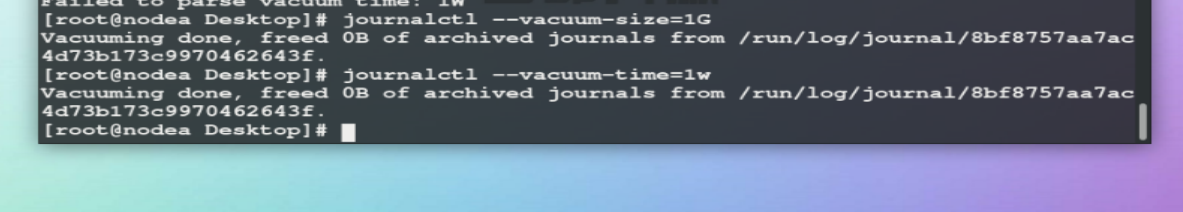
– vacuum size = 1g ## set the log storage size
– vacuum time = 1W ## maximum storage time of logs in the system
-f ## monitoring log
journalctl _PID=10924 _SYSTEMD_UNIT=sshd.service
Experiment 2 using journaled service to store logs permanently
The default log in the system is: / run/log/journal
By default, the log will be cleared after system restart. To permanently save the log, complete the following operations:
mkdir /var/log/journal chgrp systemd-journal /var/log/journal chmod 2775 /var/log/journal systemctl restart systemd-journald.service
When the service restarts, the log storage path will be specified to: / var/log/journal
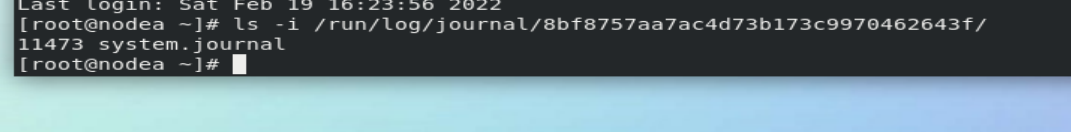
If it is not processed, the log will not be saved, and the node number 11473 will change at the next restart
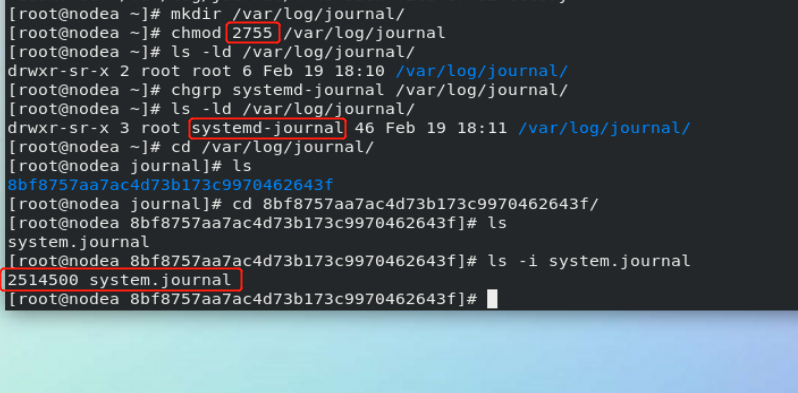
At the next restart, the node number 2514500 will not change.
2.rsyslog
Service Name: rsyslog service
The system kernel and many programs will produce various error messages, warning messages and other prompt messages. These messages are very useful for users to understand the running state of the system, so they need to be saved in the corresponding log file for subsequent analysis and monitoring of the state of the system or software. Linux system has a very flexible and powerful logging function, which can save almost all operation records and retrieve the information we need. The daemon to complete this work is rsyslog.
In the configuration file: / etc / rsyslog Conf defines collecting system logs to designated locations by categories, as follows:
/var/log/messages #System service log, general information, service error /var/log/secure #System authentication information log /var/log/maillog #System mail log information /var/log/cron #System scheduled task information /var/log/boot.log #System startup log information
Experiment 1 Custom log collection path
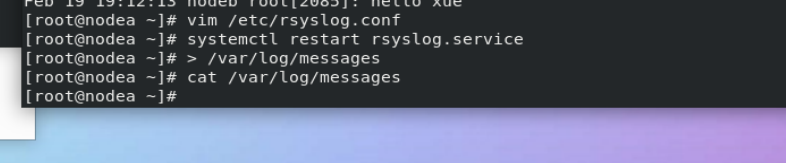
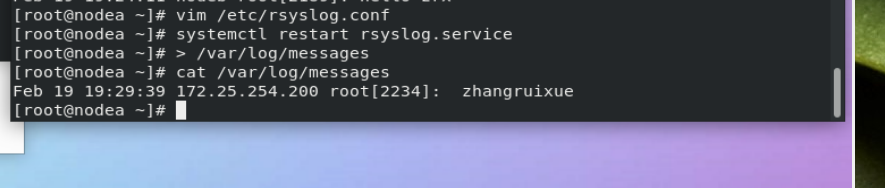
vim /etc/rsyslog.conf
Log type.Log level log storage path *.* /var/log/westos ##Store all levels of logs in the system in westos *.*;authpriv.none /var/log/westos ##The logs of all levels in the system are stored in westos, except authpriv
In the experiment, the configuration file is modified.
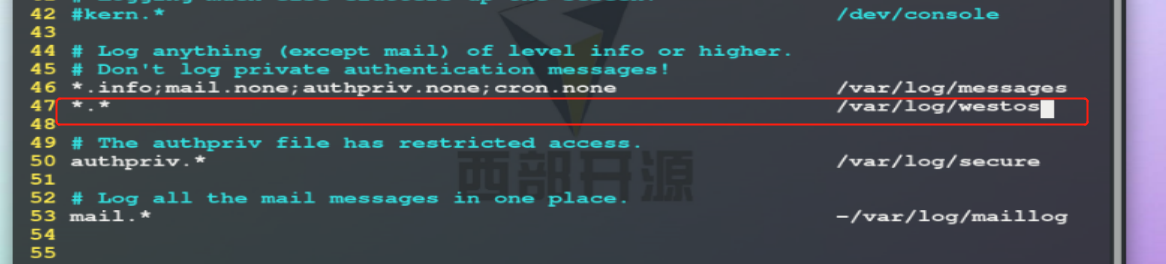
Before the experiment,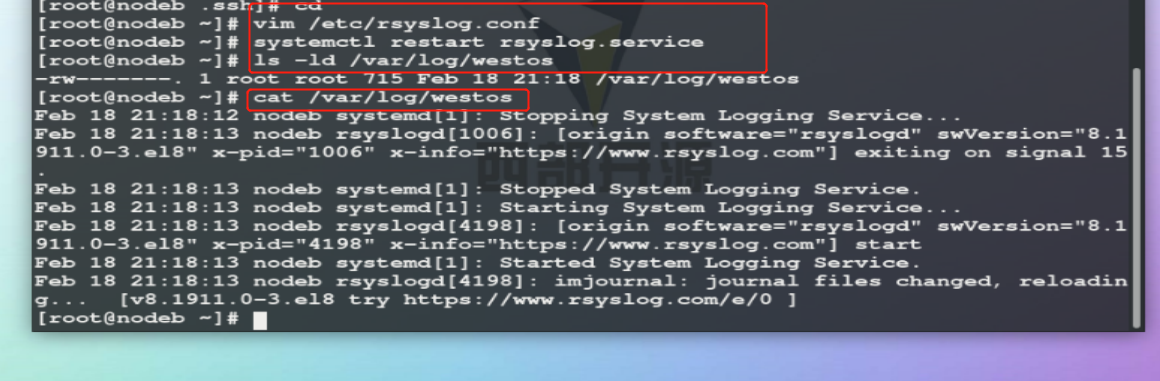
Remote login.
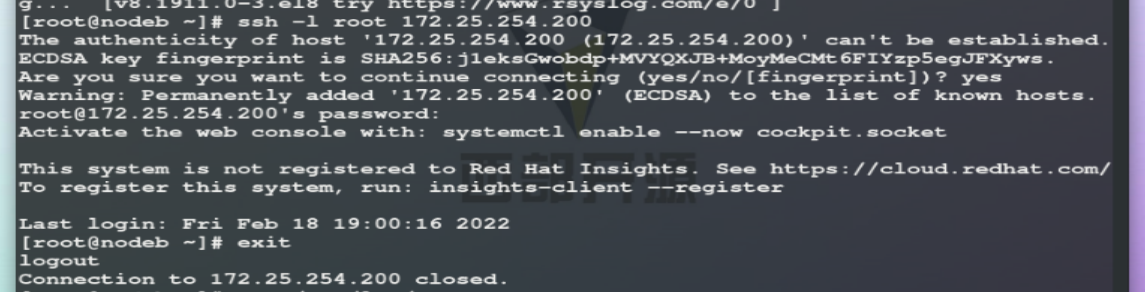
After logging in, view the log.
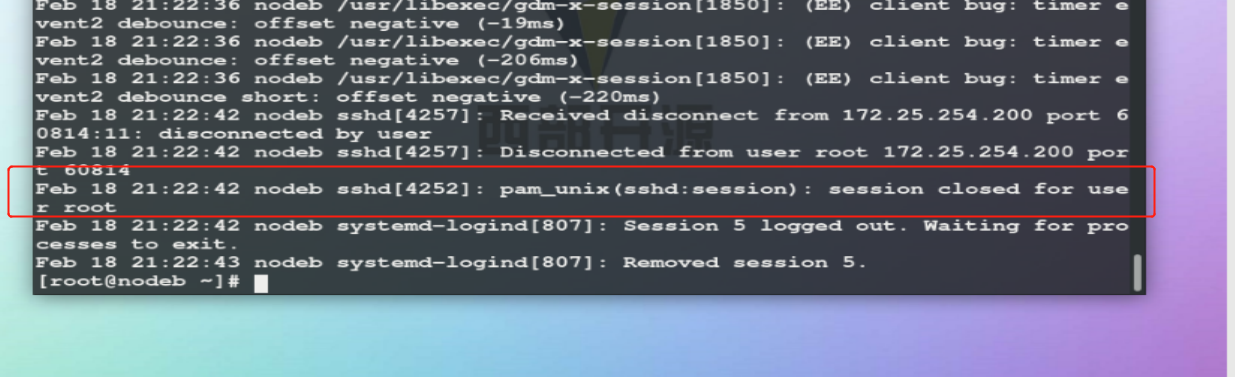
When experimenting, modify the configuration file.
Experimental results.
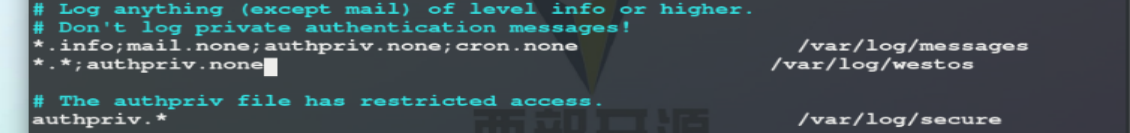
Log type auth #User authentication authpriv #Service certification cron #Time task kern #Kernel type mail #mail news #System update information user #user log level debug #Program troubleshooting information info #Program general operation information notice #General log of important information waring #Program warning err #Program error crit #The severity level will cause the system software to not work properly alert #Information in the system to be changed immediately emerg #Critical issues log for the system none #No collection
Experiment 2 How to change the log collection format
1 define log collection format
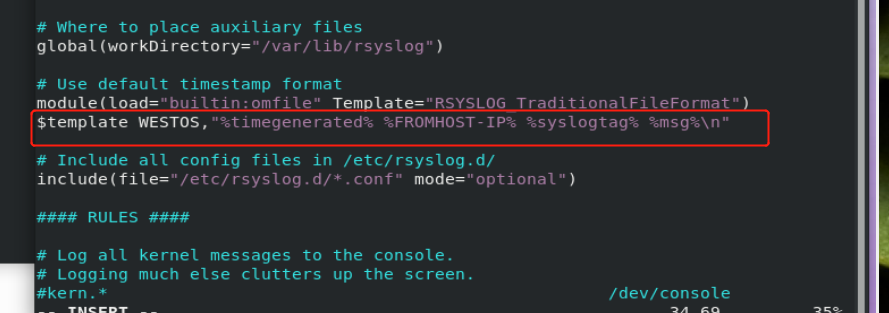
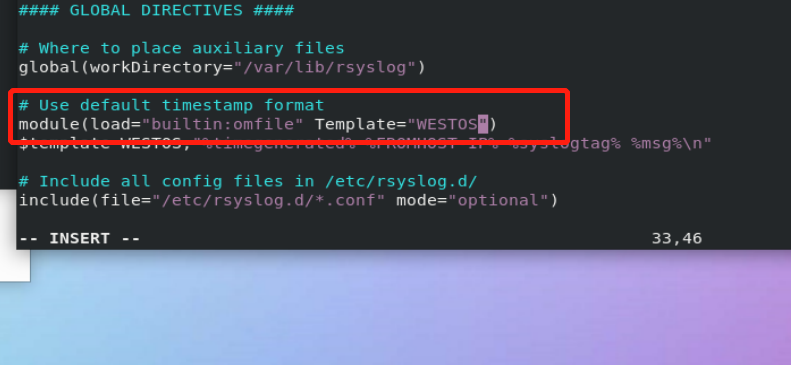
$template WESTOS_FORMAT, "%FROMHOST-IP% %timegenerated% %FROMHOST-IP% %syslogtag% %msg%\n" #WESTOS_FORMAT: format name #%FROMHOST-IP%: log source host IP #%timegenerated%: log generation time #%syslogtag%: log generation service #%msg%: log content #\n: Line feed
Experimental steps:
Note: the operation of modifying the configuration file is carried out at the receiver
Modify the configuration file / etc / rsyslog. In the log receiver westosa Conf, define the log collection format, WESTOS, / var/log/westos;WESTOS means that only the logs under the / var/log/messages path are collected in the defined format
2. Set log collection format
*.*;authpriv.none /var/log/westos;WESTOS module(load="builtin:omfile" Template="WESTOS_FORMAT") ##Westos is adopted by default_ Format format
Experiment 3 Remote synchronization of logs
1).westos_node1:172.25.254.20 store logs as the log receiver, and all logs are stored on this host
2).westos_linux:172.25.254.10 sending logs to westos_node1 host
1. The first step is in westos_ Set in node1 to accept everyone's log
systemctl stop firewalld vim /etc/rsyslog.conf 19 module(load="imudp") ##Open log acceptance plug-in 20 input(type="imudp" port="514") ##Specifies the interface used by the plug-in systemctl restart rsyslog
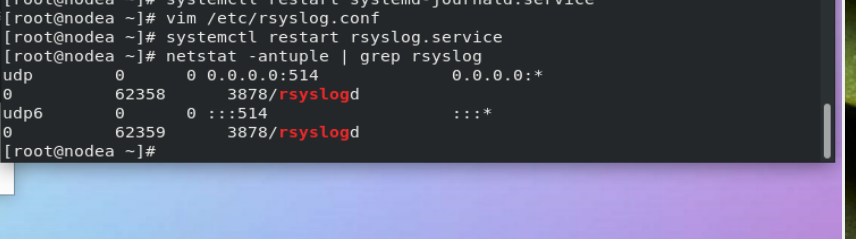
Query port:
root@rhel7_node1 ~]# netstat -antlupe | grep rsyslog udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:514 0.0.0.0:* 0 67600 11115/rsyslogd udp6 0 0 :::514 :::* 0 67601 11115/rsyslogd
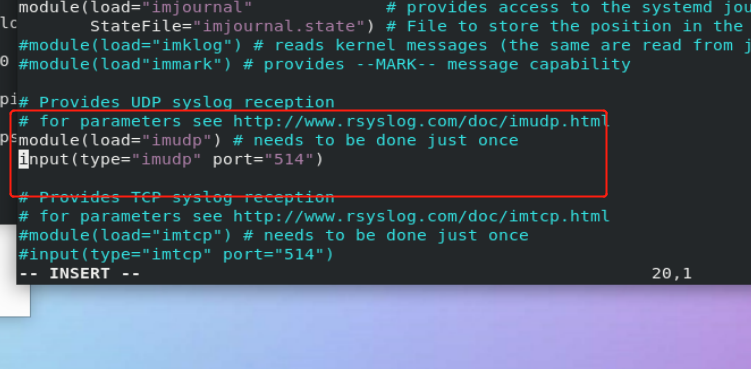
Query whether the receiver port is opened successfully
2. Step 2: westos_ Set sending logs to westos in Linux_ In node1
vim /etc/rsyslog.conf
*.* @172.25.254.20 systemctl restart rsyslog @ Indicates use udp Transmission log @@ Indicates use tcp Transmission log @172.25.254.20 Use the local log udp The transmission mode is sent to 172.25.254.20 host
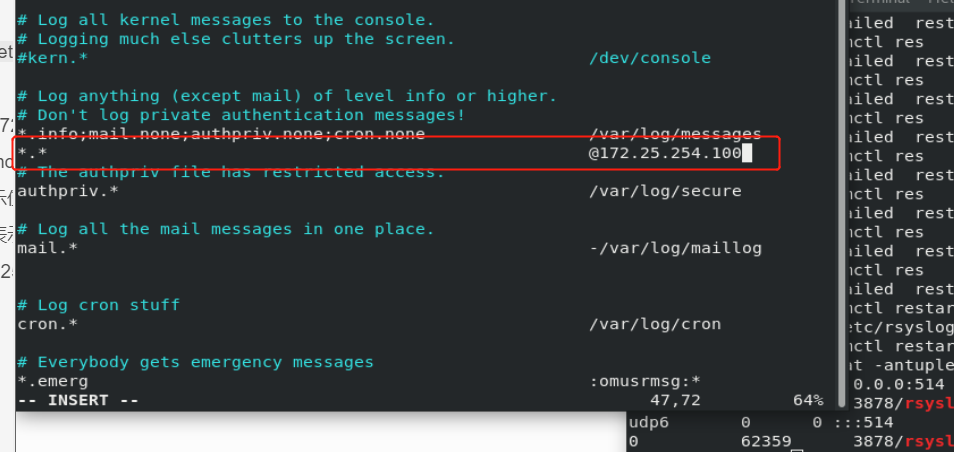

Test:
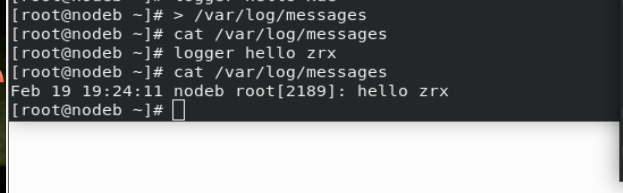
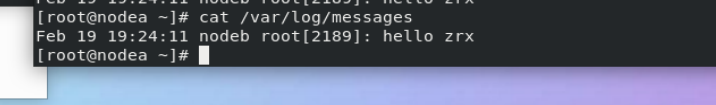
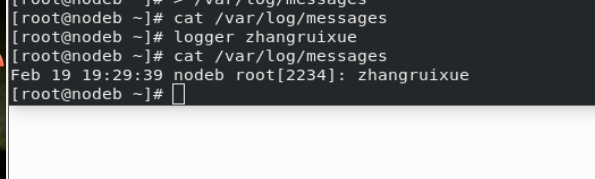
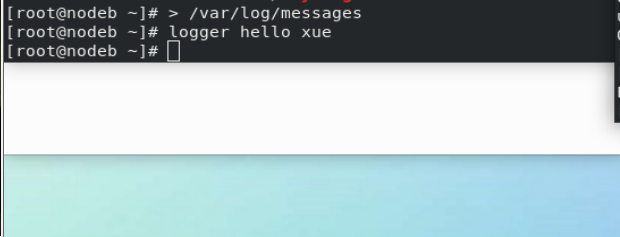
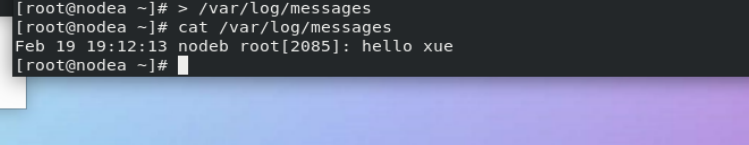
stay westos_linux and westos_node1 in > /var/log/messages stay westos_linux in logger westos test message stay westos_node1 Can be seen in westos_linux Log generated in!!
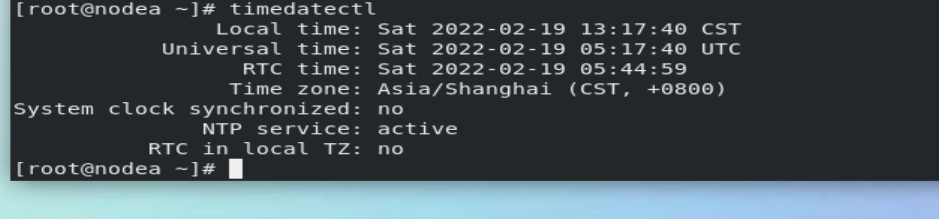
3.timedatectl
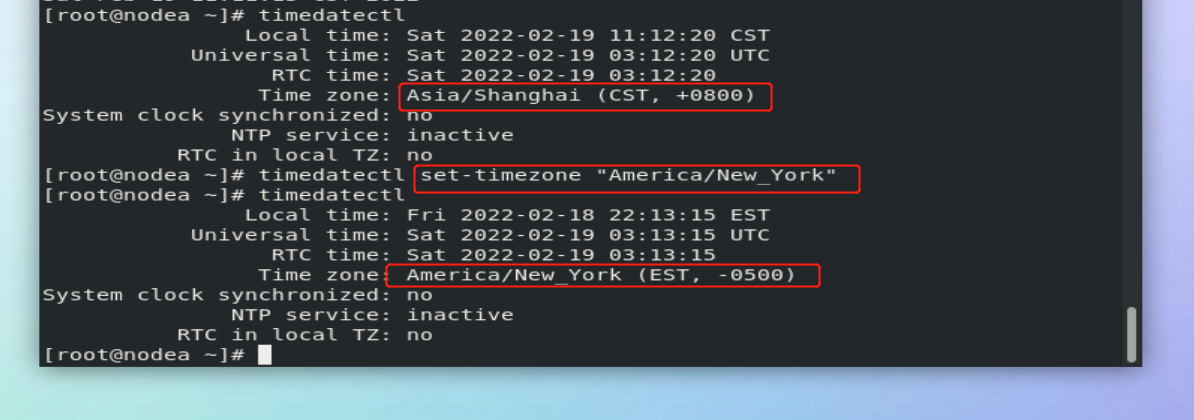
timedatectl set-time "2020-02-13 10:41:55" ##Set system time timedatectl list-timezones ##Displays all time zones of the system timedatectl set-timezone "Asia/Shanghai" ##Set system time zone timedatectl set-local-rtc 0|1 ##Set the system time calculation method ##0 means using the utc time calculation method
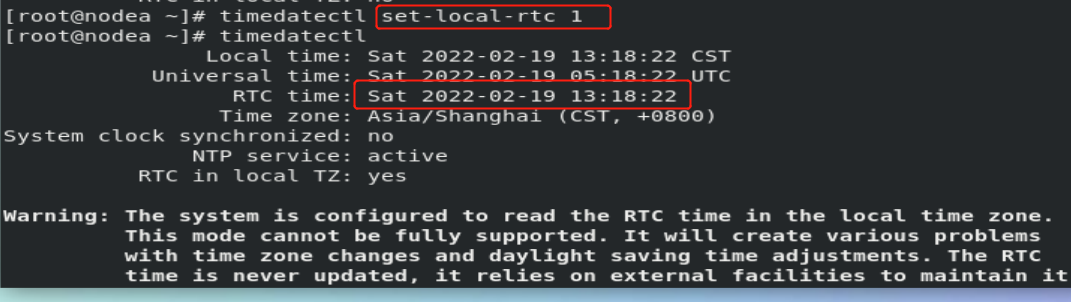
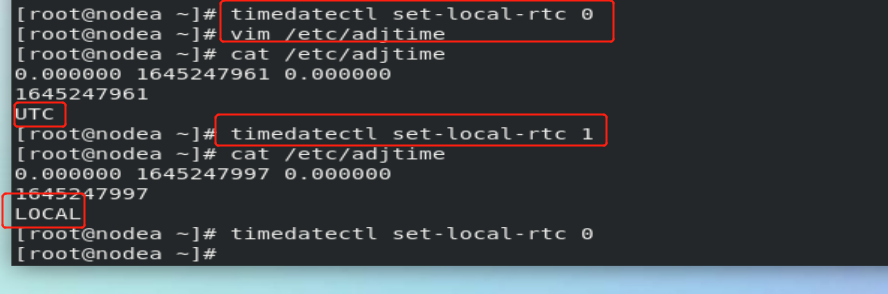
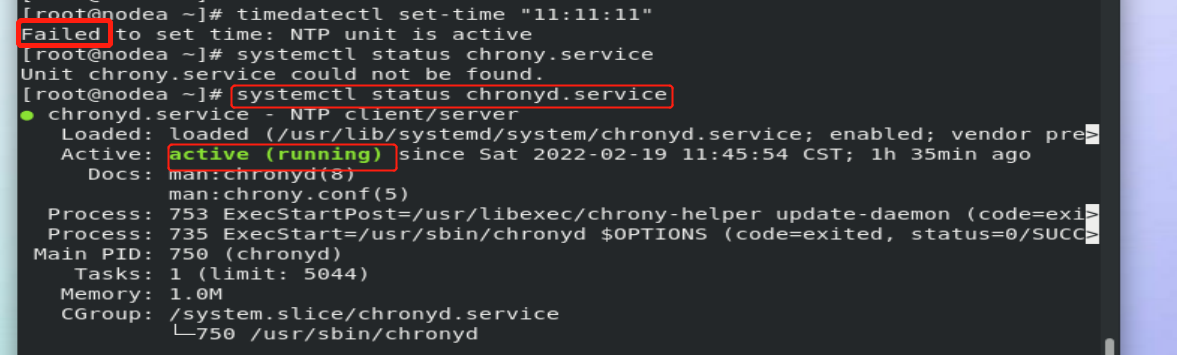
The experiment in the above figure failed. You need to turn off chronyd.
4. Time synchronization service
#Service Name: chronyd service
#Configuration file: / etc / Chrony conf
Use rhel7 as the time source rhel8 to synchronize rhel7 time
At time_server
vim /etc/chrony.conf
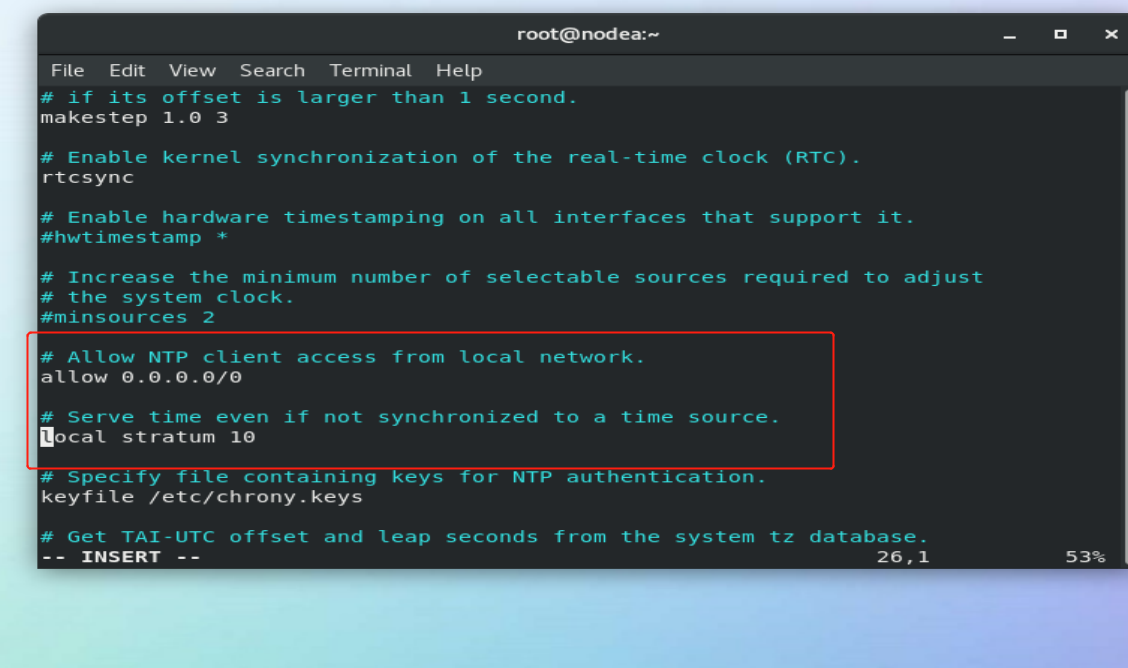
26 allow 172.25.254.0/24 ##Allow 172.25.254.0 network segment host synchronization time 29 local stratum 10 ##Turn on the time synchronization server function and set the level to 10 systemctl restart chronyd.service systemctl stop firewalld
At time_ In clinet
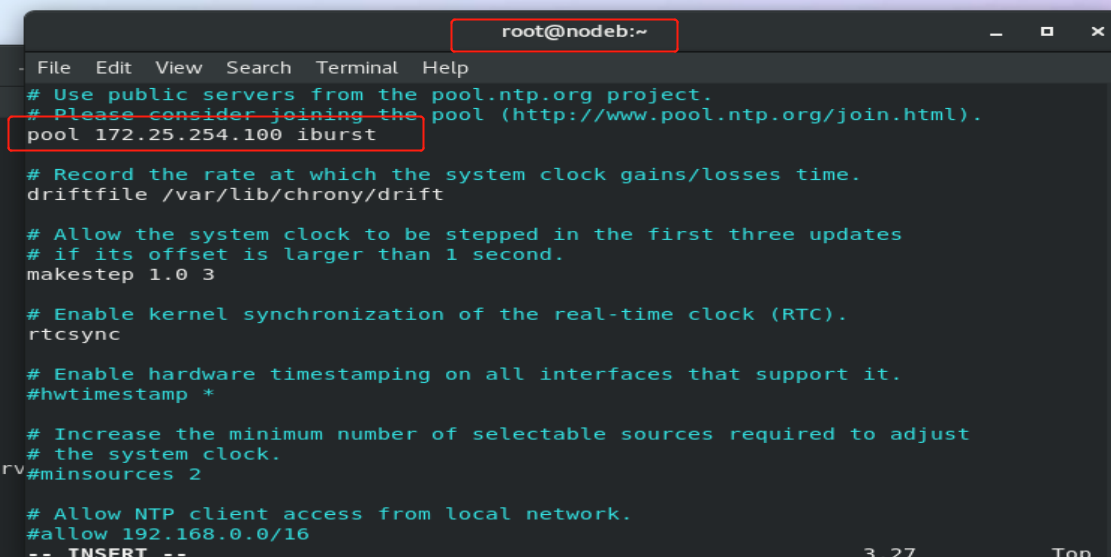
vim /etc/chrony.conf
pool 172.25.254.100 iburst systemctl restart chronyd
see:
At time_ Viewing time in client:
Reality has become time_ Time in server
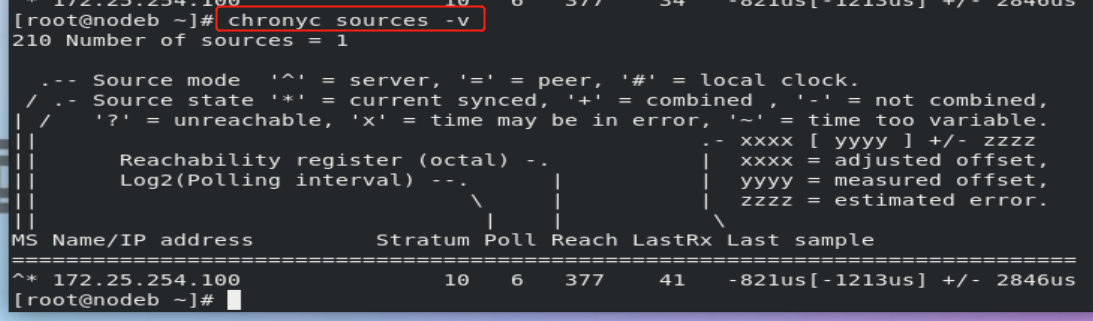
Use the chronyc command to view the time effect:
[root@rhel8_node1 ~]# chronyc sources -v 210 Number of sources = 1 .-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock. / .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined, | / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable. || .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz || Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset, || Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset, || \ | | zzzz = estimated error. || | | \ MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample =============================================================================== ^* 172.25.254.11 10 6 17 15 -6970ns[+8437ns] +/- 180u
In time server
In time client
result: