hello everyone!
If you haven't used the progress bar before, you probably think it will increase unnecessary complexity or difficult to maintain, but it's not. It only takes a few lines of code to add a progress bar. In these lines of code, we can see how to add a progress bar to the command-line script and PySimpleGUI UI.
The following describes four commonly used Python progress bar libraries:
Progress
The first Python library to introduce is Progress.
You only need to define the number of iterations, the type of progress bar, and inform the progress bar at each iteration.
import timefrom progress.bar import IncrementalBarmylist = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] bar = IncrementalBar( Countdown , max = len(mylist)) for item in mylist: bar.next() time.sleep(1) bar.finish()
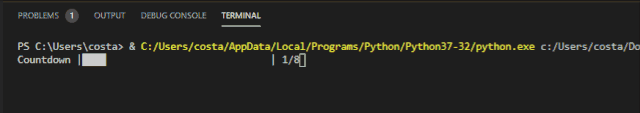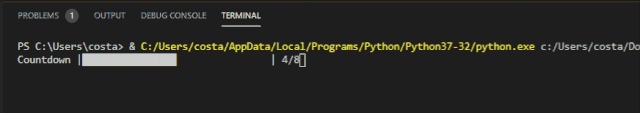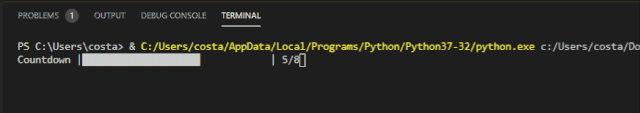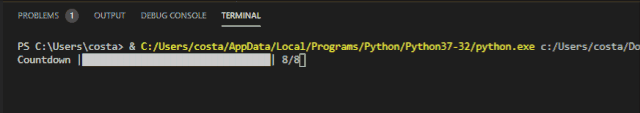
The Progress bar effect achieved by Progress is as follows:
Incremental progress bar for Progressbar
If you don't like the format of the progress bar, you can also choose from the following formats:
Progress bar supported progress bar types.
Related documents: https://pypi.org/project/progress/1.5/
tqdm
Let's take a look at the tqdm library.
Similar to the library seen before, these two lines of code are also very similar, with a little difference in settings:
import timefrom tqdm import tqdmmylist = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] for i in tqdm(mylist): time.sleep(1)
The progress bar effect achieved by tqdm is as follows:
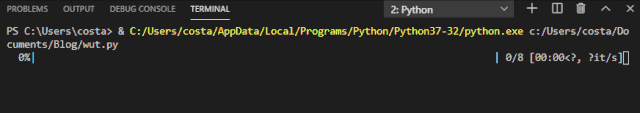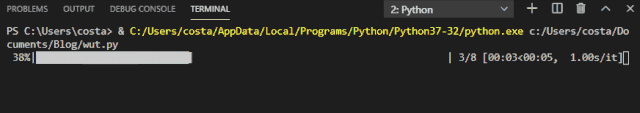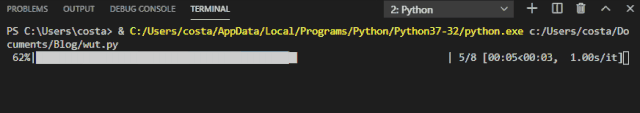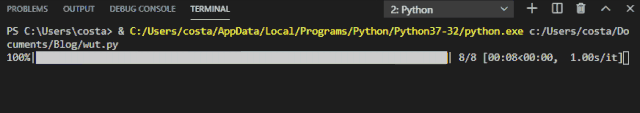
This progress bar also provides several options.
Related documents: https://tqdm.github.io/
Alive Progress
As the name suggests, this library can make the progress bar more vivid. It has more animation effects than the progress bar we have seen before.
Similar from a code perspective:
from alive_progress import alive_barimport timemylist = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] with alive_bar(len(mylist)) as bar: for i in mylist: bar() time.sleep(1)
The appearance of the progress bar is similar to that expected:
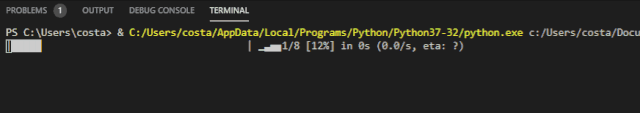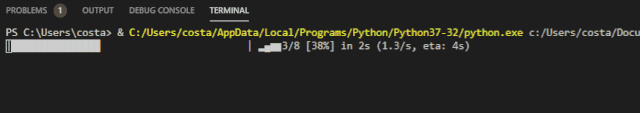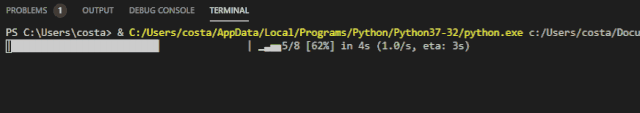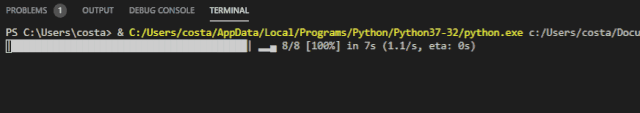
This progress bar has some unique functions, which will be interesting to use. See the project for function details: https://github.com/rsalmei/alive-progress
PySimpleGUI
Get graphical progress bar with PySimpleGUI
We can add a simple line of code to get a graphical progress bar in the command-line script.
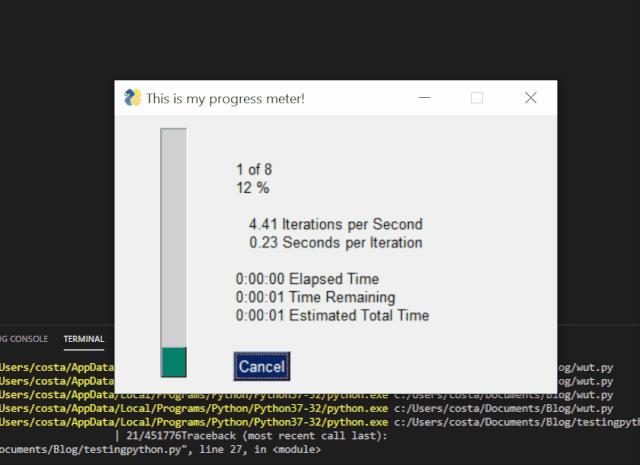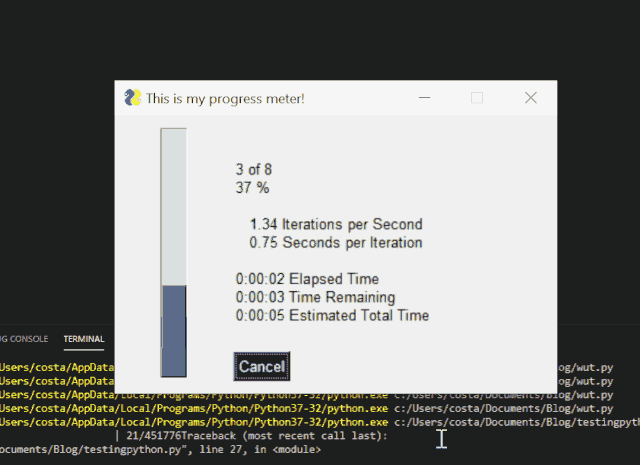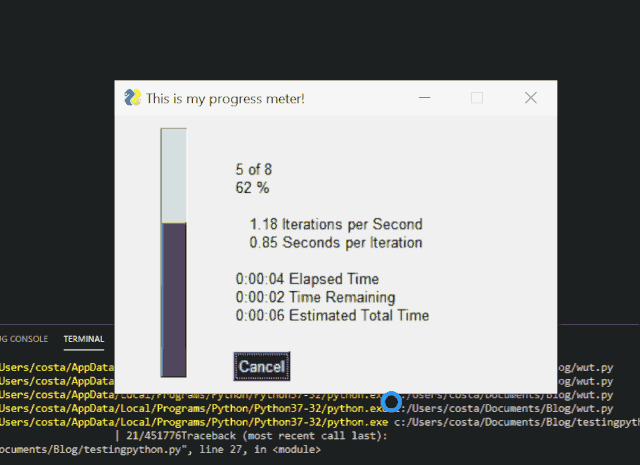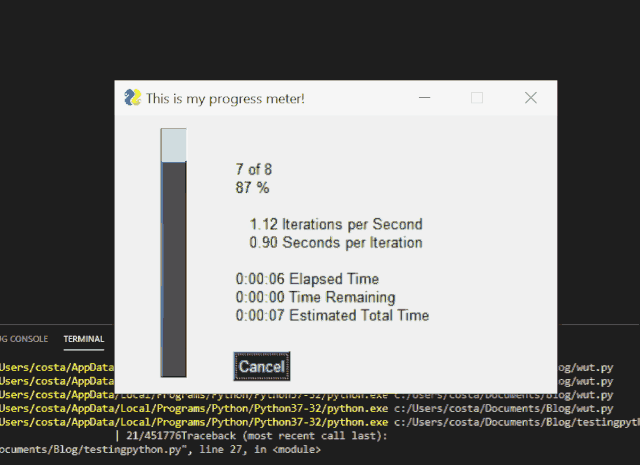
In order to achieve the above, the code we need is:
import PySimpleGUI as sgimport timemylist = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] for i, item in enumerate(mylist): sg.one_line_progress_meter( This is my progress meter! , i+1, len(mylist), -key- ) time.sleep(1)
Progress bar in PySimpleGUI application
The project author previously discussed "how to quickly start the Python UI and then use the UI to create a comparison tool" on GitHub. In this project, the author also discusses how to integrate the progress bar.
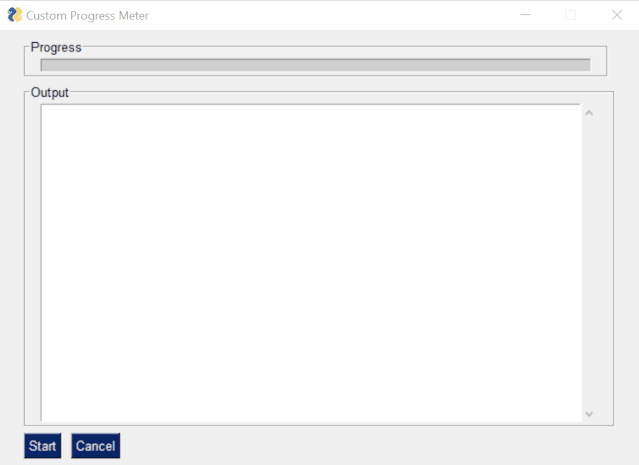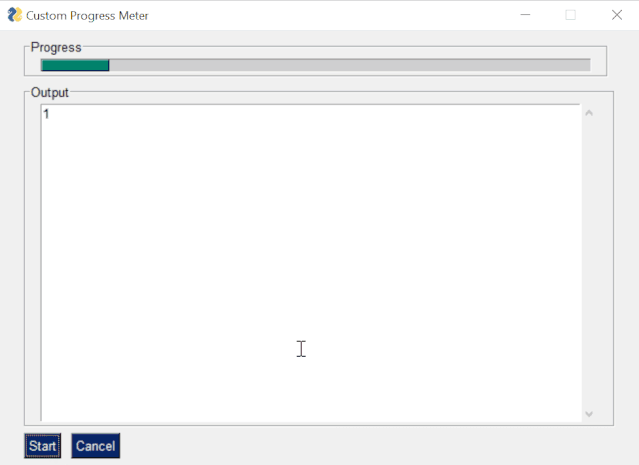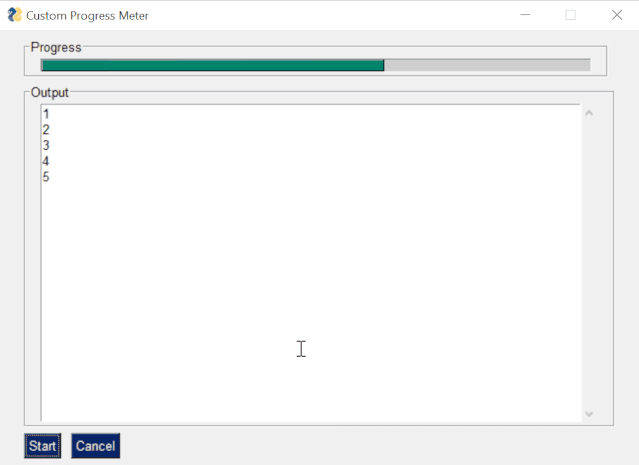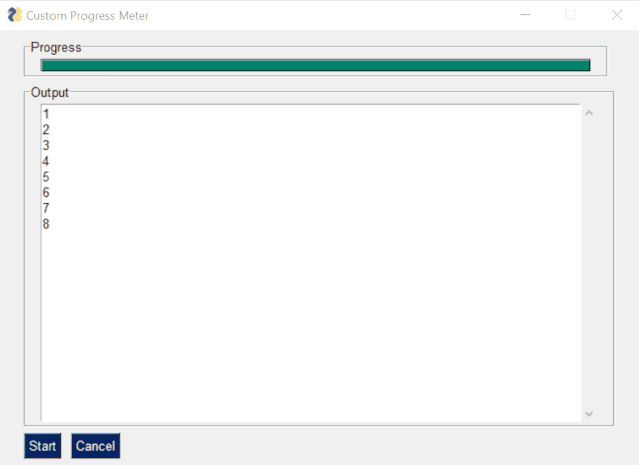
The code is as follows:
import PySimpleGUI as sgimport timemylist = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] progressbar = [ [sg.ProgressBar(len(mylist), orientation= h , size=(51, 10), key= progressbar )]] outputwin = [ [sg.Output(size=(78,20))]] layout = [ [sg.Frame( Progress ,layout= progressbar)], [sg.Frame( Output , layout = outputwin)], [sg.Submit( Start ),sg.Cancel()]] window = sg.Window( Custom Progress Meter , layout) progress_bar = window[ progressbar ] while True: event, values = window.read(timeout=10) if event == Cancel or event is None: break elif event == Start : for i,item in enumerate(mylist): print(item) time.sleep(1) progress_bar.UpdateBar(i + 1)window.close()
Yes, using the progress bar in Python scripts requires only a few lines of code and is not complicated at all. With the progress bar, you don't have to guess how the script runs in the future.