[quick reference manual of Linux common commands] pay attention to [entry station], and the background replies to "1001" for self access.
lsof (list open files) is a tool to view the current system files. In the linux environment, everything exists in the form of files. Through files, you can access not only conventional data, but also network connections and hardware. For example, transmission control protocol (TCP) and user datagram protocol (UDP) sockets, the system assigns a file descriptor to the application in the background, which provides a lot of information about the application itself.
Install lsof
Centos
> yum install lsof -y
Ubuntu
> sudo apt-get install lsof -y
Command format
lsof [parameter] [file]
Command function
It is used to view the file opened by your process, the process that opens the file, and the port opened by the process (TCP, UDP). Retrieve / recover deleted files. It is a very convenient system monitoring tool. Because lsof needs to access core memory and various files, it needs to be executed by root.
lsof open files can be:
- 1. Ordinary documents
- 2. Contents
- 3. Files of network file system
- 4. Character or device file
- 5. (function) shared library
- 6. Pipe, named pipe
- 7. Symbolic link
- 8. Network files (e.g. NFS file, network socket, unix domain name socket)
- 9. There are other types of documents, etc
Command parameters
- -a lists the processes in which the open file exists
- -C < process name > lists the files opened by the specified process
- -g list GID number process details
- -D < file number > lists the processes that occupy the file number
- +D < Directory > lists the open files in the directory
- +D < Directory > recursively list the open files in the directory
- -N < Directory > lists files using NFS
- -I < conditions > lists the processes that meet the conditions. (4. 6. Protocol,: port, @ ip)
- -P < process number > lists the files opened by the specified process number
- -u list UID number process details
- -h display help information
- -v display version information
Lists all open files in the system
> lsof | more
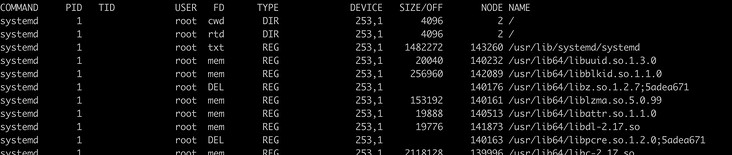
There will be a lot of data, only part of which is intercepted
Field description
- COMMAND: the name of the process
- PID: process identifier
- PPID: parent process identifier (the - R parameter needs to be specified)
- USER: process owner
- PGID: the group to which the process belongs
- FD: file descriptor, which is used by the application to identify the file. Such as cwd, txt, etc
TYPE: file TYPE, such as DIR, REG, and other common file types
- (1) DIR: indicates the directory
- (2) CHR: indicates the character type
- (3) BLK: block device type
- (4) UNIX: Unix domain socket
- (5) FIFO: first in first out (FIFO) queue
- (6) IPv4: Internet Protocol (IP) socket
- DEVICE: Specifies the name of the disk
- SIZE: the SIZE of the file
- NODE: index NODE (the identification of the file on the disk)
- NAME: the exact NAME of the open file
FD description

See who occupies / bin/bash
> lsof /bin/bash COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME bash 14443 root txt REG 253,1 960392 140072 /usr/bin/bash
Recursively view the current directory file information
> lsof . COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME bash 14443 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 131073 . lsof 16522 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 131073 . lsof 16523 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 131073 .
The occupancy of subdirectory files is also displayed
> lsof +D . COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME bash 14443 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 131073 . lsof 16426 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 131073 . lsof 16427 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 131073 . YDService 17532 root 27r REG 253,1 79613 131087 ./.bash_history
Without using the + D option, traverse the method of viewing all file information in a directory
> lsof | grep "rumenz/temp"
Lists the file information opened by a user
> lsof -u root | more
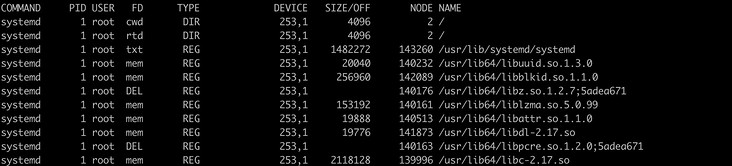
-U option, u is actually the abbreviation of user
The information listed in a program's open file
> lsof -c mysql
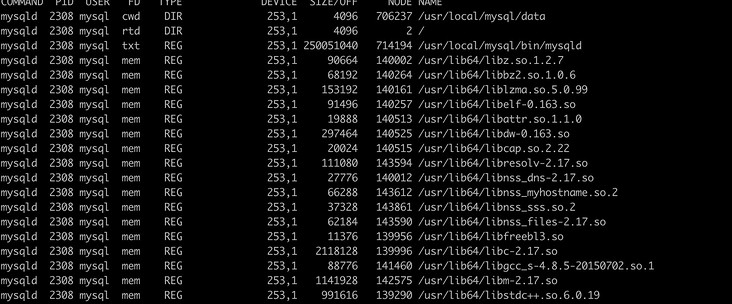
Lists information about multiple open files for multiple processes
> lsof -c mysql nginx
List the information of open files except for a certain user
> lsof -u ^root
Display the file to be opened by a process number
> lsof -p 123
List the file information corresponding to multiple process numbers
> lsof -p 123,456,789
List the file information opened by other process numbers except a process number
> lsof -p ^123
List all network connections
> lsof -i
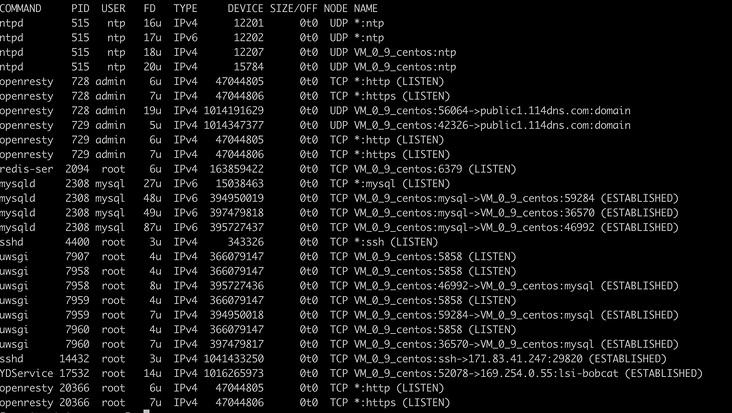
List who is using a port
> lsof -i :3306
Specify multiple ports at the same time
> lsof -i :3306,80
List who is using a particular udp port
> lsof -i udp:123
Specific tcp port
> lsof -i tcp:80
List all tcp network connection information
> lsof -i tcp
List all udp network connection information
> lsof -i tcp
Lists all active network ports for a user
> lsof -a -u root -i
List all network file systems
> lsof -N
Lists the file information that contains the string "sshd" in the COMMAND column and the file descriptor type is txt
> lsof -c sshd -a -d txt COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME sshd 4400 root txt REG 253,1 823744 143872 /usr/sbin/sshd sshd 14432 root txt REG 253,1 823744 143872 /usr/sbin/sshd
List all IPV4 network files opened by the process with process number 123
> lsof -i 4 -a -p 123
-i 4 stands for IPv4 and - I 6 stands for IPV6
File information opened by a user group
> lsof -g 123
List the corresponding file information according to the file description
> lsof -d txt > lsof -d 1 > lsof -d 2
0 indicates standard input, 1 indicates standard output, and 2 indicates standard error. Therefore, the FD of files opened by most applications starts from 3
List the file information according to the file description range
> lsof -d 1-2
Original link: https://rumenz.com/rumenbiji/...
WeChat official account: entry station
[quick reference manual of Linux common commands] pay attention to [entry station], and the background replies to "1001" for self access.
