- Installation and configuration
- 1.1 Download Installation Package on Official Website
- 1.1. Download and Install Package on Official Website
- 1.2. Configuring environment variables
- 1.3. Local Warehousing Configuration
- 1.4. Central Warehouse Configuration
- 2. Using maven in eclipse
- 2.1 eclipse configuration maven
- 2.2 Use maven to create projects in eclipse
Installation and configuration
In fact, mainstream development tools such as IDEA and Eclipse are integrated with Maven (visible importance), but in order to learn and manage the tool more deeply (such as the problem of sharing multiple IDEs), it is better to install it separately.
1.1. Download and Install Package on Official Website
Open the download address in the browser: http://maven.apache.org/download.cgi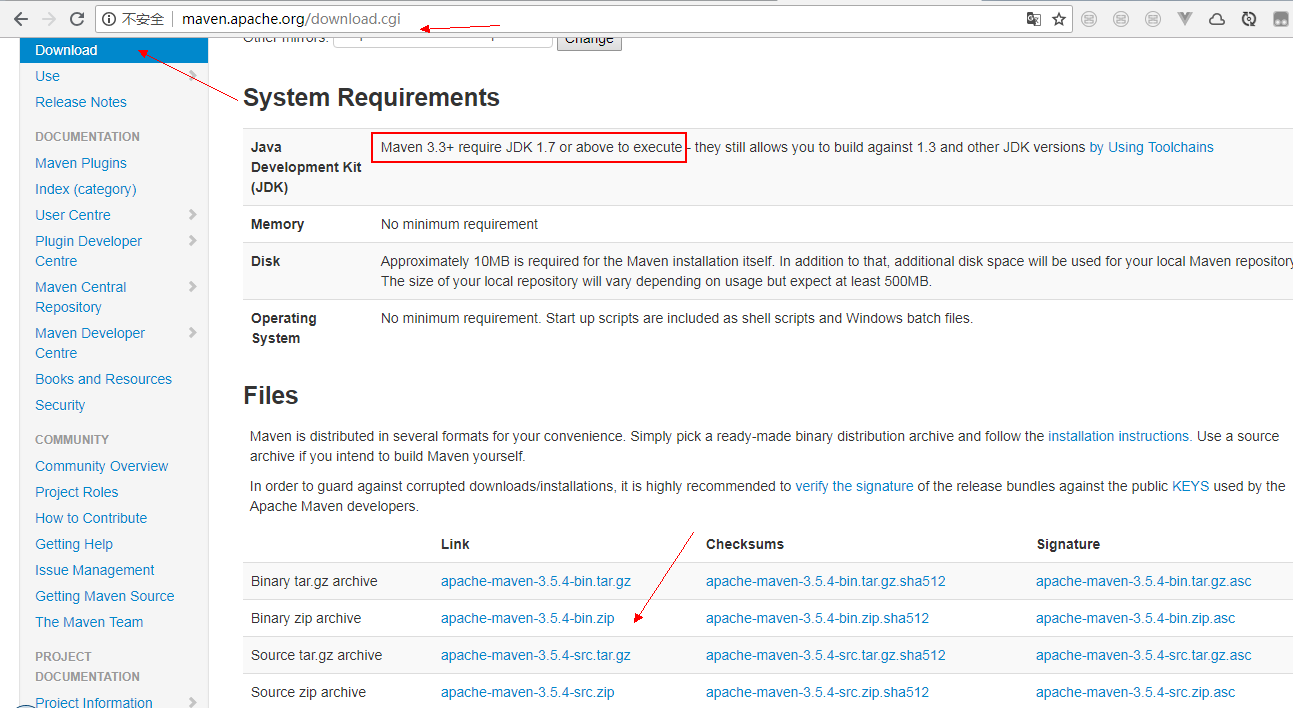
1.2. Configuring environment variables
Note: Before installing maven, you must make sure that JDK is installed on your machine. If it is Maven 3, you must have JDK 1.7 or more.
1. After downloading the decompression package, I decompressed it. In the directory D: maven apache-maven-3.6.1, note: there is no Chinese in the installation path.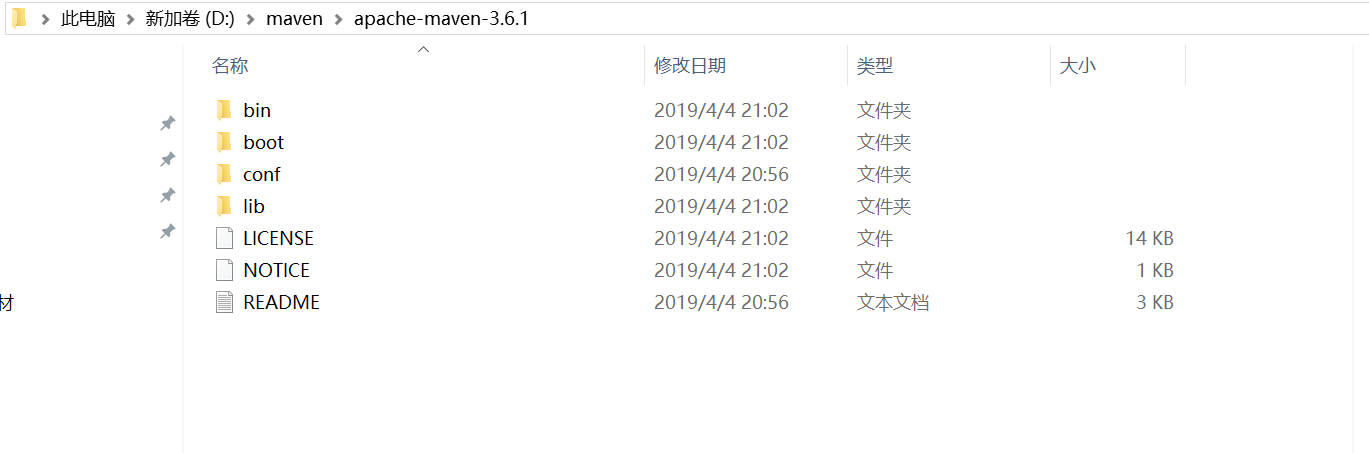
2. Add the environment variable MAVEN_HOME, which is the installation path of apache-maven (no Chinese)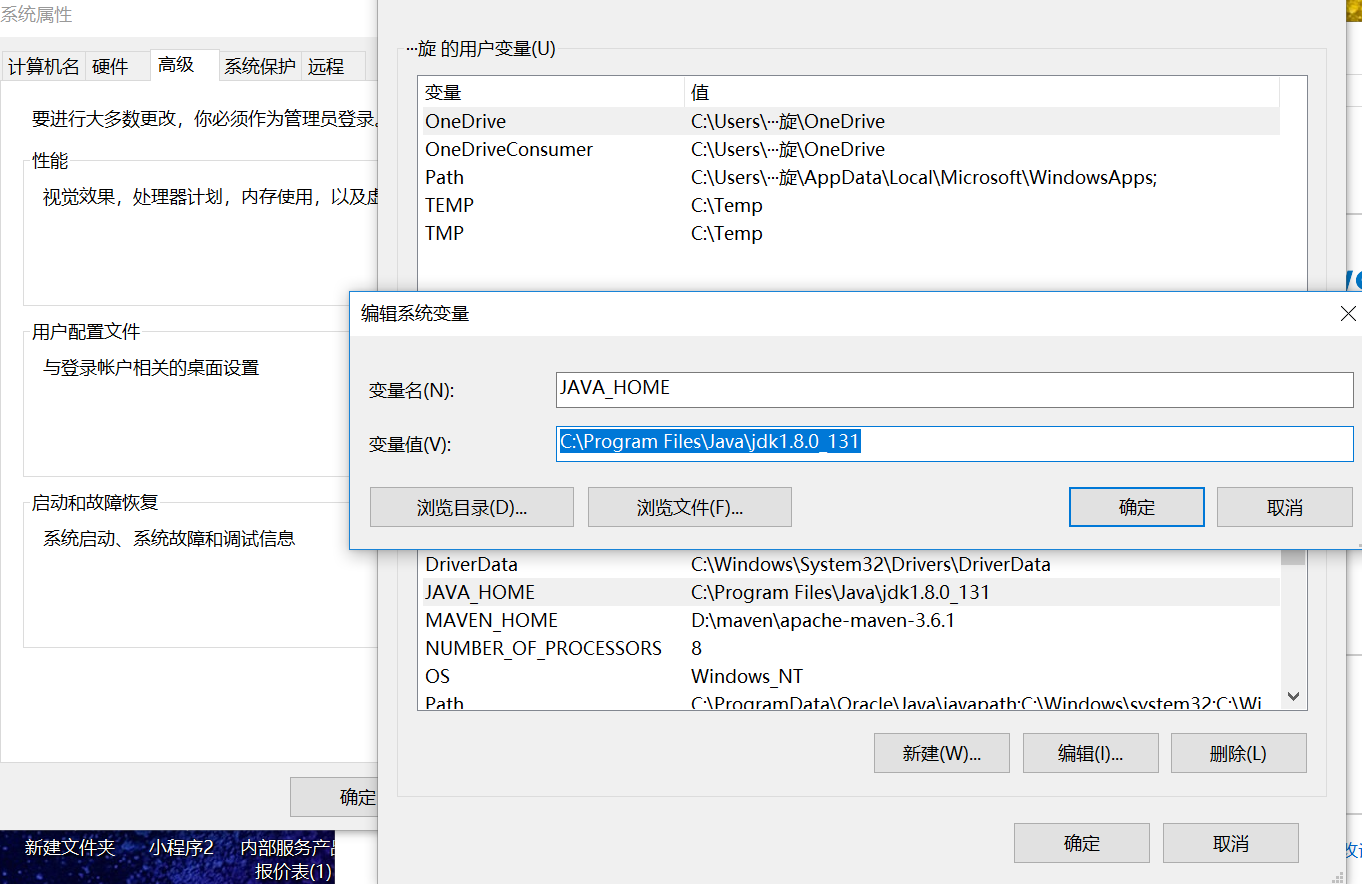
3. Add% MAVEN_HOME%bin at the end of the variable value of Path environment variable.
Windows 7 system should use ";" interval, as shown below, win10, add directly.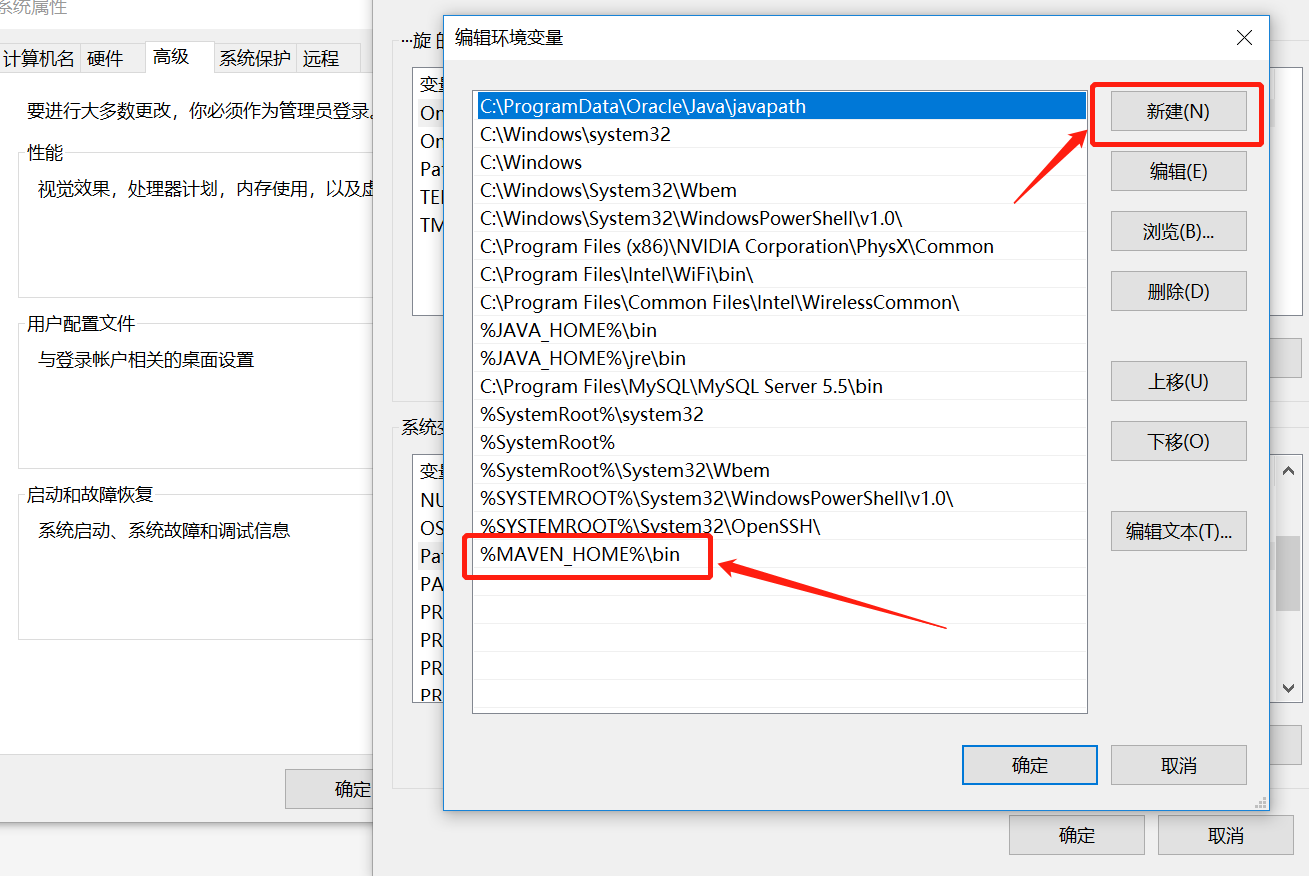
4. Enter mvn-version from the command line. If the version information of maven appears, the configuration is successful.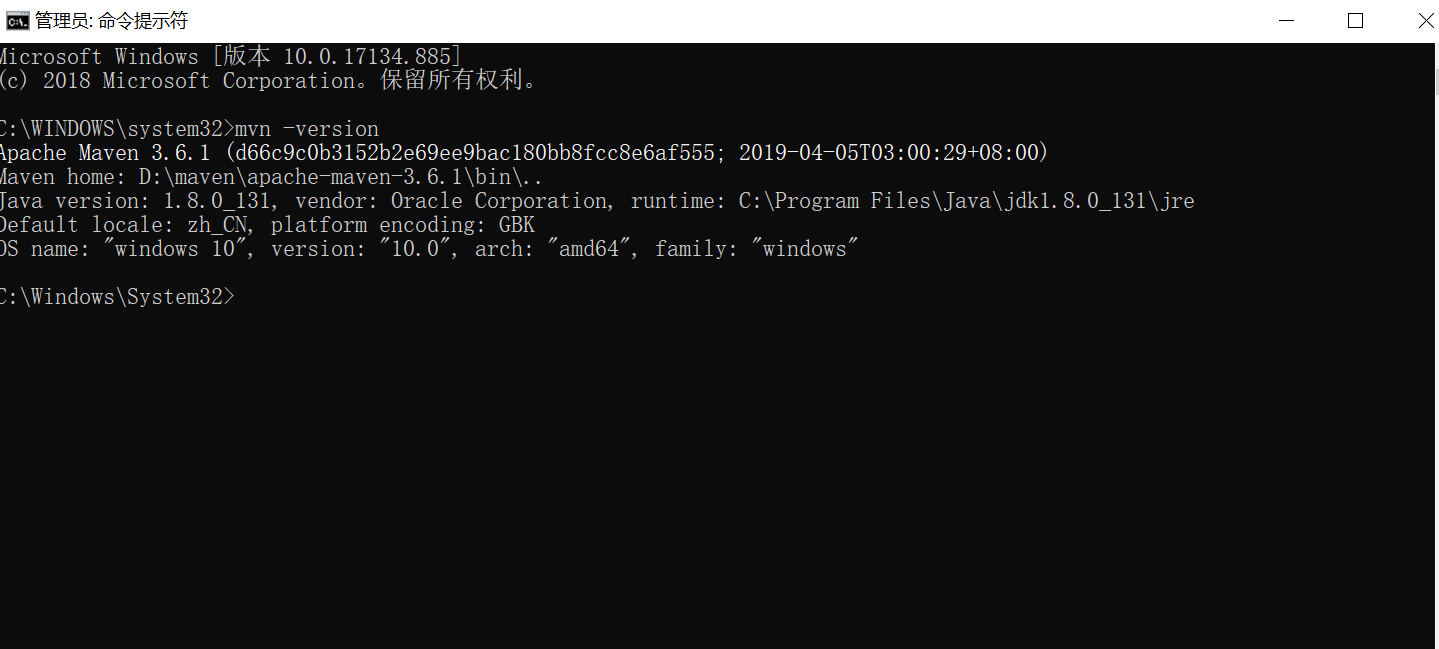
1.3. Local Warehousing Configuration
If you do not configure it, the package downloaded remotely will be stored in the following location by default: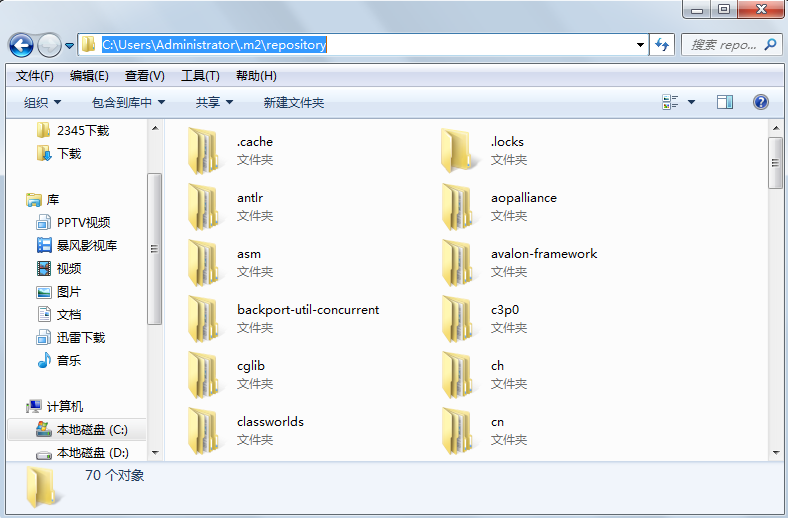
The jar packages downloaded from the central warehouse are stored uniformly in the local warehouse. We need to configure the location of the local warehouse.
Open the maven installation directory and the set. XML file under the conf directory.
Local storage locations can be configured with reference to the figure below.
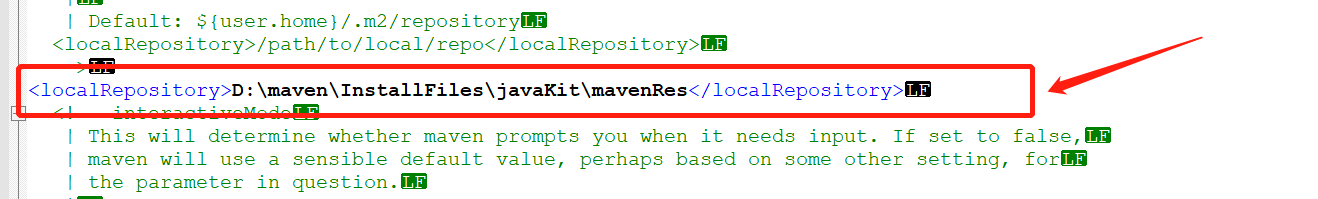
You can also specify a local warehouse location at runtime:
mvn clean install -Dmaven.repo.local=d:\yourpath
1.4. Central Warehouse Configuration
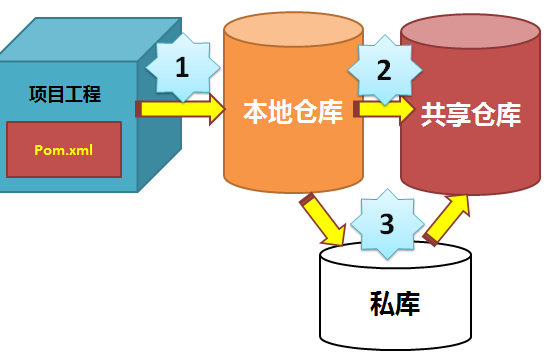
When building a Maven project, first check the pom.xml file to determine the download location of the dependent packages. The order of execution is as follows:
1. Find and obtain dependency packages from local repositories. If not, perform step 2. 2. Find and obtain dependency packages from Maven's default central warehouse. If not, execute Step 3. 3. If a custom remote warehouse is defined in pom.xml, then dependency packages are also found and retrieved in the warehouse. If they are not found, Maven throws an exception.
Modify the default central warehouse address
<mirror> <id>nexus-aliyun</id> <mirrorOf>*,!jeecg,!jeecg-snapshots</mirrorOf> <name>Nexus aliyun</name> <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url> </mirror> </mirrors>
Following is the usual address. It is recommended to use Aliyun.
1,http://www.sonatype.org/nexus/private nexus tool use 2,http://mvnrepository.com/(Recommendation) 3,http://repo1.maven.org/maven2 4,http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/Aliyun (strongly recommended) 5,http://repo2.maven.org/maven2/Private nexus Tool Use 6,http://uk.maven.org/maven2/ 7,http://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/groups/public 8,http://maven.oschina.net/content/groups/public/ 9,http://mirrors.ibiblio.org/maven2/ 10,http://maven.antelink.com/content/repositories/central/ 11,http://nexus.openkoala.org/nexus/content/groups/Koala-release/ 12,http://maven.tmatesoft.com/content/groups/public/
Provide me with complete settings.xml configuration
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
distributed with this work for additional information
regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
software distributed under the License is distributed on an
"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations
under the License.
-->
<!--
| This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels:
|
| 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user,
| and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml.
|
| NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option:
|
| -s /path/to/user/settings.xml
|
| 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven
| users on a machine (assuming they're all using the same Maven
| installation). It's normally provided in
| ${maven.conf}/settings.xml.
|
| NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option:
|
| -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml
|
| The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at
| getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default
| values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided.
|
|-->
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<!-- localRepository
| The path to the local repository maven will use to store artifacts.
|
| Default: ${user.home}/.m2/repository
<localRepository>/path/to/local/repo</localRepository>
-->
<localRepository>D:\maven\InstallFiles\javaKit\mavenRes</localRepository>
<!-- interactiveMode
| This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false,
| maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for
| the parameter in question.
|
| Default: true
<interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode>
-->
<!-- offline
| Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build.
| This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others.
|
| Default: false
<offline>false</offline>
-->
<!-- pluginGroups
| This is a list of additional group identifiers that will be searched when resolving plugins by their prefix, i.e.
| when invoking a command line like "mvn prefix:goal". Maven will automatically add the group identifiers
| "org.apache.maven.plugins" and "org.codehaus.mojo" if these are not already contained in the list.
|-->
<pluginGroups>
<!-- pluginGroup
| Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup.
<pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup>
-->
</pluginGroups>
<!-- proxies
| This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network.
| Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy
| specification in this list marked as active will be used.
|-->
<proxies>
<!-- proxy
| Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network.
|
<proxy>
<id>optional</id>
<active>true</active>
<protocol>http</protocol>
<username>proxyuser</username>
<password>proxypass</password>
<host>proxy.host.net</host>
<port>80</port>
<nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts>
</proxy>
-->
</proxies>
<!-- servers
| This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system.
| Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server.
|-->
<servers>
<!-- server
| Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by
| a unique name within the system (referred to by the 'id' attribute below).
|
| NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are
| used together.
|
<server>
<id>deploymentRepo</id>
<username>repouser</username>
<password>repopwd</password>
</server>
-->
<!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate.
<server>
<id>siteServer</id>
<privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey>
<passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase>
</server>
-->
</servers>
<!-- mirrors
| This is a list of mirrors to be used in downloading artifacts from remote repositories.
|
| It works like this: a POM may declare a repository to use in resolving certain artifacts.
| However, this repository may have problems with heavy traffic at times, so people have mirrored
| it to several places.
|
| That repository definition will have a unique id, so we can create a mirror reference for that
| repository, to be used as an alternate download site. The mirror site will be the preferred
| server for that repository.
|-->
<mirrors>
<!-- mirror
| Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that
| this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used
| for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors.
|
<mirror>
<id>mirrorId</id>
<mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf>
<name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name>
<url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url>
</mirror>
-->
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>*,!jeecg,!jeecg-snapshots</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<!-- profiles
| This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify
| the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine-
| specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment.
|
| For example, if you have an integration testing plugin - like cactus - that needs to know where
| your Tomcat instance is installed, you can provide a variable here such that the variable is
| dereferenced during the build process to configure the cactus plugin.
|
| As noted above, profiles can be activated in a variety of ways. One way - the activeProfiles
| section of this document (settings.xml) - will be discussed later. Another way essentially
| relies on the detection of a system property, either matching a particular value for the property,
| or merely testing its existence. Profiles can also be activated by JDK version prefix, where a
| value of '1.4' might activate a profile when the build is executed on a JDK version of '1.4.2_07'.
| Finally, the list of active profiles can be specified directly from the command line.
|
| NOTE: For profiles defined in the settings.xml, you are restricted to specifying only artifact
| repositories, plugin repositories, and free-form properties to be used as configuration
| variables for plugins in the POM.
|
|-->
<profiles>
<!-- profile
| Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the
| mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/>
| or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique.
|
| An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention
| for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc.
| This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting
| to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug.
|
| This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo.
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.4</id>
<activation>
<jdk>1.4</jdk>
</activation>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jdk14</id>
<name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name>
<url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url>
<layout>default</layout>
<snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy>
</repository>
</repositories>
</profile>
-->
<!--
| Here is another profile, activated by the system property 'target-env' with a value of 'dev',
| which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration
| might hypothetically look like:
|
| ...
| <plugin>
| <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId>
| <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId>
|
| <configuration>
| <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation>
| </configuration>
| </plugin>
| ...
|
| NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set 'target-env' to
| anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property.
|
<profile>
<id>env-dev</id>
<activation>
<property>
<name>target-env</name>
<value>dev</value>
</property>
</activation>
<properties>
<tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath>
</properties>
</profile>
-->
<profile>
<id>jdk1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
<!-- activeProfiles
| List of profiles that are active for all builds.
|
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>alwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile>
<activeProfile>anotherAlwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
-->
</settings>
2. maven's use in eclipse
2.1 Configuration maven
Eclipse is an integrated development environment, which is widely used in the development process. Let's see how to use maven in eclipse. maven support is added to the version of eclipse over 4.4, that is, no maven plug-ins need to be installed, but for the version below 4.4, plug-ins need to be installed by themselves. You can use the following address: http://marketplace.eclipse.org/content/maven-integration-eclipse-luna, to understand the installation process, after the installation is completed,
1. Find the maven option in windows -> preferences, as shown below.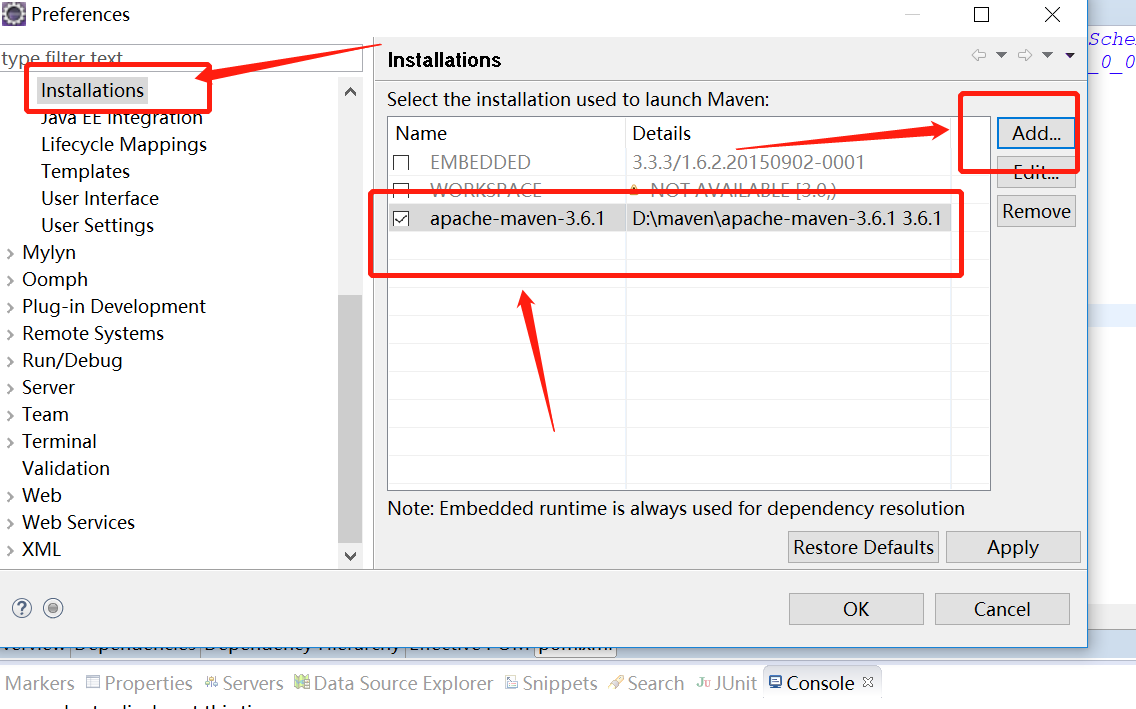
In the picture above, we find maven -> installations. We already have them, but we need to use the Maven we just installed, select the add button, and find the path of the Maven we just decompressed, as follows.
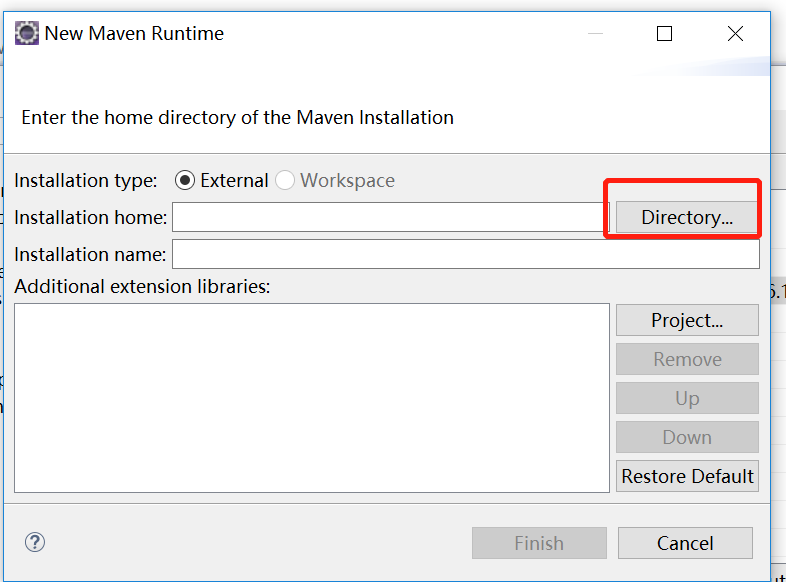
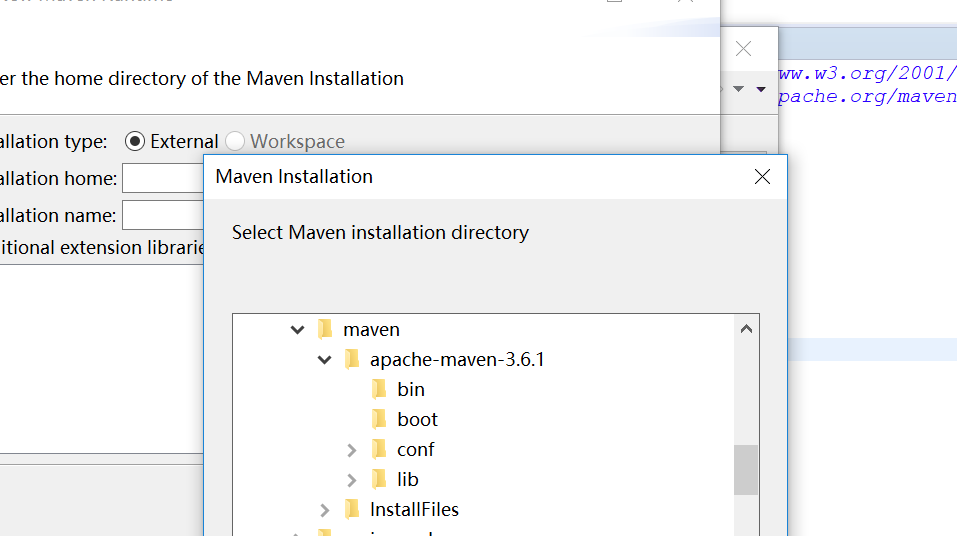
2. Update configuration files in eclipse:
In eclipse, windows -> preferences, find maven, and then, as shown in the figure below, find User settings, modify the configuration file to the configuration file you just modified.
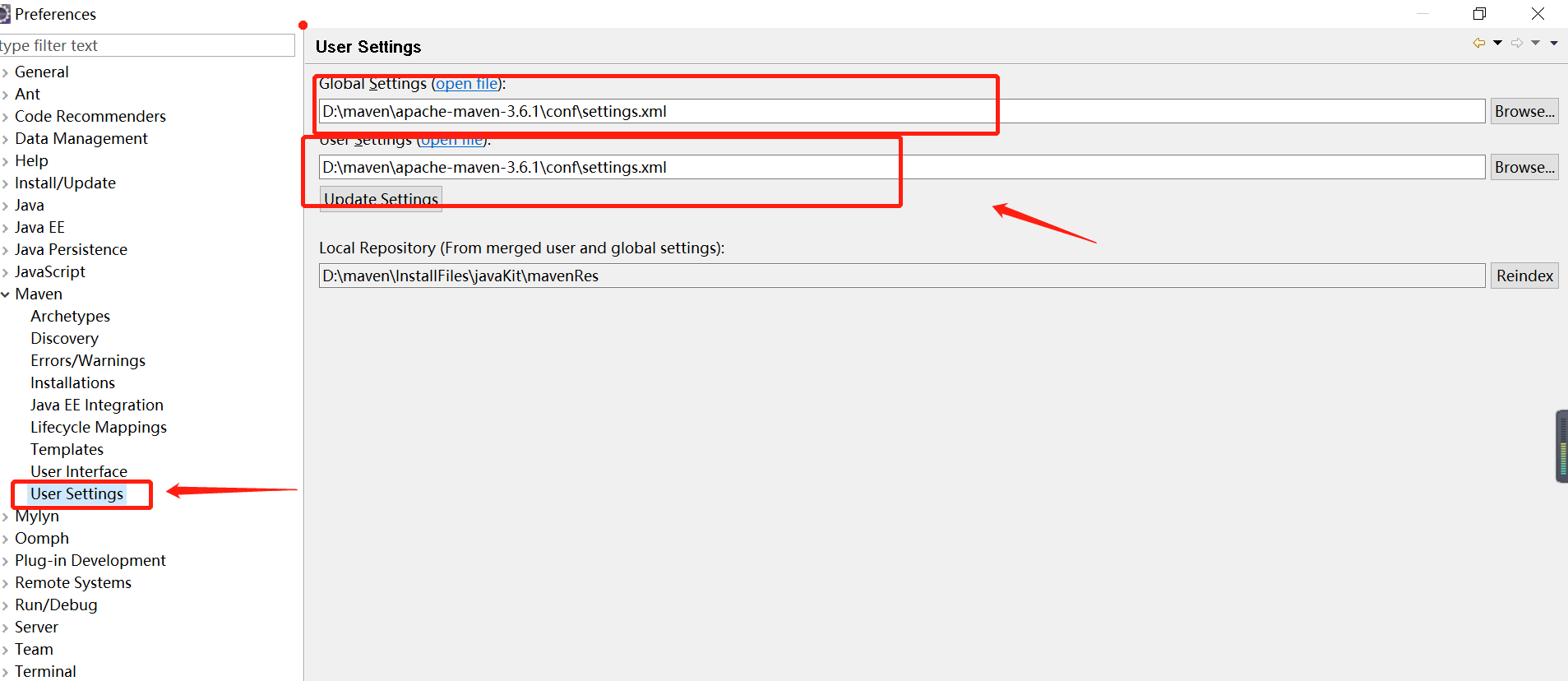
global settings
Configuration of this computer. This configuration is used by all users who use this computer.
Personal configuration (user settings)
Current user configuration
user settings override global settings
After the modification is completed, the integration with eclipse is completed.
After the above steps, the integration of Maven and eclipse is completed, and then Maven can be used. However, if your computer accesses the Internet through a proxy, you must configure the proxy in the settings.xml file, so that you can download the required files from maven's repository. The configuration of the proxy is as follows: in settings.xml Add the following to the file.
<proxy>
<id>myProxy</id>
<active>true</active>
<protocol>http</protocol>
<username></username>
<password></password>
<host>proxy.xxxxx</host>
<port>910</port>
</proxy>
<!--
ID proxy ID identity proxy
active Settings Agent Enabled
Protocol used by protocol agent
The username connection agent's username. If the agent does not need a username, the label can be deleted.
The password of the password connection agent, such as, Ibid.
The website of host agent
Ports used by port agents
The above is the configuration of using proxy to access the internet. If you do not use proxy to access the internet, you do not need to configure it.
-->
2.2 Use maven to create projects in eclipse
Java and Java Web projects are the most frequently used in the development of java.
file -> new -> project, and then find maven, as shown below.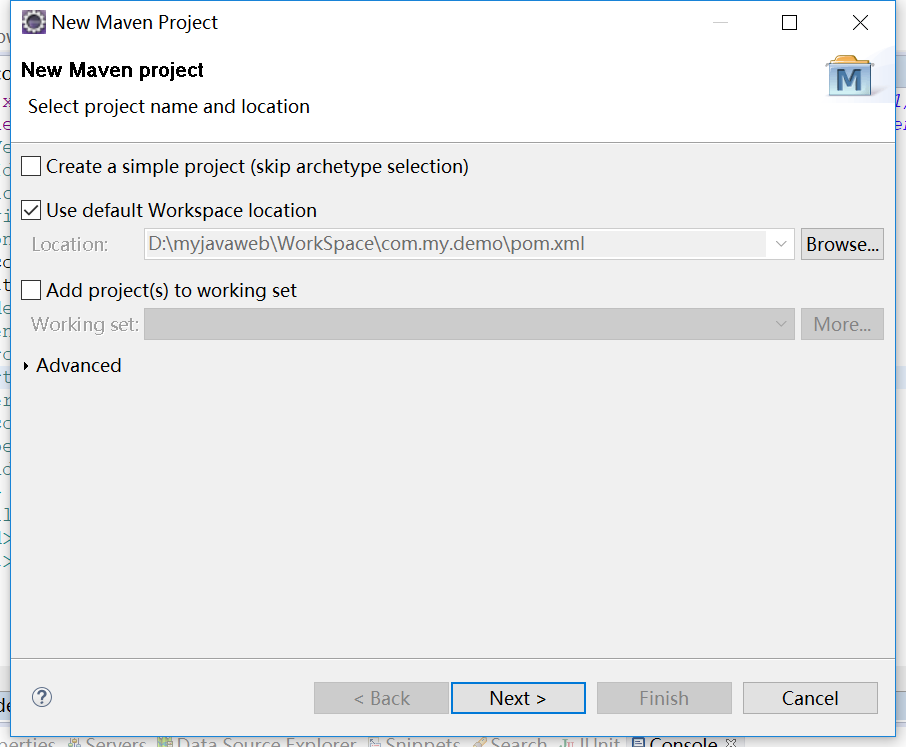
Click next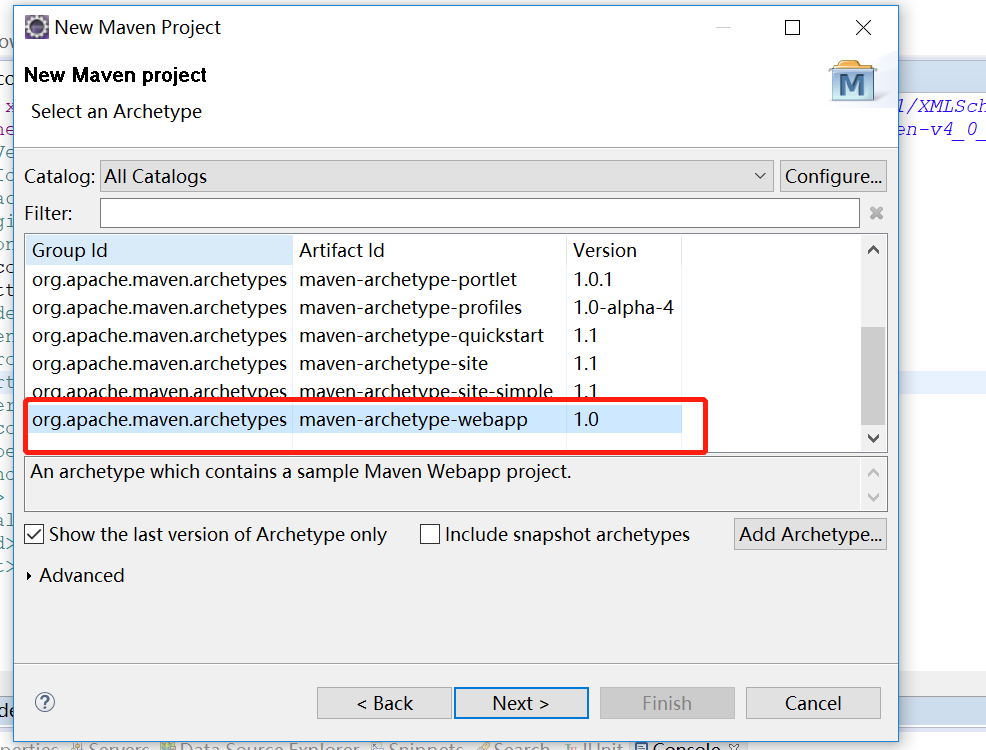
Select webapp and click next
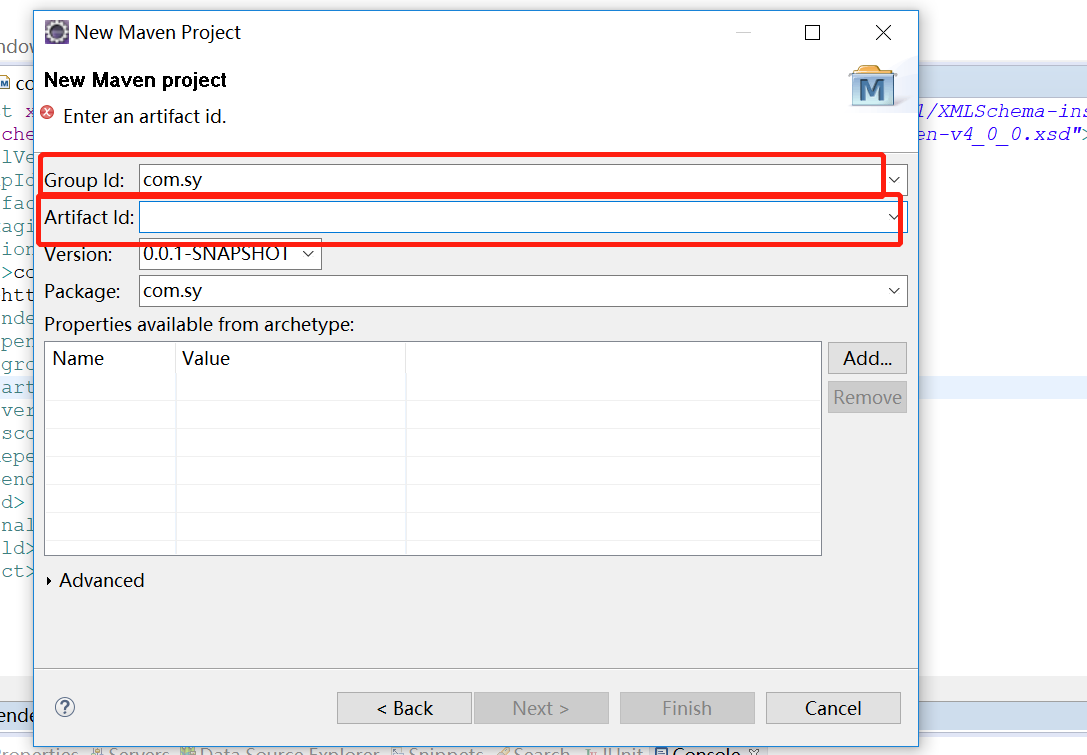
The first red box represents the new java project, and the second is the java Web project. Here, select the first one.
After entering the contents of the red box, click finish and ecplise will start to create the project. At this point, the network will connect to download the required jar packages from the Internet. The path where the jar packages are stored is the path of the configured local warehouse. My path is: D: maven InstallFiles javaKit mavenResy, under the path of D: maven InstallFiles javaKit\ mavenos Reveno. The rg apache maven plugins folder is the dependent plug-in required by the maven plug-in.
Partial reprint to
https://www.cnblogs.com/best/p/9676515.html#_lab2_1_0