ThreadLocal uses:
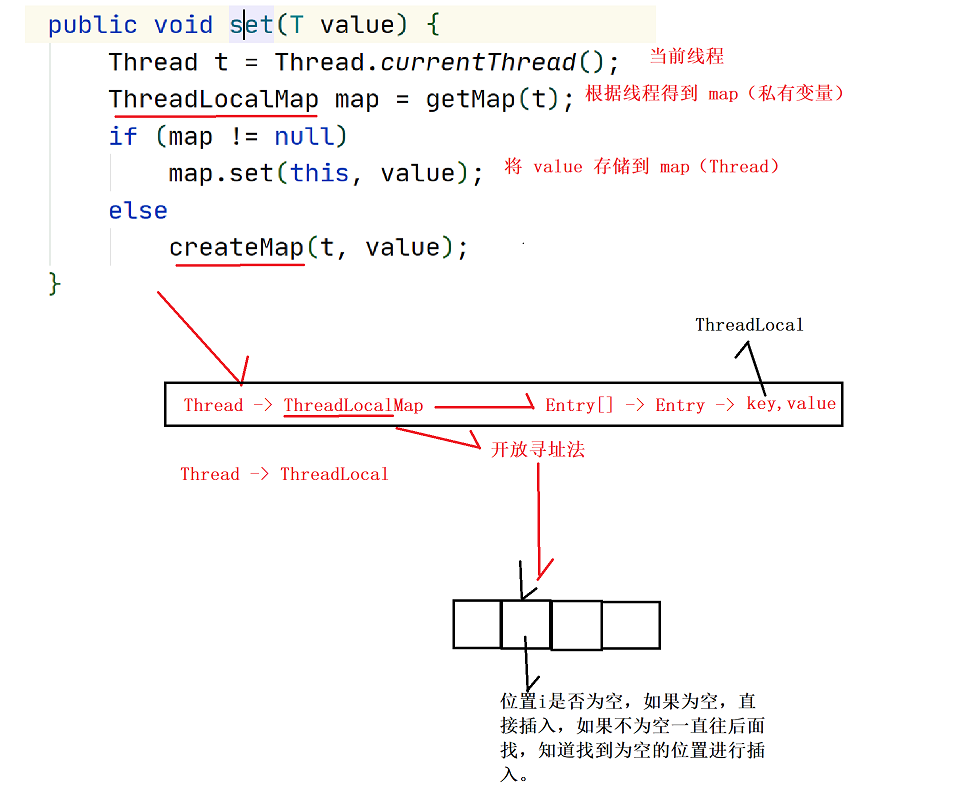
1.set: set the private variable to the thread
2.get: get ThreadLocal from thread
3.remove: remove ThreadLocal from the thread.
4.initialValue: initialization
5.withInitialValue: initialization (lambda expression)
Usage scenario:
1. Solve thread safety problems
2. Realize thread level data transmission
Disadvantages:
1. Data transfer between parent and child threads cannot be performed.
2. Dirty data. ThreadLocal + thread pool (reuse)
3. Memory overflow
Memory overflow problem
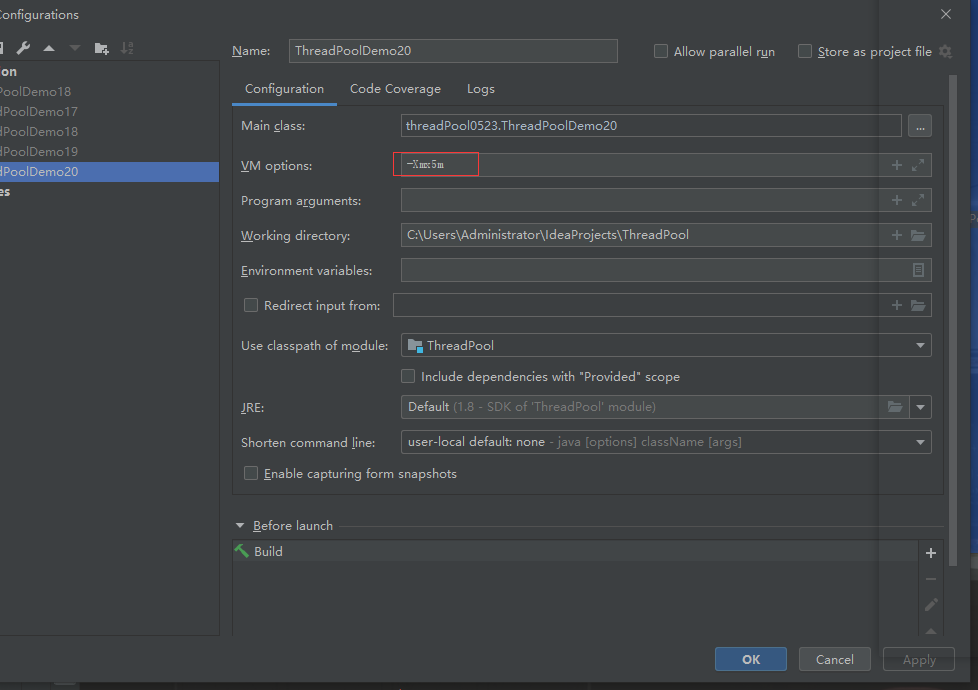
Set the maximum running memory to 5M
package threadPool0523;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadPoolDemo20 {
//1M size object
static class OOMObject{
private byte[] bytes=new byte[1*1024*1024];
}
static ThreadLocal<OOMObject> threadLocal=new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(10,10,0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
for (int i = 0; i <5 ; i++) {
int finalI=i;
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run () {
OOMObject oomObject=new OOMObject();
//set ThreadLocal
System.out.println("task"+finalI+"Yes!");
threadLocal.set(oomObject);
//No more objects
oomObject=null;
}
});
//t.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
}
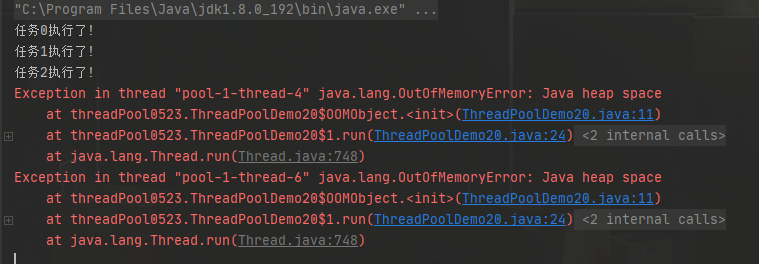
Problem analysis:
The thread pool has a long life cycle. When a thread finishes executing a task, the thread ends (the resources related to the thread will be released).
Interview questions:
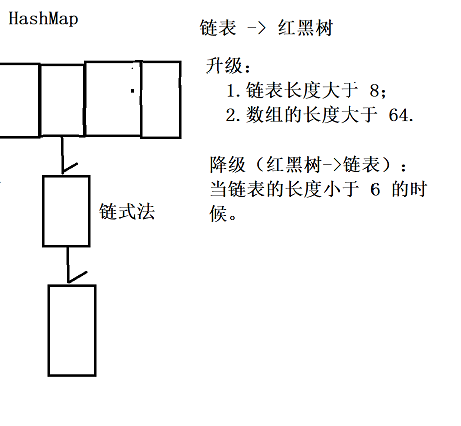
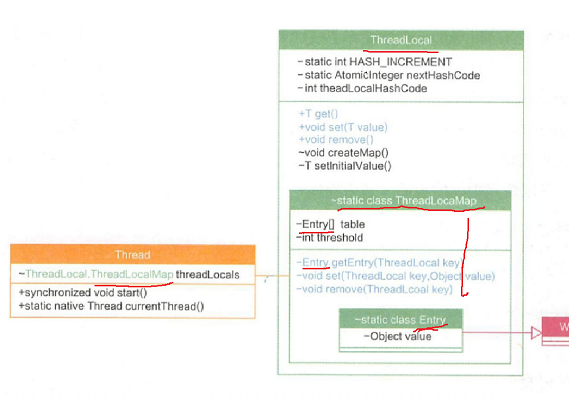
What is the difference between HashMap and ThreadLocalMap in handling hash conflicts?
hashmap uses the linked list method, while ThreadLocalMap uses the open addressing method
Why is it so?
A: the characteristics and usage scenario of open addressing method is that the performance is better when the data volume is less than the price.
The hashmap usually stores a lot of data, and the open addressing method is inefficient. It is best to use the linked list method.
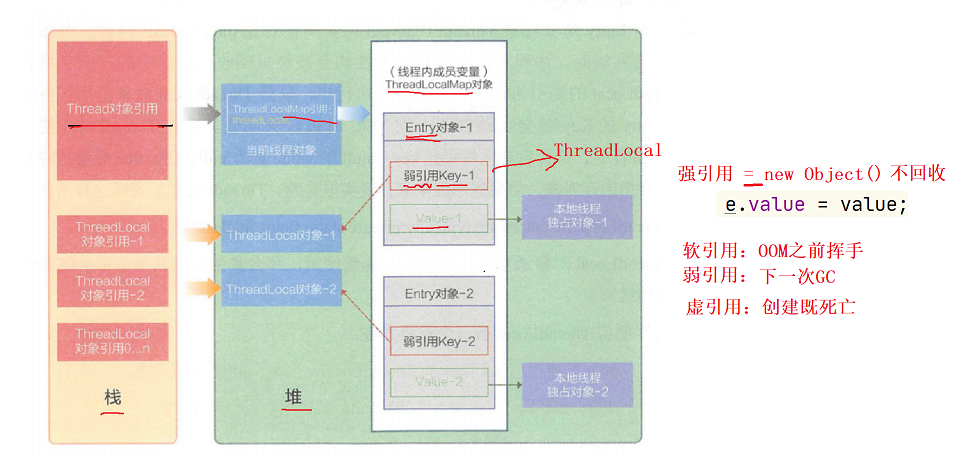
Why set the key in ThreadLocal as weak reference?
To avoid OOM for maximum length

Solve the memory overflow of ThreadLocal?
Use remove ().
Improve program performance:
1. Multithreading
2. Singleton mode
Design mode:
1. Singleton mode (handwriting)
2. Factory mode (simple factory, abstract factory)
3. Template mode
Singleton mode:
Only one object is stored in the operation of the whole program
1: Method: create objects directly (thread safe)
/**
* Hungry man model
*/
package ThreadDemo0603;
class Singleton{
//1. Create a private constructor (prevent other classes from creating directly)
private Singleton(){
}
//2. Define private variables (thread safety)
private static Singleton singleton=new Singleton();
//3. Provide public methods for obtaining instances
public static Singleton getInstance(){
return singleton;
}
}
public class ThreadDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton singleton=Singleton.getInstance();
System.out.println(singleton);
}
}
Disadvantages: the program is created after startup and may not be used, thus wasting system resources.
Lazy way: when the program starts, it will not initialize, but when to call and when to initialize

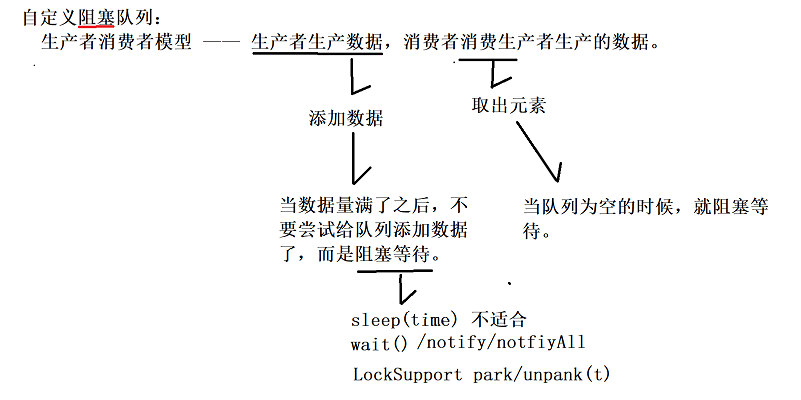
Custom blocking queue: linked list and array
/**
* Custom blocking queue
*/
package ThreadDemo0603;
import java.util.Random;
public class ThreadDemo06 {
static class MyBlockingQueue{
private int[] values;//Array of actual stored data
private int first;//Team leader
private int last;//Team tail
private int size;//Actual size of queue element
public MyBlockingQueue(int initial){
//initialize variable
values=new int[initial];
first=0;
last=0;
size=0;
}
//Add element (add to end of queue)
public void offer(int val){
synchronized (this){
//Judge whether it is full
if(size==values.length){
//Queue full
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Add element to end of queue
values[last++]=val;
size++;
//Determine whether it is the last element
if(last==values.length){
last=0;
}
//Try to wake up consumers
this.notify();
}
}
//Query method
public int poll(){
int result=-1;
synchronized (this){
//Judgment boundary value
if(size==0){
//Queue is empty, blocking waiting
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Take element
result=values[first++];
size--;
//Determine whether it is the last element
if(first==values.length){
first=0;
}
//Try to wake up the producer
this.notify();
}
return result;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyBlockingQueue myBlockingQueue=new MyBlockingQueue(100);
Thread t1=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//One piece of data is produced every 500ms
while(true){
int num=new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("Random number generated:"+num);
myBlockingQueue.offer(num);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
//Create consumer
Thread t2=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
int result=myBlockingQueue.poll();
System.out.println("Consumption data"+result);
}
}
});
t2.start();
}
}