ActiveMQ
Introduction to ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ is the most popular and powerful open source message bus produced by Apache. ActiveMQ is a
Fully support JMS1 1 and J2EE 1.4 specifications, although the JMS specification has been issued for a long time
But JMS still plays a special role in today's J2EE applications.
What is news
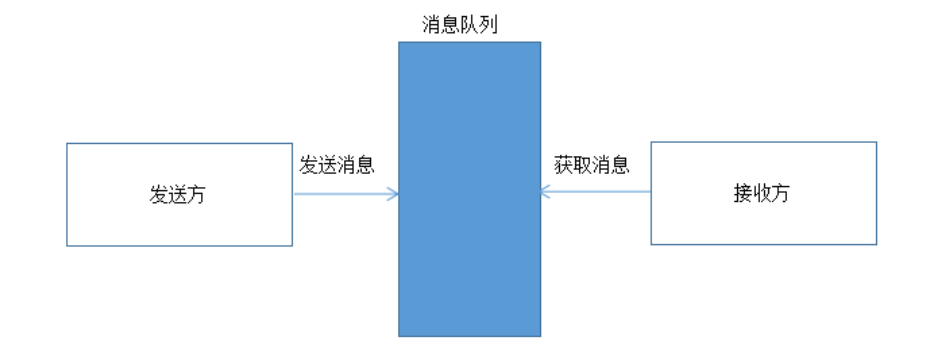
A message is a unit of data transmitted between two computers. Messages can be very simple, such as containing only text strings;
It can also be more complex and may contain embedded objects.
What is a queue
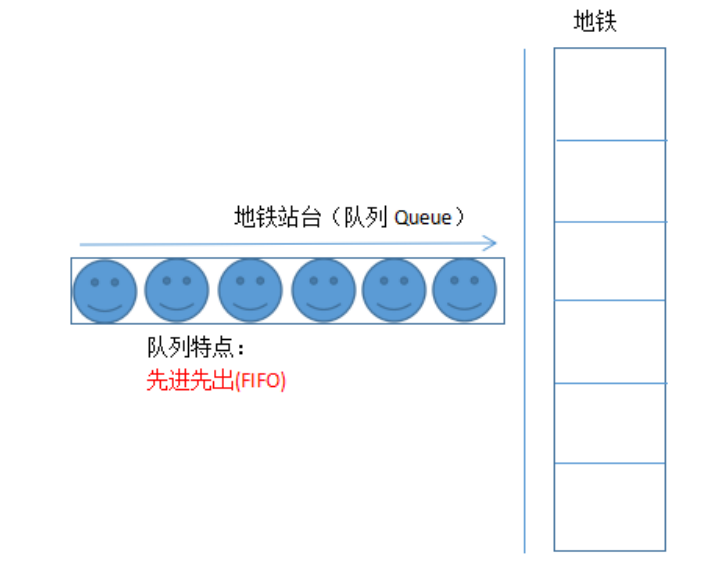
What is a message queue
Message queue is a container that holds messages during transmission
Common message service applications
- ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ is the most popular and powerful open source message bus produced by Apache. ActiveMQ is a fully supported JMS 1 1 and J2EE 1.4 specifications. - RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is a reusable enterprise message system based on AMQP. He follows the Mozilla Public License open source agreement. The development language is Erlang - RocketMQ
A set of message queue application services defined and developed by Alibaba
Application scenario of message service
The main feature of message queue is asynchronous processing. The main purpose is to reduce request response time and decoupling. Therefore, the main usage scenario is to put the operation that is time-consuming and does not need to return the result in real time (synchronization) into the message queue as a message. At the same time, due to the use of message queue, as long as the message format remains unchanged, the sender and receiver of the message do not need to contact each other or be affected by each other, that is, decoupling and
Asynchronous processing
User registration
User registration process:
- Register, process and write database
- Send SMS with successful registration
- Send mail information of successful registration
If you use message oriented middleware: you can create two threads to do these things and send messages directly to message oriented middleware,
Then let the email service and SMS service go to the message middleware to get the message, and then do the corresponding business operation after getting the message. It's so convenient
Applied decoupling
Order processing
Order generation process:
- Click settlement in the shopping cart
- Complete payment
- Create order
- Call inventory system
After the order is completed, the order system does not directly call the inventory system, but sends a message to the message middleware and writes a message
Order information. The inventory system obtains the information from the message middleware, then processes the delivery and updates the inventory, which can
Fast enough to realize the pursuit of Internet applications. After the inventory system reads the order, the operation of inventory application is also non-standard
Often fast, so having message oriented middleware is also a good direction for decoupling.
Peak clipping of flow
Second kill function
Second kill process:
- User clicks second kill
- Send request to seckill app
- Put the request into the message queue before requesting the second kill application
- The seckill application obtains the request from the message queue and processes it.
For example, the system holds second kill activities and popular goods. The flow is swarming to 100 goods, and 100000 people are crowded in. What's the matter
What? 100000 second kill operation, put it into the message queue. The second kill application processes the top 100 of the 100000 requests in the message queue
One, others call back, notification failed. The traffic peak is controlled at the message queue, and the second kill application will not be killed instantly
JMS
JMS (Java Messaging Service) is a technical specification of message oriented middleware on Java platform, which is convenient for
Java applications in the message system exchange messages, and provide standard access to generate, send and receive messages
To simplify the development of enterprise applications.
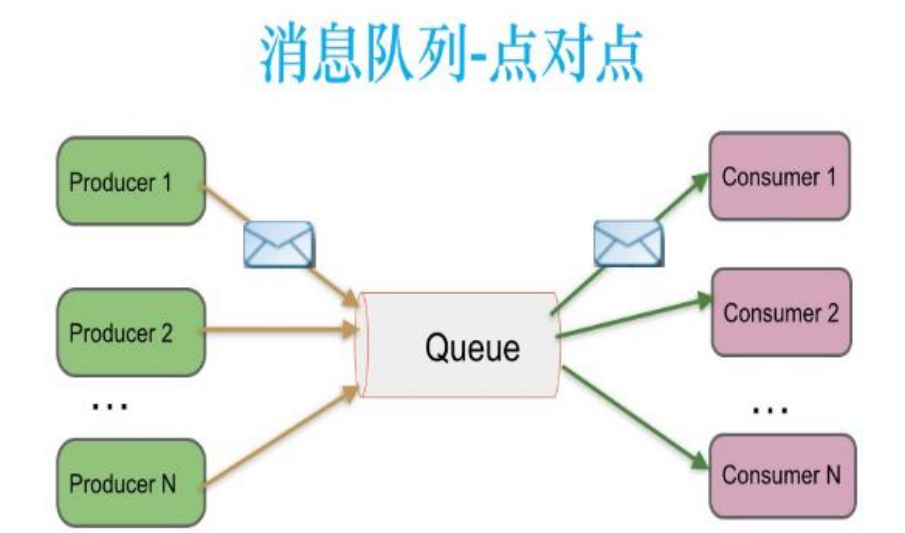
Point to point model
The producer sends a message to the queue, and only one consumer can receive it.
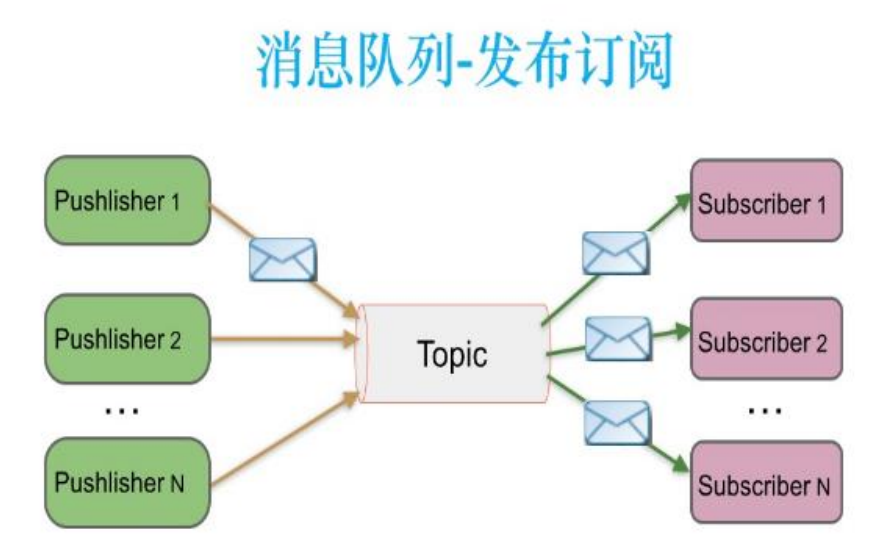
Publish / subscribe model
Only subscribers who subscribe to topic will receive messages sent by publishers to topic
ActiveMQ installation
You can download the installation package on the ActiveMQ official website: http://activemq.apache.org
be careful:
- ActiveMQ5. Version 10. X and above must use jdk1 8 can be used normally.
- ActiveMQ5.9.x and below use jdk1 7 can be used normally
Extract the installation files
tar -zxf apache-activemq-5.9.0-bin.tar.gz
Copy applied to local directory
cp -r apache-activemq-5.9.0 /usr/local/activemq
Start ActiveMQ
/usr/local/activemq/bin/activemq start
If activemq does not have permission to execute the file, it needs to be added through the chmod command
Testing ActiveMQ
ps aux | grep activemq
Seeing the following indicates successful startup
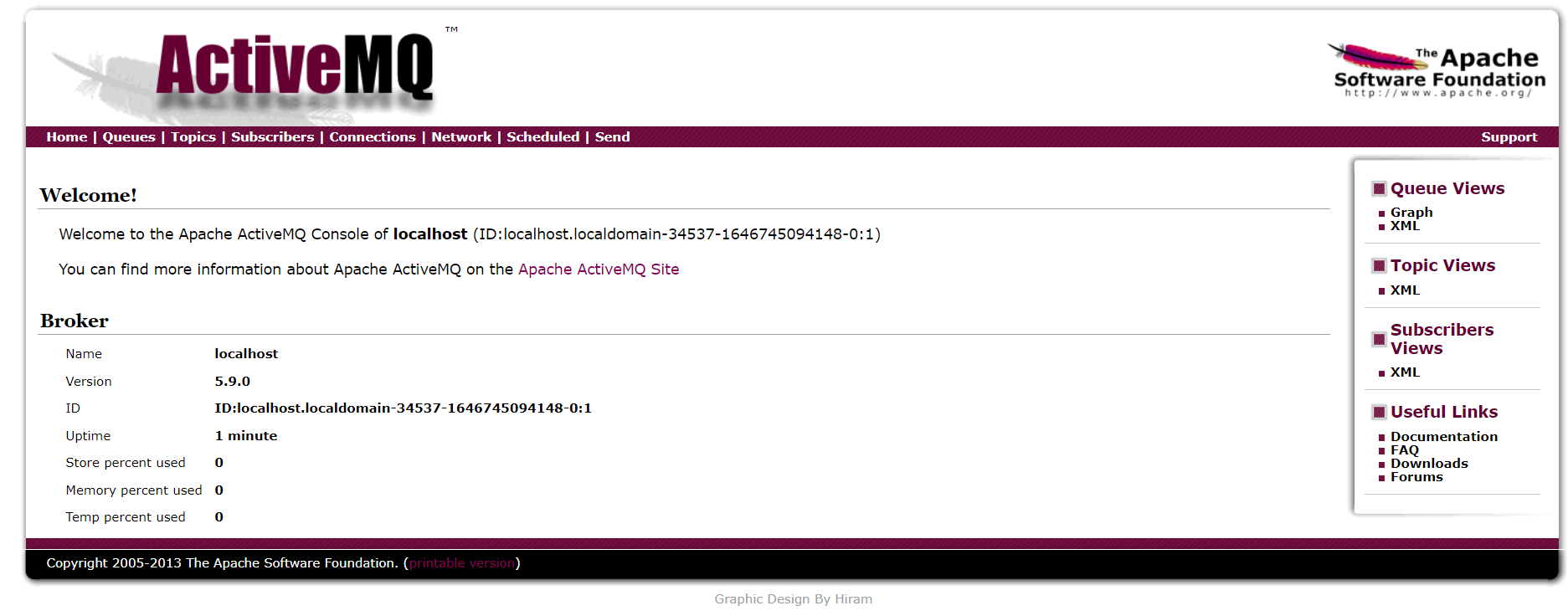
Management interface
Use the browser to access the ActiveMQ management application. The address is as follows:
http://ip:8161/admin/
User name: admin
Password: admin
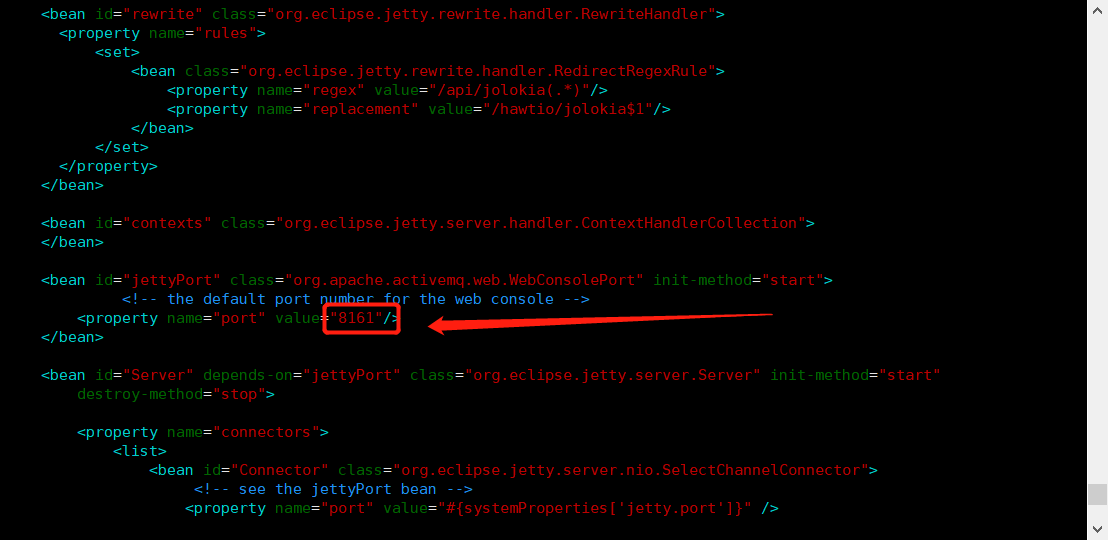
Modify access port:
vim /usr/local/activemq/conf/jetty.xml
Modify user name and password
vim /usr/local/activemq/conf/users.properties
Then set the following key value pairs

Change to
User defined user name: user defined password
that will do
Note: whether you want to change the port or the user name or password, you need to restart activemq before it takes effect
Restart ActiveMQ
/usr/local/activemq/bin/activemq restart
Turn off ActiveMQ
/usr/local/activemq/bin/activemq stop
Configuration file ActiveMQ xml
In the configuration file, the core configuration information of ActiveMQ is configured Is the configuration used when providing services Can be modified
Access port to start That is, the access port to access ActiveMQ in java programming
The default port is 61616
The protocol used is: tcp protocol
Modify port:
vim /usr/local/activemq/conf/activemq.xml
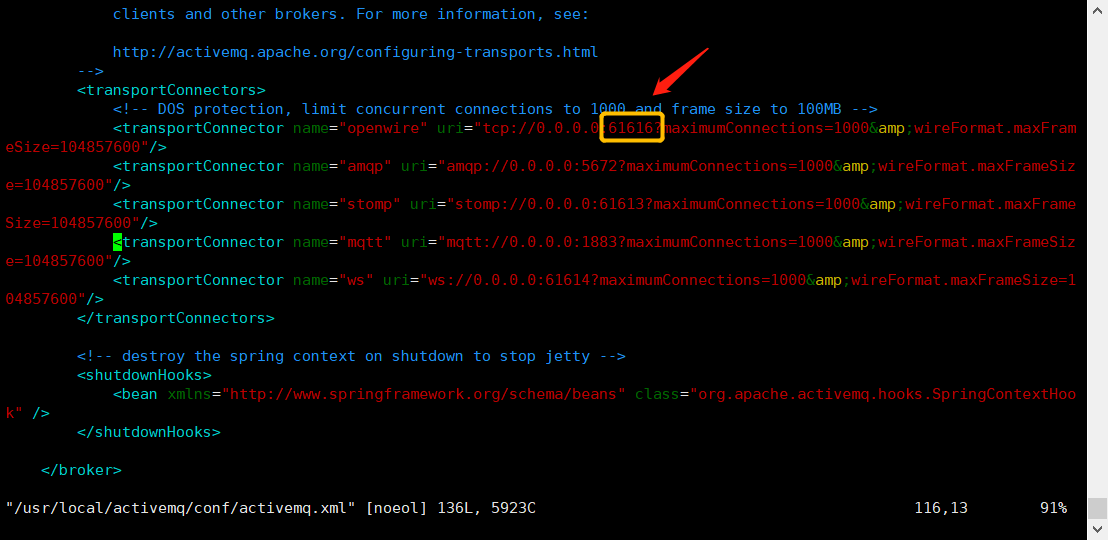
After modifying the port, save and restart ActiveMQ service
ActiveMQ directory introduction
- bin stores script files
- conf stores the basic configuration file
- data stores log files
- docs stores instruction documents
- Examples store simple examples
- lib stores the jar package required by activemq
- webapps is the directory used to store the project
ActiveMQ terminology
Destination
Destination: the JMS Provider (Message Middleware) is responsible for maintaining the object used to manage messages.
MessageProducer needs to specify a Destination to send messages, and MessageReceiver needs to specify a Destination to receive messages.
Producer
The Message generator is responsible for sending the Message to the destination.
Consumer | Receiver
The Message consumer is responsible for consuming [process | monitor | subscribe] messages from the destination
Message
Message encapsulates the content of a communication
ActiveMQ application
Introduction to ActiveMQ common API s
- ConnectionFactory: link factory, the type of factory used to create the link
- Connection: link The type used to establish a connection to ActiveMQ, created by the link factory
- Session: session, a persistent and stateful access Created by link
- Destination & Queue:
Destination, used to describe the message access destination of ActiveMQ this time That is, the specific queue in ActiveMQ service Created by session
interface Queue extends Destination· - MessageProducer:
Message consumer [message subscriber, message handler], a tool used to obtain messages from ActiveMQ service in a valid session Created by session - Message:
Message, the data carrier object used by the message generator when sending a message to ActiveMQ service or the data carrier object used by the message consumer when getting a message from ActiveMQ service It is the top-level interface of specific types of all messages [text message, object message, etc.) It can be created through a session or obtained from ActiveMQ service through a session
ActiveMQ simple instance
- pom.xml dependency
<!--https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.activemq/activemq-all --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId> <artifactId>activemq-all</artifactId> <version>5.9.0</version> </dependency>
- Message producer (first maven project)
public class HelloWorldProducer {
public void sendHelloWorldActiveMQ(String
msgTest){
//Define link factory
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = null;
//Define linked objects
Connection connection = null;
//Define session
Session session = null;
//destination
Destination destination = null;
//Defines the sender of the message
MessageProducer producer = null;
//Define message
Message message = null;
try{
/**
* userName:The user name to access the ActiveMQ service. User password. The default is admin.
* password:The user name to access the ActiveMQ service. User password. The default is admin.
* brokerURL:The path address to access the ActiveMQ service. Path structure: protocol name: / / host address: port number
*/
connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("admin", "admin", "tcp://192.168.70.151:61616");
//Create connection object
connection =
connectionFactory.createConnection();
//Start connection
connection.start();
/**
* transacted:Whether to use transactions. The optional values are: true|false
* true:Use transactions when setting this variable value. Session.SESSION_TRANSACTED
* false:Not applicable to transactions. If this variable is set, the acknowledgeMode parameter must be set
* acknowledgeMode:
* Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE:Automatic message confirmation
mechanism
* Session.CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE:Client confirmation
mechanism
* Session.DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE:Guest with copy
Client confirmation message mechanism
*/
session = connection.createSession(false,
Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//Create a destination. The destination name is the name of the queue. The consumer of the message needs to access the corresponding queue through this name
destination = session.createQueue("helloworld-destination");
//Create the producer of the message
producer = session.createProducer(destination);
//Create message object
message = session.createTextMessage(msgTest);
//send message
producer.send(message);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//Reclaim message sender resources
if(producer != null){
try {
producer.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(session != null){
try {
session.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
- Message consumer (second maven project)
public class HelloWorldConsumer {
public void readHelloWorldActiveMQ() {
// Define link factory
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = null;
// Define linked objects
Connection connection = null;
// Define session
Session session = null;
// destination
Destination destination = null;
// Defines the sender of the message
MessageConsumer consumer = null;
// Define message
Message message = null;
try {
/**
* userName:The user name to access the ActiveMQ service. The default is admin.
* password:The user name to access the ActiveMQ service. The default is admin.
* brokerURL:The path address to access the ActiveMQ service.
* Path structure: protocol name: / / host address: port number
*/
connectionFactory = new
ActiveMQConnectionFactory("admin", "admin","tcp://192.168.70.151:61616");
// Create connection object
connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
// Start connection
connection.start();
/**
* transacted:Whether to use transaction. The optional values are:
* true|false
* true:Use transactions when setting the value of this variable. Session.SESSION_TRANSACTED
* false:If this variable is not applicable to transactions, the acknowledgeMode parameter must be set
* acknowledgeMode:
* Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE:Automatic message confirmation mechanism
* Session.CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE:Client confirmation mechanism
* Session.DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE:Client acknowledgement message mechanism with replica
*/
session = connection.createSession(false,Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
// Create a destination. The destination name is the name of the queue. The consumer of the message needs to access the corresponding queue through this name
destination = session.createQueue("helloworld-destination");
// Consumer who created the message
consumer =session.createConsumer(destination);
// Create message object
message = consumer.receive();
//Processing messages
String msg = ((TextMessage)message).getText();
System.out.println("from ActiveMQ Text information obtained from the service "+msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Reclaim message sender resources
if (consumer != null) {
try {
consumer.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (session != null) {
try {
session.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
- test
producer
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloWorldProducer producer = new HelloWorldProducer();
producer.sendHelloWorldActiveMQ("HelloWorld");
}
}
consumer
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloWorldConsumer consumer = newHelloWorldConsumer();
consumer.readHelloWorldActiveMQ();
}
}
ActiveMQ processing object information
The class of the object that can be processed must implement the Serializable interface
- Changes in producer code
//When processing string information in the above simple example: // message = session.createTextMessage(msgTest); //When processing object information //Create message object message = session.createObjectMessage(users);
- Changes in consumer code
//When processing string information in the above simple example: //String msg = ((TextMessage)message).getText(); //When processing object information // Create message object message = consumer.receive(); //Processing messages ObjectMessage objMessage = (ObjectMessage)message; Users users = (Users)objMessage.getObject();
JMS - implement queue service listening
- No change in producer code
- Changes in consumer code
//In the above simple example:
//String msg = ((TextMessage)message).getText();
//Queue service
consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
//Method of ActiveMQ callback. This method passes the message to the consumer
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {
//Processing messages
String msg=null;
try {
msg = ((TextMessage)message).getText();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("from ActiveMQ Text information obtained from the service "+msg);
}
});
Publish/Subscribe processing mode (Topic)
- Changes in producer code
//In the above simple example:
//destination = session.createQueue("helloworld-destination");
//Publish/Subscribe processing mode
destination = session.createTopic("test-topic");
- Changes in consumer code
//In the above simple example:
//destination = session.createQueue("helloworld-destination");
//String msg = ((TextMessage)message).getText();
//Publish/Subscribe processing mode
destination = session.createTopic("test-topic");
consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
//Method of ActiveMQ callback. This method passes the message to the consumer
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {
//Processing messages
String msg=null;
try {
msg = ((TextMessage)message).getText();
} catch (JMSException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("from ActiveMQ Text information obtained from the service "+msg);
}
});
//The run method is overridden in the producer class
@Override
public void run() {
this.readHelloWorldActiveMQ();
}