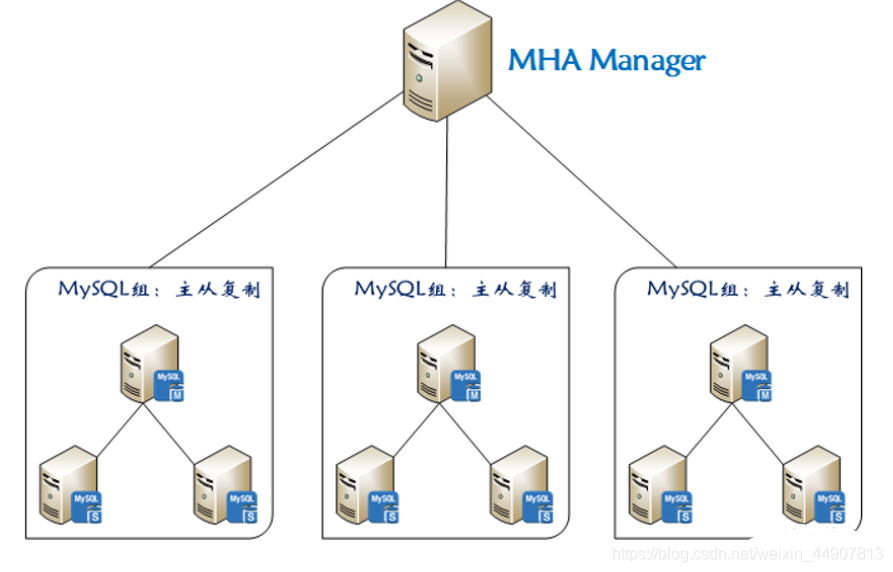
1, Introduction
At present, MHA (Master High Availability) is a relatively mature solution for MySQL high availability. It is developed by Japan DeNA company youshimaton (now working for Facebook company). It is an excellent set of high availability software for failover and master-slave improvement in MySQL high availability environment. In the process of MySQL failover, MHA can automatically complete the database failover within 0 ~ 30 seconds, and in the process of failover, MHA can ensure the consistency of data to the greatest extent, so as to achieve high availability in the real sense.
2, Composition
It consists of two parts: MHA Manager (management node) and MHA Node (data node).
When the master fails, it can automatically promote the slave of the latest data to the new master, and then point all other slave to the new master again. The entire failover process is completely transparent to the application.
3, Working process
In the process of MHA automatic failover, MHA tries to save binary logs from the down primary server to ensure no data loss to the greatest extent, but this is not always feasible. For example, if the primary server hardware fails or cannot be accessed through ssh, MHA cannot save binary logs, only fails over and loses the latest data. Using MySQL 5.5 semi synchronous replication can greatly reduce the risk of data loss. MHA can be combined with semi synchronous replication. If only one slave has received the latest binary log, MHA can apply the latest binary log to all other slave servers, so it can ensure the data consistency of all nodes.
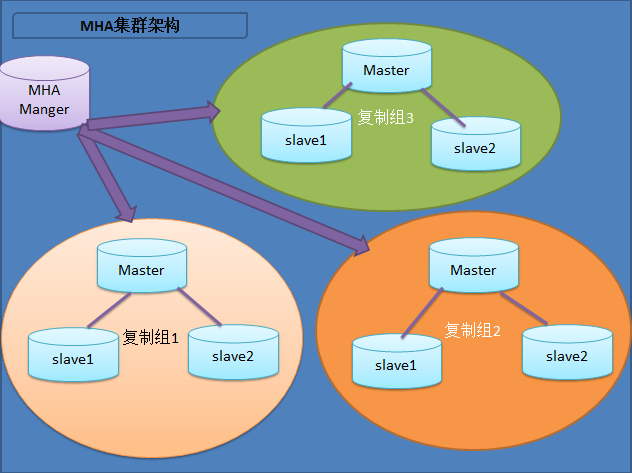
4, Structure
To build an MHA, a replication cluster must have at least three database servers, one master and two slave, that is, one serves as a master, one as a standby master and the other as a slave.
(1) Save binary log events from the master of downtime and crash;
(2) Identify the slave with the latest update;
(3) Apply different relay log s to other slave;
(4) Apply binary log events saved from the master;
(5) Upgrade a slave to a new master;
(6) Connect other slave s to the new master for replication;
Main functions of Manager Toolkit
masterha_check_ssh inspect MHA of SSH Configuration status masterha_check_repl inspect MySQL Replication status masterha_manger start-up MHA masterha_check_status Detect current MHA running state masterha_master_monitor testing master Is it down masterha_master_switch Control failover (automatic or manual) masterha_conf_host Add or remove configured server information
Node toolkit functions
save_binary_logs Save and copy master Binary log for apply_diff_relay_logs Identify differential relay log events and apply their differential events to other events slave filter_mysqlbinlog Remove unnecessary ROLLBACK Events( MHA (this tool is no longer used) purge_relay_logs Clear relay log (no blocking) SQL Thread)
5, Example display
Preparation for MHA deployment:
role ip address host name server_id type Monitor host 192.168.0.20 server01 - Monitoring replication groups Master 192.168.0.50 server02 1 write in Candicate master 192.168.0.60 server03 2 read Slave 192.168.0.70 server04 3 read
The master provides external write services, the alternative master (actual slave, hostname server03) provides read services, and the slave also provides related read services. Once the Master goes down, the alternative master will be promoted to a new master, and the slave points to the new master
## 1. Turn off the firewall systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld setenforce 0 ## 2. Set host name hostnamectl set-hostname Mysql1 hostnamectl set-hostname Mysql2 hostnamectl set-hostname Mysql3 ## 3. Node settings: Master, slave1, slave2 configuration files / etc / my cnf ## a,Master node## vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] server-id = 1 log_bin = master-bin log-slave-updates = true systemctl restart mysqld ##Slave1,Slave2 node## vim /etc/my.cnf server-id = 2 #The server IDs of the three servers cannot be the same log_bin = master-bin relay-log = relay-log-bin relay-log-index = slave-relay-bin.index systemctl restart mysqld ## 4. Create soft links ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/sbin/ ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog /usr/sbin/ ## 5. One master and two slaves: mysql authorization for all nodes mysql -uroot -p grant replication slave on *.* to 'myslave'@'192.168.80.%' identified by '123'; #Synchronize use from database grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'192.168.80.%' identified by 'manager'; #manager usage grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'Mysql1' identified by 'manager'; #Prevent the slave library from connecting to the master library through the host name grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'Mysql2' identified by 'manager'; grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'Mysql3' identified by 'manager';
## Binary files and synchronization points can be seen on the master show master status; +-------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | Executed_Gtid_Set | +-------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+ | master-bin.000002 | 1745 | | | | +-------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
## Data synchronization results of slave1 and slave2 nodes show slave status\G //Ensure that both IO and SQL threads are Yes, which means the synchronization is normal. Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes
# slave1 and slave2 are set to read-only mode set global read_only=1;
# Create database test ##stay Master Insert a piece of data into the main library to test whether it is synchronized## create database test_db; use test_db; create table test(id int); insert into test(id) values (1);
# View from database select * from test_db.test; +------+ | id | +------+ | 1 | +------+
Install MHA software
(1) MHA dependent environments are installed on all servers. First, install the epel source
yum install epel-release --nogpgcheck -y yum install -y perl-DBD-MySQL \ perl-Config-Tiny \ perl-Log-Dispatch \ perl-Parallel-ForkManager \ perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder \ perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker \ perl-CPAN
(2) To install MHA package, you must first install node components on all servers
The version of each operating system is different. Here, centos7 4. Version 0.57 must be selected.
You must first install the node component on all servers, and finally install the manager component on the MHA manager node, because manager depends on the node component.
cd /opt tar zxvf mha4mysql-node-0.57.tar.gz cd mha4mysql-node-0.57 perl Makefile.PL make && make install
(3) Install the manager component on the MHA manager node
cd /opt tar zxvf mha4mysql-manager-0.57.tar.gz cd mha4mysql-manager-0.57 perl Makefile.PL make && make install
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #After the manager component is installed, several tools will be generated under / usr/local/bin, mainly including the following: masterha_check_ssh inspect MHA of SSH Configuration status masterha_check_repl inspect MySQL Replication status masterha_manger start-up manager Script for masterha_check_status Detect current MHA running state masterha_master_monitor testing master Is it down masterha_master_switch Control failover (automatic or manual) masterha_conf_host Add or remove configured server information masterha_stop close manager #After the node component is installed, several scripts will also be generated under / usr/local/bin (these tools are usually triggered by MHAManager scripts without manual operation). The main contents are as follows: save_binary_logs Save and copy master Binary log for apply_diff_relay_logs Identify differential relay log events and apply their differential events to other events slave filter_mysqlbinlog Remove unnecessary ROLLBACK Events( MHA (this tool is no longer used) purge_relay_logs Clear relay log (no blocking) SQL Thread) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7. Configure password less authentication on all servers
(1) Configure password less authentication to all database nodes on the manager node
ssh-keygen -t rsa #Press enter all the way ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.10 ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.20 ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.30
(2) Configure password free authentication to database nodes mysql2 and mysql3 on mysql1
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.20 ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.30
(3) Configure password free authentication to database nodes mysql1 and mysql3 on mysql2
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.10 ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.30
(4) Configure password free authentication to the database nodes mysql1 and mysql2 on mysql3
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.10 ssh-copy-id 192.168.80.20
8. Configure MHA on the manager node
(1) On the manager node, copy the relevant scripts to the / usr/local/bin directory
cp -rp /opt/mha4mysql-manager-0.57/samples/scripts /usr/local/bin //After copying, there will be four execution files ll /usr/local/bin/scripts/ ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- master_ip_failover #Script for VIP management during automatic switching master_ip_online_change #Management of vip during online switching power_manager #Script to shut down the host after a failure send_report #Script for sending alarms after failover ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(2) Copy the above script of VIP management during automatic switching to / usr/local/bin directory. Here, use master_ip_failover scripts to manage VIPs and failover
cp /usr/local/bin/scripts/master_ip_failover /usr/local/bin
(3) The modified contents are as follows: (delete the original contents, directly copy and modify vip related parameters)
vim /usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use strict;
use warnings FATAL => 'all';
use Getopt::Long;
my (
$command, $ssh_user, $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip,
$orig_master_port, $new_master_host, $new_master_ip, $new_master_port
);
#############################Add content section#########################################
my $vip = '192.168.80.200'; #Specify the address of the vip
my $brdc = '192.168.80.255'; #Specify the broadcast address of the vip
my $ifdev = 'ens33'; #Specify the network card bound by vip
my $key = '1'; #Specifies the serial number of the virtual network card bound by the vip
my $ssh_start_vip = "/sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key $vip"; #Represents that the value of this variable is ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.80.200
my $ssh_stop_vip = "/sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key down"; #Represents that the value of this variable is ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.80.200 down
my $exit_code = 0; #Specifies that the exit status code is 0
#my $ssh_start_vip = "/usr/sbin/ip addr add $vip/24 brd $brdc dev $ifdev label $ifdev:$key;/usr/sbin/arping -q -A -c 1 -I $ifdev $vip;iptables -F;";
#my $ssh_stop_vip = "/usr/sbin/ip addr del $vip/24 dev $ifdev label $ifdev:$key";
##################################################################################
GetOptions(
'command=s' => \$command,
'ssh_user=s' => \$ssh_user,
'orig_master_host=s' => \$orig_master_host,
'orig_master_ip=s' => \$orig_master_ip,
'orig_master_port=i' => \$orig_master_port,
'new_master_host=s' => \$new_master_host,
'new_master_ip=s' => \$new_master_ip,
'new_master_port=i' => \$new_master_port,
);
exit &main();
sub main {
print "\n\nIN SCRIPT TEST====$ssh_stop_vip==$ssh_start_vip===\n\n";
if ( $command eq "stop" || $command eq "stopssh" ) {
my $exit_code = 1;
eval {
print "Disabling the VIP on old master: $orig_master_host \n";
&stop_vip();
$exit_code = 0;
};
if ($@) {
warn "Got Error: $@\n";
exit $exit_code;
}
exit $exit_code;
}
elsif ( $command eq "start" ) {
my $exit_code = 10;
eval {
print "Enabling the VIP - $vip on the new master - $new_master_host \n";
&start_vip();
$exit_code = 0;
};
if ($@) {
warn $@;
exit $exit_code;
}
exit $exit_code;
}
elsif ( $command eq "status" ) {
print "Checking the Status of the script.. OK \n";
exit 0;
}
else {
&usage();
exit 1;
}
}
sub start_vip() {
`ssh $ssh_user\@$new_master_host \" $ssh_start_vip \"`;
}
## A simple system call that disable the VIP on the old_master
sub stop_vip() {
`ssh $ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \" $ssh_stop_vip \"`;
}
sub usage {
print
"Usage: master_ip_failover --command=start|stop|stopssh|status --orig_master_host=host --orig_master_ip=ip --orig_master_port=port --new_master_host=host --new_master_ip=ip --new_master_port=port\n";
}
(4) Create MHA software directory and copy configuration files. Here, use app1 CNF configuration file to manage mysql node server
mkdir /etc/masterha cp /opt/mha4mysql-manager-0.57/samples/conf/app1.cnf /etc/masterha vim /etc/masterha/app1.cnf #Delete the original content, directly copy and modify the IP address of the node server [server default] manager_log=/var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log manager_workdir=/var/log/masterha/app1 master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data master_ip_failover_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover master_ip_online_change_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_online_change password=manager ping_interval=1 remote_workdir=/tmp repl_password=123 repl_user=myslave secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.80.20 -s 192.168.80.30 shutdown_script="" ssh_user=root user=mha [server1] hostname=192.168.80.10 port=3306 [server2] candidate_master=1 check_repl_delay=0 hostname=192.168.80.20 port=3306 [server3] hostname=192.168.80.30 port=3306
explain:
[server default] manager_log=/var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log #manager log manager_workdir=/var/log/masterha/app1.log #manager working directory master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data/ #The location where the master saves binlog. The path here should be consistent with the path of binlog configured in the master so that MHA can find it master_ip_failover_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover #The switching script when setting automatic failover, that is, the script above master_ip_online_change_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_online_change #Set the switching script for manual switching password=manager #Set the password of the root user in mysql, which is the password of the monitoring user created in the previous article ping_interval=1 #Set the time interval for monitoring the main database and sending ping packets. The default is 3 seconds. When there is no response after three attempts, the failover will be carried out automatically remote_workdir=/tmp #Set the save location of binlog when remote mysql switches repl_password=123 #Set the password of the replication user repl_user=myslave #Set the user of the replication user report_script=/usr/local/send_report #Set the script of the alarm sent after switching secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.80.20 -s 192.168.80.30 #Specifies the IP address of the slave server to check shutdown_script="" #Set the script to close the failed host after the failure occurs (the main function of this script is to close the host to prevent brain crack, which is not used here) ssh_user=root #Set ssh login user name user=mha #Set monitoring user root [server1] hostname=192.168.80.10 port=3306 [server2] hostname=192.168.80.20 port=3306 candidate_master=1 #Set as the candidate master. After setting this parameter, the slave library will be promoted to the master library after the master-slave switch occurs, even if the slave library is not the latest slave in the cluster check_repl_delay=0 #By default, if a slave lags behind the master by more than 100M of relay logs, MHA will not select the slave as a new master, Because for this slave The recovery of takes a long time; By setting check_repl_delay=0,MHA Trigger switching when selecting a new master of The replication delay will be ignored. This parameter is set for candidate_master=1 The host of is very useful because the candidate host must be new in the process of switching master [server3] hostname=192.168.80.30 port=3306
Enable the virtual IP of the master
/sbin/ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.80.200/24
10. Test ssh password free authentication on the manager node
masterha_check_ssh -conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf Tue Nov 26 23:09:45 2020 - [warning] Global configuration file /etc/masterha_default.cnf not found. Skipping. Tue Nov 26 23:09:45 2020 - [info] Reading application default configuration from /etc/masterha/app1.cnf.. Tue Nov 26 23:09:45 2020 - [info] Reading server configuration from /etc/masterha/app1.cnf.. Tue Nov 26 23:09:45 2020 - [info] Starting SSH connection tests.. Tue Nov 26 23:09:46 2020 - [debug] Tue Nov 26 23:09:45 2020 - [debug] Connecting via SSH from root@192.168.80.20(192.168.80.20:22) to root@192.168.80.30(192.168.80.30:22).. Tue Nov 26 23:09:46 2020 - [debug] ok. Tue Nov 26 23:09:47 2020 - [debug] Tue Nov 26 23:09:46 2020 - [debug] Connecting via SSH from root@192.168.80.30(192.168.80.30:22) to root@192.168.80.20(192.168.80.20:22).. Tue Nov 26 23:09:47 2020 - [debug] ok. Tue Nov 26 23:09:47 2020 - [info] All SSH connection tests passed successfully. # No password authentication succeeded
11. Test the mysql master-slave connection on the manager node
masterha_check_repl -conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] Slaves settings check done. Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] 192.168.80.20(192.168.80.20:3306) (current master) +--192.168.80.30(192.168.80.30:3306) Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] Checking replication health on 192.168.80.30.. Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] ok. Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] Checking master_ip_failover_script status: Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] /usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover --command=status --ssh_user=root --orig_master_host=192.168.80.20 --orig_master_ip=192.168.80.20 --orig_master_port=3306 IN SCRIPT TEST====/sbin/ifconfig ens33:1 down==/sbin/ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.80.200=== Checking the Status of the script.. OK Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] OK. Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [warning] shutdown_script is not defined. Tue Nov 26 23:10:29 2020 - [info] Got exit code 0 (Not master dead). MySQL Replication Health is OK. # Master slave connection succeeded
# Start MHA on the manager node nohup masterha_manager --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf --remove_dead_master_conf --ignore_last_failover < /dev/null > /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log 2>&1 &
--remove_dead_master_conf: This parameter represents the of the old master database after master-slave switching ip Will be removed from the configuration file. --manger_log: Log storage location. --ignore_last_failover: By default, if MHA If continuous downtime is detected and the interval between two outages is less than 8 hours, Will not proceed Failover, The reason for this restriction is to avoid ping-pong effect. This parameter represents ignoring the last MHA Files generated by trigger switching, By default, MHA After switching, the log directory will be recorded in the log directory, that is, the log set above app1.failover.complete Documents, If the file is found in the directory during the next switch, the switch is not allowed to be triggered unless the file is deleted after the first switch, For convenience, it is set here as--ignore_last_failover.
# b check the MHA status. You can see that the current master is Mysql1 node. masterha_check_status --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf # a log view cat /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log | grep "current master" # c check whether the VIP address 192.168.80.200 of Mysql1 exists. This VIP address will not disappear because the manager node stops MHA service. ifconfig //To shut down the manager service, you can use the following command. masterha_stop --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf Or it can be used directly kill process ID Close by.
Simulated fault
# a monitor and observe log records on the manager node tail -f /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log # b stop the MySQL service on Master node Mysql1 systemctl stop mysqld or pkill -9 mysql # c after normal automatic switching once, MHA process will exit. HMA will automatically modify app1 CNF file content, delete the down mysql1 node. Check whether mysql2 takes over VIP ifconfig Algorithm of failover alternative master library: 1.It is generally judged that the slave library is from( position/GTID)Judging the pros and cons, there are differences in data, which is closest to master of slave,Become an alternative master. 2.If the data is consistent, select an alternative master database according to the order of the configuration file. 3.Set weighted( candidate_master=1),Force an alternate master by weight. (1)By default, if one slave backward master 100M of relay logs If there is a weight, it will fail. (2)If check_repl_delay=0 If, even if it lags behind a lot of logs, it is forced to select it as the alternative master.
Fault repair
1.restart mysql service systemctl restart mysqld 2.Repair master-slave: first view binary files and synchronization points show master status; 3.Original master library server mysql1 Perform synchronization change master to master_host='192.168.80.20',master_user='myslave',master_password='123',master_log_file='master-bin.000001',master_log_pos=1745; start slave; 4.stay manager Modify profile on node app1.cnf vi /etc/masterha/app1.cnf ...... secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.80.10 -s 192.168.80.30 ...... [server1] hostname=192.168.80.20 port=3306 [server2] candidate_master=1 check_repl_delay=0 hostname=192.168.80.10 port=3306 [server3] hostname=192.168.80.30 port=3306
5.Slave library must be set to read-only mode: current slave library is mysql set global read_only=1; 6.stay manager Start on node MHA,And view VIP Drift to mysql2 nohup masterha_manager --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf --remove_dead_master_conf --ignore_last_failover < /dev/null > /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log 2>&1 & ##Viewing the MHA status, you can see that the current master is the Mysql2 node masterha_check_status --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf