1, Demand analysis
The following functions are required:
1) Basic addition, deletion, modification and query API
2) Query comments by article id
3) Comment like
2, Table structure analysis
The data for storing article comments is stored in MongoDB. The data structure is as follows:
Database: articledb
Column comment
| Field name | Field meaning | Field type | remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| _id | ID | ObjectId or String | Mongo's primary key field |
| articleid | Article ID | String | |
| content | Comment content | String | |
| userid | Reviewer ID | String | |
| nickname | Reviewer nickname | String | |
| createdatetime | Date and time of comment | Date | |
| likenum | Number of likes | Int32 | |
| replynum | Number of replies | Int32 | |
| state | state | String | 0: invisible; 1: Visible; |
| parentid | Parent ID | String | If it is 0, it means the top-level comment of the article |
Is it right or wrong to drink water on an empty stomach in the morning? https://www.toutiao.com/a6721476546088927748/.
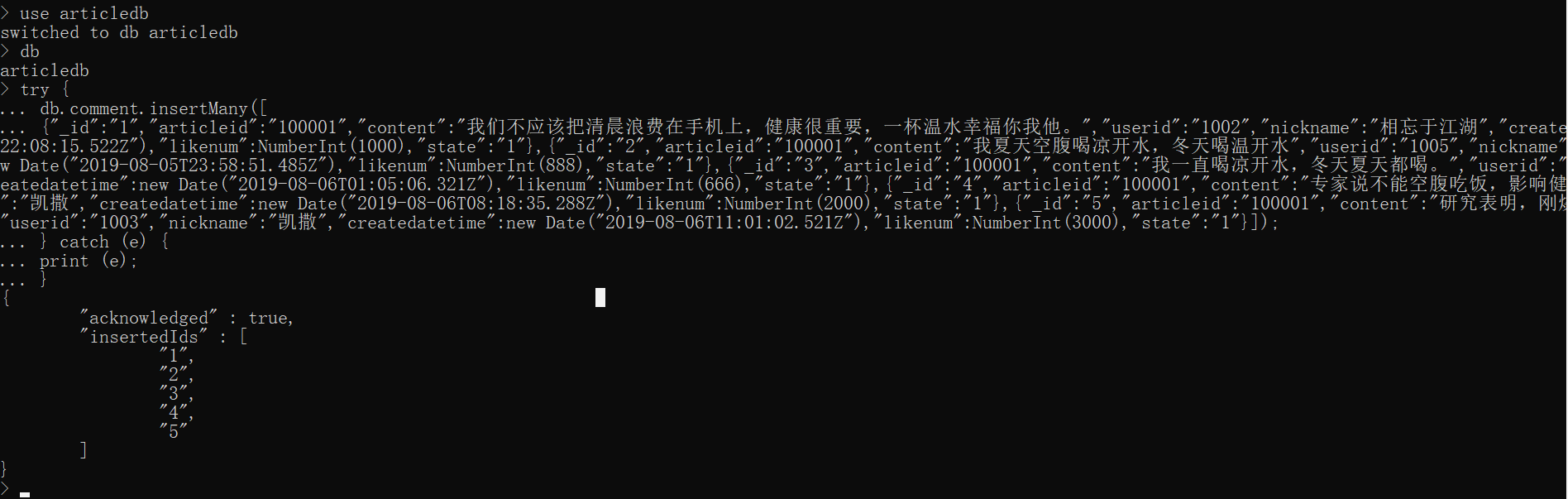
Prepare data
try {
db.comment.insertMany([
{"_id":"1","articleid":"100001","content":"We should not waste the morning on mobile phones. Health is very important. A cup of warm water is happy for you, me and him.","userid":"1002","nickname":"Forget in the Jianghu","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-05T22:08:15.522Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(1000),"state":"1"},{"_id":"2","articleid":"100001","content":"I drink cold boiled water on an empty stomach in summer and warm boiled water in winter","userid":"1005","nickname":"She is haggard","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-05T23:58:51.485Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(888),"state":"1"},{"_id":"3","articleid":"100001","content":"I always drink cold boiled water in winter and summer.","userid":"1004","nickname":"Captain Jack","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T01:05:06.321Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(666),"state":"1"},{"_id":"4","articleid":"100001","content":"Experts say you can't eat on an empty stomach, which will affect your health.","userid":"1003","nickname":"Caesar","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T08:18:35.288Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(2000),"state":"1"},{"_id":"5","articleid":"100001","content":"Research shows that you must not drink freshly boiled water because it burns your mouth.","userid":"1003","nickname":"Caesar","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T11:01:02.521Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(3000),"state":"1"}]);
} catch (e) {
print (e);
}
3, Technology selection
mongodb-driver
mongoDB driver is a java connection mongoDB driver package officially launched by mongo, which is equivalent to JDBC driver. Let's learn about mongoDB driver through an introductory case
Basic use of.
Official driver description and download: http://mongodb.github.io/mongo-java-driver/
Official driver example document: http://mongodb.github.io/mongo-java-driver/3.8/driver/getting-started/quick-start/
SpringDataMongoDB
As a member of the spring data family, it is used to operate the persistence layer framework of MongoDB and encapsulates the underlying MongoDB driver.
Official website homepage: https://projects.spring.io/spring-data-mongodb/
We make complaints about the ten party project using SpringDataMongoDB framework.
4, Article microservice module construction
(1) Build project article, pom.xml, and introduce dependencies:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itcast</groupId>
<artifactId>article</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
(2) Configure application.yml
spring:
#Data source configuration
data:
mongodb:
# Host address
host: 120.79.157.129
# database
database: articledb
# The default port is 27017
port: 27017
#You can also use uri connections
#uri: mongodb://120.79.157.129:27017/articledb
(3) Create startup class
cn.itcast.article.ArticleApplication
package cn.itcast.article;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ArticleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ArticleApplication.class, args);
}
}
(4) Start the project to see if it can be started normally. There is no error on the console.
5, Article reviews the preparation of entity classes
Create entity class package CN itcast. Article, a package po is created under the package, which is used to store entity classes and create entity classes
package cn.itcast.article.po;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.CompoundIndex;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Indexed;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Field;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Article comment entity class
*/
//Declare a java class as a mongodb document. You can specify the document corresponding to this class through the collection parameter.
//@Document(collection="mongodb corresponding collection name")
// If @ Document is not added, the bean is saved to mongo's comment collection
// If @ Document is added, save to comment collection
@Document(collection="comment")//It can be omitted. If omitted, the class name lowercase mapping collection is used by default
//Composite index
@CompoundIndex( def = "{'userid': 1, 'nickname': -1}")
public class Comment implements Serializable {
//Primary key identification. The value of this attribute will automatically correspond to the primary key field "_id" of mongodb. If the attribute name is "Id", the annotation can be omitted, otherwise it must be written
// @Id
private String id;//Primary key
//This attribute corresponds to the field name of mongodb. If it is consistent, this annotation is not required
@Field("content")
private String content;//Make complaints about content
private Date publishtime;//Release date
//Added a single field index
@Indexed
private String userid;//Publisher ID
private String nickname;//nickname
private LocalDateTime createdatetime;//Date and time of comment
private Integer likenum;//Number of likes
private Integer replynum;//Number of replies
private String state;//state
private String parentid;//Parent ID
private String articleid;
//getter and setter.....
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Date getPublishtime() {
return publishtime;
}
public void setPublishtime(Date publishtime) {
this.publishtime = publishtime;
}
public String getUserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setUserid(String userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
public String getNickname() {
return nickname;
}
public void setNickname(String nickname) {
this.nickname = nickname;
}
public LocalDateTime getCreatedatetime() {
return createdatetime;
}
public void setCreatedatetime(LocalDateTime createdatetime) {
this.createdatetime = createdatetime;
}
public Integer getLikenum() {
return likenum;
}
public void setLikenum(Integer likenum) {
this.likenum = likenum;
}
public Integer getReplynum() {
return replynum;
}
public void setReplynum(Integer replynum) {
this.replynum = replynum;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getParentid() {
return parentid;
}
public void setParentid(String parentid) {
this.parentid = parentid;
}
public String getArticleid() {
return articleid;
}
public void setArticleid(String articleid) {
this.articleid = articleid;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Comment{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", publishtime=" + publishtime +
", userid='" + userid + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
", createdatetime=" + createdatetime +
", likenum=" + likenum +
", replynum=" + replynum +
", state='" + state + '\'' +
", parentid='" + parentid + '\'' +
", articleid='" + articleid + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
explain:
The index can greatly improve the query efficiency. Generally, the index is added on the query field. The index can be added by Mongo's command or by annotation in Java entity classes.
1) Single field index annotation @ Indexed
org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Indexed.class
Declaring this field requires an index, which can greatly improve the query efficiency.
Mongo Command Reference:
db.comment.createIndex({"userid":1})
2) Compound index annotation @ CompoundIndex
org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.CompoundIndex.class
Compound index can effectively improve the efficiency of multi field query.
Mongo Command Reference:
db.comment.createIndex({"userid":1,"nickname":-1})
6, Basic addition, deletion, modification and query of article comments
(1) Create a data access interface. Create dao package under cn.itcast.article package and create interfaces under package
cn.itcast.article.dao.CommentRepository
package cn.itcast.article.dao;
import cn.itcast.article.po.Comment;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
public interface CommentRepository extends MongoRepository<Comment,String > {
}
(2) Create the business logic class cn.itcast.article, create the service package under the package, and create the class under the package
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentService
package cn.itcast.article.service;
import cn.itcast.article.dao.CommentRepository;
import cn.itcast.article.po.Comment;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Criteria;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Query;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Update;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class CommentService {
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
/**
* Save a comment
* @param comment
*/
public void saveComment(Comment comment){
//If you need to customize the primary key, you can specify it here; If you do not specify a primary key, MongoDB will automatically generate a primary key
//Set some default initial values...
//Call dao
commentRepository.save(comment);
}
/**
* Update comments
* @param comment
*/
public void updateComment(Comment comment){
//Call dao
commentRepository.save(comment);
}
/**
* Delete comments by id
* @param id
*/
public void deleteCommentById(String id){
//Call dao
commentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
/**
* Query all comments
* @return
*/
public List<Comment> findCommentList(){
//Call dao
return commentRepository.findAll();
}
/**
* Query comments by id
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Comment findCommentById(String id){
//Call dao
return commentRepository.findById(id).get();
}
}
(3) Create a Junit test class, save and query all tests:
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentServiceTest
package cn.itcast.article.service;
import cn.itcast.article.po.Comment;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class CommentServiceTest {
@Autowired
private CommentService commentService;
@Test
public void testFindCommentList() {
List<Comment> commentList = commentService.findCommentList();
System.out.println(commentList);
}
@Test
public void testFindCommentById() {
Comment commentById = commentService.findCommentById("1");
System.out.println(commentById);
}
@Test
public void testSaveComment(){
Comment comment=new Comment();
comment.setArticleid("100000");
comment.setContent("Test added data");
comment.setCreatedatetime(LocalDateTime.now());
comment.setUserid("1003");
comment.setNickname("Caesar the great");
comment.setState("1");
comment.setLikenum(0);
comment.setReplynum(0);
commentService.saveComment(comment);
}
}
Add results:
7, Query the paged list of article comments according to the superior ID
(1) New method definition for CommentRepository
//Query the paged list of child comments according to the parent id Page<Comment> findByParentid(String parentid,Pageable pageable);
(2) CommentService new method
/**
* Query paging list by parent id
* @param parentid
* @param page
* @param size
* @return
*/
public Page<Comment> findCommentListByParentid(String parentid,int page,int size) {
return commentRepository.findByParentid(parentid,PageRequest.of(page-1,size));
}
(3) junit test case:
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentServiceTest
/**
* The test queries the paged list of child comments according to the parent id
*/
@Test
public void testFindCommentListByParentid() {
Page<Comment> page = commentService.findCommentListByParentid("3", 1, 2);
System.out.println(page.getTotalElements());
System.out.println(page.getContent());
}
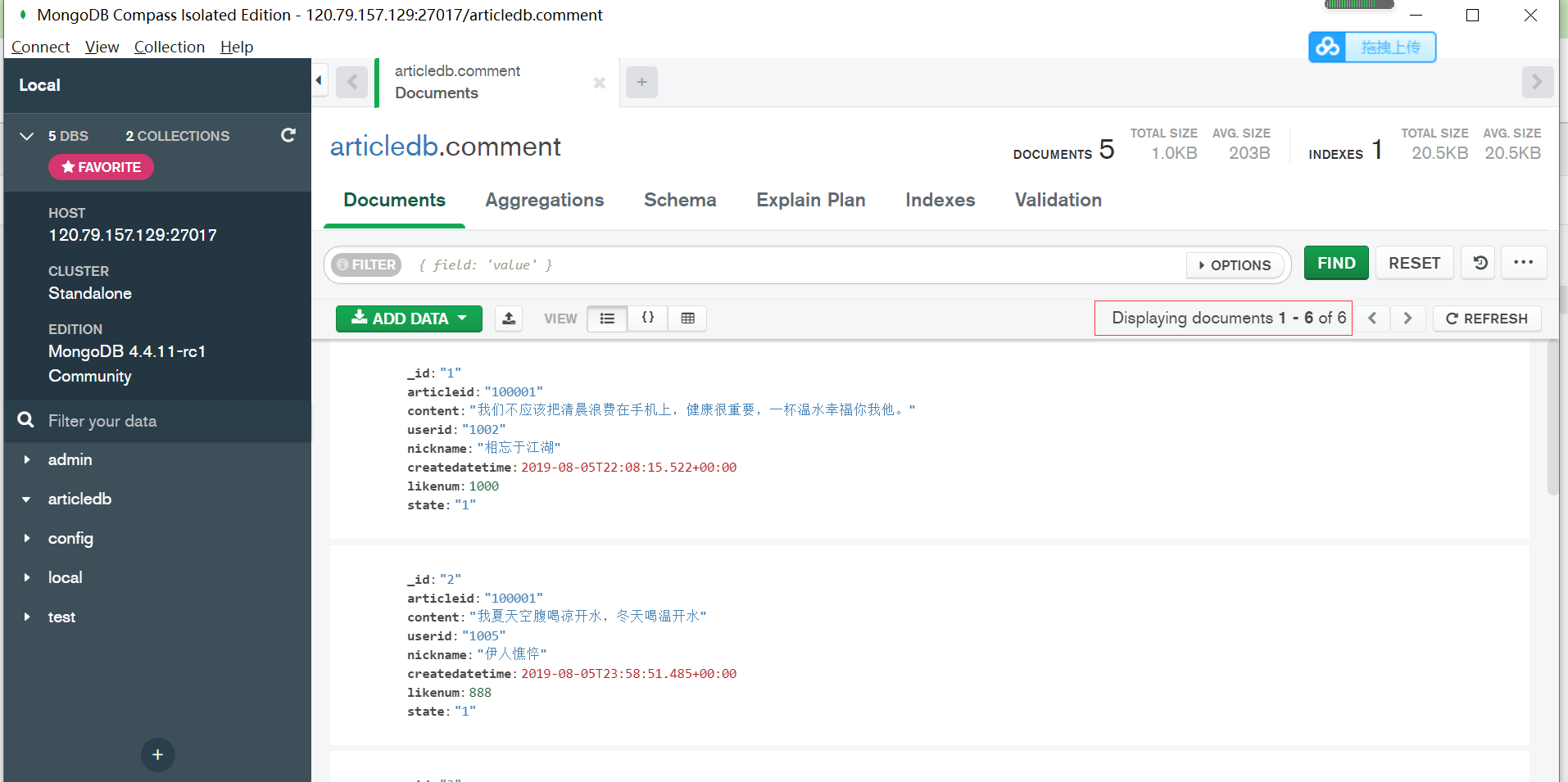
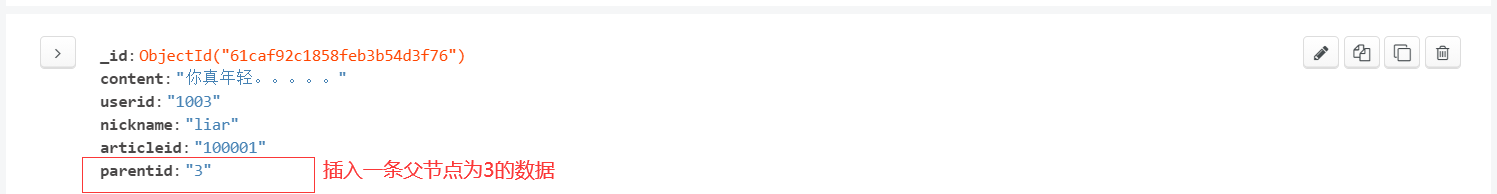
(4) Testing
Use compass to quickly insert a piece of test data. The content of the data is to comment on Comment No. 3.
The test was performed and the results were:
8, MongoTemplate implements comments and likes
Let's take a look at the following temporary sample code: the CommentService adds the updateThumbup method
/**
* Like - inefficient
* @param id
*/
public void updateCommentThumbupToIncrementingOld(String id){
Comment comment = CommentRepository.findById(id).get();
comment.setLikenum(comment.getLikenum()+1);
CommentRepository.save(comment);
}
Although the implementation of the above method is relatively simple, the execution efficiency is not high, because I only need to add 1 to the likes. It is not necessary to query all fields and update all words after modification
Paragraph. (butterfly effect)
We can use the MongoTemplate class to implement the operation on a column.
(1) Modify CommentService
//Inject MongoTemplate
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
/**
* Likes + 1
* @param id
*/
public void updateCommentLikenum(String id){
// query criteria
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("_id").is(id));
// update criteria
Update update = new Update();
//Local update, equivalent to $set
// update.set(key,value)
//Increment $inc
update.inc("likenum");
//Parameter 1: query object
//Parameter 2: update object
//Parameter 3: collection name or entity class type comment class
mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query,update,Comment.class);
}
(2) Test case:
cn.itcast.article.service.CommentServiceTest
/**
* Likes + 1
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateCommentLikenum() {
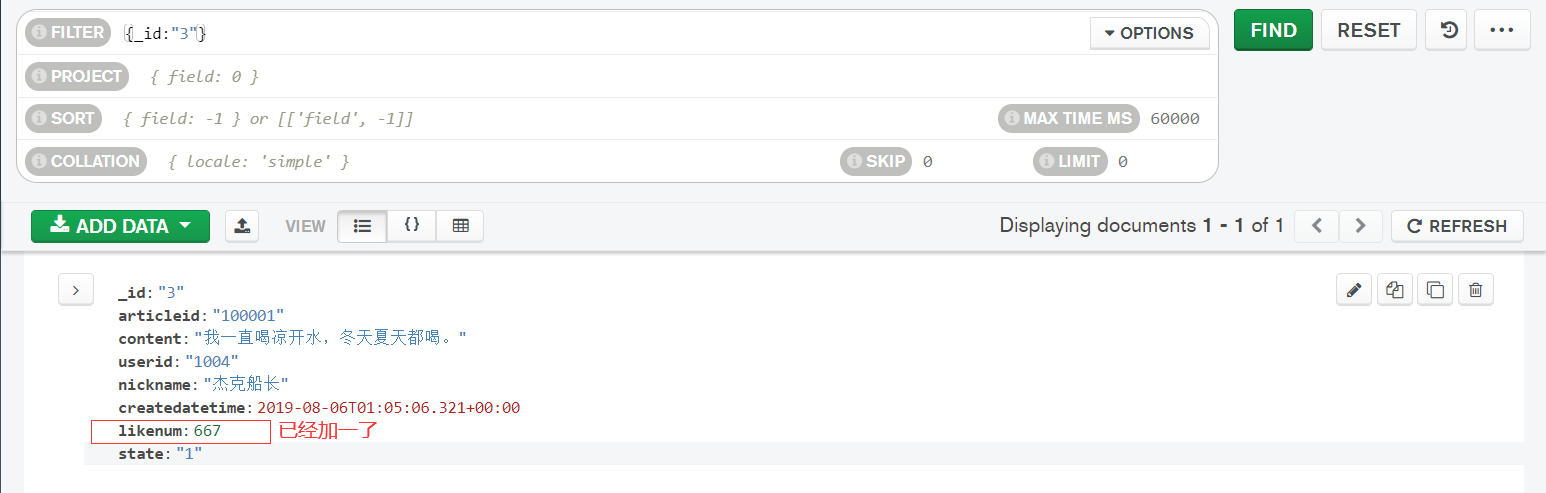
//The number of likes for Document No. 3 + 1, and the number of likes from the origin is 666
commentService.updateCommentLikenum("3");
}
After executing the test case, it is found that the number of likes + 1: