catalogue
| Numerical type | integer | |
| decimal | Fixed point number | |
| Floating point number | ||
| character | Shorter text | char,varchar |
| Long text | text, blob (long binary data) | |
| Date type |
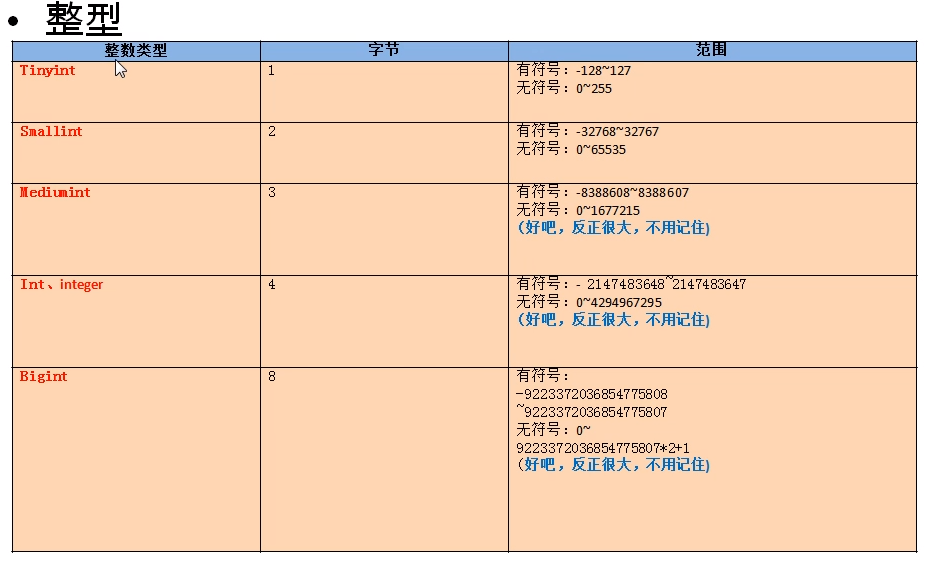
1, Integer
Classification:
| tinyint | smallint | mediumint | int/integer | bigint |
| 1 byte | 2 | 3 | 4 | 8 |
characteristic:
- If you do not set unsigned or signed, it is signed by default. If you want to set unsigned, you need to add unsigned
- If the inserted value exceeds the integer range, an out of range exception will be reported, and the critical value will be inserted
- If the length is not set, there will be a default length. The length represents the maximum width of the display. If it is not enough, it will be filled with 0 on the left, but it must be used with zerofill
1. How to set unsigned and signed
CREATE TABLE tab_int( t1 INT ); CREATE TABLE tab_int( t1 INT(7) ZEROFILL, #Signed t2 INT UNSIGNED #Unsigned ); DESC tab_int; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tab_int;
CREATE TABLE tab_int( t1 INT(7) ZEROFILL, t2 INT(7) ZEROFILL ); INSERT INTO tab_int VALUES(-123456); INSERT INTO tab_int VALUES(-123456,-123456); INSERT INTO tab_int VALUES(2147483648,4294967296); INSERT INTO tab_int VALUES(123,123); SELECT * FROM tab_int;
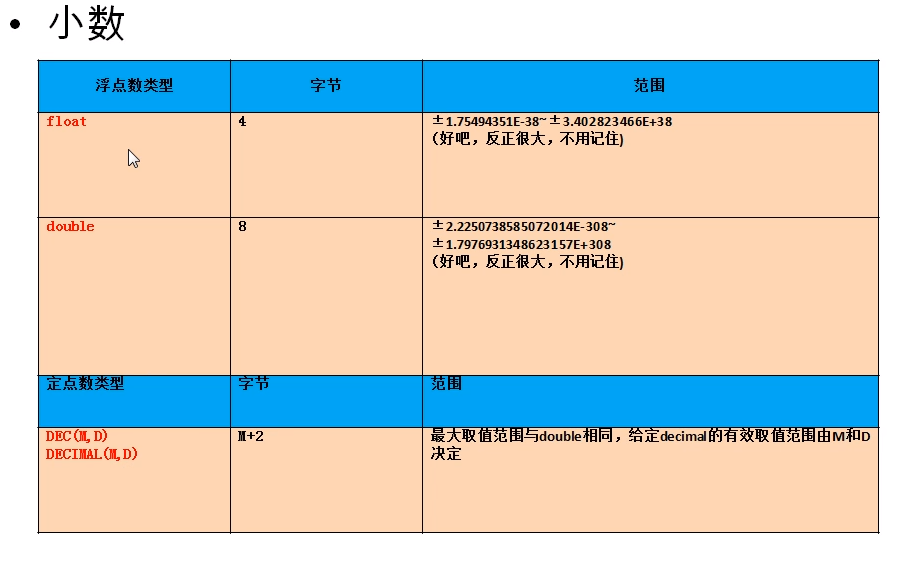
2, Decimals
Classification:
1. float
float(M,D)
double(M,D)
2. Fixed point type
dec(M,D)
decimal(M,D)
characteristic:
- M: Integer position + decimal position, D: decimal position. If it exceeds the range, insert the critical value
- . M and D can be omitted. If it is decimal, M defaults to 10 and D defaults to 0; In the case of float and double, the precision will be determined according to the precision of the inserted value
- The precision of fixed-point type is high. If the precision of inserted value is required to be high, such as currency operation, consider using it
#Test M, D CREATE TABLE tab_float( f1 FLOAT(5,2), f2 DOUBLE(5,2), f3 DEC(5,2) ); INSERT INTO tab_float VALUES(123.45,123.45,123.45); INSERT INTO tab_float VALUES(123.456,123.456,123.456); INSERT INTO tab_float VALUES(123.4,123.4,123.4); INSERT INTO tab_float VALUES(1523.4,1523.4,1523.4); SELECT * FROM tab_float; DROP TABLE tab_float; CREATE TABLE tab_float( f1 FLOAT, f2 DOUBLE, f3 DEC ); INSERT INTO tab_float VALUES(123.4523,123.4523,123.4523); DESC tab_float;
principle:
The simpler the type you choose, the better. The smaller the type that can save values, the better
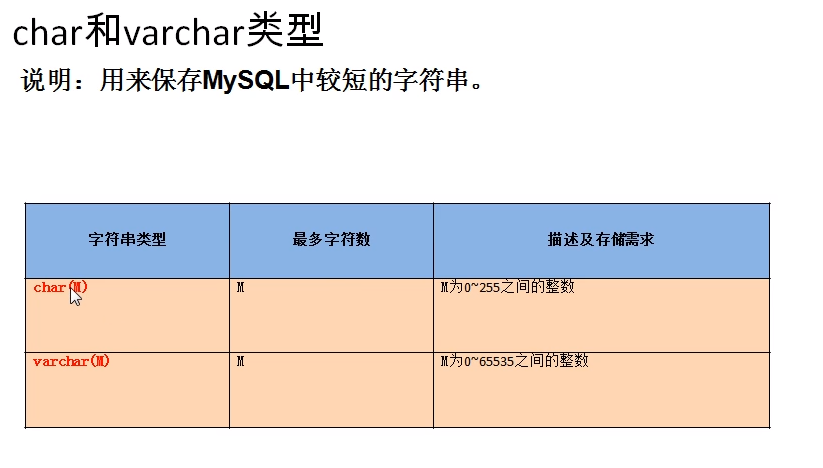
3, Character type
Shorter text: char, varchar
Others:
Binary and varbinary are used to hold shorter binary
enum is used to save enums
set is used to save the collection
Longer text: text, blob (larger binary)
Features:
| Writing method | M means | characteristic | Space consumption | efficiency | |
| char | char(M) | The maximum number of characters, which can be omitted. The default is 1 | Fixed length characters | Comparative cost | high |
| varchar | varchar(M) | The maximum number of characters cannot be omitted | Variable length characters | Relatively economical | low |



CREATE TABLE tab_char(
c1 ENUM('a','b','c')
);
INSERT INTO tab_char VALUES('a');
INSERT INTO tab_char VALUES('b');
INSERT INTO tab_char VALUES('c');
INSERT INTO tab_char VALUES('m');
INSERT INTO tab_char VALUES('A');
SELECT * FROM tab_char;
CREATE TABLE tab_set(
c1 SET('a','b','c','d')
);
INSERT INTO tab_set VALUES('a');
INSERT INTO tab_set VALUES('a,b');
INSERT INTO tab_set VALUES('a,b,c');
INSERT INTO tab_set VALUES('A');
SELECT * FROM tab_set;
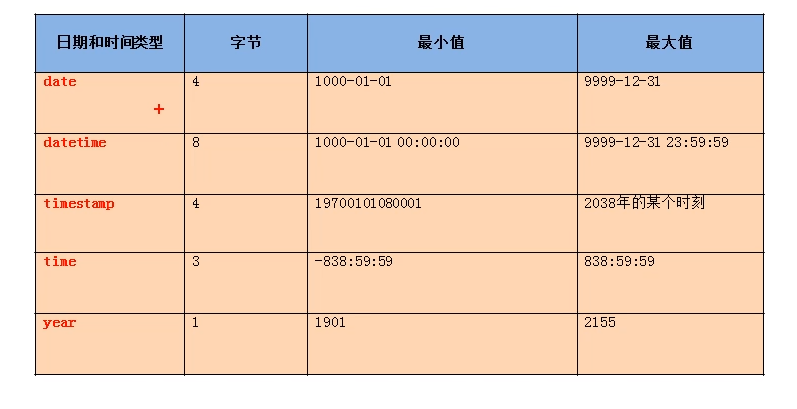
4, Date type
Classification:
date saves only dates
Time saves only time
year is only saved for years
datetime save date + time
timestamp save date + time
| characteristic | Byte | Range | Influence of time zone |
| datetime | 8 | 1000-9999 | Not affected |
| timestamp | 4 | 1970-2038 | Accept |

CREATE TABLE tab_date( t1 DATETIME, t2 TIMESTAMP ); INSERT INTO tab_date VALUES(NOW(),NOW()); SELECT * FROM tab_date; SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'time_zone'; SET time_zone='+9:00';