MySQL
Crazy God said Java MySQL video learning address
| explain | ascription | remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| database | database | command line | |
| basedir | Base directory | command line | |
| flush | Refresh | database | |
| privileges | jurisdiction | database | |
| show tables | View all tables | database | |
| describe | Display table information | database | |
| create | Create database | database | |
| drop | Delete database | database | |
| use | Use database | database | |
| success | success | database | |
| errors | error | database | |
| warnings | warning | database | |
| datetime | Date time | database | |
| timestamp | time stamp | database | |
| unsigned | Unsigned integer | database | |
| zerofill | 0 fill | database | |
| auto_increment | Self increasing | database | |
| not null | Non empty | database | |
| primary key | Primary key | database | |
| comment | explain | database | |
| default | default | database | |
| create database | Create database | database | |
| table | surface | database | |
| if not exist | If it doesn't exist | database | |
| engine | engine | database | |
| INNODB | database engine | database | Secure, multi table, multi-user |
| MYISAM | database engine | database | Small, fast |
| charset | character set | database | utf8 |
| DESC | describe | database | Displays the structure of the table |
| character-set-server | Character set setting server | database | |
| alter | modify | Table modification | |
| rename | rename | Table modification | ALTER TABLE modify table name |
| add | add to | Table modification | Add table field |
| modify | modify | Table modification | Modify constraints |
| change | change | Table modification | |
| key | Foreign key | Foreign key | |
| constraint | constraint | Foreign key | |
| foreign | foreign | Foreign key | Specify foreign key |
| references | reference | Foreign key | Boot foreign key |
| Insert | Add, insert | DML voice | |
| into | in | DML voice | insert into |
| update | Modify, update | DML voice | |
| between | be situated between | DML voice | |
| CURRENT_TIME | Recent time | DML voice | |
| delete | delete | DML voice | Delete data |
| from | from | DML voice | delete from |
| truncate | truncation | DML voice | |
| Select | choice | DQL query | query language |
| Selec...ast...from | Query specified language... Alias | Select | |
| distinct | duplicate removal | Select | |
| where | Condition query | Select | |
| Inner join | Cross matching | Join table query | |
| left join | Left matching | Join table query | |
| right jion | Right match | Join table query | |
| order by | sort | Select | ASC ascending, DESC descending |
| limit | paging | Select | Starting value, page size |
| group by having | Grouping filtering | Select | |
| SET autocommit | Automatic transaction commit | affair | 0,1 |
| commit | Submit | affair | |
| rollback | RollBACK | affair | |
| START transaction | Transaction on | affair | autocommit=1 end of transaction |
| SAVEPOINT | Transaction savepoint | affair | |
| ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT | Rollback savepoint | affair | |
| RELEASE SAVEPOINT | Undo savepoint | affair | |
| Index | Indexes | Indexes | |
| PRIMARY KEY | primary key | Indexes | |
| UNIQUE KEY | unique index | Indexes | |
| KEY / INDEX | General index | Indexes | |
| FULLTEXT | Full text index | Indexes | |
| getConnection | Connect to database | JDBC | |
| DriverManager | Connect to database | JDBC | |
| Statemen | implement | JDBC | |
| execute | implement | Statemen | |
| executeUpdate | Update, insert, delete | Statemen | |
| executeQuery | query | Statemen | |
| PreparedStatement | Prevent injection | JDBC | |
| DateSource | Data source interface | JDBC |
1. Get to know MySQL
Java EE: enterprise java development Wed
Front paragraph (page: display data)
Background (connection point: connect to database JDBC, connect to the front section (control, control view jump, transfer data to the front end))
Database (save data, Txt, Excel, word)
-
Can only write code ↓ (general programmer), need to learn database ↑
-
Operating system, data structure and algorithm! (good programmer)
-
Discrete data, digital circuit, architecture, compilation principle + practical experience (excellent programmer)
1.1 why do I need to learn database
- Job demand
- In today's world, in the era of big data ~, those who win the database win the world
- Forced demand: save data
- Database is the core DBA in all software systems
1.2. What is a database
DataBase (DB, DataBase)
Concept: data warehouse, software, installed on the operating system (window, Linux, mac...)! SQL can store a large amount of data. More than 5 million needs to be optimized
Function: store data and manage data
1.3 database classification
Relational database: (SQL)
- MySQL,Oracle,Sql Server,DB2,SQLite
- Data is stored through the relationship between tables and between rows and columns. College information table < - > attendance table
Non relational database: (NoSQL) Not Only
- Redis,MongDB
- Non relational database, object storage, is determined by the attributes of the object itself
DBMS (database management system)
- Database management software, scientific and effective management of our data. Maintain and obtain data
- MySQL, database management system
1.4 introduction to MySQL
-
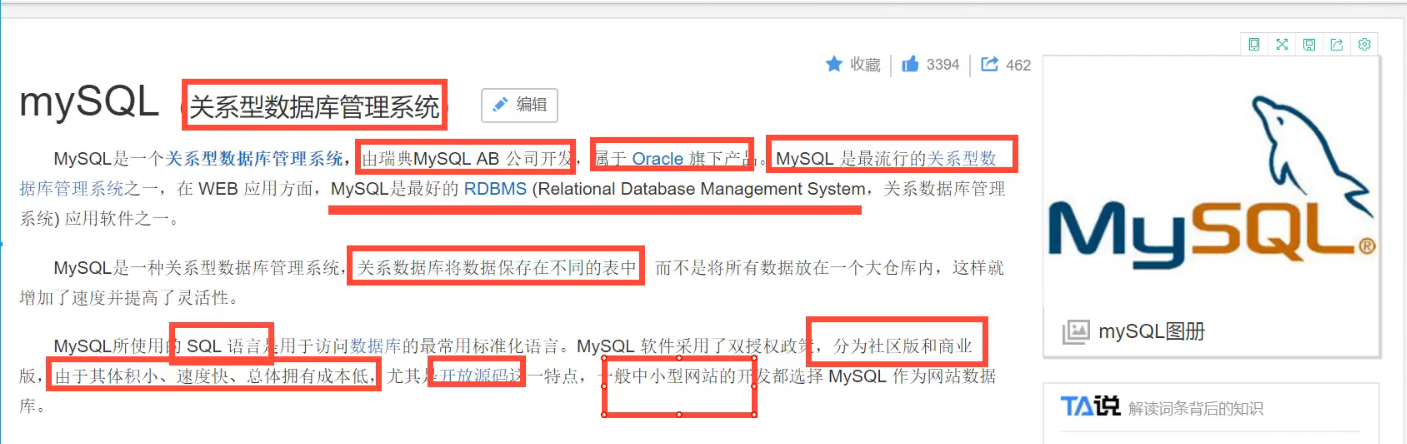
MySQL is a relational database management system,
-
Previous life: Swedish MySQL AB Company
Bensheng: Oracle products
-
MySQL is one of the best RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) applications
-
Open source database software
-
Small size, fast speed, low overall cost of ownership and low recruitment cost. Everyone must be able to
-
Small and medium-sized websites, or large websites, clusters
1.5. Installing MySQL
-
Unzip the package to the Environment directory of your computer
-
Configure environment variables, my computer - > properties - > Advanced - > environment variables - > Path
-
Create a new mysql configuration file my ini
[mysqld] # The directory should be changed to its own. I don't know whether to write after data basedir=D:\Environment\mysql-5.7.34\ datadir=D:\Environment\mysql-5.7.34\data port=3306 skip-grant-tables
-
Start CMD in administrator mode, switch the path to the bin directory under mysql, and then enter mysqld -install
CD / D D D: \ environment \ mysql-5.7.34 \ bin file address
mysqld -install
-
Initialize data file
mysqld --initialize-insecure --user=mysql
-
mysql start
net start mysql
-
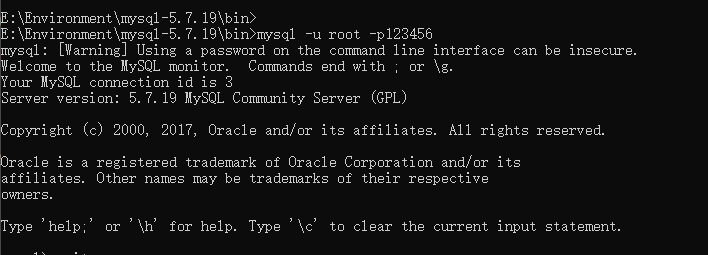
Enter the mysql management interface: - u (user name), - p (password, no spaces) due to my The skip grant tables program in ini skipped the password
mysql -u root -p
-
Enter MySQL and modify the password through the command line (mysql-5.7.19 succeeded, mysql-5.7.30 failed)
update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='root' and Host = 'localhost';
-
Refresh permissions
flush privileges;
-
Comment out my Ini #skip grant tables
-
Close mysql
Exit exit
net stop mysql stop service
-
Restart mysql
net start mysql login
mysql -u root -p123456 enter the account password
Finally, login succeeded
If the installation fails
Empty the service sc delete mysql and reinstall it
1.6. Installation of SQLyog
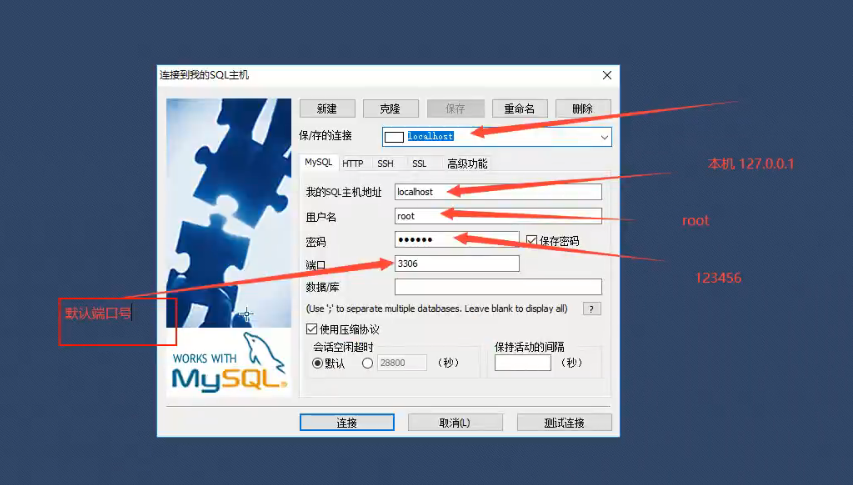
Open connection database
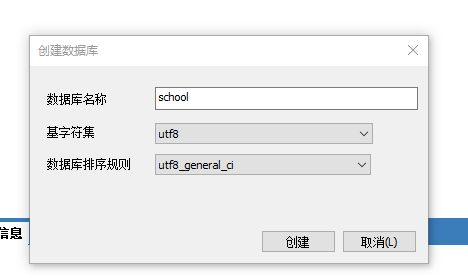
Create a new database school
Ensure that Chinese is not garbled
The execution of each sqlyog is essentially corresponding to an sql, which can be viewed in the software history
Create a new table student
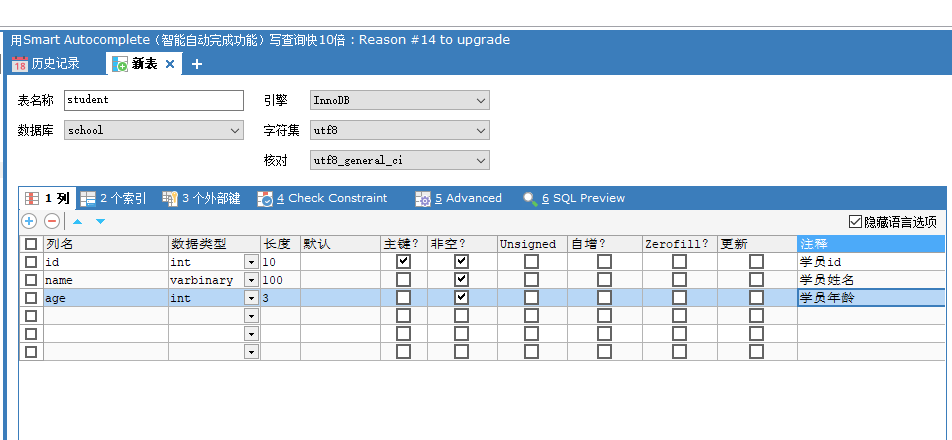
Fill in form information
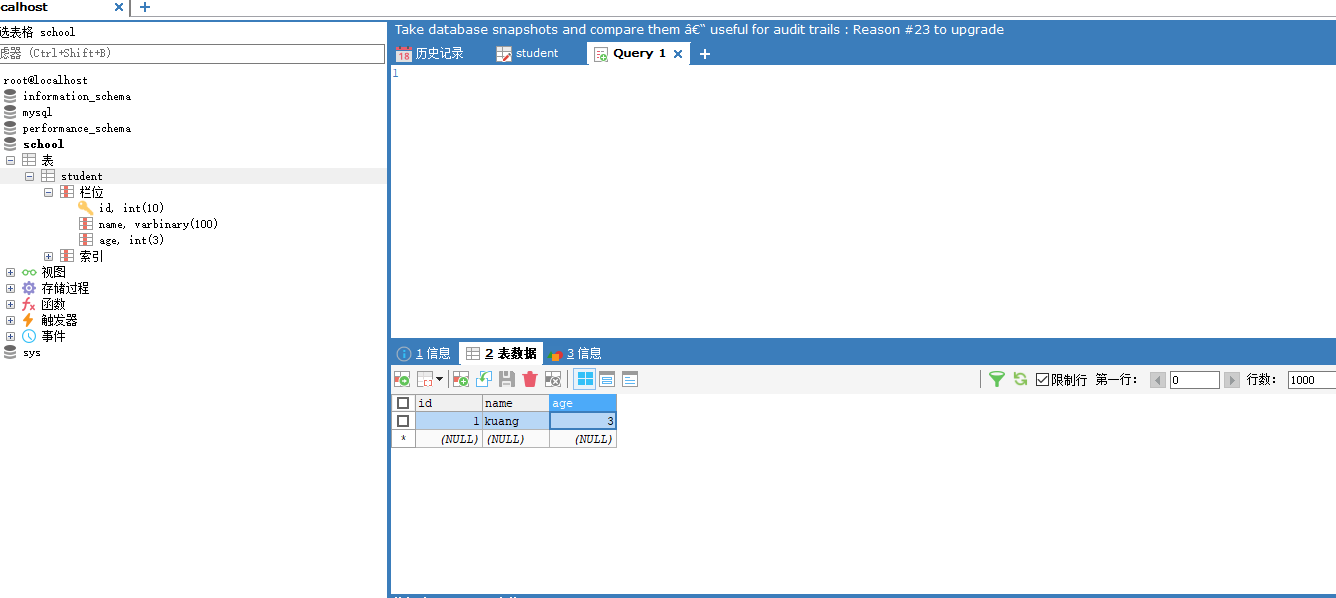
1.7. Connect to database
Command line connection!
mysql -u root -p123456 -- Connect to database
update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='root' and Host = 'localhost'; -- Modify user password
flush privileges; -- Refresh permissions
---------------------------------
--All statements use ; ending
show databases; -- View all databases
mysql> use school; --Switch database use Database name
Database changed
show tables; -- View all tables in the database
describe student; -- Displays information about all tables in the database
create database westos; -- Create a database westos
----------------------------
exit --Exit connection
ctrl+c --force finish
-- Single line note( SQL (original note)
/*
multiline comment
*/
Database xxx voice CRUD addition, deletion, modification and query CV program ape API program ape CRUD program ape
DDL definition
DML operation
DQL query
DCL control
2. Operation database
Operate database > operate tables in Database > operate data in tables in database
MySQL keywords are not case sensitive
2.1. Operation database
-
Create database
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS westos;
-
Delete database
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS westos;
-
Use database
-- tab Above the key, if your table name or field name is a special character, it needs to be marked with `` USE `school`
-
view the database
SHOW DATABASES;
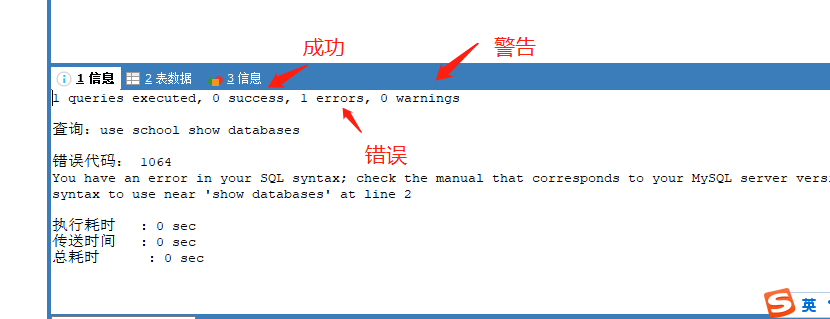
2.2. Column type of database
numerical value
- tinyint very small data 1 byte
- smallint smaller data 2 bytes
- mediumint medium size 3 bytes
- int standard integer 4 bytes (common)
- The input digit is the display width, 4 digits, 1 = 0001
- bigint larger data 8 bytes
- float floating point number 4 bytes
- double floating point number 8 bytes (precision problem)
- decimal is a floating-point number in the form of string. It is generally used in financial calculation
character string
- char string fixed size 0-255
- varchar variable String 0-65535 (common String)
- Tiny text 2 ^ 8 - 1
- Texttext string 2 ^ 16 - 1 (save large text)
Time date
java.util.Date
- date YYYY-MM-DD date
- time HH:mm:ss time format
- datetime YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss the most commonly used time format
- The number of milliseconds from timestamp 1970.1.1 to now
- Year means year
null
- No value, unknown
- Note that do not use null for operation, and the result is null
2.3. Field type of database (key)
unsigned
- Unsigned integer
- The column cannot be declared negative
zerofill
- 0 filled
- The insufficient digits are filled with 0, and the length of 10 (1 = 000000000 1)
Auto increment Auto_increment
- It is generally understood as auto increment, and automatically + 1 (default) on the basis of the previous record
- It is usually used to design a unique primary key index, which must be an integer
- You can customize the starting value and step size of the self increment of the primary key
Non NULL not Null
- If it is set to not null, an error will be reported if it is not assigned a value
- NULL if not filled in, the default value is NULL
Default default
- Set the default value!
- sex, the default value is male. If the value of this column is not specified, there will be a default value!
expand:

2.4. Create database tables (key)
--target:Create a schoo1 database --Create student table (column , field) use SQL establish --Student number int,Login password varchar(20),Name and gender varchar(2),date of birth(datatime),Home address, emai1 --Note: use English(),Table names and fields should be enclosed as much as possible -- AUTO_ INCREMENT Self increasing --Strings are enclosed in single quotes! --All statements are followed by,(English),Don't add the last one -- PRIMARY KEY Primary key. Generally, a table has only one unique primary key! CREATE DATABASE school CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student` ( `id` INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'anonymous' COMMENT 'full name', `pwd` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '123456' COMMENT 'password', `sex` VARCHAR(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'male' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'date of birth', `address` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Home address', `email` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
format
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] `Table name`( `Field name` Column type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes], `Field name` Column type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes], ... `Field name` Column type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes] )[Table type] [Character set settings for table] [notes]
Common commands
SHOW CREATE DATABASE school – view the statements that create the database
SHOW CREATE TABLE student – view the definition statement of the student data table
DESC student – displays the structure of the table
2.5 type of data sheet
About database engine
- INNODB is used by default
- MYISAM was used in earlier years
| MYISAM | INNODB | |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction support | I won't support it | support |
| Data row locking | I won't support it | support |
| Foreign key constraint | I won't support it | support |
| Full text index | support | I won't support it |
| Table space size | less | Larger (approx. 2x) |
General operation:
- MYISAM saves space and is fast,
- INNODB has high security, transaction processing, multi table and multi-user operation
Where it exists in physical space
All database files are stored in the data directory, and a folder corresponds to a database
The essence is the storage of files
Differences of MySQL engine in physical files
- innoDB has only one *. In the database table frm file and ibdata1 file in the parent directory
- Files corresponding to MYISAM
- *. frm - definition file for table structure
- *. MYD - data file (data)
- *. MYI - index file (index)
Set database character set encoding
CHARTSET=UTF8
If it is not set, it will be the default character set encoding of mysql
The default code of MySQL is Latin1, which does not support Chinese
Can be in my Ini to configure the default encoding
character-set-server=utf8
2.6. Modify and delete table
Modify ALTER TABLE
-
Modify table name ALTER TABLE old table name RENAME AS new table name
ALTER TABLE student RENAME AS student1 -
ADD table field ALTER TABLE table table name ADD field column attribute
ALTER TABLE student1 ADD age INT(11) -
Modify the fields of the table (rename, modify constraints)
-
ALTER TABLE table name MODIFY field column property [] – MODIFY constraint MODIFY
ALTER TABLE student1 MODIFY age VARCHAR(11)
-
ALTER TABLE table name CHANGE old name new name column properties [] – field rename CHANGE
ALTER TABLE student1 CHANGE age age1 INT(1)
-
-
Delete the field of the table ALTER TABLE table table name DROP field name
ALTER TABLE student1 DROP age1
delete
- Delete table (delete if table exists)
DROP TABLE (IF EXISTS) student1
All creation and deletion operations should be judged as much as possible to avoid errors
Note:
- ``Field name, use this package
- Notes –/**/
- The sql keyword is case insensitive. It is recommended to write it in lowercase
- All symbols are in English
3. MySQL data management
3.1. Foreign keys (understand)
effect:
The main purpose of maintaining data consistency and integrity is to control the data stored in the foreign key table. To associate two tables, foreign keys can only refer to the values of columns in the appearance.
Method 1: add constraints when creating tables (troublesome and complex)
CREATE TABLE `grade`( `gradeid` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'grade id', `gradename` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Grade name', PRIMARY KEY (`gradeid`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 -- Student table gradeid Field to reference the grade table gradeid -- Define foreign keys KEY -- Add constraints (execute references) to this foreign key references quote CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student` ( `id` INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'anonymous' COMMENT 'full name', `pwd` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '123456' COMMENT 'password', `sex` VARCHAR(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'male' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'date of birth', `gradeid` INT(10) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Student grade', `address` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Home address', `email` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `FK_gardeid` (`gradeid`), CONSTRAINT `FK_gardeid` FOREIGN KEY (`gradeid`) REFERENCES `grade` (gradeid) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
When deleting a table with a foreign key relationship, you must first delete the referenced table (slave table) and then the referenced table (master table)
Method 2: after the table is created successfully, add a foreign key
CREATE TABLE `grade`( `gradeid` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'grade id', `gradename` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Grade name', PRIMARY KEY (`gradeid`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student` ( `id` INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'anonymous' COMMENT 'full name', `pwd` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '123456' COMMENT 'password', `sex` VARCHAR(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'male' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'date of birth', `gradeid` INT(10) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Student grade', `address` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Home address', `email` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 -- There is no foreign key relationship when creating a table ALTER TABLE `student` ADD CONSTRAINT `FK_gradeid` FOREIGN KEY (`gradeid`) REFERENCES `grade`(`gradeid`); -- ALTER TABLE`surface` ADD CONSTRAINT Constraint name FOREIGN KEY(Columns as foreign keys) refer to which fields of which table
The above operations are physical foreign keys, database level foreign keys, and are not recommended. (to avoid the trouble caused by too many databases, just learn here)
Best practices
- A database is a simple table. It only stores data, only rows (data) and columns (fields)
- We want to use the data of multiple tables and use foreign keys (programs to implement them)
3.2. DML language (remember all)
Database meaning: data storage, data management
DML: Data Manipulation Language
- Insert add
- update modification
- Delete delete
3.3. Add insert
Insert statement (add)
insert into table name ([field name 1], [field name 2], [field name 2]) values('value 1 '), ('value 2'), ('value 3 '),...)
Insert grade (grade name) values ('senior four ')
-
Can we omit the primary key auto increment (error reporting)
Insert intergradevalues ('junior ')
-
How not to write the fields of the table? They will match one by one
Insert grade (grade ID, grade name) values ('junior ',' null ')
In general, when writing insert statements, we must correspond the data and fields one by one
-
Insert multiple fields
Insert grade (grade name) values ('sophomore '), ('freshman');Insert intervenient (name) values ('zhang San ')
Insert intervenient (name, PWD, sex) values ('zhang San ',' aaaaa ',' male ')
Insert intervenient (name, PWD, sex) values ('li Si ',' aaaaa ',' male '), (' Wang Wu ',' 23232 ',' male ')
Syntax: - insert into table name ([field 1], [field 2]) values('value 1 '), (' value 2 ')
matters needing attention:
-
Fields are separated by English commas
-
The field can be omitted, but the subsequent values must correspond to each other
Insert interactive values (5, 'Li Si', 'aaaaa', 'male', '2000-01-01', 1, 'Xi'an', 'email')
-
Multiple pieces of data can be inserted at the same time, and the VALUES after VALUES need to be separated by (comma)
values(),(),...
3.4. Modify update
update modify who (condition) set original value = new value
-- Modify the name of the student with a brief introduction UPDATE `student` SET `name`='Mad God' WHERE id =1; -- All tables are changed without specifying conditions UPDATE `student` SET `name`='Yangtze River' -- Modify multiple attributes, separated by commas UPDATE `student` SET `name`='Mad God',email = '23456789qq@.com' WHERE id =1;
Condition: where clause operator (id is equal to a value,) (greater than a value,) (modify in a certain interval...)
The operator returns a Boolean value
| Operator | meaning | Range | result |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | be equal to | 5 = 6 | false |
| < > or= | Not equal to | 5 <> 6 | true |
| > | greater than | 5 > 6 | false |
| < | less than | 5 < 6 | true |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | 6,7 >= 6 | true |
| <= | Less than or equal to | 5,6 <= 6 | true |
| BETWEEN ** and ** | Within a certain range | [2 , 5] 3 | true |
| AND | Me and you&& | 5 > 1 and 1 > 2 | false |
| OR | Me or you|| | 5 > 1 or 1 > 2 | true |
-- Locate data through multiple conditions UPDATE `student` SET `name`='Yangtze River' WHERE `name`='Mad God 66' AND sex='female';
Syntax: UPDATE table name set column_name = value,[column_name = value,...] where [condition]
be careful:
-
column_name is a database column. Try to bring it with you``
-
Condition is a filter condition. If it is not specified, all columns will be modified
-
Value is a specific value or a variable CURRENT_TIME
UPDATE `student` SET `birthday`=CURRENT_TIME WHERE `name`='Yangtze River' AND SEX = 'female'
-
The attributes of multiple settings are separated by English commas
3.5 deletion
delete command
Syntax: delete from table name [where condition]
-- Delete data (Avoid writing like this, it will be deleted completely) DELETE FROM `student` -- Delete assignment DELETE FROM `student` where id= 1
TRUNCATE command
Function: completely empty a database, and the table structure and index constraints will not change
-- empty student surface TRUNCATE 'student'
Difference between delete and TRUNCATE
- Same point: data can be deleted without deleting table structure
- Different
- TRUNCATE resets the auto increment counter to zero
- DELETE does not affect transactions
-- test delete and truncate difference
CREATE TABLE `test`(
`id` INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`coll` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO `test`(`coll`) VALUES('1'),('2'),('3')
DELETE FROM `test` -- It will not affect the auto increment. Input 1, 2 and 3 again, id Start with 4 (similar to delete)
TRUNCATE TABLE `test` -- Auto increment returns to zero (similar to initialization)
Understand: the problem of Ddelete deletion, restart the database, and solve the problem
- The innoDB engine auto increment starts from 1 (it exists in memory and loses power when powered off)
- MyISAM engine continues from the previous increment (exists in the file and will not be lost)
4. DQL query data (most important)
-- test data
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `school`;
-- Create a school database
USE `school`;-- Create student table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student`(
`studentno` INT(4) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Student number',
`loginpwd` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`studentname` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Student name',
`sex` TINYINT(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Gender, 0 or 1',
`gradeid` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Grade number',
`phone` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Contact number, can be blank',
`address` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Address, null allowed',
`borndate` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'time of birth',
`email` VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Mailbox account can be empty',
`identitycard` VARCHAR(18) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'ID number',
PRIMARY KEY (`studentno`),
UNIQUE KEY `identitycard`(`identitycard`),
KEY `email` (`email`)
)ENGINE=MYISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- Create grade table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `grade`;
CREATE TABLE `grade`(
`gradeid` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Grade number',
`gradename` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Grade name',
PRIMARY KEY (`gradeid`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT = 6 DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
-- Create chart of accounts
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `subject`;
CREATE TABLE `subject`(
`subjectno`INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Course number',
`subjectname` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Course name',
`classhour` INT(4) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Class hours',
`gradeid` INT(4) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Grade number',
PRIMARY KEY (`subjectno`)
)ENGINE = INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT = 19 DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
-- Create grade sheet
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `result`;
CREATE TABLE `result`(
`studentno` INT(4) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Student number',
`subjectno` INT(4) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Course number',
`examdate` DATETIME NOT NULL COMMENT 'Test date',
`studentresult` INT (4) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Examination results',
KEY `subjectno` (`subjectno`)
)ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
-- Insert student data and add the rest by yourself. Only 2 rows are added here
INSERT INTO `student` (`studentno`,`loginpwd`,`studentname`,`sex`,`gradeid`,`phone`,`address`,`borndate`,`email`,`identitycard`)
VALUES
(1000,'123456','Zhang Wei',0,2,'13800001234','Chaoyang, Beijing','1980-1-1','text123@qq.com','123456198001011234'),
(1001,'123456','Qiang Zhao',1,3,'13800002222','Shenzhen, Guangdong','1990-1-1','text111@qq.com','123456199001011233');
-- Insert score data. Only one group is inserted here, and the others are added by themselves
INSERT INTO `result`(`studentno`,`subjectno`,`examdate`,`studentresult`)
VALUES
(1000,1,'2013-11-11 16:00:00',85),
(1000,2,'2013-11-12 16:00:00',70),
(1000,3,'2013-11-11 09:00:00',68),
(1000,4,'2013-11-13 16:00:00',98),
(1000,5,'2013-11-14 16:00:00',58);
-- Insert grade data
INSERT INTO `grade` (`gradeid`,`gradename`) VALUES(1,'Freshman'),(2,'Sophomore'),(3,'Junior'),(4,'Senior'),(5,'Preparatory class');
-- Insert account data
INSERT INTO `subject`(`subjectno`,`subjectname`,`classhour`,`gradeid`)VALUES
(1,'Advanced mathematics-1',110,1),
(2,'Advanced mathematics-2',110,2),
(3,'Advanced mathematics-3',100,3),
(4,'Advanced mathematics-4',130,4),
(5,'C language-1',110,1),
(6,'C language-2',110,2),
(7,'C language-3',100,3),
(8,'C language-4',130,4),
(9,'Java Programming-1',110,1),
(10,'Java Programming-2',110,2),
(11,'Java Programming-3',100,3),
(12,'Java Programming-4',130,4),
(13,'database structure -1',110,1),
(14,'database structure -2',110,2),
(15,'database structure -3',100,3),
(16,'database structure -4',130,4),
(17,'C#Foundation ', 130,1);
4.1,DQL
(Data Query Language)
- It is used for all query operations
- It can do simple query and complex query
- The core language and the most important statement in the database
- The most frequently used language
be careful:
- When multiple programs run and report errors, they can run section by section. Because the running sequence is randomly selected by the cpu, it may appear that the writing section has started before the table is created, so an error is reported
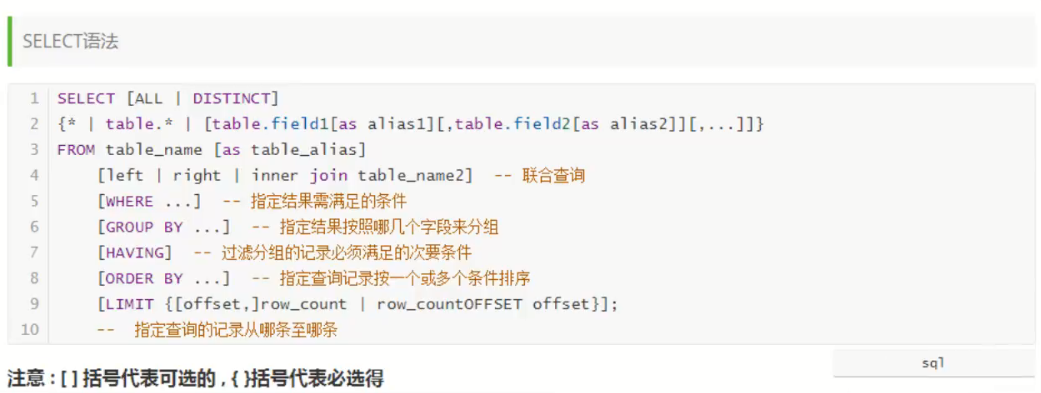
Select full syntax:
4.2. Specify query fields
-- Query all students SELECT field FROM surface
SELECT * FROM student
-- Query specified fields such as
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM student
-- alias AS,Give the result a name AS You can alias fields or tables
SELECT `StudentNo` AS Student number,`StudentName`AS Student name FROM student AS S
-- function Concat(a,b)
SELECT CONCAT('full name:',StudentName) AS New name FROM student
Syntax: SELECT field... FROM table
Sometimes, the list of names is not so well known. We use alias AS (field name AS alias) (table name AS alias)
De duplication distinct
Function: remove the duplicate statements in the query results of the select statement, and only one duplicate statement is displayed
-- Find out which students took the exam and got good grades SELECT * FROM result -- Query all test scores -- Check which students took the exam SELECT `studentNo` FROM result -- Duplicate data found, de duplication SELECT DISTINCT `studentNo` FROM result
Database columns (expressions)
-- Query System Version (function) SELECT VERSION() -- Used to evaluate (an expression) SELECT 100*3-1 AS Calculation results -- Query self increasing step size (variable) SELECT @@auto_increment_increment -- Student examination results+1 Sub view SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentResult`+1 AS 'After scoring' FROM result
Expressions in database: text value, column, Null, function, calculation expression, system variable
select expression from table
4.3 where conditional clause
Function: retrieve qualified values in data
The search criteria consists of one or more expressions! Results: Boolean
Logical operator
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| and && | a and b , a && b | Logic and, both are true, and the result is true |
| or || | a or b , a || b | Logical or, one of which is true, the result is true |
| Not ! | not a , ! a | Logical non, true is false, false is true! |
Try to use English
-- Query all students, grades SELECT `StduentNo`,`StudentResult` FROM result -- The query test score is between 95 and 100 WHERE StudentResult >=95 AND StudentResult<=100 -- Fuzzy query (interval) SELECT `StduentNo`,`StudentResult` FROM result WHERE StudentResult BETWEEN 95 AND 100 -- Grades of students other than student 1000 SELECT `StduentNo`,`StudentResult` FROM result WHERE StudentNo != 1000 -- Multiple conditions are available and to be connected WHERE NOT StudentNo = 1000
Fuzzy queries: comparison operators
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| IS NULL | a is null | If the operator is null, the result is true |
| IS NOT NULL | a is not null | If the operator is not null, the result is true |
| BETWEEN | a between b and c | If a is between b and c, the result is true |
| LIKE | a like b | SQL matches. If a matches b, the result is true |
| IN | a in (a1,a2,a3...) | If a is in one of a1,a2,a3... The result is true |
-- Inquire about students surnamed Liu
-- like combination %(Represents 0 to any character) _(One character)
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentName LIKE 'Liu%';
-- For students surnamed Liu, there is only one word after their name
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentName LIKE 'Liu_';
-- For students surnamed Liu, there are only two words after their name
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentName LIKE 'Liu__';
-- Query the students with Jiazi in the middle of their names %Jia%
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentName LIKE '%Jia%';
===================IN( One or more specific values cannot be used % )===========================
-- Query 1001 1002 1003 student information
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentNo = 1001
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentNo = 1002
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentNo = 1003
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE StudentNo IN (1001,1002,1003);
-- Query students in Beijing
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE `Address` IN('Anhui','Luoyang, Henan');
===================NULL,NOT NULL===================================
-- Query students with empty address null ''
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE address=''OR address IS NULL
-- Query students with birth date cannot be blank
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE `BornDate` IS NOT NULL;
-- It is blank to query students without birth date
SELECT `StudentNo`,`StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE `BornDate` IS NULL;
4.4. Associated table query
JOIN comparison
Three join theories
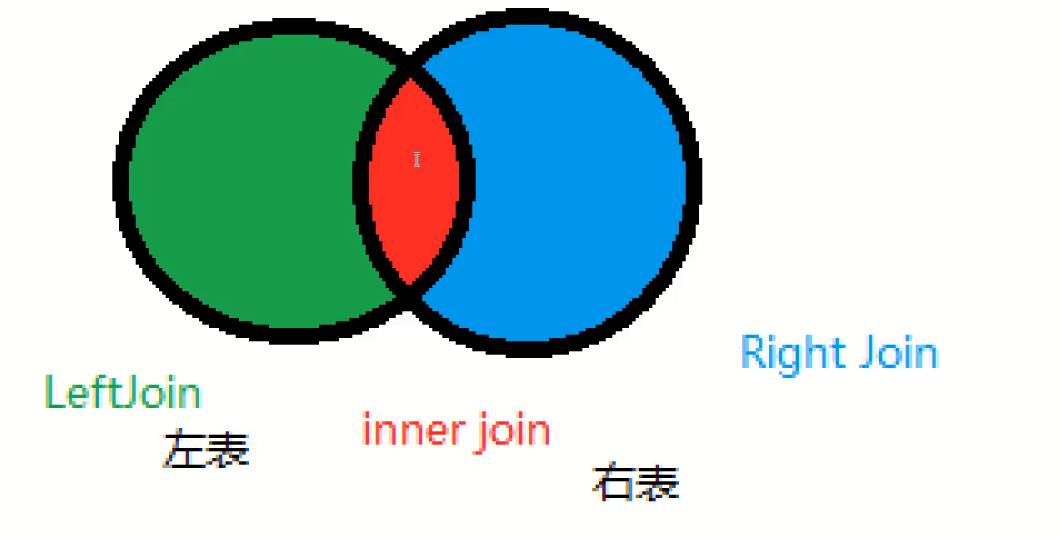
There is also the expanded seven jion theory
======================Join table query join ============================== -- Query the students participating in the examination (student number, name, examination number, score) SELECT * FROM student SELECT * FROM result /* 1. Analyze the requirements and the tables from which the query fields come (multiple tables need to be connected for query) 2.Determine which connection query to use? There are 7 kinds in total 3.Determine the intersection (which data is the same in the two tables) Conditions for judgment: studentNo in student table = studentNo in grade table */ -- join on join query join(Connected tables) on(Conditions of judgment) -- where Equivalent query SELECT s.studentNo,studentName,SubjectNo,StudentResult -- For query, the cross content needs to specify the target table FROM student AS s INNER JOIN result AS r -- query student And connect result WHERE s.studentNo = r.studentNo -- where Equivalent query -- Right Join SELECT s.studentNo,studentName,SubjectNo,StudentResult FROM student AS s RIGHT JOIN result r -- AS Can be omitted ON s.studentNo = r.studentNo -- LEFT Join SELECT s.studentNo,studentName,SubjectNo,StudentResult FROM student AS s LEFT JOIN result AS r ON s.studentNo = r.studentNo
| operation | describe |
|---|---|
| Inner join | If there is at least one match in the table, the row is returned (crossed) |
| left join | All values will also be returned from the left table, even if there is no match in the right table |
| right jion | All values will also be returned from the right table, even if there is no match in the left table, |
-- Query absent students SELECT s.studentNo,studentName,SubjectNo,StudentResult FROM student AS s LEFT JOIN result AS r ON s.studentNo = r.studentNo WHERE StudentResult IS NULL -- Inquired the information of students participating in the examination: student number: Student Name: Subject Name: score SELECT s.`studentNo`,`studentName`,`SubjectName`,`studentResult` FROM student s RIGHT JOIN result r ON r.studentNo=s.studentNo INNER JOIN `subject` sub -- Query matching again ON r.SubjectNo=sub.SubjectNo -- What data do I want to query SELECT .... -- From which tables FROM surface xxx JOIN Connected tables ON Cross condition -- Suppose there are multiple tables in one query, first query two tables, and then add them slowly --FROM a LEFT JOIN b Zuo weizhun --FROM a RIGHT JOIN b Whichever is right
thinking
- What data do I want to query SELECT
- FROM which tables can I query the ON cross conditions of the xxx JOIN table in the FROM table
- Suppose there are multiple tables in one query, first query two tables, and then add them slowly
Self connection
-- Self connected database: CREATE TABLE `school`.`category`( `categoryid` INT(3) NOT NULL COMMENT id, `pid` INT(3) NOT NULL COMMENT father id 1 if there is no parent, `categoryname` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL COMMENT Species name, PRIMARY KEY (`categoryid`) ) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_general_ci; INSERT INTO `school`.`category` (`categoryid`, `pid`, `categoryname`) VALUES (2, 1, information technology); insert into `school`.`CATEGOrY` (`categoryid`, `pid`, `categoryname`) values (3, 1, software development); insert into `school`.`category` (`categoryid`, `PId`, `categoryname`) values (5, 1, Art design); insert iNTO `School`.`category` (`categoryid`, `pid`, `categorynamE`) VAlUES (4, 3, database); insert into `school`.`category` (`CATEgoryid`, `pid`, `categoryname`) values (8, 2, Office information); insert into `school`.`category` (`categoryid`, `pid`, `CAtegoryname`) values (6, 3, web development); inserT INTO `SCHool`.`category` (`categoryid`, `pid`, `categoryname`) valueS (7, 5, ps technology);
Your own table is connected with your own table. Core: one table is split into two identical tables
Parent class
| categoryid | categoryName |
|---|---|
| 2 | information technology |
| 3 | software development |
| 5 | Art design |
Subclass
| pid | categoryid | categoryName |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | database |
| 2 | 8 | Office information |
| 3 | 6 | web development |
| 5 | 7 | ps Technology |
Operation: query the relationship between parent and child classes
| Parent class | Subclass |
|---|---|
| information technology | Office information |
| software development | database |
| software development | web development |
| Art design | ps Technology |
-- Query parent-child information SELECT a.`categroryName` AS `Parent column`,b.`categroryName` AS `Sub column` FROM `catgroy` AS a,`catgroy` AS b WHERE a.`categoryid`=b.`pid`
practice:
-- Query the grade of the student (student number, student name, grade) SELECT `studentNo`,`studentName`,`gradeName` -- Query content FROM student s -- Table to query INNER JOIN `grade` g -- Connected tables ON s.`GradeId`=g.`GradeId` -- Judgment equation condition
-- Query the age of the account (account name, age name) SELECT `studentName`, `GradeName` FROM `subject` sub INNER JOIN `grade` g ON sub.`GradeID` = g.`GradeID`
-- The database structure was queried-1 Student information of the exam: student number, student name, subject name, score SELECT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`,`SubjectName`,`StudentResult` FROM student s INNER JOIN `result` r ON r.`StudentNo` = r.`StudentNo` INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`StudentNo` = sub.`StudentNo` WHERE subjectName = 'database structure -1'
4.5 paging and sorting
Sort order by
-- ============================paging limit And sorting order by================= -- Sorting: ascending ASC Descending order DESC -- ORDER BY How to sort through that field -- The database structure was queried-1 Student information of the exam: student number, student name, subject name, score SELECT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`,`SubjectName`,`StudentResult` FROM student s INNER JOIN `result` r ON r.`StudentNo` = r.`StudentNo` INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`StudentNo` = sub.`StudentNo` WHERE subjectName = 'database structure -1' ORDER BY StudentResult DESC -- Specifies the ascending order of the sort field ASC Descending order DESC SELECT xx FROM xx JOIN xx WHERE xx ORDER BY xx ASC || DESC
Paging limit
-- Why pagination? -- Ease the pressure on the database and give people a better experience -- There is another non paged waterfall flow -- Pagination, displaying five pieces of data per page -- Syntax: limit Starting value, page size -- limit 0,5 1-5 -- limit 1,5 2-6 -- limit 6,5 Page 2 this -- Web application: current page, total pages, page size SELECT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`,`SubjectName`,`StudentResult` FROM student s INNER JOIN `result` r ON s.`StudentNo`=r.`StudentNo` INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`subjectNo`=sub.`subjectNo` WHERE subjectName='data structure-1' ORDER BY StudentResult ASC LIMIT 0,5 -- first page limit 0,5 -- Page 2 limit 5,5 -- Page 3 limit 10,5 -- The first N page limit (n-1)* pageSize,pageSize -- [pageSize Represents the page size] -- (n-1)* pageSize : Starting value -- n : Current page -- Total data/Page size = PageCount
Paging formula:
- Page 1 limit 0,5
- Page 2 limit 5,5
- Page 3 limit 10,5
- Page N limit (n-1) * pageSize,pageSize
- [pageSize represents page size]
- (n-1) * pageSize: starting value
- n: current page
- Total data / page size = total pages
Syntax: limit (query start subscript, pagesize)
practice:
-- query JAVA Information of students whose course scores in the first academic year are in the top ten and whose scores are greater than 80 (student number, name, course name, score) SELECT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`,`SubjectName`,`StudentResult` FROM `student` s INNER JOIN `result` r ON s.`StudentNo`=r.`StudentNo` INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON sub.`subjectNo` = r.`subjectNo` WHERE subjectName='JAVA First academic year' AND StudentResult >= 80 ORDER BY StudentResult DESC LIMIT 0,10
4.6 sub query
where (this value is calculated)
Essence: nest a subquery statement within a where statement
-- =========================== where =========================
-- 1.Query database structure-1 All test structures (student number, subject number, score) are arranged in descending order
-- Method 1: connection query
SELECT `StudentNo`,r.`SubjectName`,`StudentResult`
FROM `result` r
INNER JOIN `subject` sub
ON r.SubjectNo = sun.SubjectNo
WHERE subjectName = 'database structure -1'
ORDER BY StudentResult DESC
-- Method 2: use sub query(From inside to outside)
SELECT `StudentNo`,r.`SubjectName`,`StudentResult`
FROM `result`
WHERE StudentNo=(
-- All database structures will be queried-1 Nested student number formula
SELECT SubjectNo FROM `subject`
WHERE SubjectName = 'database structure -1'
)
ORDER BY StudentResult DESC
-- Student number and name of students with a score of no less than 80
SELECT DISTINCT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`
FROM student s
INNER JOIN result r
ON r.StudentNo = s.StudentNo
WHERE StudentResult>=80
-- On this basis, add a subject, advanced mathematics-2
SELECT DISTINCT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`
FROM student s
INNER JOIN result r
ON r.StudentNo = s.StudentNo
WHERE StudentResult>=80 AND `SubjectNo`=(
SELECT Subject FROM `subject`
WHERE SubjectName='Advanced mathematics-2'
)
-- The inquiry course is advanced mathematics-2 Student number and name of students with a score of no less than 80
SELECT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`
FROM student s
INNER JOIN result r
ON s.StudentNo = r.StudentNo
INNER JOIN `subject` sub
ON r.`SubjectName`='Advanced mathematics-2'
WHERE `SubjectaName`='Advanced mathematics-2' AND StudentResult >=80
-- Remoulding (From inside to outside)
SELECT StudentNo,StudentName FROM student -- A table does not need to be clear
WHERE StudentNo IN(
SELECT StudentNo result WHERE StudentResult >80 AND SubjectNo =(
SELECT SubjectNo FROM `subject` WHERE `SubjectaName`='Advanced mathematics-2'
)
)
4.7 grouping and filtering
-- Query the average score of different courses, the highest score, the lowest score, and the average score is greater than 80 -- Core: (grouped according to different courses) SELECT `SubjectName`,AVG(StudentResult) AS average,MAX(StudentResult) AS Highest score,MIN(StudentResult) AS Lowest score FROM result r INNER JOIN `Subject` sub ON r.SubjectNo = sub.SubjectNo GROUP BY r.SubjectNo -- By what field HAVING average >80 -- Secondary conditions that must be met for grouping filtered records
4.8. Summary
5. MySQL function
5.1 common functions
-
Mathematical operation
SELECT ABS(-8) – absolute (8)
SELECT CEILING(9.4) – round up (10)
SELECT FLOOR(9.4) – round down (9)
SELECT RAND() – returns a 0-1 random number
SELECT SIGN(-10) – the sign to judge a number is 0 = 0. Negative numbers return - 1. Positive numbers return 1
-
String function
SELECT CHAR_LENGTH('23232 ') – returns the length of a stringSELECT CONCAT('I ',' 233 ') – concatenate strings
SELECT INSERT('java ', 1,2,' cccc ') – replace a length from a certain position (replace 2 from the first)
SELECT UPPER('abc ') -- convert to uppercase
SELECT LOWER('ABC ') -- convert to lowercase
SELECT INSTR ('kuangshen ',' h ') – returns the index of the specified value
SELECT REPLACE('persistence leads to success', 'persistence', 'effort') – replaces the specified string
SELECT SUBSTR('persistence will succeed ', 3,2) – returns the specified string (2 from the third)
SELECT REVERSE('persistence leads to success') – reverses the string
-
Query the student surnamed Zhou and change it to Zou
SELECT REPLACE(studentname, 'Zhou', 'Zou') FROM student
WHERE studentname LIKE 'week%'
-
Time and date function (remember)
SELECT CURRENT_DATE() – gets the current date
SELECT CURDATE() - gets the current date
SELECT NOW() – get the current date and time
Select locality() - gets the local date and time
SELECT SYSDATE() - gets the system time
-
Mm / DD / yyyy H / min / S
SELECT YEAR(NOW())
SELECT MONTH(NOW())
SELECT DAY(NOW())
SELECT HOUR(NOW())
SELECT MINUTE(NOW())
SELECT SECOND(NOW())
-
system
SELECT SYSTEM_USER() – returns the current system user
SELECT USER() - returns the current system user
SELECT VERSION() - returns the version number
5.2 aggregate function (common)
| Function name | describe |
|---|---|
| COUNT() | count |
| SUM() | Sum |
| AVG() | average value |
| MAX() | Maximum |
| MIN() | minimum value |
| ... |
-- Can count the data in the table SELECT COUNT(`BornDate`) FROM student; -- Count(Specify a field), ignoring all null value -- The essence is to calculate the number of rows, but * Is to read all the contents of each line. 1 reads only one content, which is faster than 1 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM student; -- Count(*),Will not ignore null value SELECT COUNT(1) FROM student; -- Count(1),Will not ignore null value -- calculation SELECT SUM(`StudentResult`) AS the sum FROM result SELECT AVG(`StudentResult`) AS average FROM result SELECT MAX(`StudentResult`) AS Highest score FROM result SELECT MIN(`StudentResult`) AS Lowest score FROM result
5.3. Database level MD5 encryption (expansion)
What is MD5
It mainly enhances the complexity and irreversibility of the algorithm.
MD5 is irreversible, and the specific MD5 is the same
MD5 cracking principle, there is a dictionary behind it, which compares the previously simple MD5 encrypted value with the value before encryption. Copying the password is not easy to break the game
CREATE TABLE `testmd5`(
`id` INT(4) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
`pwd` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=UTF8
-- enable password
INSERT INTO testmd5 VALUES(1,'Zhang San','123456'),(2,'Li Si','123456'),(3,'Wang Wu','123456')
-- encryption
UPDATE testmd5 SET pwd=MD5(pwd) WHERE id =1
UPDATE testmd5 SET pwd=MD5(pwd) WHERE id !=1 -- Encrypt all
-- Encrypt on insert
INSERT INTO testmd5 VALUES(4,'Xiao Ming',MD5('123456'))
INSERT INTO testmd5 VALUES(5,'red',MD5('123456'))
-- How to verify the password passed by the user MD5 Encrypt and then compare the encrypted values
SELECT * FROM testmd5 WHERE `name`='red' AND pwd=MD5('123456')
6. Business
6.1. What is a transaction
Either all succeed or all fail
SQL execution, A transfers A 1000 – > 200 B200 to B
SQL execution, B receives A's money A800-B400
Execute a set of SQL in a batch
Transaction principle: ACID principle, atomicity, consistency, isolation, persistence (dirty read, phantom read...)
Atomicity
Either all succeed or all fail
Consistency
The final data integrity before and after the transaction should be consistent
Durability – transaction commit
The transaction was not committed. Restore to the original state
Once the transaction is committed, it is irreversible and persisted to the database
Isolation
When multiple users access the database concurrently, the transactions opened by the database for each user shall not be disturbed by the operation data of other transactions, and the transactions shall be isolated from each other
Problems arising from isolation
- Dirty read:
A transaction reads uncommitted data from another transaction.
- Non repeatable:
A row of data in a table is read in a transaction, and the results are different multiple times. (this is not necessarily a mistake, but it is wrong on some occasions)
- Virtual reading (unreal reading)
It means that the data inserted by another transaction is read in one transaction, resulting in inconsistent reading.
(usually affected by one line, one more line)
Execute transaction
-- mysql Automatically turn on transaction commit SET autocommit=0 -- close SET autocommit=1 -- On (default) -- Manual transaction processing SET autocommit =0 -- Turn off auto submit -- Transaction on START TRANSACTION -- Mark the beginning of a transaction, starting from the beginning SQP All within the same transaction INSERT XX INSERT XX -- Commit: persistence(Successfully submitted) COMMIT -- Rollback: return to the original state (rollback failed) ROLLBACK -- End of transaction SET autocommit = 1 -- Turn on auto submit and restore it as it is -- understand SAVEPOINT Save point name -- Set a transaction savepoint ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT Save roll call -- Rollback to savepoint RELEASE SAVEPOINT Save point -- Undo savepoint
Simulation scenario
CREATE DATABASE shop CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci
USE shop
CREATE TABLE `account`(
`id` INT(3) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
`money` DECIMAL(9,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO account(`name`,`money`)
VALUES('A',2000),('B',10000)
-- Simulated transfer: transaction
SET autocommit = 0; -- Turn off auto submit
START TRANSACTION -- Open transaction (a set of transactions)
UPDATE account SET money = money-500 WHERE `name` = 'A' -- A Transfer to B
UPDATE account SET money = money+500 WHERE `name` = 'B' -- B Receive money
COMMIT ; -- Commit transaction
ROLLBACK ; -- RollBACK
SET autocommit=1 -- Restore defaults
7. Index
MySQL's official heap Index is defined as: an Index is a data structure that helps MySQL obtain data efficiently.
By extracting the sentence trunk, we can get the essence of the index: the data structure of the index.
7.1 classification of index
In a table, there can only be one primary key index and multiple unique indexes
- PRIMARY KEY (PRIMARY KEY)
- Unique identifier. The primary key cannot be repeated. Only one column can be used as the primary key
- UNIQUE KEY
- Avoid duplicate columns. Unique indexes can be repeated, and multiple columns can identify unique indexes
- General index (KEY/INDEX)
- By default, it is set with the index and key keywords
- Full text index (FULLTEXT)
- Only under the characteristic database engine, MyISAM
- Fast positioning data
Basic grammar
-- Use of index -- 1.Add indexes to fields when creating tables -- 2.After creation, increase the index -- Show all index information SHOW INDEX FROM surface -- Add a full-text index ALTER TABLE surface ADD FULLTEXT INDEX Index name (column name) -- EXPLAIN analysis sql Status of implementation EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM student -- Non full text index EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM student WHERE MATCH(studentName) AGAINST(Contents of index) -- There is too little data, and indexing is meaningless
7.2 test index
CREATE TABLE `app_user` (
`id` BIGINT(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT '' COMMENT'User nickname',
`email` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT'User mailbox',
`phone` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT '' COMMENT'cell-phone number',
`gender` TINYINT(4) UNSIGNED DEFAULT '0' COMMENT'Gender(0: Male; 1: Female)',
`password` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT'password',
`age` TINYINT(4) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT'Age',
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`update_time` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT'app User table'
-- Insert 1 million data
DELIMITER $$ -- Must be written before writing a function
CREATE FUNCTION mock_data()
RETURNS INT
BEGIN -- Function body header
DECLARE num INT DEFAULT 1000000;
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
WHILE i<num DO
-- Insert statement
INSERT INTO app_user(`name`,`email`,`phone`,`gender`,`password`,`age`)
VALUE(CONCAT('user',i),'534240118@qq.com',CONCAT('18',RAND()*(999999999-100000000),FLOOR (RAND()*2),
UUID(),FLOOR (RAND()*100));
SET i = i+1;
END WHILE; -- Cycle stop
RETURN i;
END; -- Function body tail
SELECT mock_data(); -- Execute function generation table
SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 9999' -- Nearly 1 second
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 9999' -- rows Only 991749 records were found, so it's slow
-- id _ Table name_Field name
-- create index Index name on Table (field)
CREATE INDEX id_app_user_name ON app_user(`name`); -- 0.001 s
SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 9999' -- The time taken to complete the citation is 0.001 second
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 9999' -- rows Query a record
Indexes are not useful for small data, but the difference is obvious for large data
7.3 indexing principle
- The more indexes, the better
- Do not index data that changes frequently
- Tables with small amounts of data do not need to be indexed
- Indexes are usually added to fields commonly used for queries
Indexed data structure
Hash type index
Btree: default innodb data structure
(MySQL index, read it carefully)
read: http://blog.codinglabs.org/articles/theory-of-mysql-index.html
8. Rights management and backup
8.1 user management
SQLyog visual management
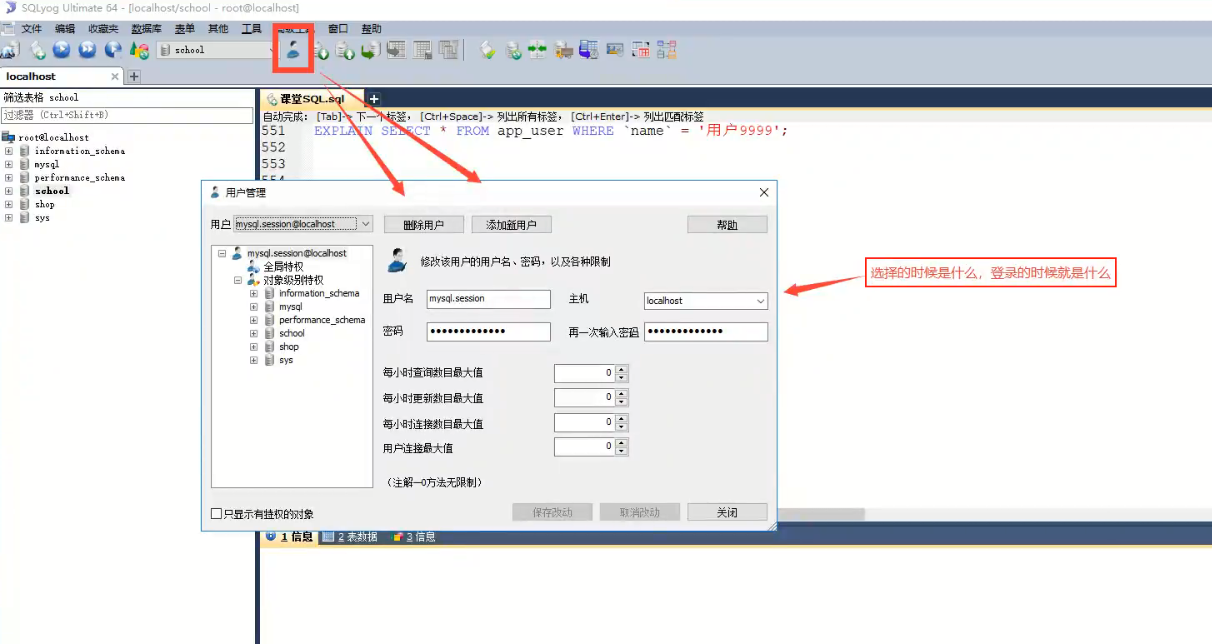
SQL command operation
User table: MySQL user
Essence: add, delete, modify and query this table
-- Create user CREATE USER user name IDENTIFIED BY 'password'
CREATE USER sanjin IDENTIFIED BY '123456'
-- Change password (change current password)
SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('111111')
-- Modify password (modify specified user password)
SET PASSWORD FOR kuangshen = PASSWORD('111111')
-- rename rename user Original name to New name
RENAME USER kuangshen TO kuangshen2
-- User authorization ALL PRIVILEGES All permission libraries, tables
-- ALL PRIVILEGES Except for authorizing others, others are capable
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO kuangshen2
-- Query authority
SHOW GRANTS FOR kuangshen2 -- View the permissions of the specified user
SHOW GRANTS FOR root@localhost
-- ROOT User rights: GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO `root`@`localhost` WITH GRANT OPTION
-- Revoke permissions REVOKE Which permissions, in which library, and to whom
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* FROM kuangshen2
-- delete user
DROP USER kuangshen2
8.2 MySQL backup
Why backup:
- Ensure that important data is not lost
- Data transfer
MySQL database backup method
-
Copy physical files directly
-
Export manually in a visualizer like SQLyog
- In the table or library you want to export, right-click to select backup and export
-
Exporting mysqldump from the command line
# mysqldump -h host - u user name - p password database table name > Logistics disk location / file name mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -p123456 shool student >D:/a.spl # mysqldump -h host - u user name - p password database table 1 Table 2 Table 3 > Logistics disk location / file name mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -p123456 shool student result >D:/b.spl # mysqldump -h host - u user name - p password database > Logistics disk location / file name mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -p123456 shool >D:/c.spl # Import table # After logging in, switch to the specified database # source backup file source d:/a.sql #Don't log in mysql -u user name -p Password storehouse < Backup files
Suppose you want to back up the database to prevent data loss
Give the database to your friends and the sql file to others
9. Standardize database design
9.1 why design is needed
When the database is complex, we need to design it
Poor database design:
- Data redundancy, waste of space
- Database insertion and deletion will be troublesome. Exceptions [shielding the use of physical foreign keys]
- Poor program performance
Good database design:
- Save memory space
- Ensure the integrity of the database
- It is convenient for us to develop the system
In software development, the design of database
- Analysis requirements: analyze the requirements of the business and the database to be processed
- Outline design: design relationship diagram E-R diagram
Steps to design a database (personal blog)
-
Collect information and analyze requirements
-
User table (user login and logout, user's personal information, blogging, creating categories)
User id, user name, user password, phone
-
Classification table (article classification, who created it)
Category ID, article name, article author id
-
Article table (information about articles)
Article id, article title, author id, category id, article content, creation time, modification time, like
-
Comment form (article comments)
Comment ID, article ID, reviewer ID, comment content, comment time, respondent id
-
Friend chain list (friend chain information)
Friend chain id, website name, website link, sorting
-
User defined table (system information, a key word, or some main fields)
-
Talk about the table (post mood... id... content... create_time)
-
-
Identify entity (landing requirements to each field)
-
Identify relationships between entities
- Blog: user – > blog
- Create category: user – > category
- Attention: user – > User
- Friend chain: links
- Comments: user – > User - > blog
Exercise aids: bbs, crm, Ant Design Pro
9.2 three paradigms
Why data normalization?
- Duplicate information
- Update exception
- Insert exception
- Delete exception
- The exception cannot be displayed normally
- Delete exception
- Missing valid information
Three paradigms
First normal form (1NF)
Atomicity: ensure that each column cannot be further divided
Second paradigm (2NF)
Premise: meet the first paradigm
Each table describes only one thing
Third paradigm (3NF)
Premise: meet the first paradigm and the second paradigm
The third paradigm needs to ensure that each column of data in the data table is directly related to the primary key, not indirectly.
(standardize the design of database)
Normative and performance issues
No more than three tables can be associated with the query
- Considering the needs and objectives of commercialization (cost and user experience), the performance of database is more important
- When re standardizing performance, we need to give proper consideration to standardization
- Deliberately add some redundant fields to some tables (from multi table query to single table)
- Deliberately add some calculated columns (query with large data volume reduced to small data volume: index)
10. JDBC (key)
10.1. Database driver
Driver: sound card, graphics card, database
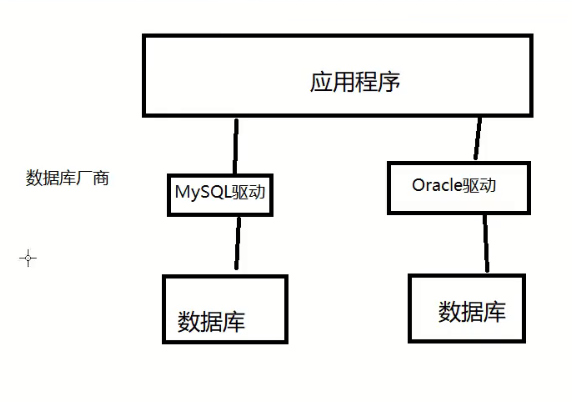
Our program will deal with the database through database driver!
However, if each database needs to write a driver, it will produce a lot of work, so JDBC appears
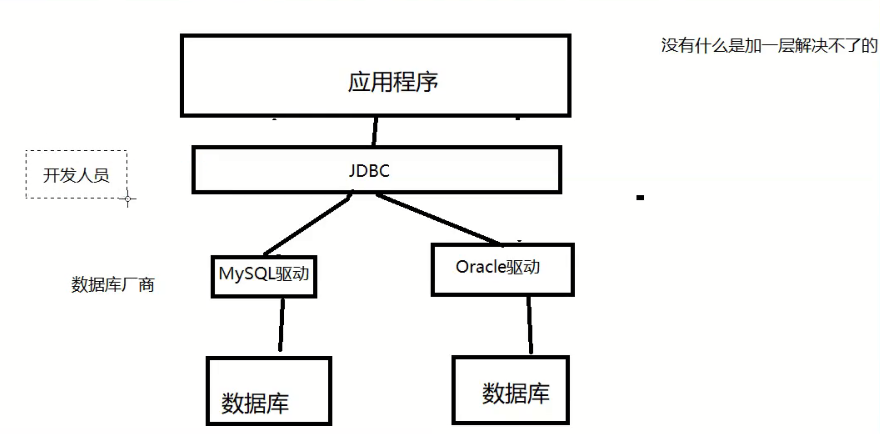
10.2,JDBC
In order to simplify the (unified database) operation of developers, SUN company provides a (Java database operation) specification, commonly known as JDBC
The implementation of these specifications is done by specific manufacturers
For developers, we only need to master the interface operation of JDBC
Packages to use:
- java.sql
- javax.sql
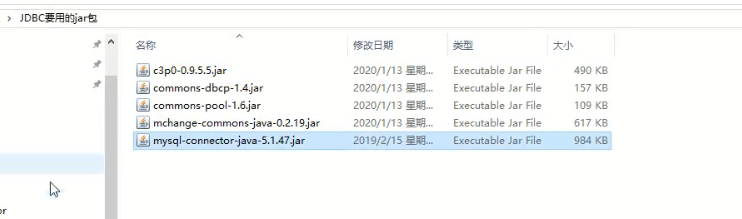
- You also need to import the database driver package mysql-connector-java-5.1.47 jar
10.3. The first JDBC program
Create test database
CREATE DATABASE jdbcStudy CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; USE jdbcStudy; CREATE TABLE `users`( id INT PRIMARY KEY, NAME VARCHAR(40), PASSWORD VARCHAR(40), email VARCHAR(60), birthday DATE ); INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday) VALUES(1,'zhansan','123456','zs@sina.com','1980-12-04'), (2,'lisi','123456','lisi@sina.com','1981-12-04'), (3,'wangwu','123456','wangwu@sina.com','1979-12-04')
-
Create a normal project
-
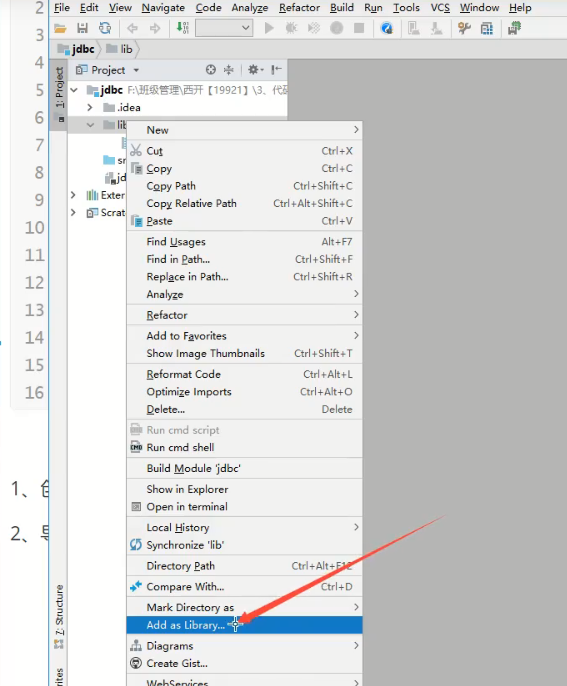
Import database driver
Create the lib directory, copy the driver to the lib directory, add the library, Add as Library
3. Write test code
//My first JDBC program
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JdbcFirstDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Load drive
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//Fixed writing
//2. User information and url
//useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&&useSSL=true
String url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String name = "root";
String password = "123456";
//3. The connection is successful, and the returned database object connection represents the database
Connection connection= DriverManager.getConnection(url,name,password);
//4. Object statement executing SQL
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5. There may be results when the object executing SQL executes SQL. View the returned results
String sql="SELECT * FROM users";
//Execute sql
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//The returned result set encapsulates the results of all our queries
while(resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("id="+resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("name="+resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println("pwd="+resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("email="+resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("birth="+resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
}
//6. Release the connection
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Step summary:
-
Load driver
-
Connect to database DriverManager
-
Gets the Statement object that executes SQL
-
Get the returned result set
-
Release connection
DriverManager
//The second one is recommended. The first one is already included in the second one
//DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//Fixed writing
Connection connection= DriverManager.getConnection(url,name,password);
//connection stands for database and database object
//Database settings auto commit
//Transaction commit
//Transaction rollback
connection.rollback();
connection.commit();
connection.setAutoCommit();
URL
String url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true"; //mysql default 3306 //Protocol: / / host address: port number / database name? Parameter1 & parameter2 & parameter3 //Oracle -- 1521 //jdbc:oralce:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
statement object to execute SQL
statement and PrepareStatement are objects that execute SQL
String sql="SELECT * FROM users";//Write Sql statement.executeQuery(); //Query operation, return ResultSet statement.execute(); //Execute any SQL (execute all SQL, so it is relatively inefficient) statement.executeUpdate(); //Update, insert and delete all use this. Returns the number of rows affected
ResultSet query result set: encapsulates all query results
Gets the specified data type
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//The returned result set encapsulates the results of all our queries
resultSet.getObject();//Used when the column type is unknown
resultSet.getString();//Specify use if known
resultSet.getInt();
resultSet.getFloat();
resultSet.getDate();
Traversal, pointer
resultSet.next(); //Move to next data
resultSet.afterLast();//Move to last
resultSet.beforeFirst();//Move to the front
resultSet.previous();//Move to previous line
resultSet.absolute(row);//Move to specified row
Free memory
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
//Resource consumption
10.4 statement object
The statement object in Jdbc is used to send SQL statements to the database. To complete the addition, deletion, modification and query of the database, you only need to send the addition, deletion, modification and query statements to the database through this object
-
The executeUpdate method of the Statement object is used to send sq | statements of addition, deletion and modification to the database. After executeUpdate is executed, an integer will be returned (that is, the addition, deletion and modification statements cause several rows of data in the database to change).
-
Statement. The executeQuery method is used to generate query statements to the database, and the executeQuery method returns the ResultSet object representing the query results
CRUD operation - create
Use the executeUpdate(String sql) method to add data. Example operations:
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "insert into user(...) values(...)";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("Insert successful");
}
CRUD operation - delete
Use the executeUpdate(String sql) method to delete data. Examples:
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "delete from user where id =1";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("Delete succeeded");
}
CURD operation - update
Use the executeUpdate(String sql) method to modify the data. Examples:
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "update user set name ='' where name = ''";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("Modified successfully");
}
CURD operation - read
Use the executeQuery(String sql) method to complete the data query operation. Example operations:
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from user where id =1";
ResultSet rs= statement.executeQuery(sql);
if(rs.next()){
System.out.println("");
}
code implementation
1. Extraction tools
-
Configuration class
Generally, the configuration class is written as a DB properties
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true"; name = "root"; password = "123456";
- Create tool class
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver = null;
private static String url = null;
private static String username = null;
private static String password = null;
static {
try{
//db. Under src, properties can be obtained directly through reflection
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
url=properties.getProperty("url");
username=properties.getProperty("username");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
//1. The drive is loaded only once
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//2. Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
//3. Release resources
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
if(rs!=null){
try{
rs.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try{
st.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try{
conn.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. Write the method of addition, deletion and modification exectueUpdate
- add to
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import static com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils.*;
public class TestInnsert {
public static void main(String[] args){
Connection conn =null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
st = conn.createStatement();//Get SQL execution object
String sql = "INSERT INTO users(id,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`)" +
"VALUES(4,'kuangshen','123456','123456@qq.com','2020-01-01')";
int i = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(i>0){
System.out.println("Insert successful");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
- delete
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import static com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils.*;
public class TestInnsert {
public static void main(String[] args){
Connection conn =null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
st = conn.createStatement();//Get SQL execution object
String sql = "DELETE FROM users WHERE id = 4";
int i = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(i>0){
System.out.println("Insert successful");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
- change
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import static com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils.*;
public class TestInnsert {
public static void main(String[] args){
Connection conn =null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
st = conn.createStatement();//Get SQL execution object
String sql = "UPDATE users SET 'NAME'='kuangshen','email'='654321@qq.com' WHERE id = 1";
int i = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(i>0){
System.out.println("Update succeeded");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
3. Query executeQuery
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import static com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils.*;
public class TestInnsert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn =null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
st = conn.createStatement();//Get SQL execution object
String sql = "select * from users where id = 1";
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);//Result set returned after query
while (rs.next()){ //output
System.out.println(rs.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
SQL injection problem
There is a vulnerability in SQL, which will be attacked, resulting in data disclosure, and SQL will be spliced
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import static com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils.getConnection;
public class SQL injection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//login("kuangshen","123456"); Normal login
//SQL injection, get all the information
login("' or '1=1","' or '1=1"); //Skills, loopholes
}
public static void login(String username,String password){
Connection conn =null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
st = conn.createStatement();//Get SQL execution object
//SELECT * FROM users WHERE 'Name' = 'kuangshen' AND 'password' = '123456'
//SELECT * FROM users WHERE 'Name' = '' or '1=1' AND 'password' = '' or '1=1'
String sql = "select * from users where `NAME`='"+ username +"' AND `PASSWORD`='"+ password +"'" ;
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);//Result set returned after query
while (rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("password"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
10.5 PreparedStatement object
PreparedStatement can prevent SQL injection and is more efficient
1. Add
import com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st =null; //Statement subclass
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//difference
//use? Placeholder instead of parameter
String sql = "insert into users(id,`NAME`,'PASSWORD','email','birthday') values(?,?,?,?,?)";
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Precompiled sql, write sql first and then do not execute
//Manual assignment, 1 represents subscript (first?), 4 represents the inserted value
st.setInt(1,4);
st.setString(2,"qing");
st.setString(3,"987654321");
st.setString(4,"987654@qq.com");
// Note:
//sql.Date() database setDeta() requires Java sql.Date(), but cannot be obtained directly
//util.Deta Java Java's new deta() is required Gettime() timestamp conversion
st.setDeta(5,java.sql.Date(new Date().getTime()));
//implement
int i = st.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("Insert successful");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(comm,st,null);
}
}
}
2. Delete
import com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st =null; //Statement subclass
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//difference
//use? Placeholder instead of parameter
String sql = "delete from users where id=?"
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Precompiled sql, write sql first and then do not execute
//Manual assignment, 1 represents subscript (first?), 4 represents the inserted value
st.setInt(1,4);
//implement
int i = st.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("Delete succeeded");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(comm,st,null);
}
}
}
3. Renew
import com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st =null; //Statement subclass
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//difference
//use? Placeholder instead of parameter
String sql = "update users set'NAME'=? where id=?"
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Precompiled sql, write sql first and then do not execute
//Manual assignment, 1 represents subscript (first?), 4 represents the inserted value
st.setString(1,"Mad God")
st.setInt(2,1);
//implement
int i = st.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("Update succeeded");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(comm,st,null);
}
}
}
4. Inquiry
import com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st =null; //Statement subclass
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//difference
//use? Placeholder instead of parameter
String sql = "select * from users where id=?"
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Precompiled sql, write sql first and then do not execute
//Manual assignment, 1 represents subscript (first?), 4 represents the inserted value
st.setString(1,1)
//implement
int i = st.executeQuery();
if (i>0){
System.out.println(rs.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(comm,st,rs);
}
}
}
5. SQL injection
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import static com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils.getConnection;
public class SQL injection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//login("kuangshen","123456"); Normal login
//SQL injection, get all the information
login("' or '1=1","' or '1=1"); //Skills, loopholes
}
public static void login(String username,String password){
Connection conn =null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
//The essence of prepareStatement() preventing SQL injection is to treat the parameters passed in as characters
//Suppose there are escape characters, such as' will be directly escaped
String sql = "select * from users where `NAME`=? and 'PASSWORD'=?"; //Mybatis
st = conn.prepareStatement();//Get SQL execution object
st.setString(1,username);
st.setString(2,password);
rs=st.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("password"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
The essence of prepareStatement() preventing SQL injection is to treat the parameters passed in as characters
Suppose there are escape characters, such as' will be directly escaped
10.6. Connect to the database using IDEA
Note: import the toolkit in advance
- Connect to database
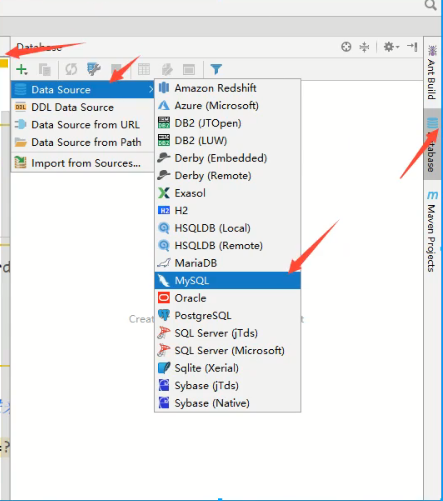
- Select database
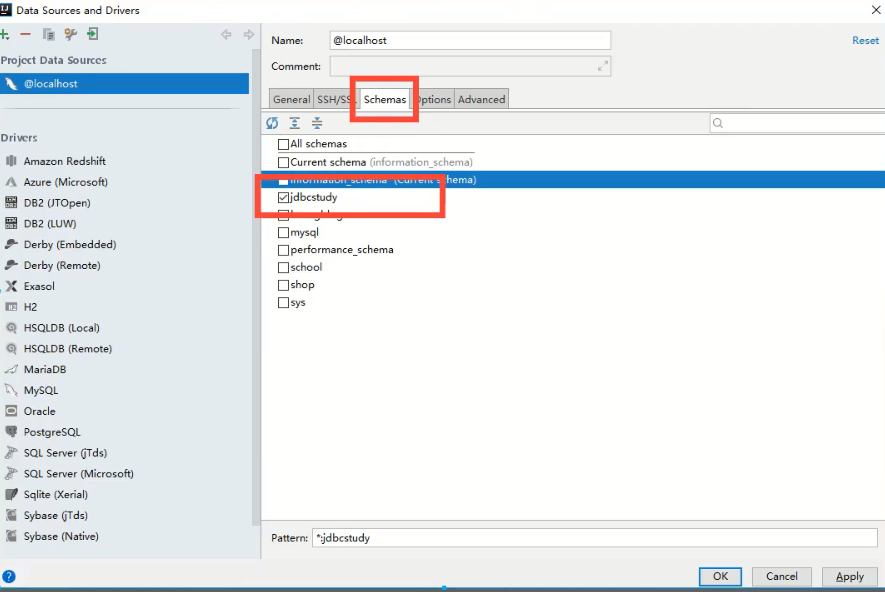
-
View table information: double click the database directory to open it
-
Update data: enter the information to be changed and click DB above to save
-
Where to write sql code
Unable to connect. Check the reason
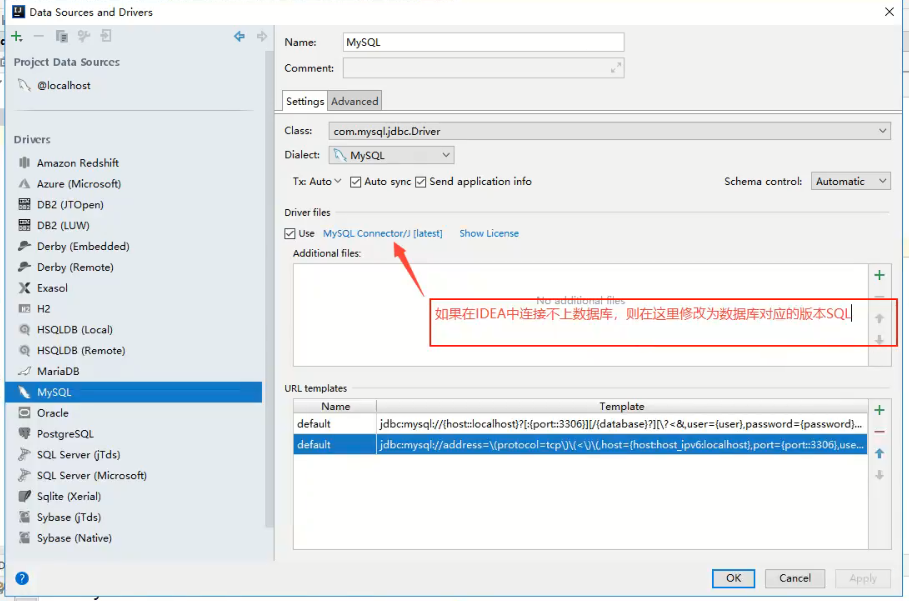
10.7. JDBC transaction
Either all succeed or all fail
ACID principle
Atomicity: either complete or not complete
Consistency: the total number of results remains unchanged
Isolation: multiple processes do not interfere with each other
Persistence: once the commit is irreversible, it is persisted to the database
Isolation problem
Dirty read: a transaction reads another uncommitted transaction
Non repeatable reading: in the same transaction, the data in the table is repeatedly read, and the table has changed
Virtual reading (unreal reading): in a transaction, data inserted by others is read, resulting in inconsistent results before and after reading
code implementation
- Start the transaction conn.setAutoCommit(false);
- After a group of business is executed, submit the transaction
- You can define the rollback statement displayed in the catch statement, but the default failure will also be rolled back
import com.kuang.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Action {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn =null;
PreparedStatement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//Turning off the auto commit function of the database will automatically start the transaction
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql1 = "update account set money = money-100 where name = 'A'";
st =conn.prepareStatement(sql);
st.executeUpdate();
String sql2 = "update account set money = money+100 where name = 'B'";
st=conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
st.executeUpdate();
//After the business is completed, submit the transaction
conn.commit();
System.out.println("Operation succeeded");
} catch (Exception e) {
//If it does not write, it will roll back if it fails
try {
conn.rollback();//Roll back the transaction if it fails
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
10.8. Database connection pool
Database connection - execution complete - release
Connect – release (very wasteful of resources)
Pooling Technology: prepare some pre prepared resources and connect the pre prepared resources
Number of common connections: 10
-
Minimum number of connections: 10
-
Maximum number of connections: 15 service maximum bearing limit
-
Queue waiting, waiting timeout: 100ms
Write a connection pool to implement an interface DateSource
Implementation of open source data source (ready to use)
DBCP
C3P0
Druid: Alibaba
After using these database connection pools, we don't need to write code to connect to the database in the project development
DBCP
The required jar package commons-dbcp-1.4 Jar and commons-pool-1.6 jar
DBCP has its own configuration file. The data names are fixed and cannot be modified arbitrarily
To create a DBCP tool class, you only need to modify it in two steps
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
try{
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcpconfig.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
//1. Create data source factory pattern - > create object
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
//2. Get connection from data source
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
//Release resources
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
if(rs!=null){
try{
rs.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try{
st.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try{
conn.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
To use, you only need to activate conn = JdbcUtils_DBCP.getConnection();
C3P0
Required jar package: c3p0-0.9.5.5 Jar and mchange-commons-java-0.2.19 jar
C3P0 has its own configuration file and can add different data sources
Create C3P0 tool class
Just change one position
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = null;
static {
try{
//1. There are two configuration methods
//Code version configuration (not recommended)
//dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//dataSource.setDriverClass();
//dataSource.setUser();
//...
//Configuration file writing
dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("MySQL");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
// This is a fixed port and does not need to be modified
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
//Release resources
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
if(rs!=null){
try{
rs.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try{
st.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try{
conn.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
conclusion
No matter what data source is used, its essence remains unchanged. The DateSource interface will not change and the method will not change
Apache Software Foundation
It has its own configuration file. The data names are fixed and cannot be modified arbitrarily
To create a DBCP tool class, you only need to modify it in two steps
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
try{
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcpconfig.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
//1. Create data source factory pattern - > create object
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
//2. Get connection from data source
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
//Release resources
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
if(rs!=null){
try{
rs.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try{
st.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try{
conn.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
To use, you only need to activate conn = JdbcUtils_DBCP.getConnection();
C3P0
Required jar package: c3p0-0.9.5.5 Jar and mchange-commons-java-0.2.19 jar
C3P0 has its own configuration file and can add different data sources
Create C3P0 tool class
Just change one position
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = null;
static {
try{
//1. There are two configuration methods
//Code version configuration (not recommended)
//dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//dataSource.setDriverClass();
//dataSource.setUser();
//...
//Configuration file writing
dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("MySQL");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
// This is a fixed port and does not need to be modified
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
//Release resources
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
if(rs!=null){
try{
rs.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (st!=null){
try{
st.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try{
conn.close();
}catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
conclusion
No matter what data source is used, its essence remains unchanged. The DateSource interface will not change and the method will not change
Extension: Apache Software Foundation