1, Date and time functions
1. Function to get the current date
It's the same. It's different
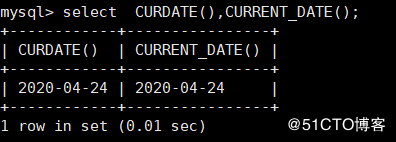
CURDATE() : Used to get the current date of the system CURRENT_DATE() Used by the system to get the current date mysql> select CURDATE(),CURRENT_DATE();
2. Get function of current time
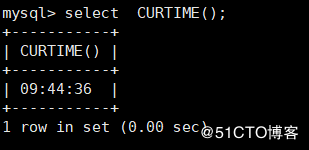
CURTIME() : Used to get the current time of the system mysql> select CURTIME();
3. Function to get the current date and time
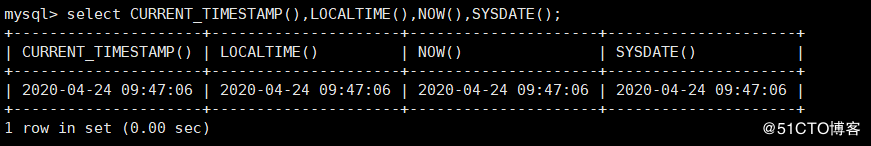
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() : Used to get the current date and time of the system LOCALTIME() : Used to get the current date and time of the system NOW() : Used to get the current date and time of the system SYSDATE(): Used to get the current date and time of the system mysql> select CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(),LOCALTIME(),NOW(),SYSDATE();
4. Function to get time stamp
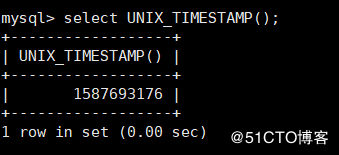
UNIX_TIMESTAMP() For obtaining UNIX Time stamp in format mysql> select UNIX_TIMESTAMP();
A time stamp is a complete and verifiable data that can represent the existence of a data at a specific point in time.
5. Function to convert timestamps
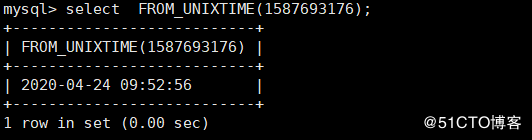
FROM_UNIXTIME() Used to UNIX Time stamp in format converted to time in normal format mysql> select FROM_UNIXTIME(1587693176); # Add time stamp found before
6. Function to get UTC date
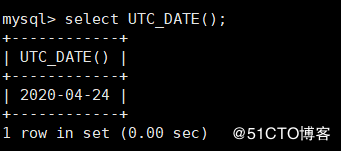
UTC_DATE() : Used to get the current UTC (World standard time) Date value mysql> select UTC_DATE();
7. Get UTC time function
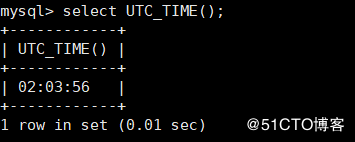
UTC_TIME() Used to get the current UTC (World standard time) Time value mysql> select UTC_TIME();
8. Get function of month
MONTH(date) : For return date Corresponding month
MONTHNAME(date): For return date English full name of corresponding month
mysql> select MONTH('2020-4-24'),MONTHNAME('2020-4-24');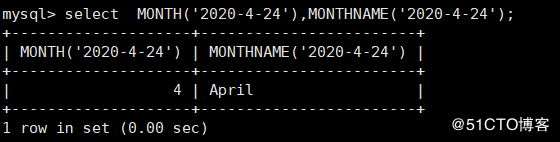
9. Get week function
DAYNAME(date) : For return date English name of the corresponding working day
DAYOFWEEK(date) : For return date The index of the corresponding week, 1 for Sunday, 2 for Monday,...... ,7 For Saturday
WEEKDAY(date): Used to return the working day index corresponding to the date, 0 for Monday, 1 for Tuesday,...... ,6 For Sunday
WEEK(date): For calculation date Is the week of the year, 53 weeks of the year
WEEKOFYEAR(date) : Used to calculate date date Is the week of the year, 53 weeks of the year
mysql> select DAYNAME('2020-4-24'),DAYOFWEEK('2020-4-24'),WEEKDAY('2020-4-24'),WEEK('2020-4-24'),WEEKOFYEAR('2020-4-24');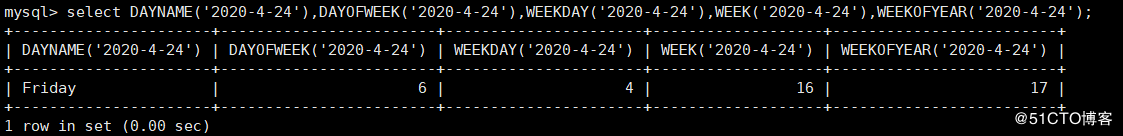
10. Function to get days
DAYOFYEAR(date) :For return date Is the day of the year, 365 days of the year
DAYOFMONTH(date): For calculation date The day of the month
mysql> select DAYOFYEAR('2020-4-24'),DAYOFMONTH('2020-4-24');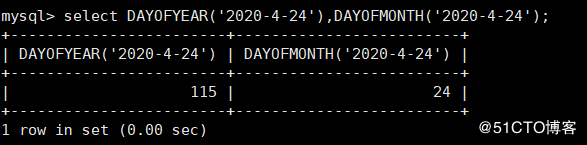
11. Function to get the year
YEAR(date) : return date Corresponding year
mysql> select YEAR('20-04-24'),YEAR('98-04-24');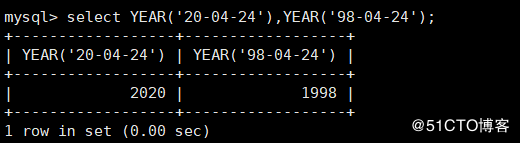
12. Get function of quarter
QUARTER(date) : return date Corresponding quarter value in a year
mysql> select QUARTER('20-04-24');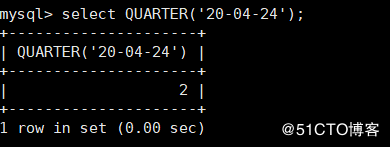
13. Get function for minutes
MINUTE(time) return time Corresponding minute value
mysql> select MINUTE('20-04-24 10:18:00');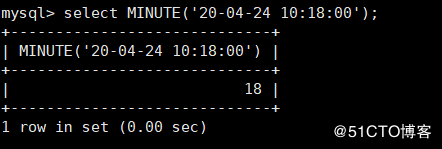
14. Get function for seconds
SECOND(time) return time Corresponding seconds
mysql> select SECOND('10:18:22');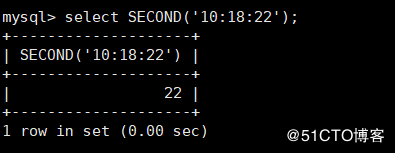
15. Function to get the specified value of a date
EXTRACT(type FROM date) Used to get the specified date value
mysql> select EXTRACT(YEAR FROM '2020-04-24') AS col1, # When type is YEAR, only the annual value is returned
-> EXTRACT(YEAR_MONTH FROM '2020-04-24 10:18:22') AS col2, # Returns year and month when type is year ﹣ month
-> EXTRACT(DAY_MINUTE FROM '2020-04-24 10:18:22') AS col3; # Returns day, hour, and minute when the type is day [minute] 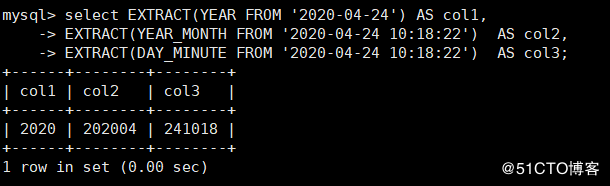
16. Functions of time and second conversion
TIME_TO_SEC(time) : Used to time Convert to seconds, formula is " Hour 3600 + Minutes 60 + second "
SEC_TO_TIME(time): Used to convert second values to time format
mysql> select TIME_TO_SEC('23:23:00'),SEC_TO_TIME('84180'); 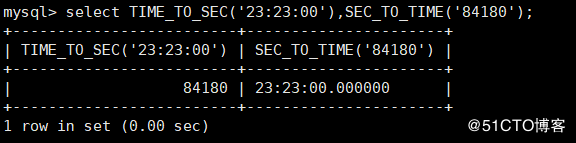
17. Function to calculate date and time
DATE_ADD(): used to add a date. The format is DATE_ADD(date, INTERVAL expr type) Date UU sub(): used to subtract the date. The format is date UU sub (date, interval expr type) Submit(): used to subtract the date. The format is submit (date, interval expr type) ADDTIME(): used to add a date. The format is ADDTIME(date, expr) Subtitle(): used to subtract the date. The format is subtitle (date, expr) Date? Diff(): used to calculate the number of days between two dates
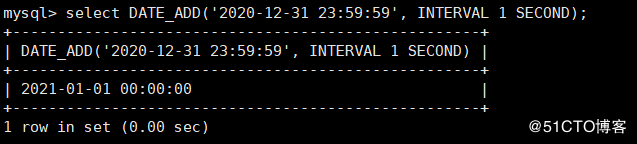
MySQL > select date ﹐ add ('2020-12-31 23:59:59 ', interval 1 second); ﹐ add 1 second to the specified date
mysql> select DATE_ADD('2020-12-31 23:59:59', INTERVAL '1:1' MINUTE_SECOND); 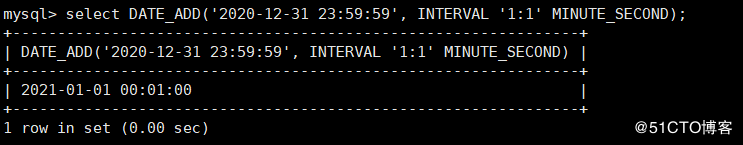
MySQL > select date ﹐ sub ('2020-01-01 ', interval 31 day); ﹐ subtract 31 days from the specified date 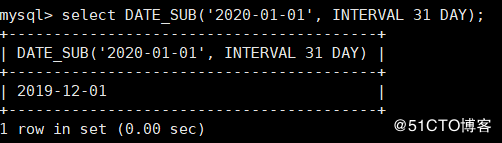
mysql> select SUBDATE('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 31 DAY); 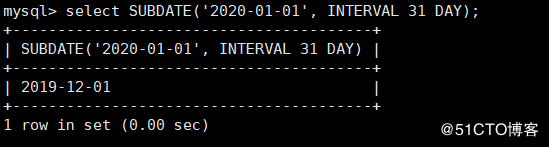
MySQL > select addtime ('2020-12-31 23:59:59 ','1:1:1'); ා add 1 hour, 1 minute and 1 second to the specified date 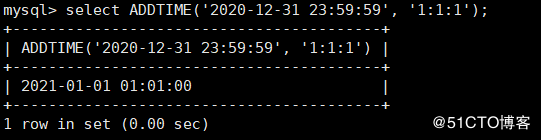
MySQL > select subtitle ('2020-12-31 23:59:59 ',' 1:1:1 '); ා subtract 1:1 minute and 1 second from the specified date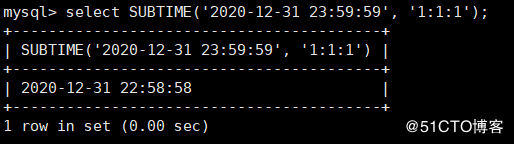
mysql> select DATEDIFF('2020-06-01', '2020-04-24');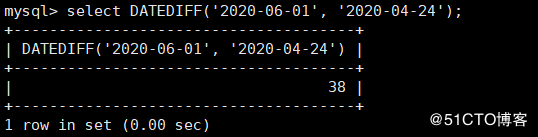
18. Functions that format date and time
DATE_FORMAT(date, format) Used to format the date according to format Display in specified format date value
TIME_FORMAT(time, format) Used to format the time according to format Display in specified format time value
GET_FORMAT() ,We specify the value type and format type, and then the format string will be displayed
mysql> select DATE_FORMAT('1997-10-04 22:23:00', '%W %M %Y'); 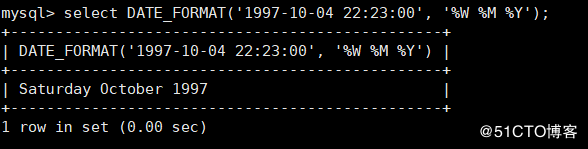
mysql> select TIME_FORMAT('16:00:00', '%H %k %I'); 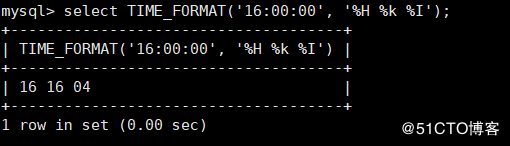
mysql> select DATE_FORMAT('2000-10-05 22:23:00', GET_FORMAT(DATE,'USA')); 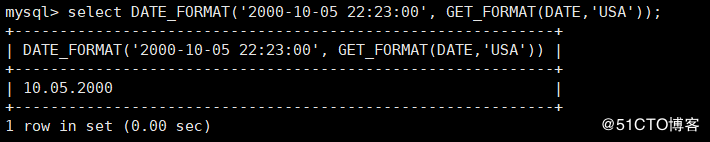
%d date of the month in numerical form (00.. 31) %e date of the month in numerical form (0.. 31) %f microseconds (000000... 999999) %H in 2 digits for 24 hours (00.. 23) %h. % I in 2 digits for 12 hours (01.. 12) %i minute, digital form (00-59) %j number of days in a year (001366) %k for 24 hours (0-23) %l in 12 hours (0.. 12) %M month name (january..December) %m month numerical form (00.. 12) %p AM or PM %r time, 12 hour system (hour hh: minute mm: second ss followed by AM or PM) %S. % s in 2-digit seconds (00.. 59) %T time, 24-hour system (hours hh: minutes mm: seconds ss) %U week (00.. 53), where Sunday is the first day of the week %u week (00.. 53), where Monday is the first day of the week %V week (01.. 53), where Sunday is the first day of the week, used with% X %Week v (01.. 53), where Monday is the first day of the week, used with% x %W working day name (Sunday.. Saturday) %w day of the week (0 = Sunday.. 6 = Saturday) %X the year of the week, where Sunday is the first day of the week; the number is in 4 digits and is used with% V %x the year of the week, where Monday is the first day of the week; the number is in 4 digits and is used with% v %Year in Y4 digits %y2 digit represents year %%'%' text character
2, Conditional judgment function
IF() IF(expr, v1, v2) If the expression expr by TRUE ,The return value is v1 ,Otherwise return v2 mysql> select IF(1>2,2,3);
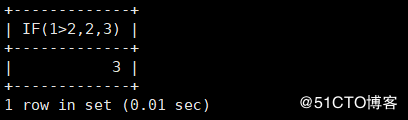
It can be seen that one is no more than two, so v2 is returned, that is, 3
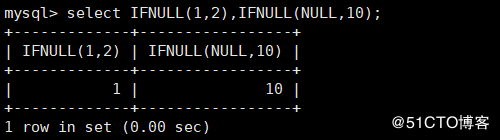
IFNULL() IFNULL(v1, v2) ,If v1 Not for NULL ,The return value is v1 ;If v1 by NULL ,The return value is v2 mysql> select IFNULL(1,2),IFNULL(NULL,10);
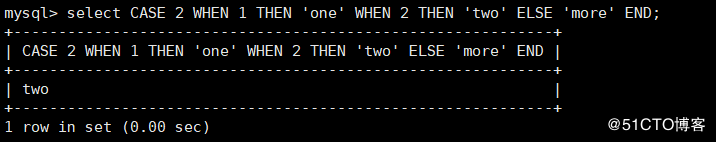
CASE Syntax: CASE expr WHEN v1 THEN r1 [WHEN v2 THEN r2] [ELSE rn] END Meaning: if expr Equal to vn ,Then return to the corresponding position THEN The following result, if not equal to all values, returns ELSE hinder rn mysql> select CASE 2 WHEN 1 THEN 'one' WHEN 2 THEN 'two' ELSE 'more' END;
3, System information function
1. Function to get MySQL version number
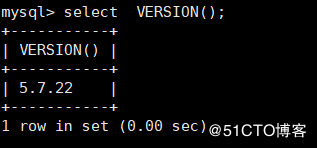
VERSION() For obtaining MySQL Version No mysql> select VERSION();
2. ID function to view the number of connections for the current user
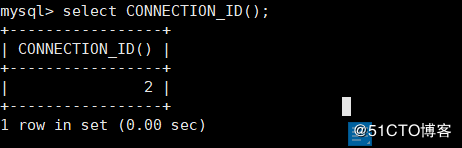
CONNECTION_ID() Used to view the number of connections for the current user mysql> select CONNECTION_ID();
MySQL & gt; show processlist; view the connection information of the current user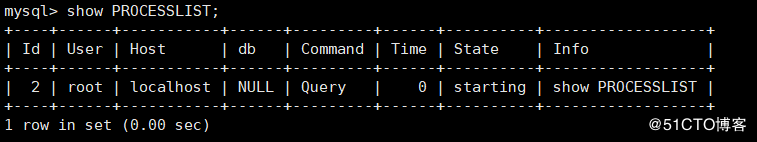
**The meaning of the above label is as follows:** id: the system assigned connection id when the user logs in to MySQL User: currently connected user Host: shows which IP and which port this statement is issued from. It can be used to track the users of the statement in question db: show which database this process is currently connected to Command: displays the commands executed by the current connection. The values are sleep, query and connect Time: displays the duration of this status, in seconds State: displays the state of the SQL statement using the current connection Info: show this SQL statement
3, Functions to view the currently used database
DATABASE() : Used to view the currently used database SCHEMA(): Used to view the currently used database mysql> select database(),SCHEMA();
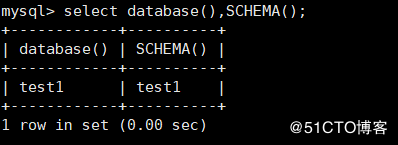
4. Function to view the currently logged in user name
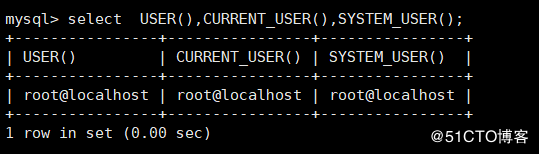
USER() :Return the currently logged in user and host name CURRENT_USER(): Used to return the currently logged in user and host name SYSTEM_USER() :Used to return the currently logged in user and host name mysql> select USER(),CURRENT_USER(),SYSTEM_USER();
5. Function to view the character set of a specified string
CHARSET(str) For viewing strings str Character set for
mysql> select CHARSET('abc'); 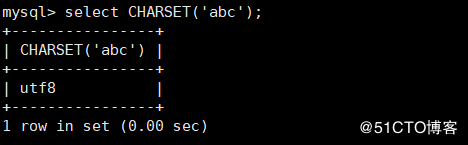
6. Function to view the arrangement of a specified string
COLLATION(str): For viewing strings str Character arrangement of
mysql> select COLLATION('abc'); 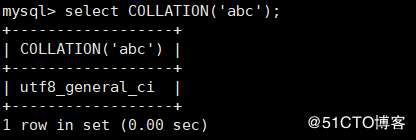
7. Get the last auto generated ID value function
LAST_INSERT_ID() : Used to get the next automatically generated ID value
#First, create a table with an auto increment constraint for its id field
mysql> create table tab1(
-> id int auto_increment primary key,
-> name varchar(30)
-> );
mysql> insert into tab1 values (NULL,'zhangsan'); #Insert a piece of data. If the id is not specified, it will be generated automatically. The id is 1
mysql> insert into tab1 values (NULL,'lisi'); # Insert a piece of data. If the id is not specified, it will be generated automatically. The id is 2
mysql> select * from tab1; # View table information
+----+----------+
| id | name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | zhangsan |
| 2 | lisi |
+----+----------+
mysql> select LAST_INSERT_ID();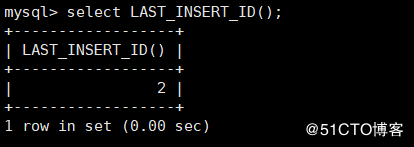
mysql> insert into tab1 values (NULL,'aaa'),(NULL,'bbb'),(NULL,'ccc'); mysql> select * from tab1; # If we insert multiple pieces of data at once, though the id is 5 +----+----------+ | id | name | +----+----------+ | 1 | zhangsan | | 2 | lisi | | 3 | aaa | | 4 | bbb | | 5 | ccc | +----+----------+ mysql> select LAST_INSERT_ID(); # However, when we view it with last ﹣ insert ﹣ id(), it is 3. This is because last ﹣ insert ﹣ id() only returns the first row of inserted data +------------------+ | LAST_INSERT_ID() | +------------------+ | 3 | +------------------+
4, Encryption / decryption function
1. Encryption function
PASSWORD(str) : From plaintext password str Calculates and returns the encrypted password string, when the parameter is NULL , return to NULL
MD5(str) Is a string str Work out a MD5 128 Bit checksums
ENCODE(str, pswd_str) use pswd_str As a password, encrypt str
mysql> select PASSWORD('newpwd');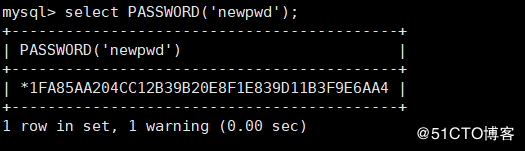
mysql> select MD5('newpwd');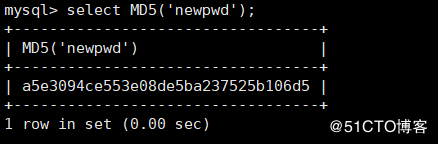
mysql> select ENCODE('secret','123.com');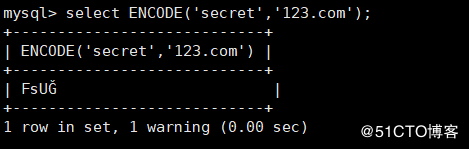
2. Decryption function
DECODE(crypt_str, pswd_str) use pswd_str Decrypt encrypted string as password crypt_str
mysql> select DECODE(ENCODE('secret','cry'),'cry');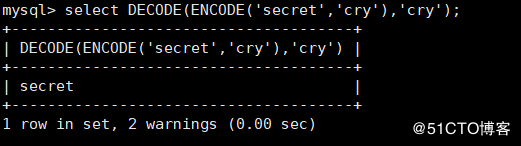
3, Other functions
1. Format function
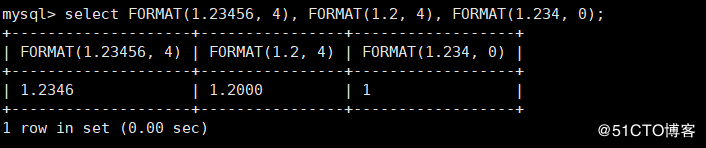
FORMAT(x, n) : Put numbers x Format and round to the decimal point n Bit, the result is returned as a string mysql> select FORMAT(1.23456, 4), FORMAT(1.2, 4), FORMAT(1.234, 0);
2. Functions for converting numbers in different bases
CONV() : Used for conversion between different base numbers
mysql> select CONV('a',16,2), # Convert hexadecimal a to binary
-> CONV(15,10,2), # Convert decimal 15 to binary
-> CONV(15,10,8), # Convert decimal 15 to octal
-> CONV(15,10,16); # Convert 15 of 10 to 16 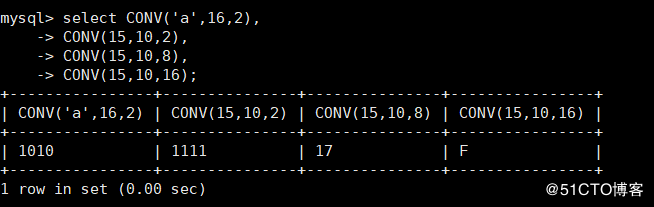
3. Functions of IP address and number conversion
INET_ATON(expr) : Used to convert a network address to an integer representing the address value
mysql> select INET_ATON('192.168.1.1');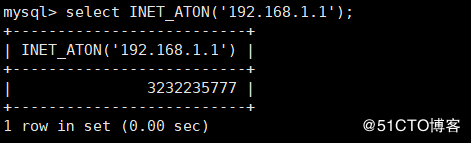
4. Lock function and unlock function
GET_LOCK(str, timeout) : Use string str Get a lock, duration timeout second
* If the lock is obtained successfully, 1 will be returned
* 0 if the operation times out
* If an error occurs, return NULL
mysql> select GET_LOCK('lock1',10); # The returned result is 1, indicating that a lock named 'lock1' has been successfully obtained, with a duration of 10 seconds 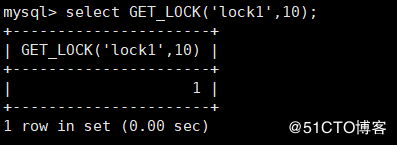
RELEASE_LOCAK(str) : Used to untie the quilt GET_LOCK() Obtained with string str Named lock
* If the lock is unlocked, return to 1
* Returns 0 if the thread has not created a lock
* Returns if the named lock does not exist NULL
* If the lock has never been GET_LOCK() The lock does not exist if the lock has been unlocked in advance
mysql> select RELEASE_LOCK('lock1'); # If the return value is 1, the unlocking is successful 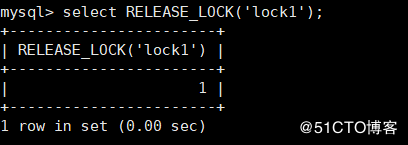
IS_FREE_LOCK(str): The name of the check is str Whether the lock of can be used
* If the lock can be used, return 1
* 0 if lock is in use
* If an error occurs, return NULL
mysql> select IS_FREE_LOCK('lock1');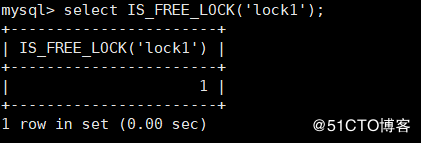
IS_USED_LOCK(str) : Used to check the name str Whether the lock of is being used. If it is blocked, the connection identifier of the client using the lock will be returned. Otherwise, the connection identifier of the client using the lock will be returned NULL
mysql> select IS_USED_LOCK('lock1');
5. Functions that repeat the specified operation
BENCHMARK(count, expr): For repetition count Secondary expression expr
* Can be used for calculation MySQL Speed at which expressions are processed
* You can MySQL Client internal report statement execution time
mysql> select PASSWORD('newpwd'); # # It took 0.00 seconds to perform 1 encryption operation 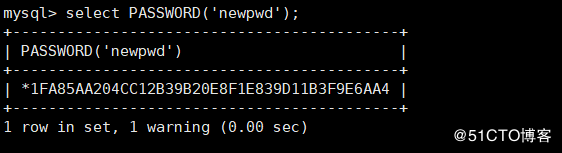
mysql> select BENCHMARK( 500000, PASSWORD('newpwd') );
+-----------------------------------------+
| BENCHMARK( 500000, PASSWORD('newpwd') ) |
+-----------------------------------------+
| 0 |
+-----------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.06 sec) # It took 0.06 seconds to perform 500000 encryption operations 6. Function to change character set
CONVERT(... USING ...) Default character set for changing strings
mysql> select CHARSET('abc'); # The default is utf8
+----------------+
| CHARSET('abc') |
+----------------+
| utf8 |
+----------------+
mysql> select CHARSET(CONVERT('abc' USING latin1)); # Convert to latin1 character set
+--------------------------------------+
| CHARSET(CONVERT('abc' USING latin1)) |
+--------------------------------------+
| latin1 |
+--------------------------------------+7. Function to change data type
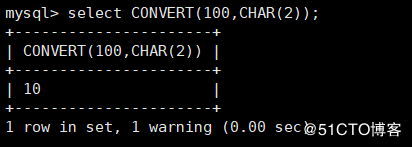
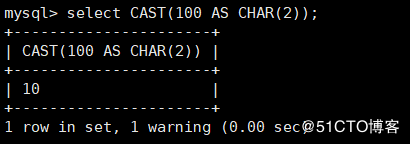
CAST(x, AS type) : Used to convert a value of one data type to another CONVERT(x, type) : Used to convert a value of one data type to another mysql> select CAST(100 AS CHAR(2)); # Convert integer type 100 to a string type with two display widths, resulting in '10'
MySQL & gt; select convert (100, char (2)); ා convert 100 of integer type to string type with two display widths, and the result is' 10 '