1, Basic query
Syntax: select Query list from Table name; characteristic: 1,The query list can be fields, constant values, expressions and functions in the table 2,The result of the query is a virtual table
database structure
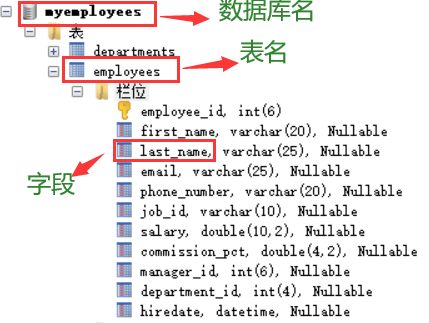
Employee table
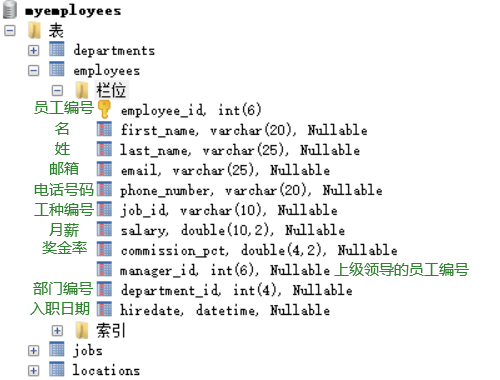
Department table
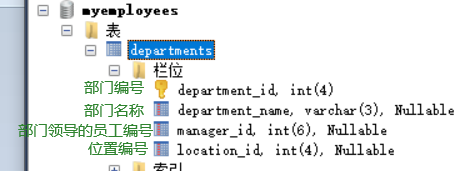
Location table

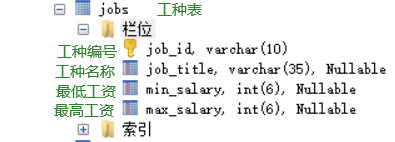
List of types of work
USE myemployees;#Choose to use a specific database
1.Single field in query table
select last_name from employees;
2.Multiple fields in the query table
select last_name,salary,email from employees;
3.Query all fields in the table
select * from employees;#The order is the same as the original table
4.Query constant value
select 100;
select 'join';
5.Query expression
select 100%99;
6.Query function
select version();
7.Alias
/*
1.Easy to understand
2.If the fields to be queried have duplicate names, they can be distinguished by using aliases
*/
Method 1: use AS
select 100%98 AS result;
select last_name AS surname first_name AS name from employees;
Method 2: use spaces
select last_name surname first_name name from employees;
If there are special symbols in the alias, it is recommended to put double quotation marks on the alias, otherwise ambiguity will occur
8.duplicate removal
Case: query all department numbers involved in the employee table
select distinct department_id From employees;
9.+Function of No
java Medium+number;
1.Operator, both operands are numeric
2.Connector, as long as one operand is a string
mysql in+number:
There is only one function: operator
select 100+99;If both operands are numeric, add
select '123'+90;One of them is character type, trying to convert character type numerical value to numerical value,
select '123'+90; If the conversion is successful, continue the addition operation;
select'join'+22; If the conversion fails, the character value is converted to 0
select null+10; As long as one of them is null,The result must be null
#Case: query the employee's first name and last name, connect them into a field, and display them as names
select concat('a','b','c') AS result;
select concat(last_name,first_name) AS full name from employees;
2, Condition query
Syntax:
select Query list from Table name where Screening conditions;
Classification:
2.1. Filter by conditional expression
Conditional operator:> < = != <> >= <= #Case 1: query employee information with salary > 12000 select * form employees salary>12000 #Case 2: query the employee name and department number whose department number is not equal to 90 select last_name,department_id from employees where department_id<>90;
2.2. Filter by logical expression
Logical operators:&& || ! and or not Action: used to connect conditional expressions &&or and: Both conditions are true,The result is true,On the contrary false ||or or: As long as one condition is true,The result is true,On the contrary false !or not: If the connection condition itself is false,The result is true,On the contrary false #Case 1: query employee name, salary and bonus with salary between 10000 and 20000 select last_name,salary,commission_pct from employees where salary >= 10000 and salary <= 20000
2.3. Fuzzy query
like ; between and ; in ; is null
1.like
Features: 1.Generally used with wildcards
Wildcard: %Represents any number of characters, including 0 characters
_Represents a single character
#Employee information contained in the query case: a
select * from employee where last_name like '%a%';#%Represents any character
#Case 2: query the employee name and salary with the third character of c and the fifth character of h in the employee name
select last_name,salary from employees where last_name like '__c_h%';
#Case 3: the second character in the employee name is_ Employee name
select last_name from employees where last_name like '_\_%';#Escape by \ escape
select last_name from employees where last_name like '_$_%' ESCAPE '$';#Use ESCAPE keyword to specify ESCAPE characters at will
2.between and
Features: improve the brevity of sentences
Including critical value
#Case 1: query employee information with employee number between 100 and 120
select * from employees where employee_id between 100 and 120;
3.in
Meaning: judge whether the value of a field belongs to in An item in the list
Features: 1.use in Improve sentence conciseness
2.in The value types of the list must be consistent or compatible
#Case: the job number of the employee queried is IT_ADVP,AD_char,Hr_Anna
Select last_name,job_id
From employees
where job_id IN('IT_ADVP','AD_char','Hr_Anna');
4.is null
=or<>Cannot be used for judgment null value
is null or is not null Can judge null Value, but ordinary value cannot be judged
#Case: query employee name and bonus rate without bonus
select last_name,commission_pct
from employees
where commission_pct IS NULL;
Safety equals <=>
<=>Can judge null Value, which can also judge ordinary values, with poor readability
select last_name,commission_pct
from employees
where commission_pct <=> NULL;
3, Sort query
Syntax: select Query list
from surface
[where Screening criteria]
order by Sort list[ asc | desc]
characteristic:
1.asc It represents ascending order, desc It represents descending order
If you do not write, the default is ascending
2.order by Clause can support single field, multiple fields, expressions, functions and aliases
3.order Unused clauses are usually placed at the end of the query statement, limit Except clause
Case:
#Case 1: query employee information and require the salary to be sorted from high to low select * From employees order by salary DESC; #Case 2: query employee information with department No. > = 90 and sort by employment time select * from employees where department_id >=90 order by hiredate ASC; #Case 3: display employee information and annual salary by annual salary (sorted by expression) select *,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) Annual salary from employees order by salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) DESC; #Case 4 Display employee information and annual salary by annual salary (sorted by alias) select *,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) Annual salary from employees order by Annual salary DESC; #Case 5: display employee's name and salary by name length (sorted by function) select length(last_name) Byte length,last_name,salary from employees order by length(last_name) DESC; Case 6: querying employee information requires sorting by salary first, and then by employee number (sorting by multiple fields) select * from employees order by salary ASC, employee_id DESC;
4, Common functions
Call: select Function name (argument list)[ from [table];
characteristic:
1.What is it called (function name)
2.What to do (function function)
Classification:
1.Single-Row Functions
For example: concat,length,ifnull etc.
2.Grouping function
Function: used for statistics, also known as statistical function, aggregation function and group function
4.1. Character function
1.length Gets the number of bytes of the parameter value
select length('host');
2.concat Splice string
select concat(last_name,'_',first_name) from employees;#Pass_ Connect last_name and first_name
3.upper,lower
select upper('host');
#Case: change the last name to uppercase, the first name to lowercase, and then splice
select concat(upper(last_name),lower(first_name)) full name from employees;
4.substr/substring Intercept string
Note: the index starts with 1
Intercepts the character with the specified length from the specified index
select substr('Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows',1,4) out_put;# out_put: Harry Potter
5.instr Returns the index of the first occurrence of the substring in the string; If not found, return 0
select instr('Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows','Deathly Hallows');# 6
6.trim Remove the front and back spaces
select trim(' harry ');
select trim('a' from 'aaaaaaHarryaaaaaaaaaaaaa');#Remove the front and back a and output Harry
7.lpad Fill the specified length with the specified character
select LPAD('harry',10,'*') # *****harry
8.rpad Fill the specified length with the specified character
9.replace replace
select replace('aabbccddeeaacc','a','f');#Replace all a's in the string with f's
4.2 mathematical function
1.round rounding select round(1.65); # 2 select round(1,567,2);# Keep two digits 1.57 after the decimal point 2.ceil Round up,return>=The minimum integer of the parameter; select ceil(-1.02); # -1 3.floor Round down and return<=The maximum integer for this parameter 4.truncate truncation select truncate(1.65,1);#1.6 one digit shall be reserved after the decimal point 5.mod Surplus select mod(-10,-3);# -1 6.rand:Get random number and return 0-1 Decimal between
4.3. Date function
1.now Returns the current system date+time
select now();
2.curdate Returns the current system, excluding the date
select curdate();
3.curtime Returns the current time, excluding the date
select curtime();
4.Can get the specified part, year( year),month(month),day(day),hour(hour),minute(minute),second(second)
select year(now()) year;
select month(now()) month;
5.str_to_date:Converts characters into dates in the specified format
select STR_TO_DATE('9-24-1999','%m-%d-%Y');#1999-9-24
6.date_format:Convert date to character
select data_format(now(),'%y year%m month%d day');
#Case: query the name and employment date of the employee with bonus (xx month / xx day, xx year)
select last_name,data_format(hiredate,'%m month/%d day %y year') Entry date
from employees
where commission_pct is not null;
7.datediff(Date 1,Date 2)#The number of days between dates 1 and 2
Case: query the difference days between the maximum enrollment time and the minimum enrollment time in the employee table( difference)
select DATEDIFF(max(hiredate),min(hiredate)) difference
from employees;
8.monthname:Return month in English
year:Return year
month: Return month
day:Return day
hour:hour
minute:minute
second: second
4.4. Other functions
select version();#View version number
select database();#View current database
select user();#View current user
password('character'): Returns the password form of this character
md5('character'):Returns the of the character md5 Encryption form
4.5. Process control function
1.if Function: if else Effect of
select if(10>5,'large','Small');
select last_name,commission_pct,if(commission_pct is null,'No bonus','Bonus');
2.case Function I: switch case Effect of
java Medium:
switch(Variable or expression){
case Constant 1: statement 1; break;
...
default:sentence n; break;
}
mysql Medium:
case Field or expression to judge
when Constant 1 then Value 1 or statement 1 to display
when Constant 2 then Value 2 or statement 2 to display
...
else Value to display n Or statement n
end
/*Case: query employee salary and requirements
Department number = 30, the displayed salary is 1.1 times
Department number = 40, the displayed salary is 1.2 times
Department number = 50, the displayed salary is 1.3 times
For other departments, the displayed salary is the original salary
*/
select salary Original salary,department_id,
case department_id
when 30 then salary*1.1
when 40 then salary*1.2
when 50 then salary*1.3
else salary
end AS New salary
from employees;
case Use of function 2: similar to multiple if
java Medium:
if(Condition 1){
Statement 1;
}else if(Condition 2){
Statement 2;
}else if(Condition 3){
Statement 3;
}
...
else{
sentence n;
}
mysql Medium:
case
when Condition 1 then Value 1 or statement 1 to display
when Condition 2 then Value 2 or statement 2 to display
...
else Value to display n Or statement n
end
/*
Case: query employee's salary
If salary > 20000, level A is displayed
If salary > 15000, level B is displayed
If salary > 10000, level C is displayed
Otherwise, level D is displayed
*/
select salary,
case
when salary > 20000 then 'A'
when salary > 15000 then 'B'
when salary > 10000 then 'C'
else 'D'
end AS Wage scale
from employees;
5, Grouping function
Function:
Used for statistics, also known as aggregate function or statistical function or group function
Classification:
sum, avg average, Max max, min Min, count
characteristic:
1.sum,avg Suitable for dealing with numerical type
max,min,count Can handle any type
2.Ignore the above grouping functions null value
3.Can and distinct Collocation to realize the operation of de duplication
select sum(distinct field) from surface;
4.count Function introduction
count(field): Count the number of non null values of this field
count(*):Count the number of rows in the result set
Case: query the number of employees in each department
1 xx 10
2 dd 20
3 mm 20
4 aa 40
5 hh 40
count(1):Count the number of rows in the result set
Efficiency:
MyISAM Storage engine, count(*)highest
InnoDB Storage engine, count(*)and count(1)efficiency>count(field)
5.The fields to be queried together with the grouping function are group by Field after
1.Simple use select sum(salary) from employees; select sum(salary) and, AVG(salary) average,MAX(salary),MIN(salary); 2.and distinct collocation select sum(distinct salary),sum(salary) From employees; select count(distinct salary) from employees; 3.count Detailed introduction of function select count(salary) from employees; select count(*) from employees;#How many lines are counted select count(1) from employees; #How many lines are counted Efficiency: MYISAM Under the storage engine, count(*)High efficiency INNODB Under the storage engine, count(*) and count(1)The efficiency is about the same, better than count(field)Higher 4.There are restrictions on the fields queried with the grouping function select avg(salary),employee_id from employees;
6, Grouping query
Syntax:
select Grouping function, column (required to appear in group by (behind)
from surface
[where Screening criteria]
group by List of groups
[having [filter after grouping]
[order by Clause]
Note: the query list must be special, which requires grouping function and group by Fields that appear after
characteristic:
1.There are two types of filter criteria in grouping query
data source position keyword
Filter before grouping Original table group by Before clause where
Filter after grouping Grouped result set group by After Clause having
- The condition of grouping function must be placed in having Clause (grouping function has no field in the original table)
- If you can filter before grouping, grouping is preferred
2.group by Clause supports single field grouping, multiple field grouping (multiple fields are separated by commas without order requirements), expression or function (used less)
3.You can also add sorting (sorting is placed at the end of the whole grouping query)
6.1. Simple grouping query
#Case 1: query the maximum wage of each type of work select max(salary),job_id from employees group by job_id; #Case 2: query the number of departments in each location select count(*),location_id from departments group by location_id;
6.2. Filter criteria before adding grouping
#Case 1: query the average salary of each department with a character in the mailbox select avg(salary),department_id from employees where email like '%a%' group by department_id; #Case 2: query the maximum salary of employees under each leader with bonus SELECT MAX(salary) ,manager_id FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL GROUP BY manager_id;
6.3. Add (after grouping) complex filter criteria
#Case 1: query the number of employees in that department > 2
1.Query the number of employees in each department
SELECT COUNT(*) ,department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id;
2.Filter according to the results of 1 and query the number of employees in that department>2
SELECT COUNT(*) ,department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING COUNT(*)>2;
#Case 2: query the maximum wage of employees with bonus in each type of work, and the number and maximum wage of the type of work > 12000
SELECT job_id,MAX(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL#commission_ The PCT field is from the original employees table. Use where
GROUP BY job_id
HAVING MAX(salary) >12000;#MAX(salary) the original table does not have, use having
#Case 3 Query the minimum wage of each leader with leader number > 102, the leader number with leader number > 5000 and its minimum wage
SELECT manager_id,MIN(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE manager_id >102
GROUP BY manager_id
HAVING MIN(salary)>5000;
6.4. Group by expression or function
#Case: Group employees according to the length of their names, query the number of employees in each group, and filter those with more than 5 employees SELECT COUNT(*),LENGTH(CONCAT(last_name,first_name)) FROM employees GROUP BY LENGTH(CONCAT(last_name,first_name)) HAVING COUNT(*)>5;
6.5. Group by multiple fields
#Case: query the average salary of employees in each department and type of work SELECT AVG(salary),department_id,job_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id,job_id;
6.6. Add sort
#Case: query the average salary of employees in each department and type of work. The average salary is required to be > 10000, the department number is not blank, and is displayed according to the average salary SELECT AVG(salary),department_id,job_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL GROUP BY department_id,job_id HAVING AVG(salary)>10000 ORDER BY AVG(salary) DESC;
7, Connection query
meaning:
It is also called multi table query. When the query fields come from multiple tables, the Cartesian product phenomenon of link query will be used: Table 1 has m rows, table 2 has n rows, and the result is m*n rows
Cause: there is no valid connection condition. How to avoid: add a valid connection condition
Classification:
Classification by age:
sql92 Standard: only internal connection is supported
sql99 Standard [recommended]: support internal connection+Outer connection (left outer and right outer)+Cross connect
Classification by function:
Internal connection:
Equivalent connection
Non equivalent connection
Child link
External connection:
Left outer connection
Right outer connection
Total external connection
Cross connect
7.1.sql92 standard
7.1.1. Equivalent connection
Syntax:
select Query list from Table 1 aliases,Table 2 aliases where Table 1.key=Table 2.key [and Screening criteria] [group by Grouping field] [having [filter after grouping] [order by Sort field]
characteristic:
① General alias table
② The order of multiple tables can be changed
③ N table connection requires at least n-1 connection conditions
④ The result of equivalent connection is the intersection of multiple tables
1.The result of multi table equivalent connection is the intersection of winning the bid
2.n Table connection, at least n-1 Multiple connection conditions
3.The order of multiple tables is not required
4.It is generally necessary to name the table
5.It can be used with all the clauses mentioned above, such as sorting, filtering and grouping
Case 1: query employee name and corresponding department name SELECT last_name,department_name FROM employees,departments WHERE employees.department_id = departments.department_id
1. Alias the table
Improve the concise reading of sentences Distinguish multiple fields with duplicate names Note: if the table is aliased, the query field cannot be qualified with the original table name Case: query employee name, company number and type of work name SELECT e.last_name,e.job_id,j.job_title#Second cloth FROM employees e, jobs j #First step WHERE e.job_id = j.job_id;#Step 3
2. The order of the two tables can be reversed
3. Screening can be added
#Case 1: query the employee name and department name with bonus SELECT last_name,department_name,commission_pct FROM employees e,departments d WHERE e.department_id = d.department_id AND e.commission_pct IS NOT NULL; #Case 2: query the Department name with the second character o in the city name and the corresponding city name SELECT department_name,city FROM departments d,locations l WHERE d.`location_id` = l.`location_id` AND city LIKE '_o%';
4. Groups can be added
Case 1: query the number of departments in each city select count(*) number, city from departments d,location l where d.location_id = l.location_id group by city;
5. Sorting can be added
#Case: query the name of each type of work and the number of employees, in descending order by the number of employees SELECT job_title,COUNT(*) FROM employees e, jobs j WHERE e.job_id = j.job_id GROUP BY job_title ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;
6. Three meter connection can be realized
#Case: query employee name, department name and city SELECT last_name,department_name,city FROM departments d,employees e,locations l WHERE d.department_id = e.department_id AND d.location_id = l.location_id;
7.1.2 non equivalent connection

Syntax:
select Query list
from Table 1 aliases, table 2 aliases
where Non equivalent connection conditions
[and Screening criteria]
[group by Grouping field]
[having [filter after grouping]
[order by Sort field]
Case: query employee's salary and salary level
SELECT salary,grade_level
FROM employees e,job_grades j
WHERE salary BETWEEN j.lowest_sal AND j.highest_sal;
7.1.3 self connection
Syntax: select Query list from Table alias 1,Table alias 2 where Equivalent connection conditions [and Screening criteria] [group by Grouping field] [having [filter after grouping] [order by Sort field] Case: query employee name and superior name SELECT e.employee_id,e.last_name,m.employee_id,m.last_name FROM employees e,employees m WHERE e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
7.2 SQL99 syntax
Syntax:
select Query list
from Table 1 alias [connection type]
join Table 2 aliases
on Connection conditions
[where Screening criteria]
[group by [group list]
[having [filter after grouping]
[order by Sort list]
[limit Clause];
Classification:
Internal connection: inner
External connection:
Left outer: left [outer]
Right outer: right[outer]
All external: full [outer]
Cross connect: cross
7.2.1 internal connection
Syntax:
select Query list from Table 1 aliases inner join Table 2 aliases on Connection conditions [where Screening criteria] [group by [group list] [having [filter after grouping] [order by Sort list] [limit Clause];
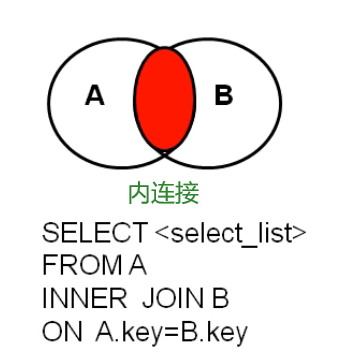
characteristic:
① The order of tables can be changed
② Result of inner join = intersection of multiple tables
③ N table connection requires at least n-1 connection conditions
Classification:
1. Equivalent connection
#Case: query employee name and department name SELECT last_name,department_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id; #Case: query the city name and department number with department number > 3 SELECT city,COUNT(*) FROM departments d INNER JOIN locations l ON d.`location_id` = l.`location_id` GROUP BY city HAVING COUNT(*) > 3; #Case: query employee name, department name and type of work number in descending order by department name SELECT city,COUNT(*) FROM departments d INNER JOIN locations l ON d.`location_id` = l.`location_id` GROUP BY city HAVING COUNT(*) > 3;
2. Non equivalent connection
#Case: query employee salary level SELECT salary ,grade_level FROM employees e JOIN job_grades g ON e.`salary` BETWEEN g.`lowest_sal` AND g.`highest_sal`; #Case: query the number of salary levels > 20, in descending order by salary level SELECT COUNT(*),salary ,grade_level FROM employees e JOIN job_grades g ON e.`salary` BETWEEN g.`lowest_sal` AND g.`highest_sal` GROUP BY grade_level HAVING COUNT(*) > 20 ORDER BY grade_level DESC;
3. Self connection
#Case: query the name of the employee whose name contains the character k and the name of the superior SELECT e.`last_name`,m.`last_name` FROM employees e JOIN employees m ON e.`manager_id` = m.`employee_id` WHERE e.`last_name` LIKE '%k%';
7.2.2 external connection
Application scenario: used to query records in one table but not in another
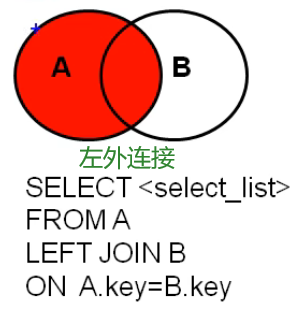
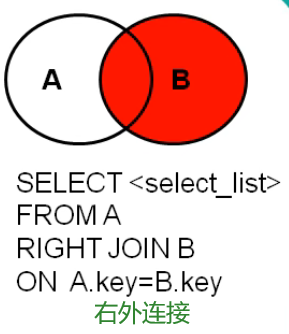
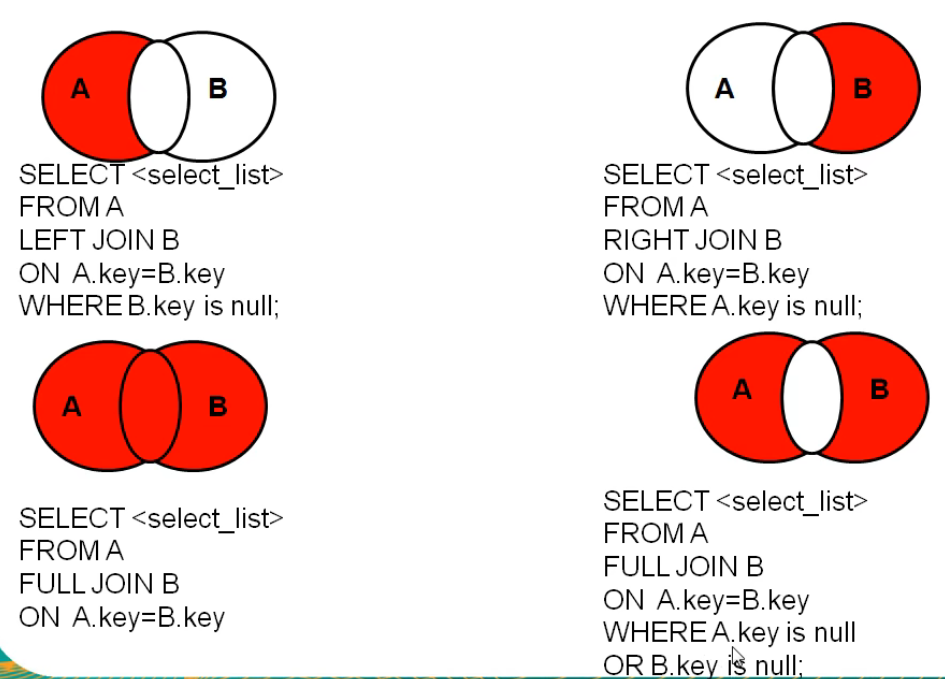
Syntax:
select Query list from Table 1 aliases left|right|full[outer] join Table 2 aliases on Connection conditions where Screening conditions group by Group list having Filtering after grouping order by Sort list limit clause;
characteristic:
①Query results=For all rows in the master table, if the slave table matches it, the matching row will be displayed. If there is no matching row in the slave table, the matching row will be displayed null ②left join On the left is the main table, right join On the right is the main table full join Both sides are main tables ③It is generally used to query the remaining mismatched rows except the intersection part 4.The same effect can be achieved by exchanging the order of the two tables outside the left and right 5.Total external connection= Result of internal connection+There are in Table 1, but not in Table 2+Those in Table 2 but not in Table 1
Case: query which department has no employees
#Left outer connection SELECT d.*, e.employee_id FROM departments d LEFT OUTER JOIN employees e ON d.`department_id` = e.`department_id` WHERE e.`employee_id` IS NULL #Right outer connection SELECT d.*, e.employee_id FROM employees e RIGHT OUTER JOIN departments d ON d.`department_id` = e.`department_id` WHERE e.`employee_id` IS NULL
7.2.3 cross connection
Syntax:
select Query list from Table 1 aliases cross join Table 2 aliases;
characteristic:
Similar to Cartesian product
8, Subquery
8.1 meaning
select statements nested inside other statements are called subqueries or intra queries,
The external statements can be insert, update, delete, select, etc. generally, select is used as the external statement
If the external is a select statement, this statement is called an external query or a main query
8.2 classification
8.2.1. According to the occurrence position
select After: Only scalar subqueries are supported from After: Table subquery where or having After:※ scalar subquery Column subquery Row subquery exists After: scalar subquery Column subquery Row subquery Table subquery
8.2.2. Rows and columns by result set
Scalar subquery (single row subquery): the result set is one row and one column
Column subquery (multi row subquery): the result set is multiple rows and one column
Row sub query: the result set is multi row and multi column
Table sub query: the result set is multi row and multi column
8.2.3. Example: after where or having
characteristic:
1.Subqueries are enclosed in parentheses
2.Subqueries are generally placed on the right side of conditions
3.Scalar subqueries are generally used with single line operators > < >= <= <>
Column subqueries are generally used with multi row operators in,any/some,all
4.The execution of the sub query takes precedence over the main query. The conditions of the main query use the results of the sub query (execute the sub query first)
1. Scalar subquery
Case 1: query the name and salary of the minimum wage employee
① Minimum wage
select min(salary) from employees
② Query the employee's name and salary. The required salary = ①
select last_name,salary from employees where salary=( select min(salary) from employees );
Case 2: return job_ The ID is the same as that of employee 141. Salary is more than that of employee 143_ ID and salary
①. Query the job of employee 141_ id
SELECT job_id
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 141;
②. Query salary of employee 143
SELECT salary
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 143;
③. Query employee's name, job_id and salary, job required_ Id = ① and salary > ②
SELECT last_name,job_id,salary
FROM employees
WHERE job_id = (
SELECT job_id
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 141
)
AND salary >(
SELECT salary
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 143
);
Case 3: query the Department id and the minimum wage of the Department whose minimum wage is greater than the minimum wage of No. 50 department
① Check the minimum wage of department No. 50
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = 50;
② Query the minimum wage of each department
SELECT department_id,MIN(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY department_id;
③ Screening ②, meeting min (salary) > ①
SELECT department_id,MIN(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY department_id HAVING MIN(salary) > ( SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = 50 );
2. Column subquery (one column and multiple rows)
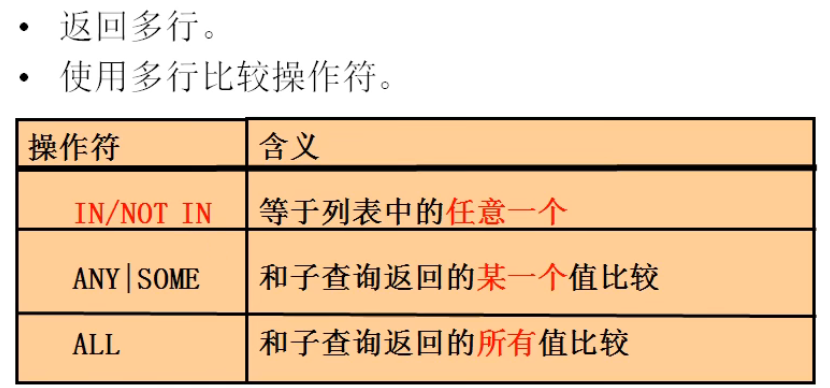
Case 1: query the names of all employees who are leaders
① Query managers of all employees_ id
select manager_id from employees
② Query name, employee_id belongs to one of the ① lists
select last_name from employees where employee_id in( select manager_id from employees ); select last_name from employees where employee_id = any( select manager_id from employees );
3. Row sub query (the result set is one row with multiple columns or multiple rows with multiple columns)
Case 2: query the information of the employee with the smallest employee number and the highest salary
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id =(
SELECT MIN(employee_id)
FROM employees
)AND salary = (
SELECT MAX(salary)
FROM employees
);
#Row subquery
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE (employee_id,salary) = (
SELECT MIN(employee_id),MAX(salary)
FROM employees
);
8.2.4. Example: after select
Case 1: query the number of employees in each department
SELECT d.*,( SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees e WHERE e.department_id =d.`department_id` ) FROM departments d;
Case 2: query the department number with employee number = 102
SELECT (
SELECT department_name
FROM departments d
INNER JOIN employees e
ON d.department_id = e.department_id
WHERE e.employee_id = 102
) Department name; #Row by column
8.2.5. Example: after from
It is required to alias the sub query results as a table
Case 1: query the salary grade of the average salary of each department
① Query the average salary of each department
SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id;
② Result set job of connection ①_ Grades table, filter criteria, average salary between lowest_sal and highest_sal
SELECT ag_dep.*,j.grade_level FROM ( SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id FROM employees GROUP BY department_id ) ag_dep INNER JOIN job_grades j ON ag_dep.ag BETWEEN lowest_sal AND highest_sal;
Case 2: query the employee number, name and salary of employees whose salary is higher than the average salary of the Department in each department
#1. Query the average salary of each department
SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id;
#2. Connect the result set employees table in 1 to filter
SELECT employee_id,last_name,salary
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN(
SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
)ag_dep
ON e.`department_id` = ag_dep.department_id
WHERE salary > ag_dep.ag;
8.2.6. Example: after exists (related sub query)
Syntax: exists (complete query statement)
Result: 1 or 0
Exists determines whether it exists (1 exists, 0 does not exist)
Case 1: query the Department name with employees
SELECT department_name
FROM departments d
WHERE EXISTS(
SELECT *
FROM employees e
WHERE d.`department_id` = e.`department_id`
);
#in
SELECT department_name
FROM departments d
WHERE d.`department_id` IN(
SELECT department_id
FROM employees
)
9, Paging query
1, Application scenario
When the number of items to be queried is too many, one page cannot be displayed completely
2, Grammar
select Query list from surface [join type join Table 2 on Link condition where Screening conditions group by Grouping field having Filtering after grouping order by Sorted fields] limit [offset,]size; be careful: offset Represents the initial entry index, which starts from 0 by default size Represents the number of items displayed
characteristic:
1.limit The statement is placed at the end of the query statement
2.Formula:
If the number of pages to be displayed is page,The number of entries on each page is size
select Query list
from surface
limit (page-1)*size,size;
Case 1: query the first five employee information
SELECT * FROM employees LIMIT 0,5; SELECT * FROM employees LIMIT 5;
Case 2: query employee information from Articles 11 to 25
SELECT * FROM employees LIMIT 10,15;
Case 3: the information of employees with bonus and the top 10 with higher salary are displayed
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 10;
Case 4: query the information of the Department with the lowest average wage
Mode 1:
1.Average wage of each department
select avg(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
2.Minimum average wage on the result in query 1
select min(ag)
from(
select avg(salary) ag,department_id
from employees
group by department_id
)ag_dep
3.Which department's average salary is queried = 2
select avg(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
having avg(salary) = (
select min(ag)
from (
select avg(salary) ag,department_id
from employees
group by department_id
)ag_dep
);
4.Query department information
SELECT d.*
FROM departments d
WHERE d.`department_id` = (
SELECT department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING AVG(salary)=(
SELECT MIN(ag)
FROM (
SELECT AVG(salary) ag,department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
)ag_dep
)
);
Mode 2:
1.Average wage of each department
select avg(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
2.Department number to find the minimum average wage
SELECT department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
ORDER BY AVG(salary)
LIMIT 1;
3.Query department information
SELECT *
FROM departments
WHERE department_id = (
SELECT department_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
ORDER BY AVG(salary)
LIMIT 1
);
10, union Union query
1, Meaning
union: merge, combine, merge multiple query results into one result
2, Grammar
Query statement 1
union [all]
Query statement 2
union [all]
Application scenario:
When the results to be queried come from multiple tables, and multiple tables have no direct connection relationship, and the query information is consistent
3, Meaning
1. Split a complex query statement into multiple statements
2. When querying multiple tables, the query columns are basically the same
4, Characteristics
1. It is required that the number of query columns of multiple query statements must be consistent
2. The type and order of each column of the query that requires multiple query statements should be consistent
3. union de duplication. union all contains duplicates
5, Introduction case: query employee information with department number > 90 or email containing a
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE email LIKE '%a%' OR department_id >90; SELECT * FROM employees WHERE email LIKE '%a%' UNION SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id > 90;
11, Summary:
Syntax:
select query list ⑦
from table 1 alias ①
Connection type join table 2 ②
on connection condition ③
where filter ④
group by group list ⑤
having screening ⑥
order by list ⑧
limit start entry index, number of entries; ⑨