Logging is a logging framework that comes with the Core framework
Simple use of Logging
configuration file
{
"Logging": {
"Debug": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information"
}
},
"Console": {
"IncludeScopes": false,
"LogLevel": {
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Razor.Internal": "Warning",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Razor.Razor": "Debug",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Razor": "Error",
"Default": "Information"
}
},
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Debug"
}
}
}This json creates six filtering rules Debug for debugging Console for console programs where LogLevel sets the logging minimum log level for the specified assembly. The first three sets the logging level unmatched for the specified assembly. Whether the IncludeScopes configuration is enabled as the enabled domain LogLevel sets all Programs automatically select a rule for each provider when creating logging objects
Configure Logging
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.ConfigureLogging(logging =>
{
logging.ClearProviders();
logging.AddConsole();
});Use
First Dependency Injection Receiving Example
private readonly ILogger _logger;
public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger)
{
this._logger = logger;
}Reuse directly
public IActionResult Index()
{
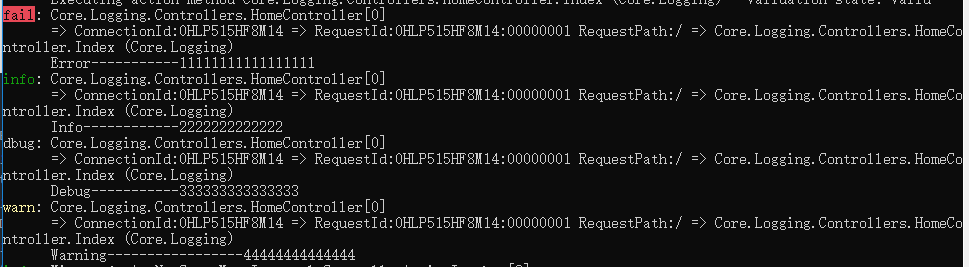
_logger.LogError("Error-----------11111111111111111");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
_logger.LogInformation("Info------------2222222222222");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
_logger.LogDebug("Debug-----------333333333333333");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
_logger.LogWarning("Warning-----------------44444444444444");
return Content("success");
}Operation results
Note: Using Logging to get services directly in Program does not require dependency injection
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build();
var logger = host.Services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>();
logger.LogInformation("Seeded the database.");
host.Run();
}Setting Log ID
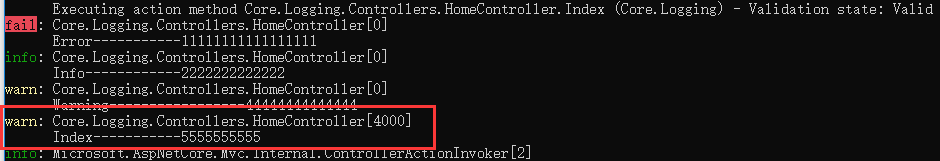
_logger.LogWarning(LoggingEvents.GetItemNotFound, "Index-----------5555555555");
Logging Events Definition This section defines the severity of logging itself
public class LoggingEvents
{
public const int GenerateItems = 1000;
public const int ListItems = 1001;
public const int GetItem = 1002;
public const int InsertItem = 1003;
public const int UpdateItem = 1004;
public const int DeleteItem = 1005;
public const int GetItemNotFound = 4000;
public const int UpdateItemNotFound = 4001;
}Running test
Setting the filter level in the code
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.ConfigureLogging(logging =>
{
logging.ClearProviders();
logging.AddConsole();
logging.AddFilter("System", LogLevel.Debug).AddFilter<DebugLoggerProvider>("Microsoft", LogLevel.Trace);
});How to Apply Screening Rules
The configuration data shown in the previous example and the AddFilter code create the rules shown in the table below. The first six are created by configuration examples and the last two are created by code examples

Algorithms for Selecting Screening Rules
- Select all rules that match the provider or its alias. If no matches can be found, all rules with empty providers are selected.
- Based on the results of the previous step, the rule with the longest matching class prefix is selected. If no matches can be found, all rules that do not specify a category are selected.
- If multiple rules are chosen, the last one is adopted.
- Minimum Level is used if no rules are selected.
Simply put, when generating ILogger instances, look for filter rules to name the most specific rules first. If there are no matches, follow the rules of the unspecified category. If there are no matches, use the system's default. If more than one is defined, use the last one.
Provider aliases
Each provider defines an alias; it can be used in configuration instead of a fully qualified type name. For built-in providers, use the following aliases:
- Console
- Debug
- EventSource
- EventLog
- TraceSource
- AzureAppServicesFile
- AzureAppServicesBlob
- ApplicationInsights
Setting the lowest level in the code
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.ConfigureLogging(logging => logging.SetMinimumLevel(LogLevel.Warning));System Categories and Levels
Below are some categories used by ASP.NET Core and Entity Framework Core, and the notes describe the specific logs available from these categories:
| category | Explain |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.AspNetCore | Conventional ASP.NET Core diagnosis. |
| Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection | Consider, find and use which keys. |
| Microsoft.AspNetCore.HostFiltering | Allowed host. |
| Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting | HTTP request completion time and start time. Which hosted startup assemblies are loaded. |
| Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc | MVC and Razor diagnosis. Model binding, filter execution, view compilation and operation selection. |
| Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing | Route matching information. |
| Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server | Connection starts, stops, and maintains active response. HTTP certificate information. |
| Microsoft.AspNetCore.StaticFiles | Documents provided. |
| Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore | Conventional Entity Framework Core diagnosis. Database activities and configuration, change detection, migration. |
Log Scope
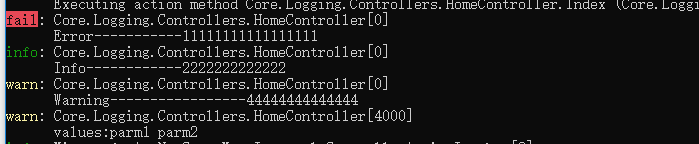
using (_logger.BeginScope("Messages attached to logs created in use blocks"))
{
_logger.LogError("Error-----------11111111111111111");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
_logger.LogInformation("Info------------2222222222222");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
_logger.LogDebug("Debug-----------333333333333333");
Thread.Sleep(3000);
_logger.LogWarning("Warning-----------------44444444444444");
string p1 = "parm1";
string p2 = "parm2";
_logger.LogWarning(LoggingEvents.GetItemNotFound, "values:{0} {1}", p1, p2);
}
I didn't understand the specific role and I'll study it later.