Network communication data transmission TCP/IP model PORT IP
Network programming: connect computers distributed in different geographical regions with special external equipment with communication lines to form a large-scale and powerful network system, so that many computers can easily transfer information to each other and share hardware, software, data information and other resources. Data transmission and sending / receiving between devices in the network.
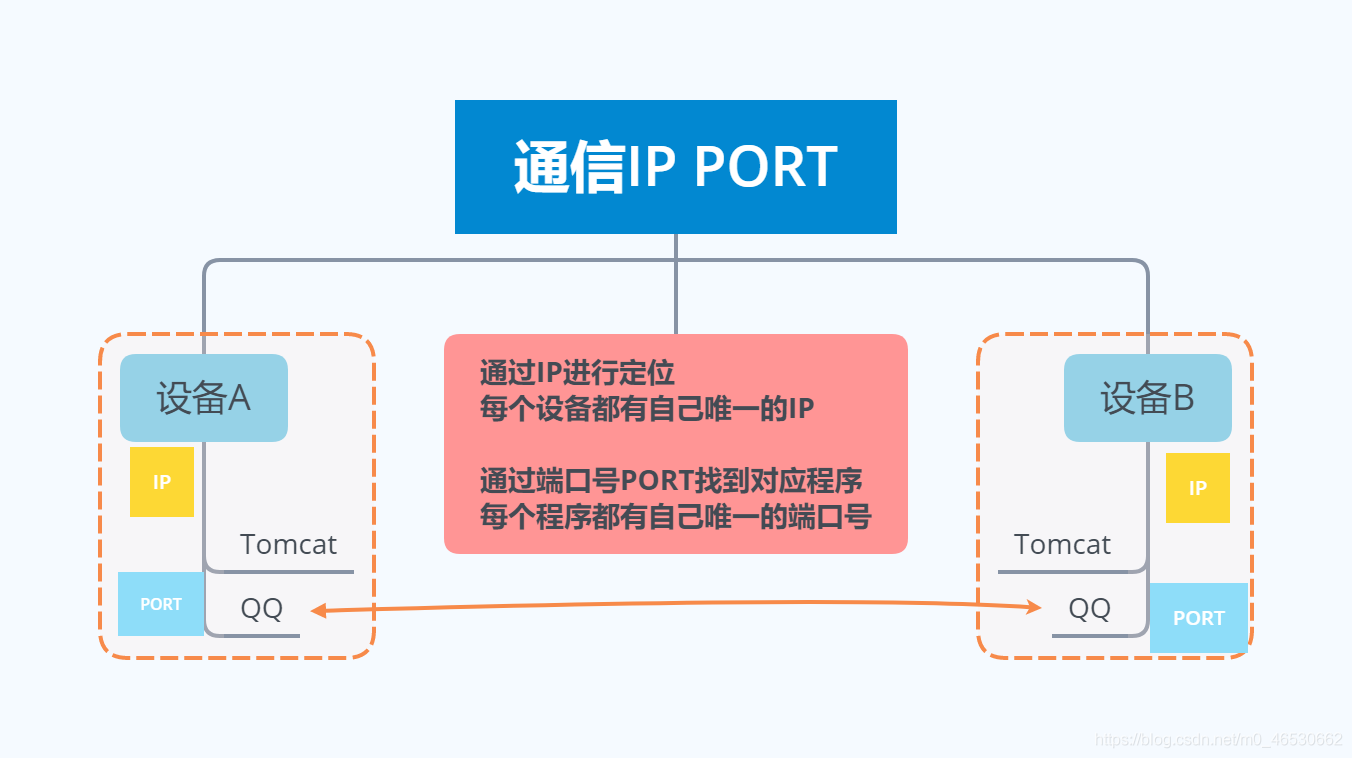
IP PORT
The domain name we use to visit the website is actually IP. Domain name -- DNS resolution -- > IP
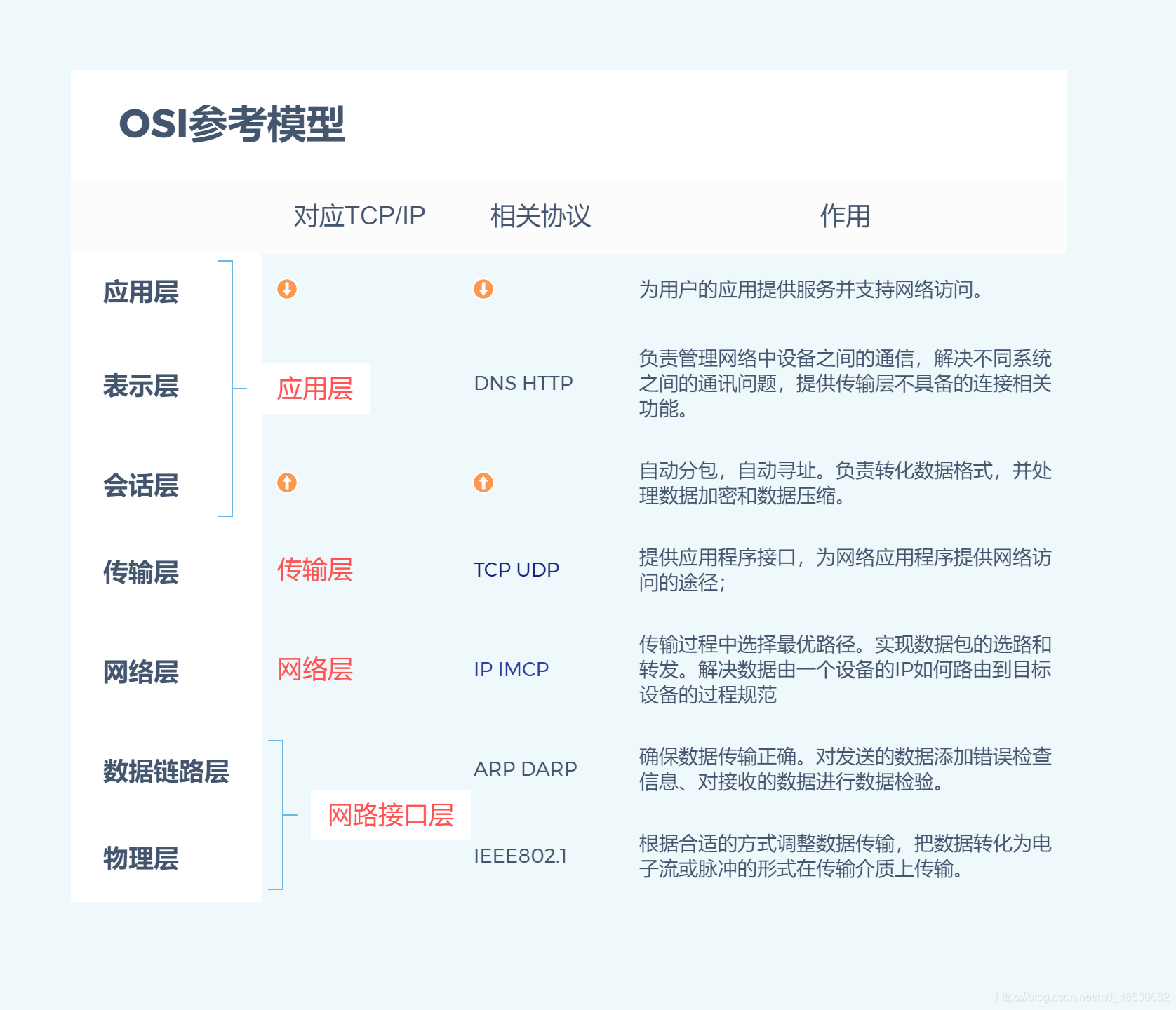
TCP/IP four layer model:
Although OSI is only a nominal standard, although we do not divide it into seven layers according to OSI in the actual process, it has guiding significance for us to understand TCP/IP.
| OSI reference model | Corresponding TCP/IP | Related agreements | effect |
| application layer | application layer | DNS HTTP | Provide services for users' applications and support network access. |
| Presentation layer | Manage the communication between devices in the network, solve the communication problems between different systems, and provide connection related functions that the transport layer does not have. | ||
| Session layer | Automatic subcontracting, automatic addressing. Responsible for converting data format and handling data encryption and data compression. | ||
| Transport layer | Transport layer | TCP UDP | Provide application program interface to provide network access for network applications; |
| network layer | network layer | IP IMCP | Select the optimal path in the transmission process. Realize packet routing and forwarding. A process specification that addresses how data is routed from the IP of a device to the target device |
| data link layer | Network interface layer | ARP DARP | Ensure that the data transmission is correct. Add error check information to the sent data and perform data verification on the received data. |
| physical layer | IEEE802.1 | Adjust the data transmission according to the appropriate way, and convert the data into the form of electronic flow or pulse for transmission on the transmission medium. |
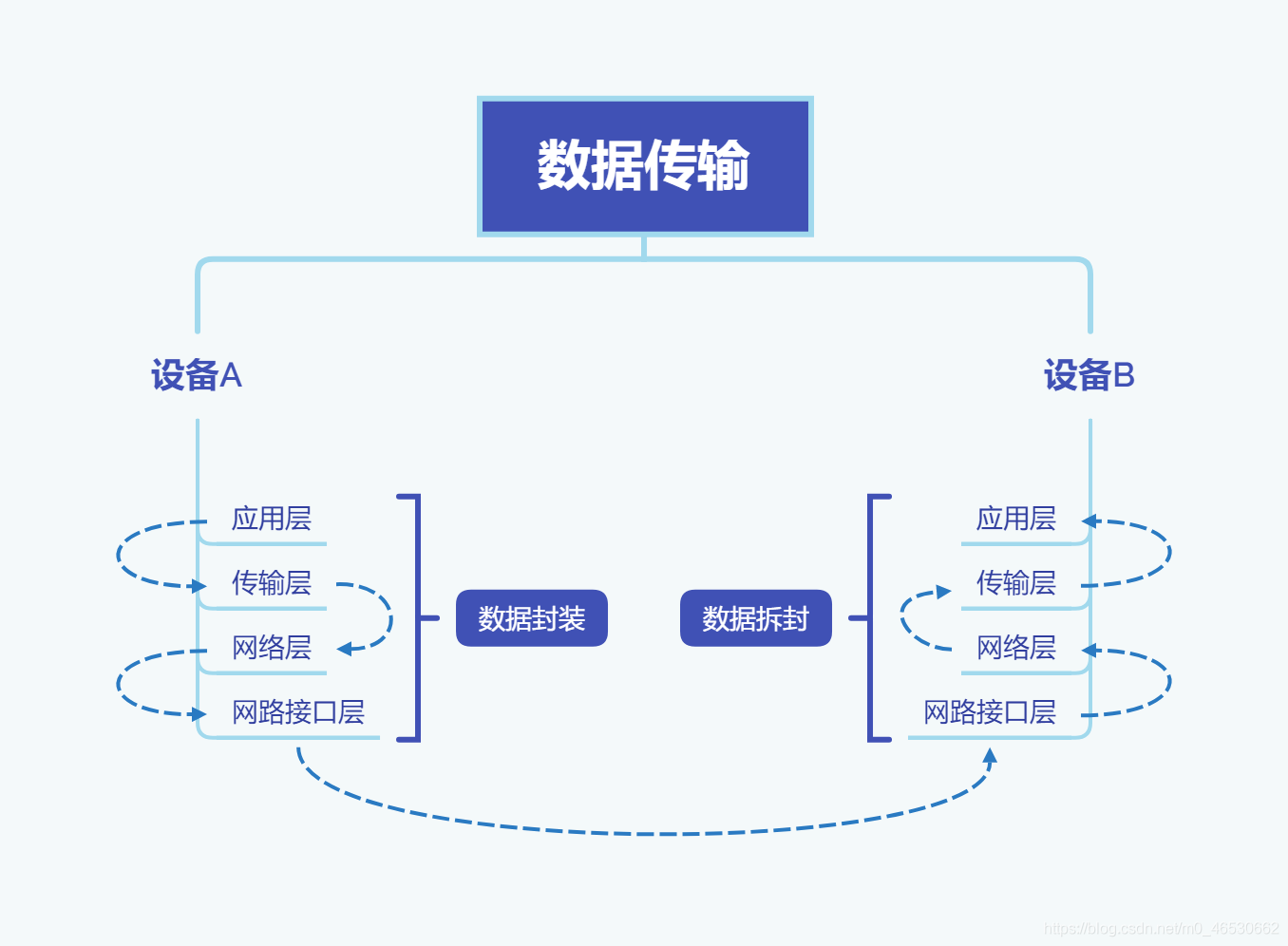
On the surface, data transmission between different devices is communication between application layers. In fact, it needs to transmit multiple layers to realize data encapsulation and splitting
TCP protocol
The connection is reliable, three handshakes and four waves
UDP protocol: it is unreliable. Packet loss is easy to occur during packet transmission
IP PORT
MAC address
The network adapter address is the unique identifier that can distinguish our computer. It is composed of a complex English string specified by the manufacturer when it is produced.
IP address
Internet protocol address needs a set of logic operation rules for fast routing to the target computer in the network, but the MAC address is a complex string composition, which is not conducive to logic operation. Therefore, ARP protocol is used to convert the MAC address into a digital IP address that can be used for logic operation.
domain name
A group of IP address numbers is not easy to remember, so choose a meaningful and easy to remember name for the server on the Internet, The address of this name is the domain name address (domain name server). In order to make it easier for users to remember, DNS has derived a DNS service. DNS completes the conversion of IP addresses into domain names that are easy to remember. After users enter a domain name, the browser must first go to a host with a database corresponding to domain names and IP addresses to query the IP address of this computer. The queried host is called a domain name server (Domain Name Server,DNS).
InetAddress
Encapsulated IP
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
//Cannot directly new InetAddress(); Create the object because InetAddress() is decorated with default.
InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.253.3");
System.out.println(ia); // /192.168.253.3
InetAddress ia2 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");//localhost refers to the ip address of the local machine
System.out.println(ia2); // localhost/127.0.0.1
InetAddress ia3 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");//127.0. 0.1 refers to the ip address of the machine
System.out.println(ia3); // /127.0.0.1
InetAddress ia4 = InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-VUQ1HT6K");//Package computer name
System.out.println(ia4); // LAPTOP-VUQ1HT6K/192.168.172.135
InetAddress ia5 = InetAddress.getByName("www.bilibili.com");//Encapsulated domain name
System.out.println(ia5); // www.bilibili.com/117.148.143.200
System.out.println(ia5.getHostName());// www.bilibili.com get domain name
System.out.println(ia5.getHostAddress());// 117.148. 143.200 get ip address
}
}
InetSocketAddress
Encapsulation IP+PORT
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8888);
System.out.println(isa); //localhost/127.0.0.1:8888
System.out.println(isa.getHostName()); //IP intercepted by localhost
System.out.println(isa.getPort()); //8888 intercepting PORT
InetAddress ia = isa.getAddress(); // IP is encapsulated as an InetAddress object
System.out.println(ia.getHostName()); // localhost
System.out.println(ia.getHostAddress()); // 127.0.0.1
}
}
(); // IP is encapsulated as an InetAddress object
System.out.println(ia.getHostName()); // localhost
System.out.println(ia.getHostAddress()); // 127.0.0.1
}
}