Review yesterday
- Basic use of socket
Built in module
import socket s = socket.socket() # Create network transmission, default TCP protocol s.bind((IP+port)) # Bind IP + port s.listen(5) # Semi connection pool sock, addr = s.accept # Listen, listen state of three handshakes sock.recv(1024) # Receive content sock.send(Content sent) # send content c = socket.socket() c.connect((IP+port))
- Communication cycle
Loop recv and send with while - Connection cycle
The listening code loops using while - Code robustness verification
- Exception capture
- Port conflict
- System problems
Judge whether the user input is blank at the client
Judge whether the acceptance is empty at the server
- TCP sticky packet characteristics
- There is a large amount of data in the two-way same channel, and there is residual reception
- TCP will package and send the data with small amount of data and short time at one time (Streaming Protocol)
- How to solve the sticking problem
-
Header: fixed length, containing a lot of information
The module struct that can be fixed and packaged
client- Pack the header of a fixed length dictionary and send it
- Send dictionary data
- Send real data
Server
- First receive the header of a fixed length dictionary
- Parse the length of the dictionary
- Receive dictionary data and analyze the contents related to real data
- Receive real data
-
- How to transfer large files
- How to verify the consistency of file data
The hashlib module is used to encrypt the file content. After the file is sent successfully, the random string is taken out for comparison
Slice decryption comparison
Read part of the contents of the file and encrypt (divide the area) - Data storage
for loop sends line by line and stores line by line
- How to verify the consistency of file data
Yesterday's code must be mastered
Yesterday's demand analysis
- The client and server are all written using the software development directory specification
- Write each function as a function
1. UDP coding
# Server
import socket
amg = socket.socket(type = socket.SOCK_DGRAM) # UDP protocol
amg.bind(('127.0.0.1', 9000)) # Bind IP address
msg, addr = amg.rescvfrom(1024)
amg.sendto(Content sent, addr Send address)
amg.close()
# client
import socket
ip_port = ('127.0.0.1', 9000)
udp_sk = socket.socket(type=socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
udp_sk.sendto(Content, ip_port)
back, addr = udp_sk.recvfrom(1024)
print(back.decode('utf-8'),addr)
# Suggested QQ program practice
2. History of operating system
Learning concurrent programming is actually learning the development history of the operating system (underlying logic)
- Punch card era:
- CPU utilization is extremely low (all inputs can only be operated through punched cards, and only one person can operate the exclusive code each time for each calculation, and there is no way to execute other codes)
- Online batch processing system
- The programs of multiple programmers are input into the tape at one time, and then input by the input machine and executed by the CPU
- off-line batch processing system
- Prototype of modern computer (remote input, high-speed tape, host)
3. Multiprogramming system (multiprogramming Technology)
Premise: for single core CPU (the computer can only be higher by one thing at the same time)
Single channel technology (serial)
Multichannel technology (single core)
- Switch + save state
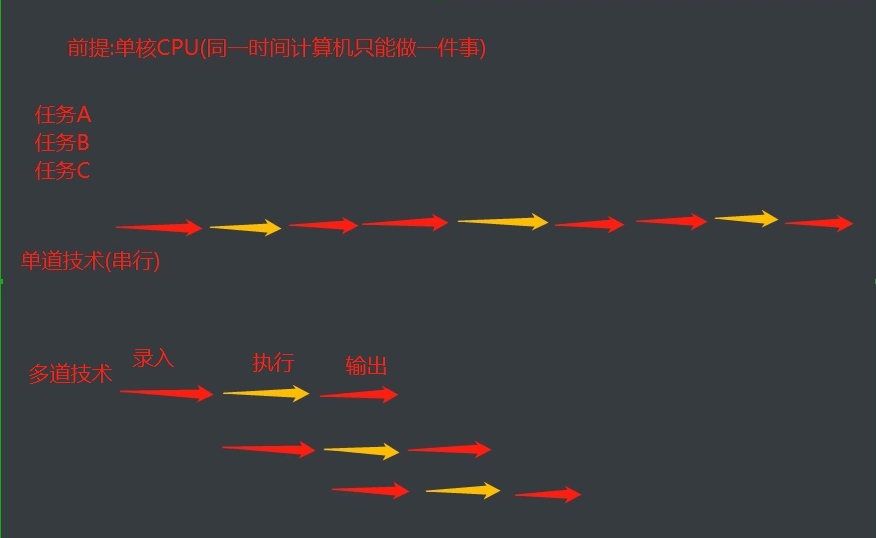
Working mechanism of CPU (single core)
- When a program enters the IO state, the system will automatically deprive the CPU execution permission of the modified program
- When a program occupies the CPU for a long time, the operating system will also deprive the CPU of the program
Parallelism and concurrency
- Parallel: multiple programs are executed at the same time (multiple CPU s are required)
- Concurrency: multiple programs can look like running at the same time
Simple questions:
- Single core CPU can realize parallelism
No, but concurrency can be achieved - 12306 can support hundreds of millions of users to buy tickets at the same time. Is it concurrent or parallel
Concurrency (high concurrency)
Satellite orbit: microblog can support multiple satellite orbits at the same time
4. Process theory (important focus)
-
Difference between process and program
- Program: and code, code in similar py files (dead)
- Process: running program (code) (Live)
- As a separate space in memory (running programs)
-
Process scheduling in the case of single core
- Evolution of process scheduling algorithm
- FCFS: first come, first served
Disadvantages: unfriendly to short assignments - Short job first scheduling algorithm
Disadvantages: unfriendly to long operation - Time slice Round forwarding + multi-level feedback queue (algorithm currently used by computers)
First assign the same time slice to multiple processes of concern
Then it is classified according to the time slice consumed by the process
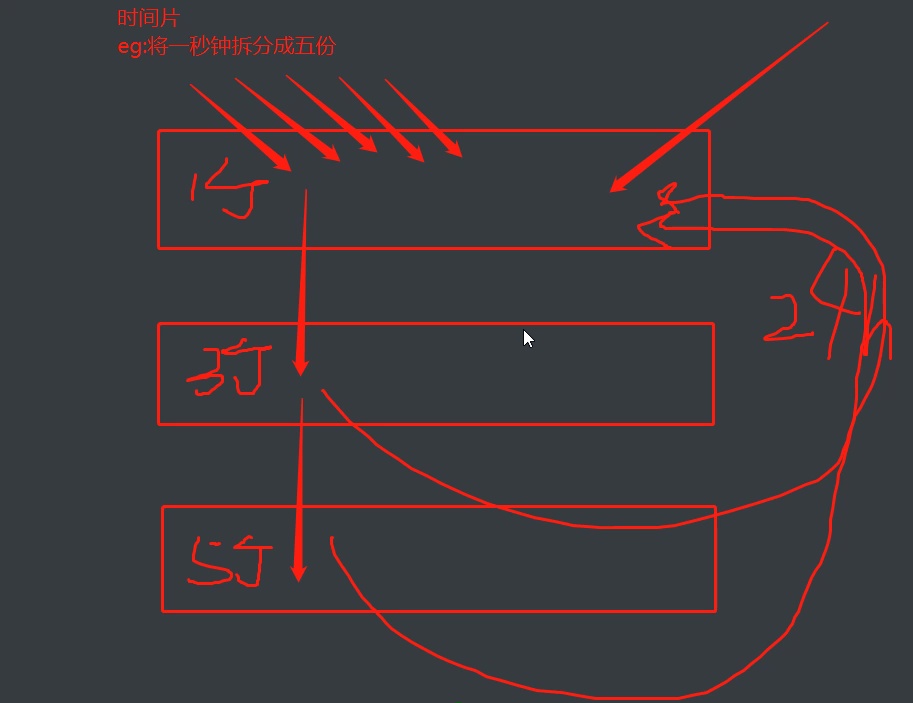
- FCFS: first come, first served
- Evolution of process scheduling algorithm
-
Process three state diagram
- Ready
- Running state
- Blocking state
- In order to enter the running state, the program must go through the ready state first

- Synchronous & asynchronous (for submitting familiar tasks)
- Synchronization:
- After submitting the task, wait for the return structure of the task in place, and do nothing during the period
- Asynchronous:
- After the physical examination task has, do not wait for the return result of the task, and directly do other things. The structure is automatically reminded by the feedback mechanism
- Blocking & non blocking (describes the execution status of the task)
- Blocking: blocking state
- Non blocking: ready state, running state
5. Create process
# Code level creation process
# High end module
from mulirocessing import Process
import time
def test(name):
print('%s Running'%name)
time.sleep(3)
print('%s It's already over.'%name)
if __name__ = '__main__':
p = Process(target=test, args=('kk',)) # s generates a process object
p.start() # Tell the operating system to open a new process and run it. Asynchronous commit
'''
stay win The setup process in the system is similar to the import module
Execute the code again from top to bottom
Be sure to__main__Determine the code block of the execution process in the statement
if __name__ = '__main__':
print(123)
stay linux A complete copy of the code is directly copied and executed in the system
unwanted__main__Execute within judgment statement
'''
# Class creation process
class MyProcess(Process):
def __init__(self, name):
super().__init__()
self.name = name
def run(self):
print('%s Running'%name)
time.sleep(3)
print('%s It's already over.'%name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = MyProcess('kk')
p.start()
6. join method of process
from multiprocessing import Process
import time
def test(name, n):
print('%s is running' % name)
time.sleep(n)
print('%s is over' % name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
p_list = []
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(1, 4):
p = Process(target=test, args=(i, i))
p.start()
p_list.append(p)
# p.join() # Serial 9s+
for p in p_list:
p.join()
print(time.time() - start_time)
"""
p = Process(target=test, args=('jason',))
p1 = Process(target=test, args=('kevin',))
p2 = Process(target=test, args=('oscar',))
p.start()
p1.start()
p2.start()
"""
print('Main process')
7. No interaction between processes by default
# Data between processes is isolated from each other
from multiprocessing import Process
money = 100
def test():
global money
money = 999
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = Process(target=test)
p.start()
# Make sure the subprocess is running before printing
p.join()
print(money)
8. Object method
from mulirocessing import Process
import time
import os
def test(name):
print('%s Running'%name)
time.sleep(3)
print('%s It's already over.'%name)
if __name__ = '__main__':
p = Process(target=test, args=('kk',)) # s generates a process object
p.start() # Tell the operating system to open a new process and run it. Asynchronous commit
p.join() # Wait for the child process to finish running, and then run the main process
p.terminate() # End child process now
print(p.is_alive()) # Check whether the process exists and return a Boolean value
print(current_process().pid) # View current process number
print(os.getpid()) # View current process number
print(os.getppid()) # View parent process number
"""
1.current_process View process number
2.os.getpid() View process number os.getppid() View parent process number
3.The name of the process, p.name There is a direct default, or it can be passed in the form of keywords when instantiating the process object name=''
3.p.terminate() Kill child process
4.p.is_alive() Determine whether the process is alive 3,4 No results can be seen in combination, because the operating system needs reaction time. Main process 0.1 You can see the effect
"""
extend
Implementation principle of time server
- 1. Internal capacitance small battery
- Dedicated power supply for time module
- 2. Remote time synchronization
- The time will be updated automatically after networking
linux multi server scheduled tasks
- Randomly select the time of a server as the standard, and all machines execute timed scripts at a certain time