1, Byte order
1. Classification
Small end format: store low byte data in low address
Big end format: store high byte data in low address

Small segment storage format is adopted in linux
2. Features
- The network protocol specifies that the communication byte order is the big end format
- Byte order needs to be considered only in multi byte data processing
- Processes running on the same computer communicate with each other without considering byte order
- The communication between heterogeneous computers needs to convert their own byte order into network byte order
3. Byte order conversion function
linux provides special functions for converting byte order. In the following functions, h represents host, n represents network, and N represents network. The end of l is used for the conversion of 32-bit data, and the end of s is used for the conversion of 16 bit data.
#include <arpa/inet.h> uint32_t htonl(uint32_t hostint32); Function: convert 32-bit host byte order data into network byte order data Parameter: 32-bit host byte order data to be converted Return value: the value of network byte order is returned successfully uint16_t htons(uint16_t hostint16); Function: convert 16 bit host byte order data into network byte order data Parameter: 16 bit host byte order data to be converted Return value: the value of network byte order is returned successfully uint32_t ntohl(uint32_t netint32); Function: convert 32-bit network byte order data into host byte order data Parameter: 32-bit host byte order data to be converted Return value: successfully returns the value of host byte order uint16_t ntohs(uint16_t netint16); Function: convert 16 bit network byte order data into host byte order data Parameter: 16 bit host byte order data to be converted Return value: successfully returns the value of host byte order
For example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int main(){
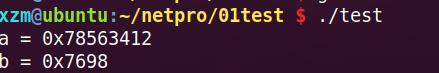
int a = 0x12345678;
short b = 0x9876;
printf("a = %#x",htonl(a));
printf("b = %#x",htons(b));
return 0;
}
2, Address translation function
1. Why do I need address translation?
In order to facilitate human identification of network address, we generally use dotted decimal system to represent ip address, such as 192.168 1.88 in this way, the dotted decimal system is actually a string of strings. The computer can't understand it. The ip value (ipv4) recognized by the computer is a string of 32-bit unsigned shaping data, so we need to convert the dotted decimal system we know into 32-bit data, so we need to go to the address conversion function.
2.inet_pton function
#include <arpa/inet.h> int inet_pton(int af, const char *src, void *dst);
Function: convert dotted decimal ip address to unsigned integer
Parameters: af: protocol family
AF_INET ipv4 network protocol
AF_INET6 ipv6 network protocol
src: dotted decimal string
dst: save address of unsigned ip address
Return value: 1 = other
3.inet_ntop function
#include <arpa/inet.h> const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src, char *dst, socklen_t size);
Function: convert 32-bit unsigned integer ip address to dotted decimal
Parameters: af: protocol family
src: ip address data
dst: save address of dotted decimal ip address
Size: the size of dst cache. There are two macros to select, which are used to save ipv4, ipv6
#define INET_ADDRSTRLEN 16
#define INET6_ADDRSTRLEN 46
Return value: the first address of the string is returned successfully, and NULL is returned in case of failure
4. Examples
#include <stdio.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
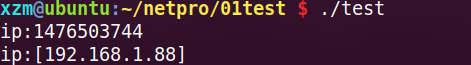
char *str = "192.168.1.88";
unsigned int addr = 0;
if(inet_pton(AF_INET,str,&addr)!=1){
perror("fail to inet_pton");
exit(1);
}
printf("ip:%d\n",addr);
char buf[16];
if(inet_ntop(AF_INET,&addr,buf,INET_ADDRSTRLEN)==NULL){
perror("fail to ntop");
exit(1);
}
printf("ip:[%s]\n",buf);
return 0;
}
5.inet_addr function and inet_ntoa function
These two functions can only be used in ipv4 address translation
#include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> int inet_aton(const char *cp, struct in_addr *inp); in_addr_t inet_addr(const char *cp); Function: get 32-bit unsigned integer from dotted decimal system IP address Parameter: dotted decimal address Return value: successfully returned ip char *inet_ntoa(struct in_addr in); Function: 32-bit unsigned shaping ip Get fractional decimal Parameters: saving ip Structure of address Return value: dotted decimal ip address