Interface
meaning
It is a special abstract class and a constraint and specification.
specific characteristics
- First, there is no specific (ordinary) method, but there can be a default implementation method after 1.8
- Abstract methods add the public abstract modifier by default (write it right or not)
- The field will be added with the public static final modifier by default (either write right or not)
- Interfaces can inherit multiple interfaces
- Modifier of internal class in interface public static (write right or not)
- Does the interface have a constructor? TODO
case
make designs of one's own
Inner class
meaning
Class inside class
classification
- Method inner class
- Member inner class
- static modifies the inner class
- Non static decorated inner class
case
make designs of one's own
Packaging data type
meaning
The eight basic data types have corresponding reference data types.
-
byte Byte
-
int Integer
-
short Short
-
long Long
-
char Character
-
float Float
-
double Double
-
boolean Boolean
Why use wrapper data types
-
The default values of basic data type and wrapper data type are different
-
Wrapper data types provide many API s
Common APIs (integer as an example)
- parseInt
- valueOf
- intValue
- compare
- wait
Packing
meaning
Basic data becomes packaging data type
type
- Automatic boxing (it is found that the manual boxing method is called during compilation)
- Manual packing
case
Self written
Unpacking
meaning
Packaging data type becomes basic data
type
- Automatic unpacking (it is found that the manual unpacking method is called during compilation)
- Manual unpacking
case
Self written
Shared element design mode
meaning
Shared cache design defaults
Usage scenario
When some objects need to be used frequently, we can create them in advance and put them into the cache, and get them directly from the cache next time
It is widely used in packaging data types. It is recommended to check it by yourself
abnormal
meaning
It is also called abnormal event. When the software is running, many situations will lead to abnormal events. For example, the file does not exist, the network is disconnected, the accessed database cannot be opened, the class cannot be found, 0 / 0, null pointer
Exception handling mechanism
When an exception occurs to a method at runtime, the method will create an exception object and throw the object to the runtime system (i.e. throw Legacy). The exception object contains all the information of the exception, including exception type, calling process, line code, etc.
Exception handling type
- capture
- Throw exception
Abnormal system
TODO
Custom exception
TODO
thread
Common concepts
-
serial
Multiple events are executed in sequence
-
parallel
Multiple events occur simultaneously at the same time
-
Concurrent
The occurrence of multiple events over a period of time.
process
The running program, the process has its own independent memory space.
At least one thread
thread
meaning
Index TODO executed
Execution process
From the macro point of view, threads run in parallel, but from the micro point of view, they execute alternately (concurrent). When the system has only one CPU, multiple threads will be executed in a certain order, which is thread scheduling.
Creation method
- Inherit Thread
- Implement Runnable interface
Mode 1
public class ThreadFirstDemo {
//Serial: multiple events are executed in sequence
//Parallel: multiple events occur together at the same time
//Concurrency: the occurrence of multiple events over a period of time
//process
//meaning:
//Running programs
//There is independent memory space and at least one thread
//thread
//Meaning: executed index (Branch)
//Creation method
//extends Thread
//implements Runnabel
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Main main thread
//Thread.currentThread() gets the current thread
//Thread.currentThread().getName() gets the name of the current thread
System.out.println("start");
//Create a thread
Thread buyThread = new BuyThread();
//Start calls the start method
buyThread.start();
int i=10;
while(i>0){
System.out.println("main end"+i);
i--;
}
//reflection
//Which thread executes first??
}
}
class BuyThread extends Thread{
//Override the run method. Run is the task of the current thread
@Override
public void run() {
int i=10;
while(i>0){
System.out.println("Purchased No"+i+"second");
i--;
}
}
}
Mode II
public class ThreadSecondDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create thread
Runnable runnable = new BuyTicketThread();
//First thread
Thread one = new Thread(runnable,"Xiao Hong");
//Second thread
Thread two = new Thread(runnable,"Xiao Liang");
//Start thread start
one.start();
two.start();
}
}
class BuyTicketThread implements Runnable{
int count = 40;
@Override
public void run() {
//Task of thread
while(count > 0){
//Thread.currentThread().getName() gets the current thread name
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"The ticket number purchased is"+count);
count--;
}
}
}
difference
- The inheritance method cannot inherit other classes. The implementation method can also inherit other classes
- Inheritance mode resources are not shared, and implementation mode resources are shared
- Implementation mode
Multithreading security
meaning
Multiple threads modify the same resource, resulting in data confusion.
Treatment method
- Synchronization mechanism
- Synchronization method
- Different code blocks
- Reentrant lock
case
public class SafeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new BuyTicketThread();
//First thread
Thread one = new Thread(runnable,"Xiao Hong");
//Second thread
Thread two = new Thread(runnable,"Xiao Liang");
//Start thread start
one.start();
two.start();
}
}
class BuyTicketThread implements Runnable{
int count = 40;
//Reentrant lock
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("To grab tickets...");
lock.lock();
try {
while(count > 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"The ticket number purchased is"+count);
count--;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//Synchronous code block
/*
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("To grab tickets... ");
//Monitoring object
//If the method is not static, write this
//If the method is static, write the class name Class / / bytecode object
synchronized(this){
while(count > 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"The ticket number purchased is "+ count";
count--;
//Sleep and release the lock, and the execution will continue when the time arrives
try {
wait(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
*/
//Synchronization method
//If the method is non static, the monitoring object is this
//If the method is static, the monitoring object is the class name class
/*
@Override
public synchronized void run() {
System.out.println("To grab tickets... ");
while(count > 0){
//Thread.currentThread().getName() Gets the current thread name
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"The ticket number purchased is "+ count";
count--;
if(count%4==0){
try {
//Thread.sleep(100); //The lock will not be released
wait(100); //Wait. The lock will be released. / / Xiaoliang
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
*/
}
Singleton design pattern
Lazy style
The corresponding object will be created only when it is used for the first time.
case
public class LazySingle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ATM atm1 = ATM.getInstance();
ATM atm2 = ATM.getInstance();
System.out.println(atm1==atm2);
}
}
class ATM{
private static ATM atm;
private ATM(){
}
public static final ATM getInstance(){
if(atm==null){
synchronized(ATM.class){
if(atm==null){
atm = new ATM();
}
}
}
return atm;
}
private void saveMeney(){
System.out.println("save money");
}
}
Object common methods
- hasCode
- toString
- equals
- getClass
- finalize
- wait(long time) / / wait and release the lock. Execution will continue after the time expires
- wait() / / wait indefinitely and release the lock. Execution will continue after waking up
- notify() / / wake up one of the waiting threads
- notifyAll() / / wake up all waiting threads
Common thread methods
- Thread.getCuurentThread();
- Thread.sleep / / wait. The lock will not be released
- getName
- setName
- getId
- setPriority
- getPriority
- join
bounded-buffer problem
public class Factory {
private String name;
//Does the representative have any
private boolean isEmpty = true;
//synchronized monitoring object this
/**
* production
* @param name
*/
public synchronized void push(String name){
while(!isEmpty){ //produce
//... Not empty, wait until consumed
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.name = name;
System.out.println("Produced="+name);
isEmpty = false;
notifyAll();
}
/**
* consumption
*/
public synchronized void pop(){
while(isEmpty){
//Can't consume, need to wait
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Represents consumption
System.out.println("Consumption="+name);
isEmpty = true;
notifyAll();
}
}
public class Producer extends Thread{
private Factory factory;
public Producer(Factory factory){
this.factory = factory;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 10;
while(i>0){
factory.push(i%2==0?"watermelon":"Hami melon");
i--;
}
}
}
public class Comsumer extends Thread{
private Factory factory;
public Comsumer(Factory factory){
this.factory = factory;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 10;
while(i>0){
factory.pop();
i--;
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Factory factory = new Factory();
Producer produce = new Producer(factory);
Comsumer comsume = new Comsumer(factory);
produce.start();
comsume.start();
}
}
Thread control
TODO
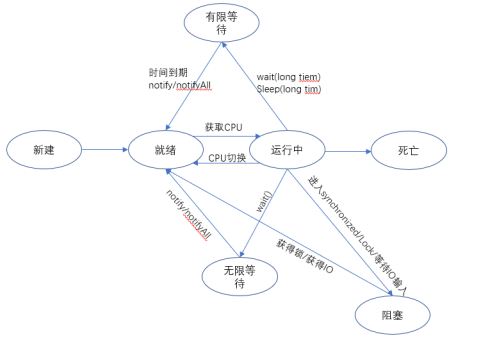
Thread life cycle
timer
Use Timer's schedule, which has three parameters:
schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) the first is a scheduled task,
Rewrite the run method of TimerTask according to business needs;
The second is delayed start, in milliseconds;
How often does the third bit run, in milliseconds;
new Timer().schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//do Something
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},0,5L * 60 * 1000);
task
-
Self learning java timer
-
Write their own producer consumer cases
-
Write 2 threads to grab tickets and have a chance to draw
-
Summarize thread life cycle
-
Is the following procedure reasonable
int a = 10; //Suppose the variable is entered from the console int b = 20; if(a-b>0){ System.out.println("a large"); } -
Self analyze the following procedures
Integer a = 10; Integer b = 10; syso(a==b); //What is the result? Why? a = 200; b =200; syso(a==b); //What is the result? Why? a = new Integer(1); b = new Integer(1); syso(a==b); //What is the result? Why?
-
Write a User's meta design pattern.
requirement:
When User objects with common names such as ZS, LS, ZL and WW are created, they are retrieved from the cache and returned
When you create a User object with another name, you can directly create a new object and return it