1, Hide version number
- You can use Fiddler to grab packets and view the Nginx version
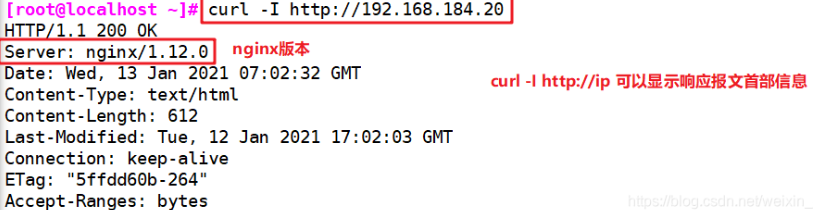
- You can also use the command curl - I in CentOS http://192.168.0.102 Display header information of response message
curl -I http://192.168.184.20
Method 1: modify the configuration file mode
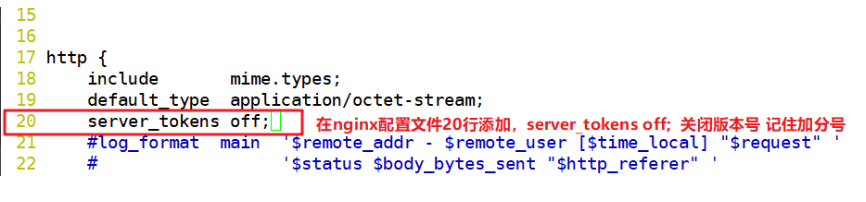
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_tokens off; #Add, close version number
......
}
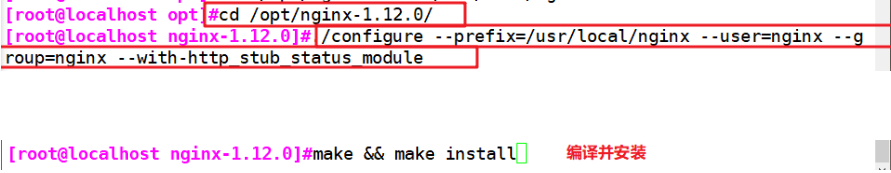
Method 2: modify the source file and recompile the installation
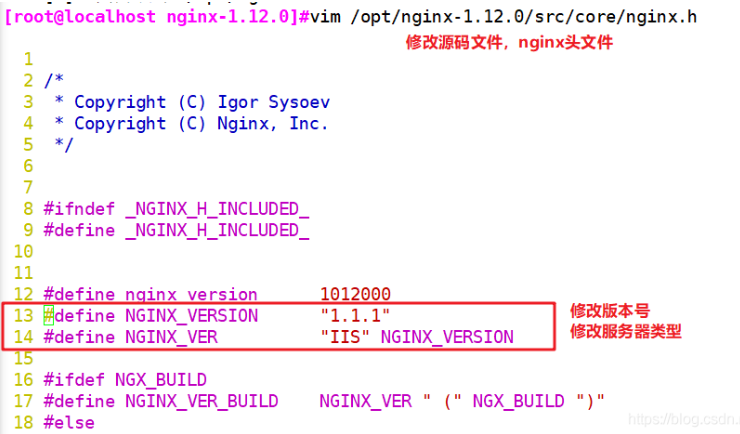
vim /opt/nginx-1.12.0/src/core/nginx.h #define NGINX_VERSION "1.1.1" #Modified version number #define NGINX_VER "IIS" NGINX_VERSION #Modify server type
cd /opt/nginx-1.12.0/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module make && make install
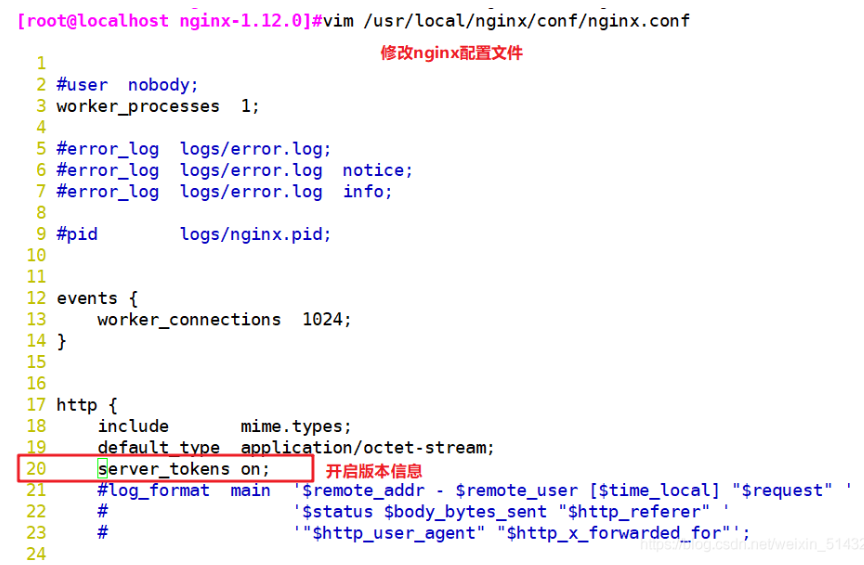
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_tokens on;
......
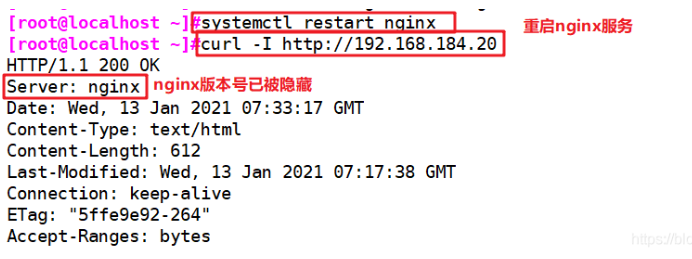
}systemctl restart nginx curl -I http://192.168.184.10
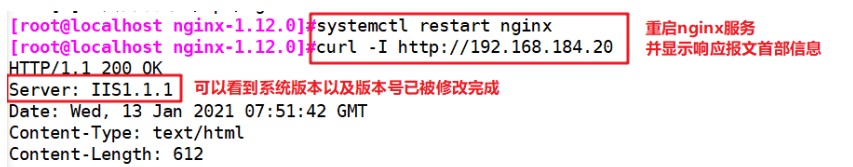
II. Modify users and groups
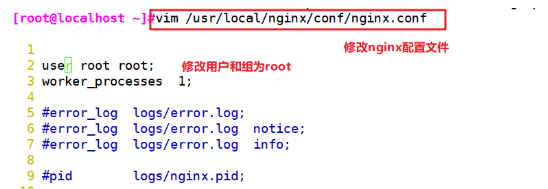
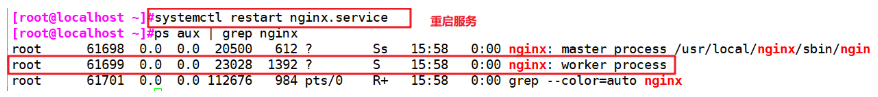
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf user nginx nginx; #Cancel the comment and change the user to nginx and the group to nginx systemctl restart nginx ps aux | grep nginx
III. cache time
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
server {
......
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|jepg|png|bmp|ico)$ { #Add a new location and take the picture as the cache object
root html;
expires 1d; #Specify cache time, 1 day
}
......
}
}
systemctl restart nginx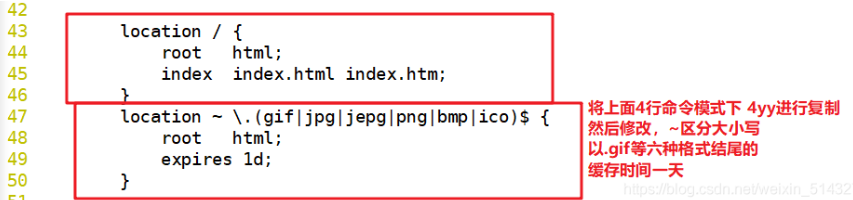
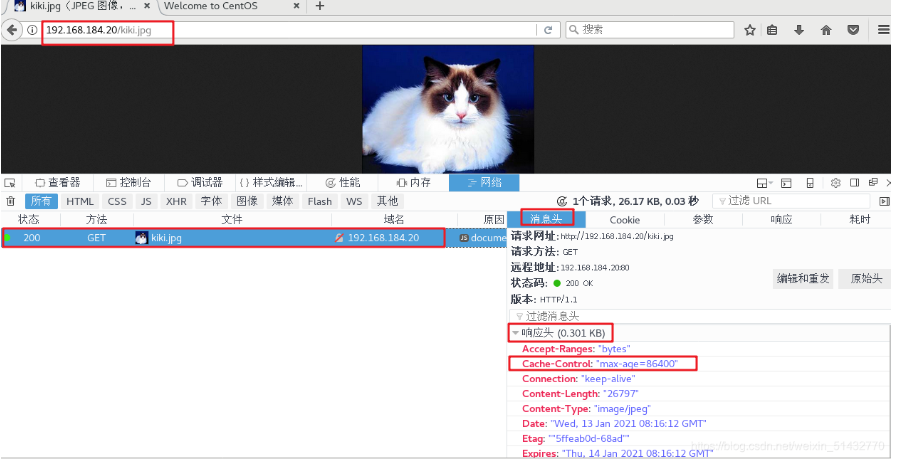
In Linux system, open Firefox browser, right-click to view elements, select network - > select HTML, WS and other
visit http://192.168.80.10 , double-click the 200 response message to see that the response header contains cahce control: Max age = 86400, indicating that the cache time is 86400 seconds. That is, the time of caching for one day. The browser accesses this page within one day by using the data in the cache without sending a new request to the Nginx server, which reduces the bandwidth used by the server.
IV. log cutting
vi /opt/fenge.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Filename: fenge.sh
d=$(date -d "-1 day" "+%Y%m%d") #Displays the time of the previous day
logs_path="/var/log/nginx"
pid_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
[ -d $logs_path ] || mkdir -p $logs_path #Create log file directory
mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log ${logs_path}/kgc.com-access.log-$d #Move and rename log files
kill -USR1 $(cat $pid_path) #Rebuild new log file
find $logs_path -mtime +30 -exec rm -rf {} \; #Delete log files 30 days ago
#find $logs_path -mtime +30 |xargs rm -rf
chmod +x /opt/fenge.sh
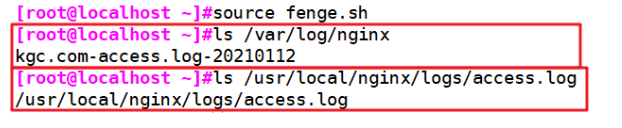
/opt/fenge.sh
ls /var/log/nginx
ls /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log
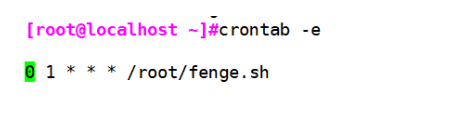
crontab -e
0 1 * * * /opt/fenge.sh

Little knowledge
In the linux operating system, each file has many time parameters, of which three are more important: CTime, atime and mtime
ctime(status time):
When the permissions or attributes of the file are modified, the time will be updated. ctime is not create time, but more like change time,
The time will be updated only when the attributes or permissions of the file are updated, but the time will not be updated if the content is changed.
atime(accesstime):
This time is updated when this file is used.
mtime(modification time):
When the content data of the file is modified, the time will be updated, but the permissions or attributes will not be changed. This is the difference between mtime and ctime.
5, Connection timeout
HTTP has a KeepAlive mode, which tells the web server to keep the TCP connection open after processing a request. If other requests are received from the client, the server will use the unclosed connection without establishing another connection.
KeepAlive remains open for a period of time, during which time they occupy resources. Taking up too much will affect performance.
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
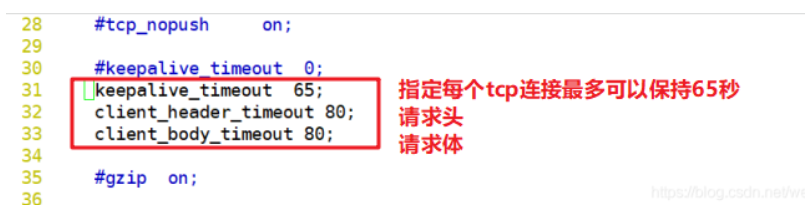
keepalive_timeout 65 180;
client_header_timeout 80;
client_body_timeout 80;
......
}
systemctl restart nginxkeepalive_timeout appoint KeepAlive Timeout for( timeout). Specify each TCP How long can the connection last? The server will close the connection after this time. Nginx The default value of is 65 seconds. Some browsers only hold it for 60 seconds at most, so it can be set to 60 seconds. If it is set to 0, it is disabled keepalive connect. The second parameter (optional) specifies the response header Keep-Alive:timeout=time Medium time Value. This header enables some browsers to actively close the connection, so that the server does not have to close the connection. Without this parameter, Nginx Will not send Keep-Alive Response header. client_header_timeout The client sends a complete message to the server request header Timeout for. If the client does not send a complete message within the specified time request header,Nginx return HTTP 408(Request Timed Out). client_body_timeout Send after the specified client establishes a connection with the server request body Timeout for. If the client does not send any content within the specified time, Nginx return HTTP 408(Request Timed Out).


Vi. number of change processes
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep -c "physical id" #View cpu cores ps aux | grep nginx #See how many child processes are included in the nginx main process vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 2; #Change to the same or twice the number of cores worker_cpu_affinity 01 10; #Set each process to be processed by different CPUs. When the number of processes is set to 4, 0001 0010 0100 1000 systemctl restart nginx
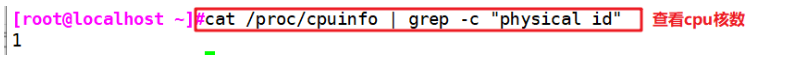

VII. Configure web page compression
• NGX of Nginx_ http_ gzip_ Module compression module provides the function of compressing file content
• allow the Nginx server to compress the output content before sending it to the client, so as to save the website bandwidth and improve the user's access experience. It is installed by default
• corresponding compression function parameters can be added to the configuration file to optimize the compression performance
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
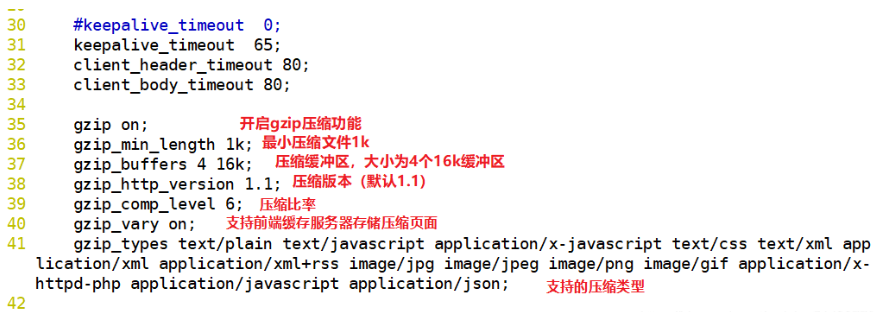
gzip on; #Uncomment and enable gzip compression
gzip_min_length 1k; #Minimum compressed file size
gzip_buffers 4 16k; #Compression buffer, with a size of 4 16k buffers
gzip_http_version 1.1; #Compressed version (default: 1.1, if the front end is squid 2.5, please use 1.0)
gzip_comp_level 6; #compression ratio
gzip_vary on; #Support the front-end cache server to store compressed pages
gzip_types text/plain text/javascript application/x-javascript text/css text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss image/jpg image/jpeg image/png image/gif application/x-httpd-php application/javascript application/json; #Compression type, indicating which web documents enable compression
......
}cd /usr/local/nginx/html First game.jpg File transfer/usr/local/nginx/html Directory vim index.html ...... <img src="game.jpg"/> #Insert picture in web page </body> </html> systemctl restart nginx
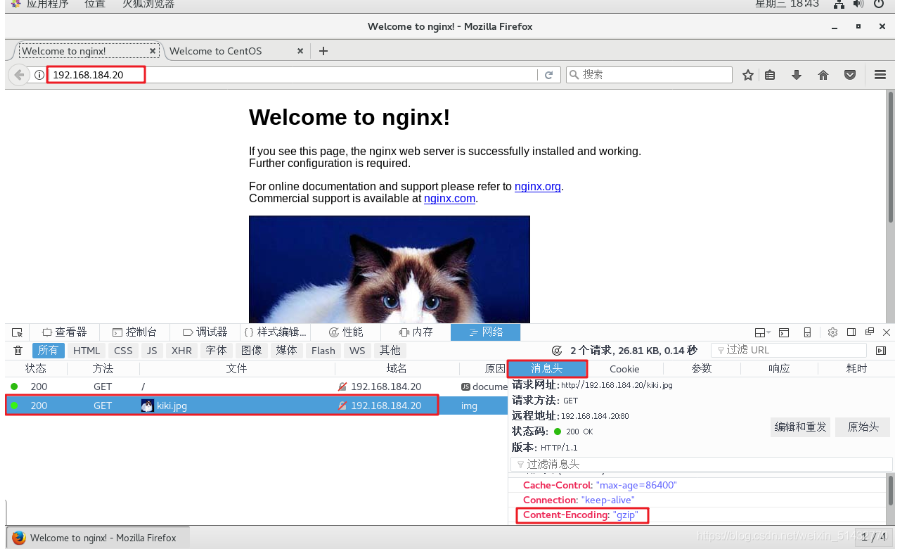
stay Linux In the system, open Firefox browser and right-click to view elements Select network ---> choice HTML,WS,other visit http://192.168. 80.10, double-click the 200 response message to see that the response header contains content encoding: gzip

VIII. Configure anti-theft chain
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
server {
......
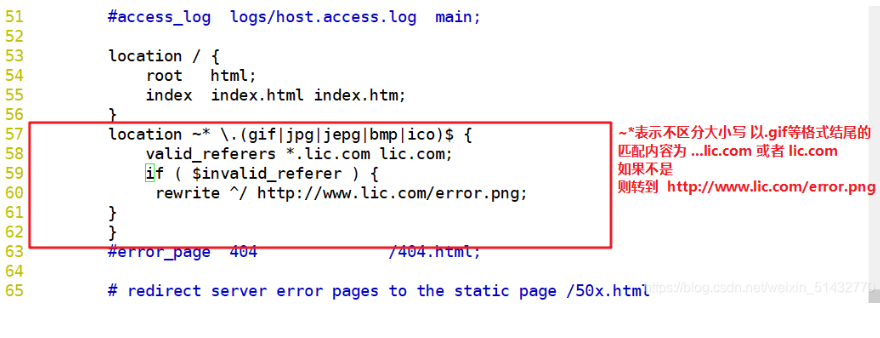
location ~*\.(jpg|gif|swf)$ {
valid_referers *.kgc.com kgc.com;
if ( $invalid_referer ) {
rewrite ^/ http://www.kgc.com/error.png;
#return 403;
}
}
......
}
}~* \.(jpg|gif|swf)$ : This regular expression represents a match. It is not case sensitive to.jpg or.gif or.swf Ending documents; valid_referers : Set up a trusted website to use pictures normally; The following web address or domain name: referer The URL containing the relevant string in the; if Statement: if the source domain name of the link is not in valid_referers In the list listed, $invalid_referer If it is 1, perform the following operations, that is, rewrite or return to page 403
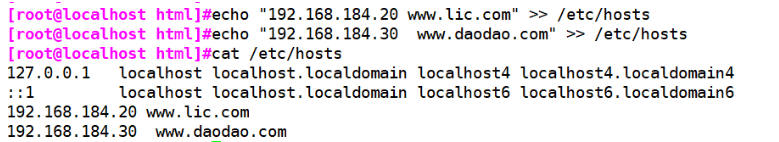
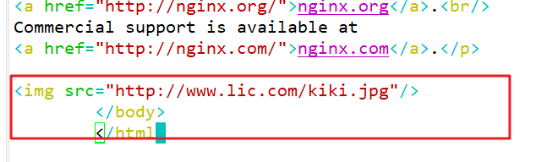
Web page preparation: Web Source host (192).168.80.10)to configure: cd /usr/local/nginx/html take game.jpg,error.png File transfer/usr/local/nginx/html Directory vim index.html ...... <img src="game.jpg"/> </body> </html> echo "192.168.80.10 www.kgc.com" >> /etc/hosts echo "192.168.80.11 www.benet.com" >> /etc/hosts Stealing website host (192).168.80.11): cd /usr/local/nginx/html vim index.html ...... <img src="http://www.kgc.com/game.jpg"/> </body> </html> echo "192.168.80.10 www.kgc.com" >> /etc/hosts echo "192.168.80.11 www.benet.com" >> /etc/hosts Verify the browser on the host of the map stealing website http://www.benet.com


IX. fpm parameter optimization
vim /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf pid = run/php-fpm.pid
vim /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf --96 that 's ok-- pm = dynamic #fpm process startup mode, dynamic --107 that 's ok-- pm.max_children=20 #Maximum number of processes started by fpm process --112 that 's ok-- pm.start_servers = 5 #The number of processes started by default when starting in dynamic mode is between the minimum and maximum --117 that 's ok-- pm.min_spare_servers = 2 #Minimum number of idle processes in dynamic mode --122 that 's ok-- pm.max_spare_servers = 8 #Maximum number of idle processes in dynamic mode kill -USR2 `cat /usr/local/php/var/run/php-fpm.pid` #Restart PHP FPM netstat -anpt | grep 9000