Northwest University of technology NOJ-Python programming problem set:
Noj Python Programming: Season 1: season 1-easy (1-10)
Noj Python Programming: Season 2: Season 2 snippet (11-20)
Noj Python Programming: Season 3: season 3-loop (21-30)
NOJ-Python programming: Season 4: enumeration algorithm (31-40)
NOJ-Python programming: Season 5: modularization (41-50)
Noj Python Programming: Season 6: season 6-string (51-60)
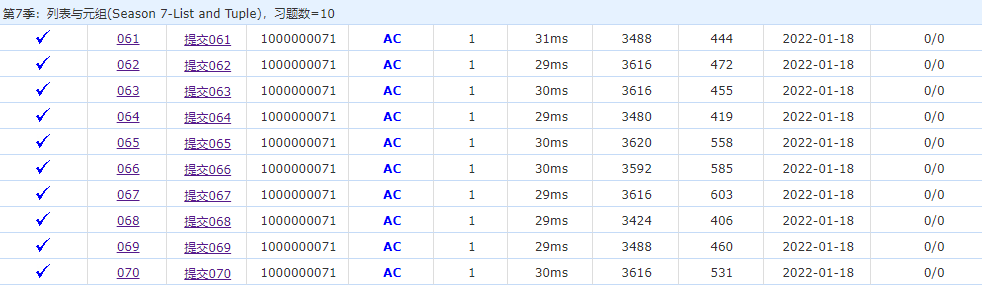
NOJ-Python programming: Season 7: season 7-list and tuple (61-70)
Noj Python Programming: Season 8: season 8-sets and Dictionary (71-80)
Noj Python Programming: Season 9: class (81-90)
Noj Python Programming: Season 10: Season 10 challenges (91-100)
Season 7: season 7-list and tuple (61-70)
Pre knowledge points
It is recommended to understand the basic application of the following function library before completing the topic.
List sorting:
Common methods: assuming L is a list and all elements are integers, you can directly sort from small to large by default. If l.sort(reverse=True), you can sort from large to small. You can also set the key sorting rule internally. For example, l.sort(key=lambda a:a[1]) is equivalent to sorting with the second parameter as the keyword (key=lambda is a fixed writing method).
List element statistics:
l.count(n) indicates the same number of elements in L and n
Tuple type conversion:
If l is a list, it can be converted into tuple by l=tuple(l)
Sorting I
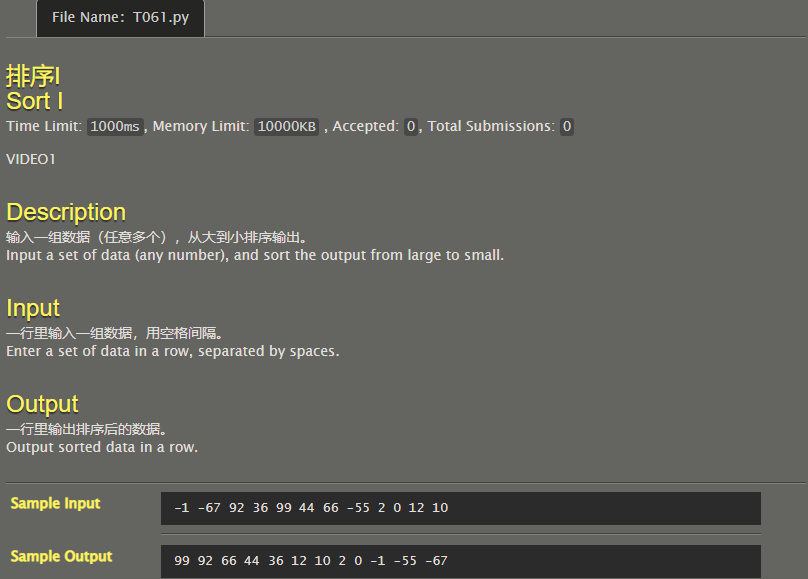
l=list(map(int,input().split()))
l.sort(reverse=True)
for it in l:
print(it,end=' ')
#-1 -67 92 99
# Code By Phoenix_ZH
Inverted tuple
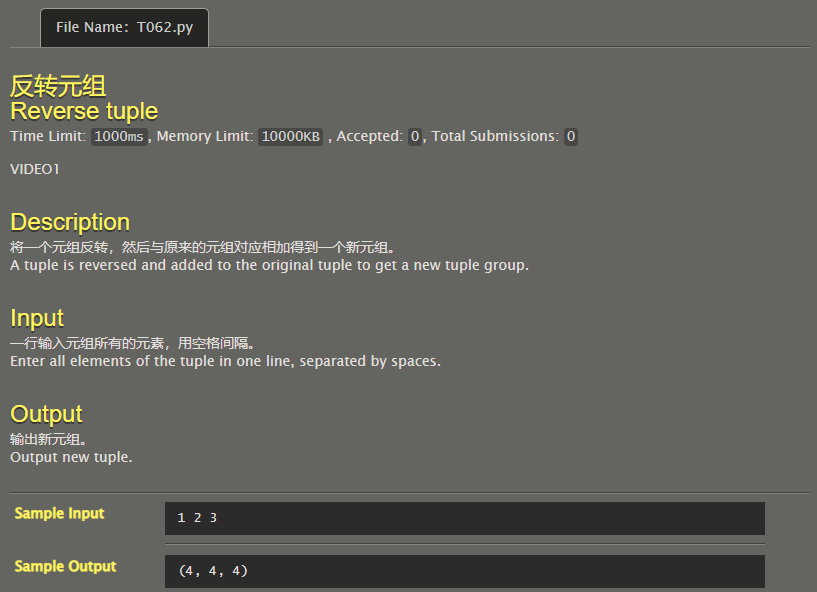
l1=list(map(int,input().split()))
l2=list(reversed(l1))
for i in range(0,len(l1)):
l2[i]=l1[i]+l2[i]
ans=tuple(l2)
print(ans)
# Code By Phoenix_ZH
List slice
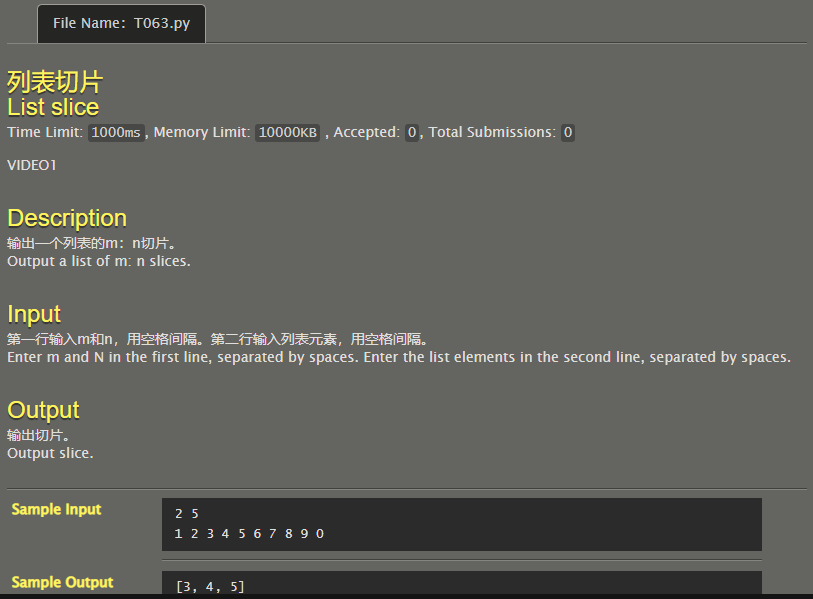
x1,x2=map(int,input().split()) l=list(map(int,input().split())) print(l[x1:x2]) ''' 2 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 ''' # Code By Phoenix_ZH
Element multiplication
l=list(map(int,input().split()))
ans=1
for it in l:
ans=ans*it
print(ans)
# Code By Phoenix_ZH
List differences
First enumerate the elements of l1 list, judge whether they exist in l2, and output non-existent ones; Similarly, just enumerate l2.
l1=list(map(int,input().split()))
l2=list(map(int,input().split()))
for it in l1:
if(it in l2):
continue
print(it,end=' ')
for it in l2:
if(it in l1):
continue
print(it,end=' ')
# Code By Phoenix_ZH
Same cycle
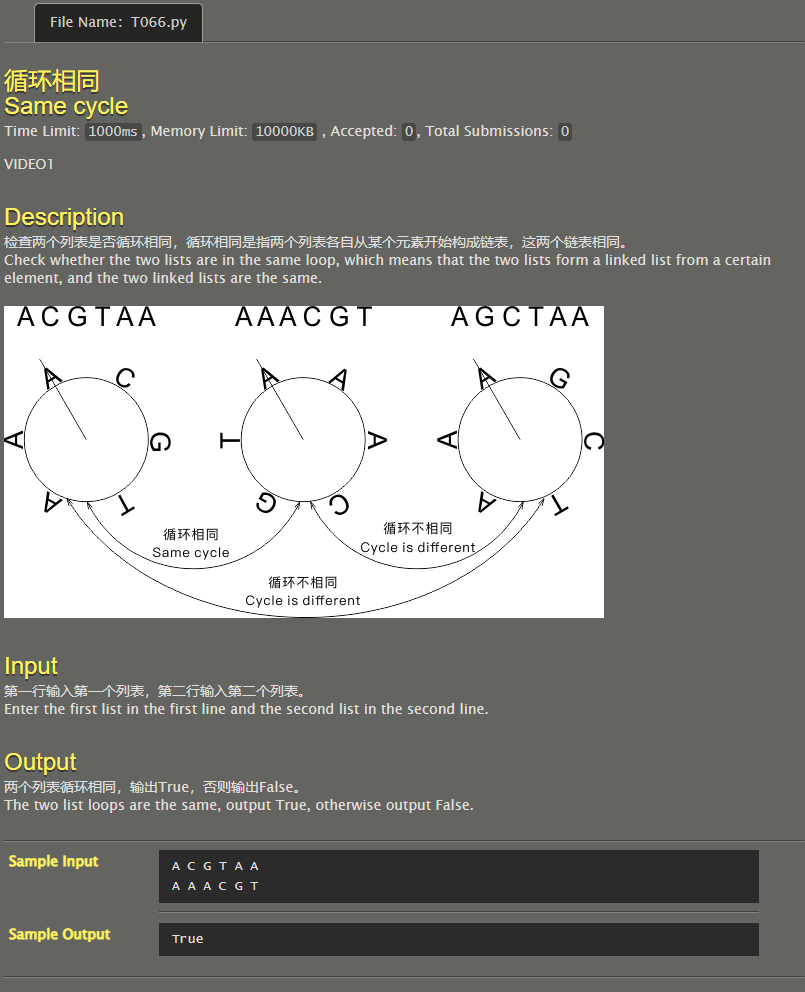
Judge whether the list l1 is the same as l2. Once it is the same, output True and interrupt the program. Otherwise, add the element of the header to the end and delete the element of the header.
import sys
l1=list(input().split())
l2=list(input().split())
for i in range(len(l2)):
if(l1==l2):
print("True")
sys.exit(0)
x=l1[0]
del l1[0]
l1.append(x)
print("False")
'''
A C G T A A
A A A C G T
'''
# Code By Phoenix_ZH
Sort III
Sort with the second element as the keyword
l=input().split(';')
result=[]
for it in l:
it=it.strip('(')
it=it.strip(')')
x,y=map(int,it.split(','))
result.append((x,y))
result.sort(key=lambda a:a[1])#Take the second element of the tuple as the keyword
print(result)
#(1,105);(2,102);(3,104);(4,103);(5,101)
# Code By Phoenix_ZH
Tuple duplicates
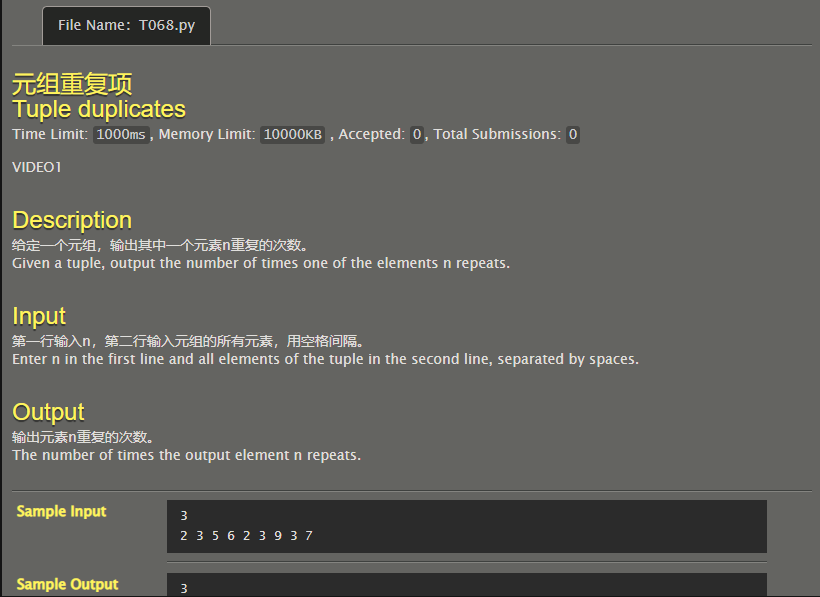
Directly use the count function of the list.
n=int(input()) l=list(map(int, input().split())) print(l.count(n)) # Code By Phoenix_ZH
Sorting II
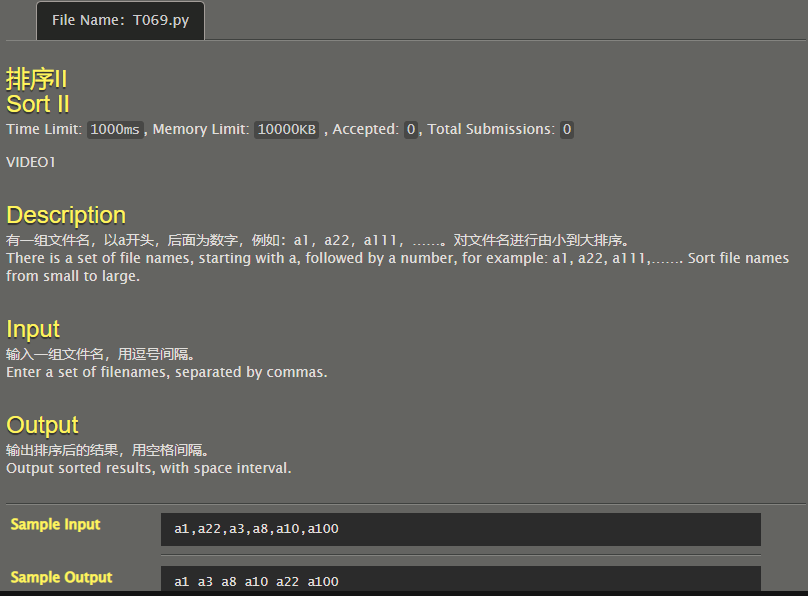
Sort from small to large in integer parts.
l=list(input().split(','))
l.sort(key=lambda a:(int(a[1:])))
for it in l:
print(it,end=' ')
#a1,a22,a3,a8,a10,a100
# Code By Phoenix_ZH
Repeat character
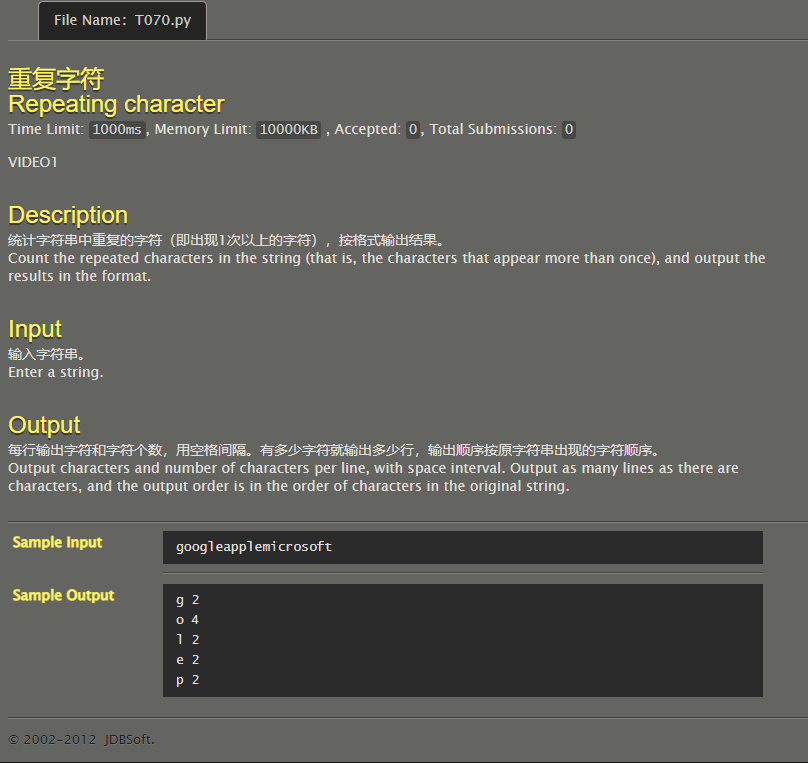
Set a v i s [ ] vis[] vis [] marks characters, traverses them, and then outputs them in order if the number is greater than 1.
vis=[0 for i in range(200)]
s=input()
for it in s:
vis[ord(it)]+=1
for it in s:
if(vis[ord(it)]>=2):
print(it,vis[ord(it)])
vis[ord(it)]=0
#googleapplemicrosoft
# Code By Phoenix_ZH