1, Environment construction
Install centos7 (install locally)
Download vmware
Official website address: https://www.vmware.com/cn.html
Download CentOS7
Official website address: https://www.centos.org/
2, Basic operation
1. Startup and shutdown
Shut down
Command: shutdown
Synchronizing data: sync
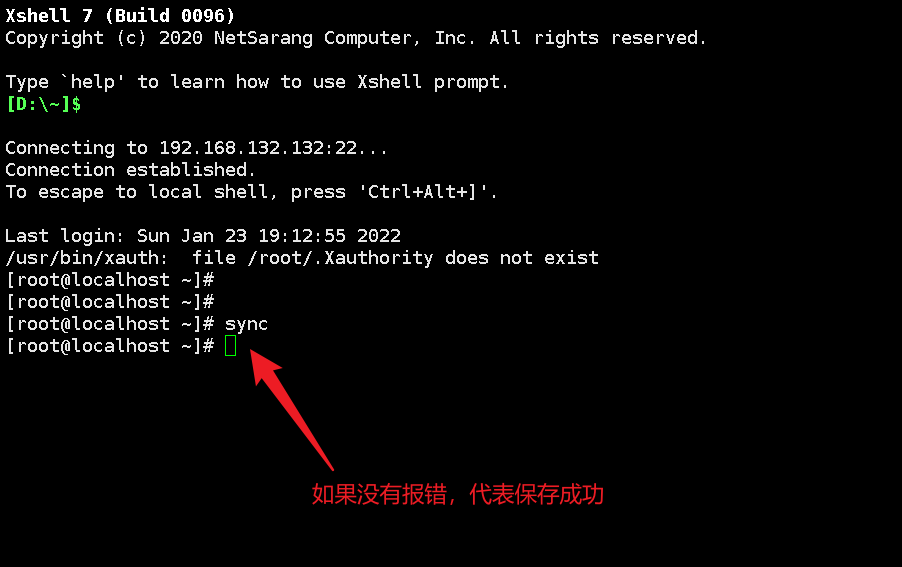
Restart: reboot
2. Directory structure
The functions of each directory are as follows:
| catalogue | |
|---|---|
| /Bin (don't move) | Store binary executable files (ls,cat, mkdir And so on), common commands are generally here. |
| /etc | Store system management and configuration files |
| /home | The root directory where all user files are stored is the base point of the user's home directory. For example, the user's home directory is / home/user, which can be represented by ~ user |
| /usr | It is used to store system applications. The more important directory / usr/local is the installation directory of local system administrator software (installing system level applications). This is the largest directory. Almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory/ usr/x11r6 directory where x window is stored / usr/bin numerous applications / usr/sbin some hypervisors of super users / usr/doc Linux Document / usr / include header files required for developing and compiling applications under linux / usr/lib common dynamic link libraries and configuration files of software packages / usr/man help document / usr/src source code. The source code of Linux kernel is placed in / usr/src/linux / usr/local/bin locally added commands / usr/local/lib locally added libraries |
| /opt | The location of the optional application package for additional installation. In general, we can install tomcat here. |
| /proc | Virtual file system directory is the mapping of system memory. You can directly access this directory to obtain system information. |
| /root | Home directory of super user (system administrator) (privilege class o) |
| /sbin | Store binary executable files, which can only be accessed by root. Here are the system level management commands and programs used by the system administrator. Such as ifconfig. |
| /dev | Used to store equipment files. |
| /mnt | The system administrator installs the installation point of the temporary file system. The system provides this directory for users to temporarily mount other file systems. |
| /Boot (don't move) | Store various files used for system boot |
| /lib | Store the shared libraries and kernel modules required for the operation of programs in the file system. The shared library is also called dynamic link shared library, and its function is similar to that in windows dll file, which stores the shared files required for the operation of the root file system program. |
| /tmp | It is used to store various temporary files. It is a public temporary file storage point. |
| /var | The file used to store the data that needs to be changed during operation is also the overflow area of some large files, such as the log file of various services (system startup log, etc.) Wait. |
| /lost+found | This directory is usually empty. The "homeless" files left by the abnormal shutdown of the system (what's the name of. chk under windows) are here |
3, Common commands
Directory management
Absolute path and relative path
Absolute path: full name
Relative path: relative open
cd
Switch Directory: cd directory name
Current directory:/
Return to the previous level: cd
ls
List directories: ls
Clear command: clear
-a: That is, all, view all files, including hidden files
-l: List all files, including file attributes and permissions, without hidden files
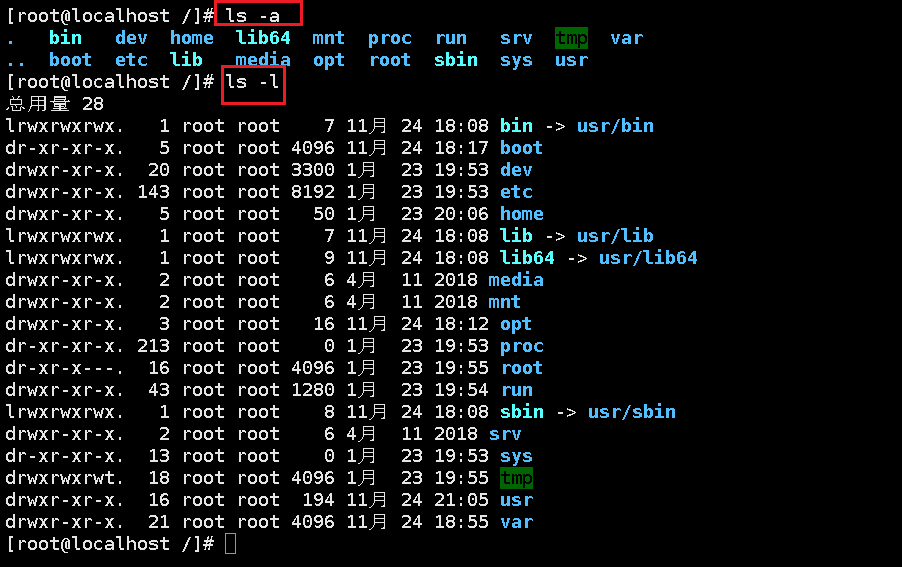
Specific implementation:
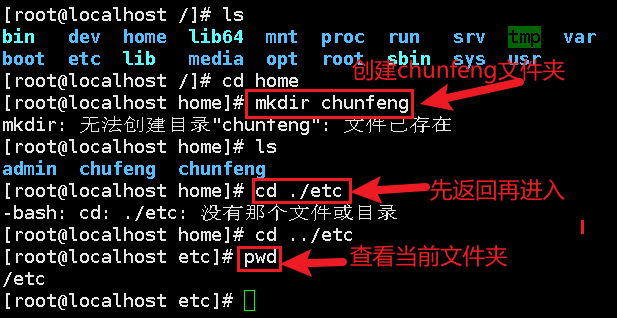
mkdir
Create folder: mkdir folder
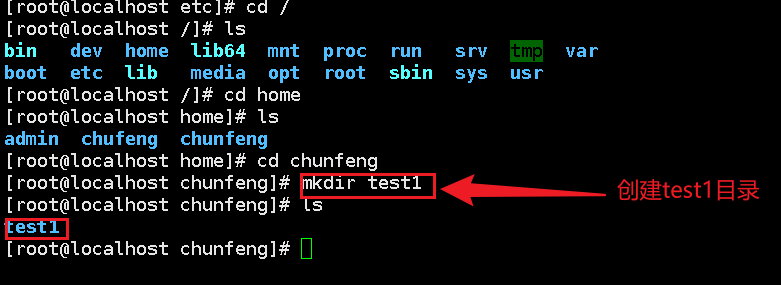
Recursive creation: mkdir -p folder / folder /

rmdir
Delete directory: rmdir folder
Only empty directories can be deleted. If necessary, recursive deletion can be used

cp
Copy directory: cp file location

rm
Note: this command is dangerous and should be used with caution
-f ignore nonexistent files, that is, force deletion
-r recursively delete directories
-I interactive, i.e. asking whether to delete
Danger command:
rm -rf / #Delete all files in the system, delete the library and run away

mv
Moving files: mv file locations
-f forced movement
-u replace only updated files
[root@localhost admin]# cd .. [root@localhost home]# ls admin test.sh [root@localhost home]# mv test.sh admin #move file [root@localhost home]# ls admin [root@localhost home]# cd admin [root@localhost admin]# ls test.sh Public template video picture document download music desktop
Additional effects:

Basic properties
ls
View file properties: ls
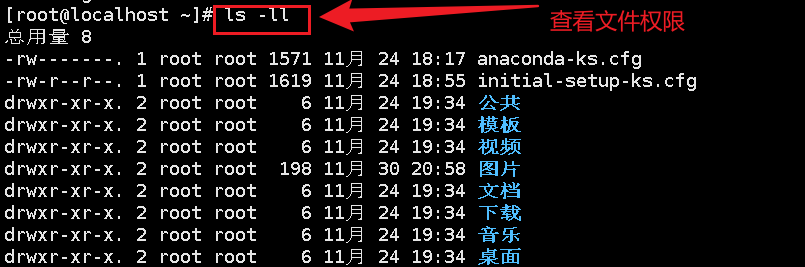
Of which:
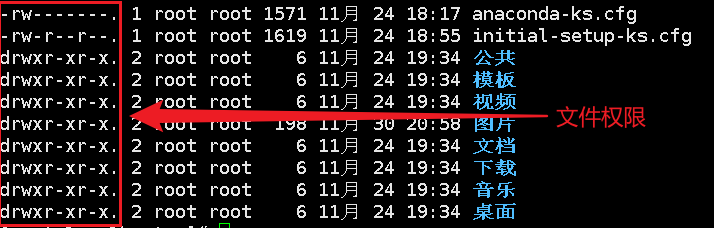
The first letter represents the file type:
[d] Representative directory
[-] Representative document
[l] Represents a linked document
[b] Interface device
The next characters are a group of three, all of which are parameter combinations of [rwx]
[r] Stands for read, [w] stands for write, [x] stands for execute
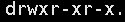
The first group is the primary authority, i.e. root user
For example: rwx
The second group is the group authority, that is, the tourist user
For example: -xr
The third group is other user permissions
For example: - x

chgrp
Change file group: chgrp properties file
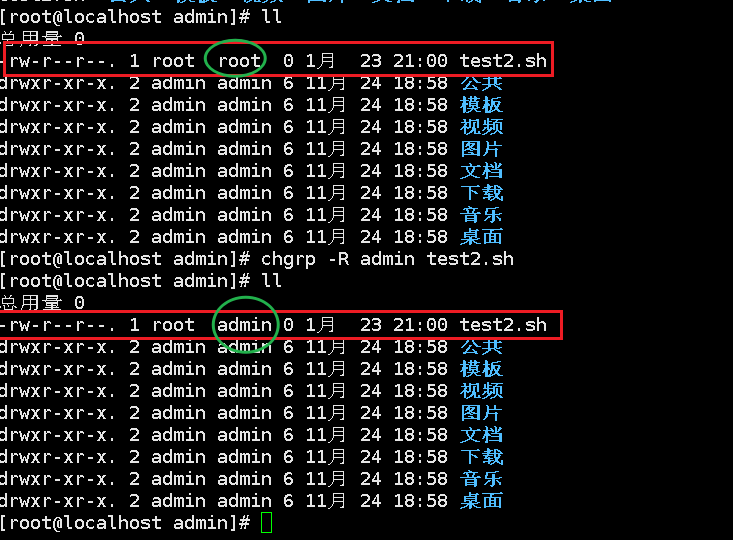
chown
Change owner: chown
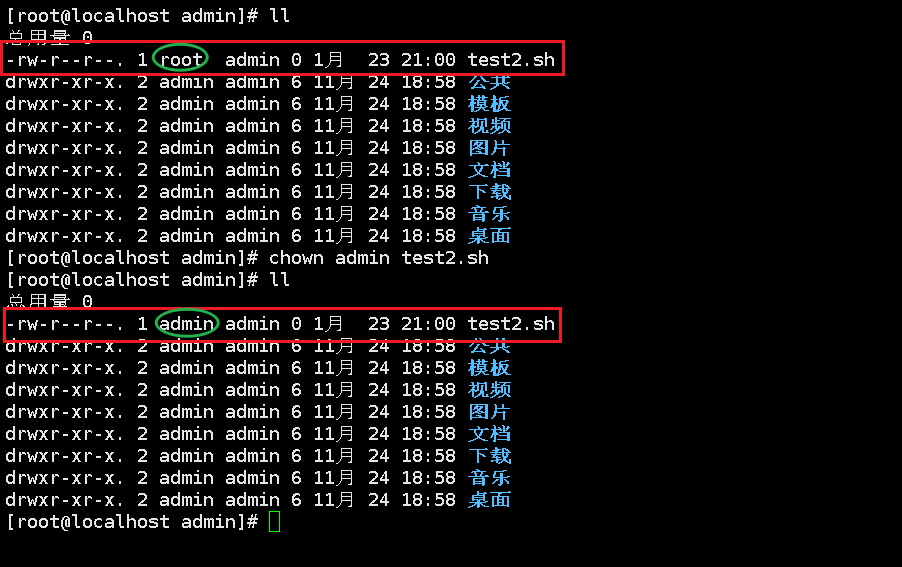
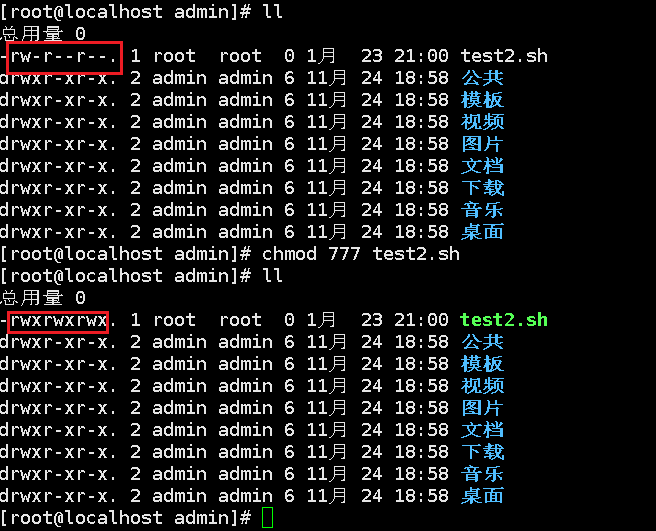
Chmod (to be mastered)
Change file permissions: chmod
Digital identification:
r:4 w:2 x:1
For example:
(rwx)(rwx)(rwx): 4 + 2 + 1 = 7 = > Chmod 777 = > give the highest permission
(rw-)(rw-)(rw-): 4+2=6 => chmod 666
(rwx)(-rw)(--x): 7,6,1 =>chmod 761
File content viewing
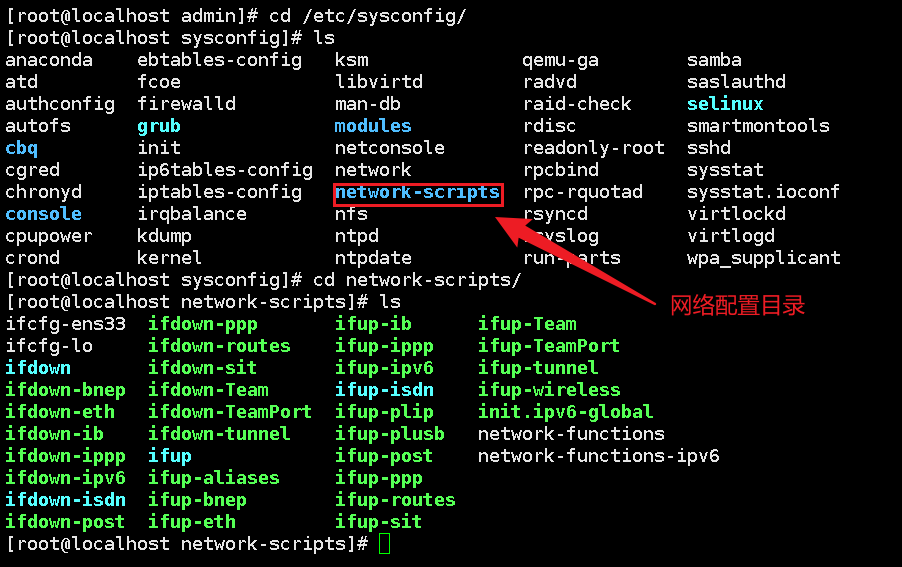
[root@localhost network-scripts]# ping www.baidu.com #ping
PING www.a.shifen.com (112.80.248.75) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 112.80.248.75 (112.80.248.75): icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=30.8 ms
64 bytes from 112.80.248.75 (112.80.248.75): icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=30.5 ms
64 bytes from 112.80.248.75 (112.80.248.75): icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=30.4 ms
64 bytes from 112.80.248.75 (112.80.248.75): icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=32.5 ms
64 bytes from 112.80.248.75 (112.80.248.75): icmp_seq=5 ttl=128 time=30.6 ms
64 bytes from 112.80.248.75 (112.80.248.75): icmp_seq=6 ttl=128 time=30.4 ms
64 bytes from 112.80.248.75 (112.80.248.75): icmp_seq=7 ttl=128 time=30.5 ms
^Z
[1]+ Stopped ping www.baidu.com
[root@localhost network-scripts]# ifconfig #View network configuration
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.132.132 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.132.255
inet6 fe80::39d0:133e:3579:df42 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:4c:d1:b1 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 884 bytes 72358 (70.6 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 709 bytes 72580 (70.8 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 64 bytes 5568 (5.4 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 64 bytes 5568 (5.4 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
virbr0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.122.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.122.255
ether 52:54:00:a0:a3:cc txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
cat
Read file contents in positive order: cat file name
Read configuration file
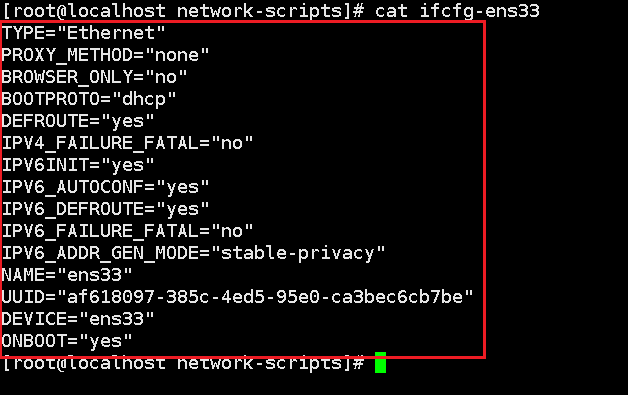
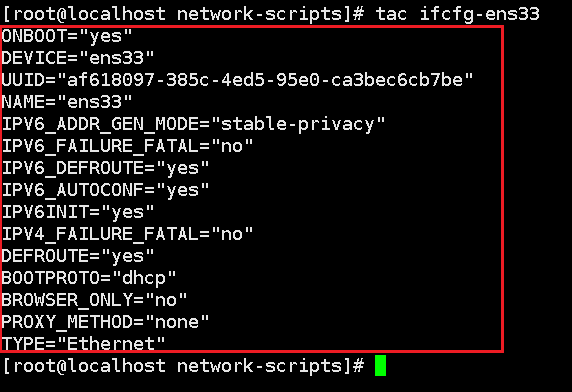
tac
Read file contents in reverse order: tac file name
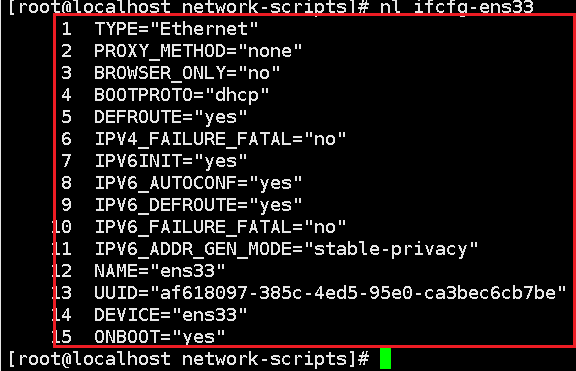
NL (common)
Number of lines you want to display when reading code: nl file
more
Page turning reading: more file
It is recommended to use less, which can turn up the page (space page, enter the next line, up and down keys represent turning the page, press q to exit, look up the string / character, look down the "character", n next, n previous)
Just look at the first few lines: head -n lines file
Just look at the last few lines: tail -n lines file
vim editor
Keyboard diagram:
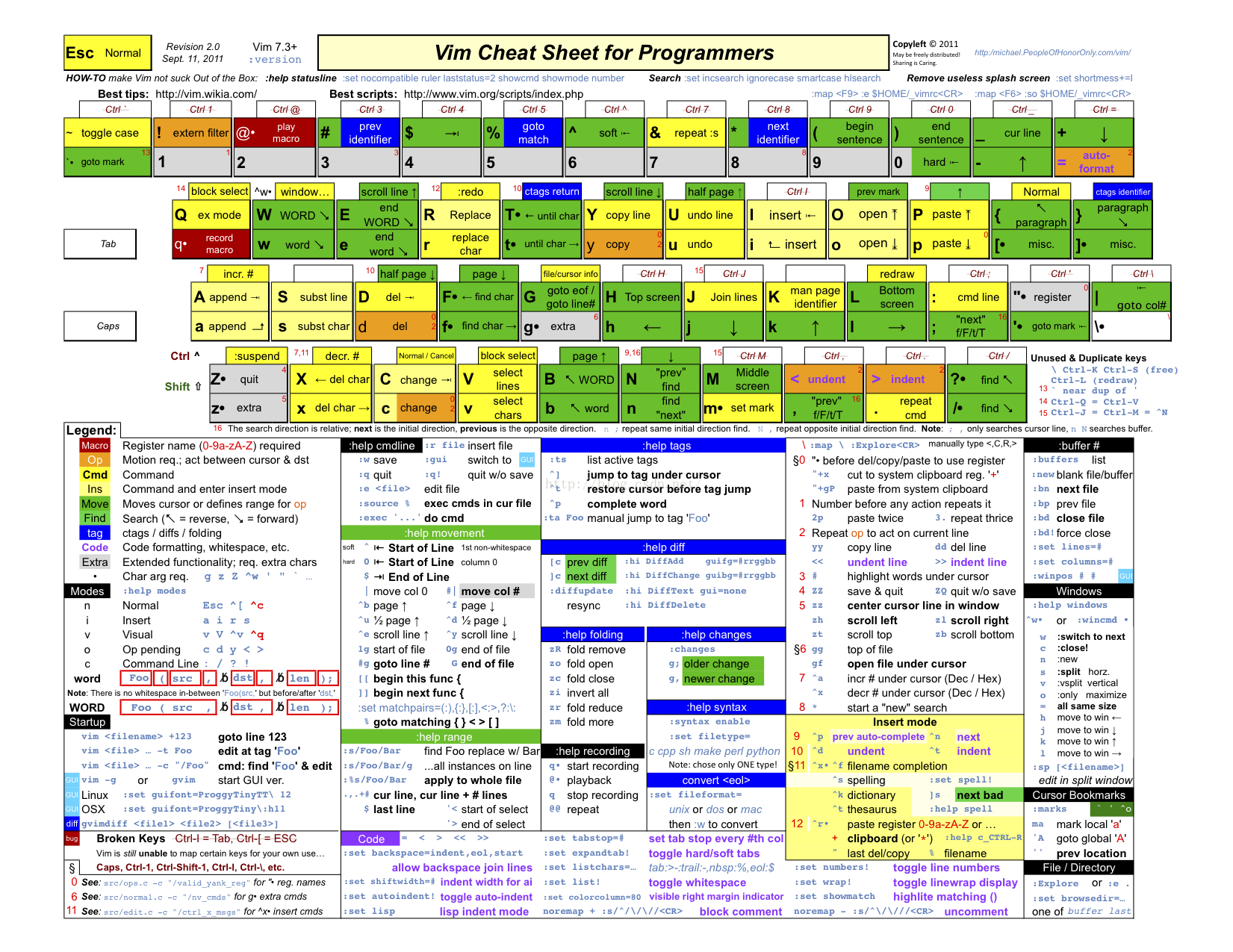
vim has three modes:
Command mode, input mode, bottom line command mode
vim file name create file = > type [i] to enter editing mode = > [ESC] to exit editing mode = > type [:] to enter baseline command mode = > [w] save + [q] to exit
set nu displays the line number
4, Management module
Account management
Add user: useradd - option user name
-m: Automatically create user home directory
-G: Assign user groups
[root@localhost home]# useradd -m chunfeng #Create user home directory [root@localhost home]# ls admin chunfeng
Delete user: userdel -r user name
Modify user: usermod modify content user
Switch user: su user name
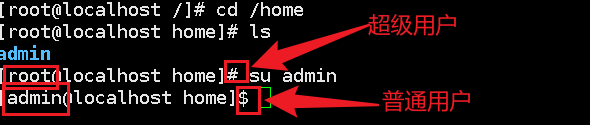
Modify host name: hostname
Modify user password: passwd user name
Freeze user: passwd -l user name
User group management
Add user group: groupadd
Add and specify id: groupadd -g id number group name. If not specified, the id defaults to self increment
Delete user group: groupdel
Modify user group: groupmod -g id number - n name
Switch group: newgrp
View user group: cat /etc/passwd
View password: cat /etc/shadow
Disk management
List disk usage: df
-h detailed
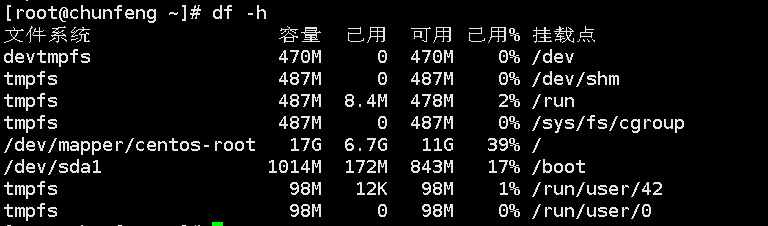
Check current disk usage: du
-a view hidden files
-sm brief information
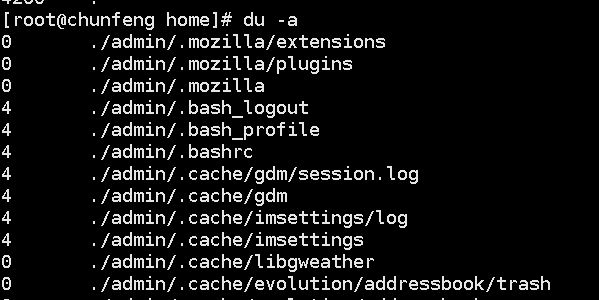
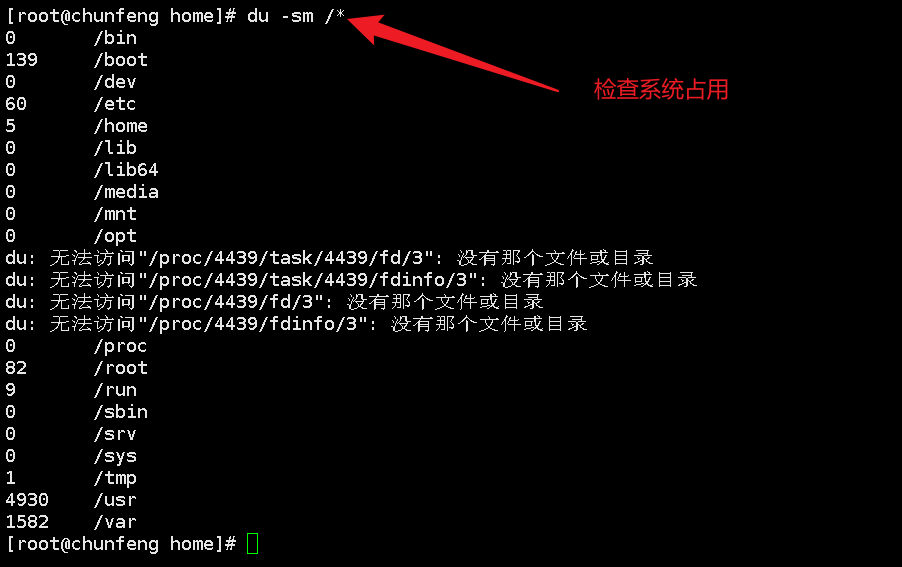
Mount: Mount external device mount directory
Uninstall: umount
-f mandatory
Process management
View current process: ps
-a show all processes
-u displays the current user's progress
-x display background operation
Common commands: ps -aux|grep related applications
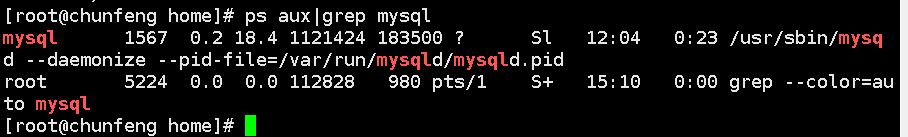
Just remember one command: ps -xx|grep process name
ps -ef: you can view the parent process
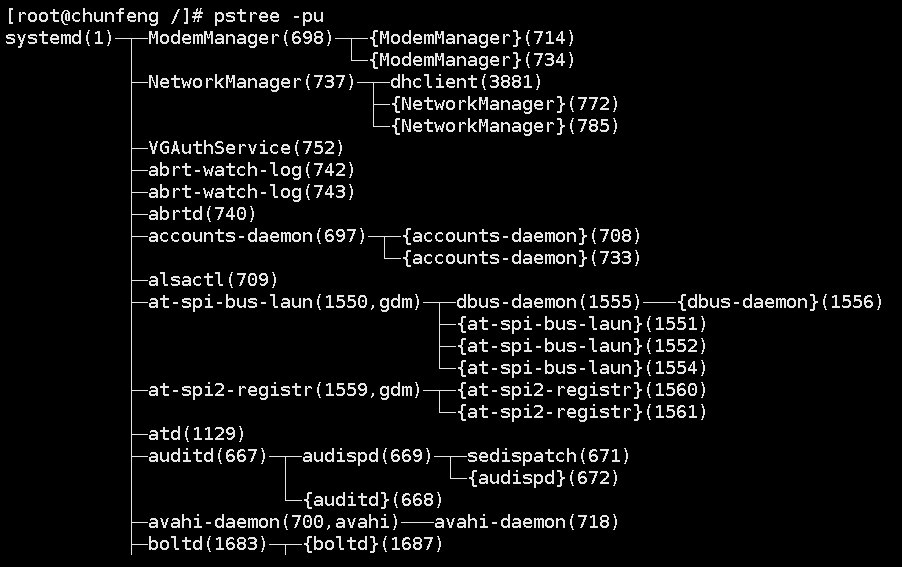
pstree process tree
-p displays the parent id
-u display user groups
pstree -pu is also commonly used
End process: kill id
Force end process: kill -9 id
5, Case
There are three ways to install software:
rpm, decompression installation, yum online installation
jdk installation
1. Download jdk. It is recommended to download it on the official website
2. Installation jdk environment
Note: check the jdk environment java -version,rpm -qa|grep jdk
If so, you need to uninstall RPM - E -- nodeps JDK_ one point eight
After uninstallation, you can install
Installation: rpm -ivh rpm package
3. Configure environment variables
vim /etc/profile
Add this variable: (jdk installation path is followed)
JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7 CLASSPATH=%JAVA_HOME%/lib/;%JAVA_HOME%/jre/lib PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin;$JAVA_HOME/jre/bin export PATH JAVA_HOME CLASSPATH
4. Effective environment configuration
source /etc/profile