Constructor and prototype object
1. Constructor
Constructor: the constructor is mainly used to create an object and assign initial values to the members of the object.
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var p1 = new Person('Zhang San', 18);
var p2 = new Person('Li Si', 19);
console.log(p1.name); // Output result: Zhang San
console.log(p2.age); // Output result: 19
2. Static members and instance members
Instance members refer to members of instance objects, while static members refer to members accessed through classes or constructors.
class Student{
constructor(name){
this.name = name;
}
show(){
console.log("school:",Student.school);
console.log("full name:",this.name);
}
}
Student.school = "University of Posts and Telecommunications"; //Add static member school
var s1 = new Student("Zhang San");
var s2 = new Student("Li Si");
s1.show();
s2.show();
3. Prototype object
Prototype object: each constructor has a prototype object, which is accessed through the prototype attribute of the constructor.
function Person() {} // Define function
console.log(Person.prototype); // Output result: Person {}
console.log(typeof Person.prototype); // Output result: object
be careful:
- The prototype object of the constructor is of type object
- The prototype attribute exists by default
Case: using prototype object sharing method
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
function sayHello(){
console.log("Xi'an");
}
}
//Output the prototype object of Person
console.log("Person Prototype object:",Person.prototype);
//What is the prototype type of construction method:
console.log("Type of prototype object:",typeof Person.prototype);
var p1 = new Person("Zhang San");
var p2 =new Person("Li Si");
//Adding methods to Person through prototype objects
Person.prototype.showAddress = function(address){
console.log("address:",address);
}
Person.prototype.showName = function(){
console.log("full name:",this.name);
}
p1.showAddress("Chang'an District, Xi'an City");
p2.showAddress("Yanta District, Xi'an");
console.log(p1.showAddress === p2.showAddress); //The result is true
p1.showName();
p2.showName();
Prototype chain
1. Prototype object of access object
Prototype object of object: each object has one__ proto__ Property, which points to the prototype object of the object.
function Person() {}
var p1 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__); //Output result: Person {}
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // Output result: true
2. Instance object and prototype object
(1) Instance object
Instance object: an object created using the new operator.
(2) Prototype object
- By constructing the method name (class name) Object from prototype
- By object__ proto__ Property
3. Relationship between instance object and prototype object
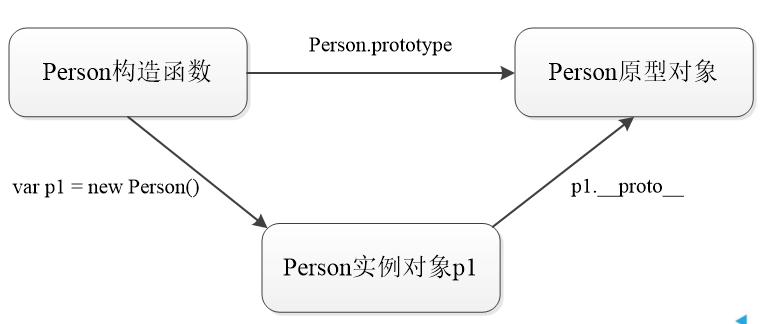
4. Construction method of access object
Constructor of object: there is a constructor attribute in the prototype object, which points to the constructor.
(1) Accessing constructors through prototype objects
Construction method name(Class name).prototype.constructor
function Student(name,gender){ //Construction method
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
}
var s1 = new Student("Guo Jing","male");
var s2 = new Student("Huang Rong","female");
console.log("Prototype object access construction method:",Student.prototype.constructor);
console.log("Prototype object access construction method:",Student.prototype.constructor === Student); //The result is true
(2) Accessing construction methods through instance objects
Object name.constructor
function Student(name,gender){ //Construction method
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
}
var s1 = new Student("Guo Jing","male");
var s2 = new Student("Huang Rong","female");
console.log(s1.constructor); //Instance object construction method
Case: if the prototype object is modified into a new object by assignment, the constructor function cannot be accessed.
function Person(){}
var p1 = new Person();
console.log("Construction method:",p1.constructor); //The result is: construction method: function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {
satHello: function(){ //Method 1
console.log("Hello");
}
}
// Person. prototype. Sathello = fun tion() {/ / method 2. Add a method to the object through the prototype
// console.log("Hello");
// }
var p2 = new Person();
console.log("Construction method:",p2.constructor); //The result is: construction method: function object() {[native code]}
5. Relationship among constructor, prototype object and instance object
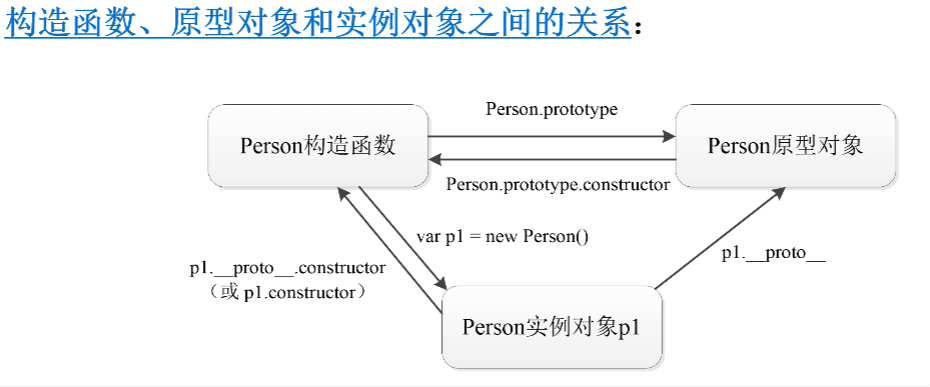
6. Prototype object of prototype object
Prototype object of prototype object: the prototype object is also an object, so this object should also have a prototype object.
function Person(){}
//Output the prototype object of Person
console.log("Person Prototype object:",Person.prototype); //The output result is: prototype object of Person: Person {}
//Prototype object that outputs the prototype object of Person
console.log("Person Prototype object of prototype object:",Person.prototype.__proto__); //The output result is: prototype object of Person prototype object: {}
//Construction method of prototype object for outputting prototype object of Person
console.log("Person Construction method of prototype object:",Person.prototype.__proto__.constructor); //Construction method of prototype object of Person prototype object: function object() {[native code]}
7. Structural features of prototype chain
- Each constructor has a prototype attribute pointing to the prototype object.
- The prototype object points to the constructor through the constructor property.
- By instance object__ proto__ Property to access the prototype object.
- Prototype of Object__ proto__ Property is null.
Structure diagram of prototype chain:
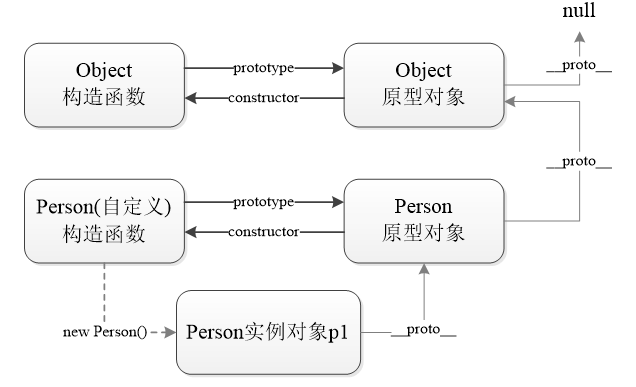
8. Member search mechanism
- JavaScript first determines whether the instance object has this member
- If the prototype object is not found, continue to find the prototype object
- If it is not found until the end, it returns undefined.
function Person(){
this.name = "Zhang San";
}
Person.prototype.name = "Li Si";
var p = new Person();
console.log(p.name); //The output result is: Zhang San
delete p.name; //Delete the name attribute of the object p
console.log(p.name); //The output result is: Li Si
delete Person.prototype.name; //Delete the name attribute of the prototype object
console.log(p.name); //The output result is: undefined
9. [case] using prototype object to expand array method
Array.prototype.sum = function(){
var sum = 0;
for(var i=0;i<this.length;i++){
sum += this[i];
}
return sum;
}
var arr = new Array(1,2,3);
console.log(arr.sum()); //The output is 6