VMware DHCP Service and VMware NAT Sevice
After vmware is installed, these two network services will be installed on the host by default. DHCP is used for IP allocation and NAT service is used for address translation. It is only required in NAT mode.
Adapter VMnet8 and Adapter VMnet1 on the host
The two virtual network cards of the host computer are mainly used to facilitate communication with the virtual machine. Disabling them does not affect the access of the virtual machine to the external network.
VMnet0, VMnet8 and VMnet1 in Vmware
In the NAT connection mode, VMnet8 acts as a virtual router, the ensxx network card of the virtual machine and the Adapter of the host machine VMnet8, NAT device and DHCP server are all connected to the router by default.
VMnet1 is used in host only mode, which is different from NAT mode, This mode does not forward virtual machine requests to the external network.
Bridged mode
In the bridge mode, the system will create a virtual switch on the host. The virtual machine and the host are connected to the switch. The virtual machine and the host are in the same status and in the same network. Equivalent to when the virtual machine is directly connected to the external network. In this case, the virtual machine IP can be manually configured as static IP, or set as DHCP dynamic acquisition if the host computer's network changes frequently. However, whether it is dynamic or static, the virtual machine is required to be consistent with the network segment and subnet mask of the host.
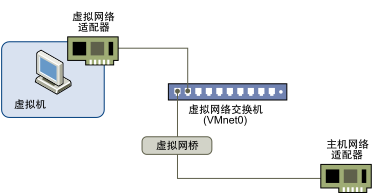
Practice (Bridged mode construction)
For example, the following is the relevant information of the host wireless network card
WLAN adapter WLAN:
Connect specific DNS suffix . . . . . . . :
describe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : Intel(R) Dual Band Wireless-AC 3165
Physical address. . . . . . . . . . . . . : DC-53-60-C8-30-66
DHCP Enabled . . . . . . . . . . . : yes
Auto configuration enabled. . . . . . . . . . : yes
Local link IPv6 address. . . . . . . . : fe80::a121:42ee:8d07:2703%2(be the first choice)
IPv4 address . . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.96.86(be the first choice)
Subnet mask . . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.254.0
Time to obtain lease . . . . . . . . . : 1885 June 29, 2009:11:03
Time when the lease expires . . . . . . . . . : 2019 August 5, 2016:47:21
Default gateway. . . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.96.1
DHCP The server . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.96.1
DHCPv6 IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 232543072
DHCPv6 client DUID . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-1D-D3-7B-ED-20-47-47-72-C9-99
DNS The server . . . . . . . . . . . : 180.168.255.118
116.228.111.18
TCPIP Upper NetBIOS . . . . . . . : EnabledThe related configurations in the virtual machine (taking CentOS 7 as an example) are as follows
[root@localhost network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-ens33 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=static #Static means to set the static IP, and dhcp means to obtain the dynamic IP from the dhcp server through the dhcp protocol. DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=ens33 DEVICE=ens33 ONBOOT=yes GATEWAY=192.168.96.1 #Default gateway (consistent with the host) NETMASK=255.255.254.0 #Subnet mask (consistent with the host) DNS1=180.168.255.118 DNS2=116.228.111.18 IPADDR=192.168.96.222 #Static IP address
NAT mode (Figure 1 is the official picture)
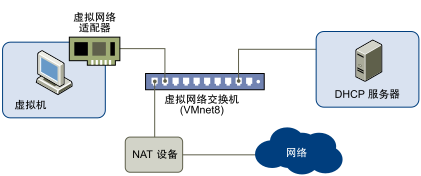
Several characteristics of NAT mode can also be seen from the figure:
- Adapter of virtual machine network card and host VMnet8 (by default), NAT device and DHCP server are all connected to VMnet8 virtual switch by default.
- Virtual machines in NAT network can obtain IP dynamically from DHCP or manually configure static IP.
- In NAT mode, all packets sent by the virtual machine will undergo address translation through the NAT device.
- The host communicates with the virtual machine (in a NAT network) through the Adapater VMnet 8 virtual network card.
- Disabling the Adapater VMnet 8 network card will not affect the communication between the virtual machine and the outside.
In short, in NAT mode, virtual machines can access external networks and hosts. The host can access the virtual machine through the virtual network card. The data packets sent by the virtual machine will be modified by the NAT Service. After the source IP < is changed to the host IP > and the source port < is usually randomly mapped to a port >, they will be sent to the physical LAN through the physical network card, and then sent out< If the host is accessed, it will be received by the physical network card >.
When the response package arrives, Then find the virtual machine in the corresponding intranet through IP and Port, and then transfer the data packet to the virtual machine.
The advantage of NAT mode is network isolation, but the disadvantage is that intranet users share bandwidth (from the perspective of home router) and each request / response packet needs to be converted by the host. Home routers are usually NAT mode.
Default IP address usage in NAT mode (official document: agreement of network IP in NAT mode and host mode)
| Range | Address purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Network. 1 | host | 192.168.0.1 |
| Network. 2 | NAT device | 192.168.0.2 |
| Network. 3 – network. 127 | Static address | 192.168.0.3–192.168.0.127 |
| Network.128 – network.253 | Assigned by DHCP | 192.168.0.128–192.168.0.253 |
| Network.254 | DHCP server | 192.168.0.254 |
| Network.255 | radio broadcast | 192.168.0.255 |
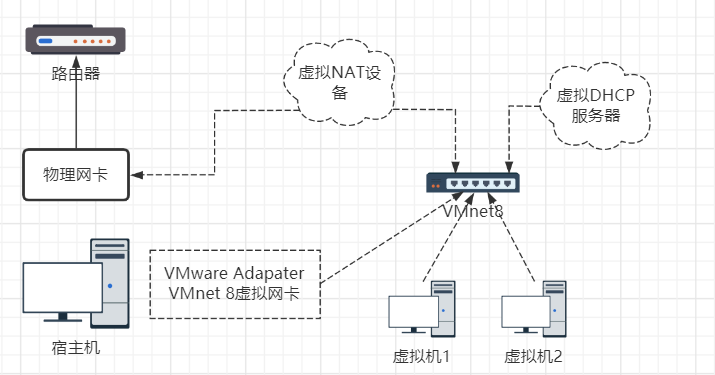
As shown below, as the official said, the default address of Adapter VMnet8 on the host is net.1, the default address of DHCP server is net.254, the default address of NAT device is net.2 (the default is also the gateway address and DNS server address), and the address 128 dynamically assigned to the virtual machine is also in the range of 128 ~ 253.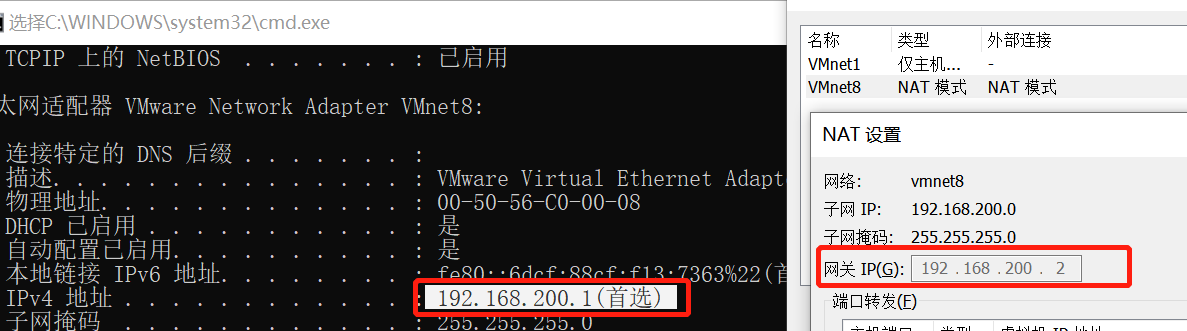
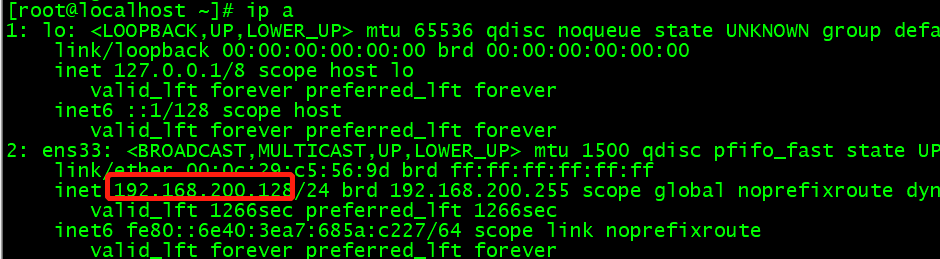
Practice (NAT mode construction)
The construction of NAT is very simple. Just cut the grid mode into NAT, but pay attention to several points
1. Pay attention to the firewall status, which may result in mutual ping with the host.
2. If there is a switch between bridge mode and Nat mode, it is recommended to restore the network, or modify the ifcfg-ens33 file, and then restart the network to avoid mutual influence.
2. It is recommended to modify the / etc / sysconfig / network scripts / ifcfg-ens33 file. It is best to manually configure GATEWAY. If it is not configured after testing, the external network cannot be accessed in some cases.
[root@localhost network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-ens33 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=dhcp #Changing to dhcp means dynamically obtaining the IP address from the dhcp server through the dhcp protocol DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=ens33 DEVICE=ens33 ONBOOT=yes #Change to yes to automatically obtain IP during boot. GATEWAY=192.168.200.2 #After testing, it is not configured in some cases, which may affect the virtual machine's access to the external network, but will not affect the mutual access with the host.
Host only mode (official picture)
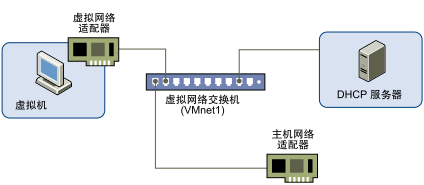
It can be seen from the above that the main difference from NAT mode is that there is no NAT forwarding. VMnet8 of the virtual machine and the host is connected to the private network VMnet1. The virtual machine only communicates with the Adapter VMnet1 virtual network card on the host, and the network is completely included in the host system. Therefore, by default, the virtual machine cannot access the external network. However, it can be realized through the network sharing function The proposed machine is connected to the external network.
The purpose of the default IP address is as follows
| Range | Address purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| net.1 | host | 192.168.0.1 |
| net.2–net.127 | Static address | 192.168.0.2–192.168.0.127 |
| Network.128 – network.253 | Assigned by DHCP | 192.168.0.128–192.168.0.253 |
| Network.254 | DHCP server | 192.168.0.254 |
| Network.255 | radio broadcast | 192.168.0.255 |
In host only mode, the virtual machine can access the external network
The principle is very simple. As mentioned earlier, the virtual machine only communicates with the adapter VMnet1 virtual network card on the host, so we just hang the adapter VMnet1 to other network cards that can access the external network, and then point the gateway of the virtual machine network card (such as ens33) to the adapter VMnet1. (data flow process: ens33 -- > apadapter VMnet1 -- > external network card -- > external network)
The operation steps are as follows:
1. Set host only mode
2. Shared network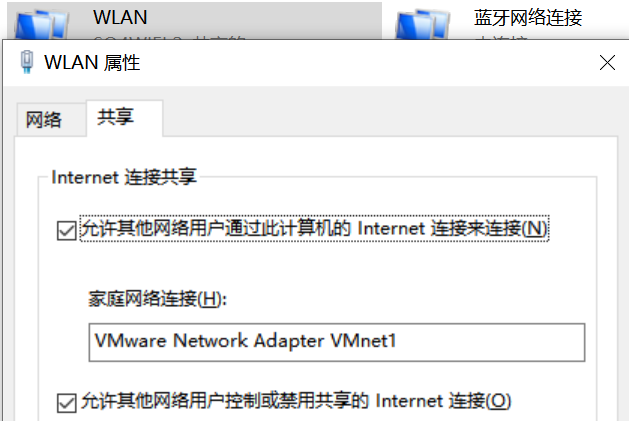
3. Manually set the address of Adapter VMnet1 on the host.
- Auto fetch cannot be set because Adapter VMnet1 is required to act as a gateway
- The IP address needs to be on the same network as Vmnet1, and it is best to comply with the provisions in the above table, that is, configure it as net.1

4. Set the virtual machine ens33 network card gateway and point to the IP of Adapter VMnet1.
[root@localhost network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-ens33 TYPE="Ethernet" PROXY_METHOD="none" BROWSER_ONLY="no" BOOTPROTO="dhcp" ... NAME="ens33" DEVICE="ens33" ONBOOT="yes" GATEWAY=192.168.113.1 #Point to Adapter VMnet1 [root@localhost network-scripts]#
5. Execute dhclient ens33.
(doubtful point: after each systemctl restart network, dhclient ens33 needs to be executed locally to access the external network)
[root@localhost network-scripts]# ps -ef | grep dhclient root 3520 1 0 02:09 ? 00:00:00 dhclient ens33 root 4231 771 0 02:28 ? 00:00:00 /sbin/dhclient -d -q -sf /usr/libexec/nm-dhcp-helper -pf /var/run/dhclient-ens33.pid -lf /var/lib/NetworkManager/dhclient-c96bc909-188e-ec64-3a96-6a90982b08ad-ens33.lease -cf /var/lib/NetworkManager/dhclient-ens33.conf ens33 root 4307 2907 0 02:29 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto dhclient [root@localhost network-scripts]# kill -9 3520 [root@localhost network-scripts]# dhclient ens33 [root@localhost network-scripts]# ping www.baidu.com PING www.a.shifen.com (180.101.49.12) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 180.101.49.12 (180.101.49.12): icmp_seq=1 ttl=52 time=13.1 ms ^C --- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 13.185/13.185/13.185/0.000 ms [root@localhost network-scripts]#