nginx
Open status interface
Enable status:
location /status {
stub_status on;
allow 172.16.0.0/16;
deny all;
}
Example:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /status {
stub_status ;
allow 192.168.129.33;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
How to access the status page: http://server_ip/status
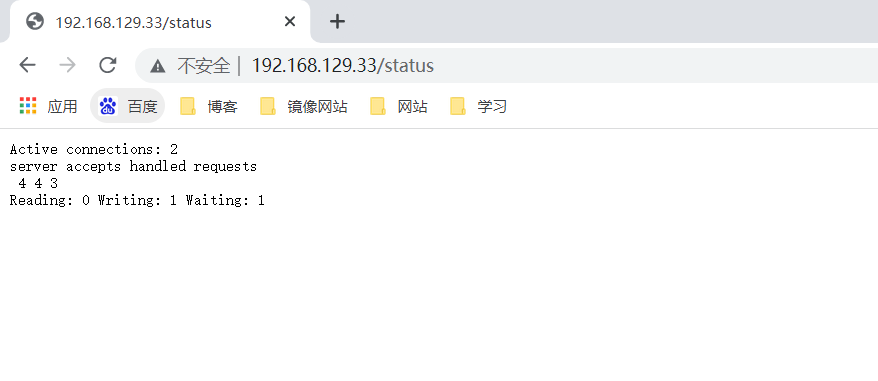
be careful
Reading:
Reasons for large Writing value: low end-to-end processing capacity and slow network
The reason for the large value of Waiting: it means he didn't work
The reason why the Waiting value is small: it means that it is saturated
Detailed information of status page:
| Status code | Meaning of expression |
|---|---|
| Active connections 2 | Current number of all open connections |
| accepts | How many connections were processed in total |
| handled | How many handshakes were successfully created |
| requests | How many requests were processed in total |
| Reading | The number of Header information read by nginx from the client, indicating the number of connections in the receiving request state |
| Writing | The number of Header information returned by nginx to the client, indicating that the request has been received and is in the process of processing the request or sending the response |
| Waiting | When keep alive is enabled, this value is equal to active - (reading + writing), which means that Nginx has processed the resident connection waiting for the next request instruction |
Status page monitoring and configuration
| host name | ip | service | system |
|---|---|---|---|
| localhost | 192.168.129.33 nginx zabbix_agent | centos7 | |
| Server | 192.168.129.250 | zabbix_server | redhat8 |
preparation
localhost installs nginx and zabbix_agent service
Server installation zabbix_server service
Detailed steps view this article
to configure
//Modify the agent configuration file / usr/local/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf
[root@localhost zabbix-5.4.4]# vim /usr/local/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf
UnsafeUserParameters=1 #Uncomment and change the value to 1
Server=192.168.129.250
ServerActive=192.168.129.250 #Server IP
Hostname=NGINX
//Start service
[root@localhost zabbix-5.4.4]# zabbix_agentd
[root@localhost zabbix-5.4.4]# ss -anlt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:10050 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:443 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::*
//Script written
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /scripts
[root@localhost ~]# vim /scripts/check_status.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ `curl -s http://192.168.129.33/status|awk 'NR==4 {print $6}' ` -ne 0 ]
then
echo "1"
else
echo "0"
fi
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /scripts/check_status.sh
[root@localhost ~]# chown -R zabbix.zabbix /scripts/check_status.sh
[root@localhost ~]# ll
Total consumption 4
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 zabbix zabbix 127 10 28 / 22:30 check_status.s
//Modify / usr/local/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf
Test script
[root@localhost ~]# ./scripts/check_status.sh 0
Configuring zabbix profiles
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf Write the following: UserParameter=check_keepalived[*],/scripts/check_status.sh $1 #Uncomment line 331 and add content [root@localhost ~]# pkill zabbix [root@localhost ~]# zabbix_agentd
Server test
[root@Server ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.129.33 -k check_status #Server test 0
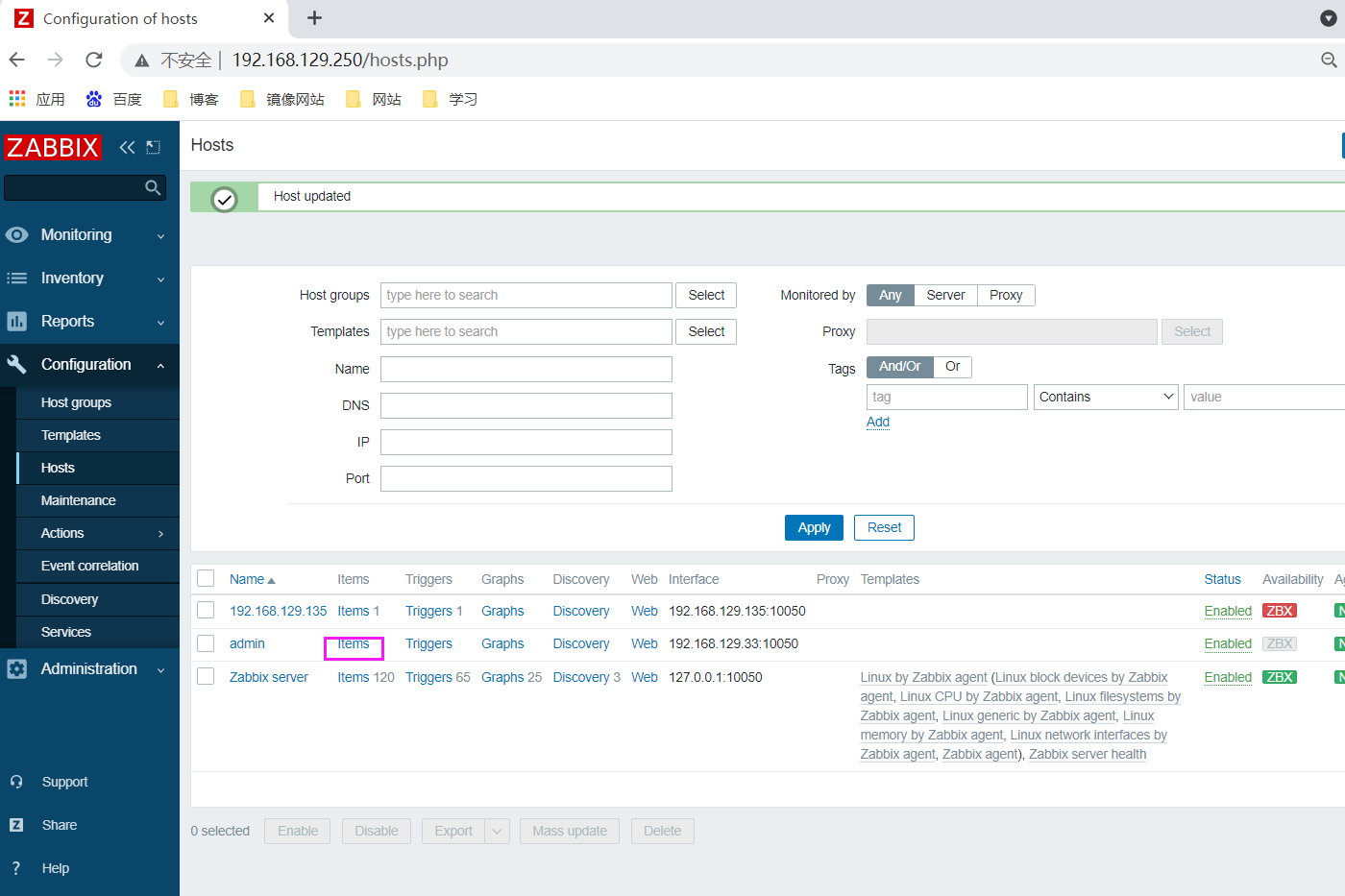
Configure zabbix page
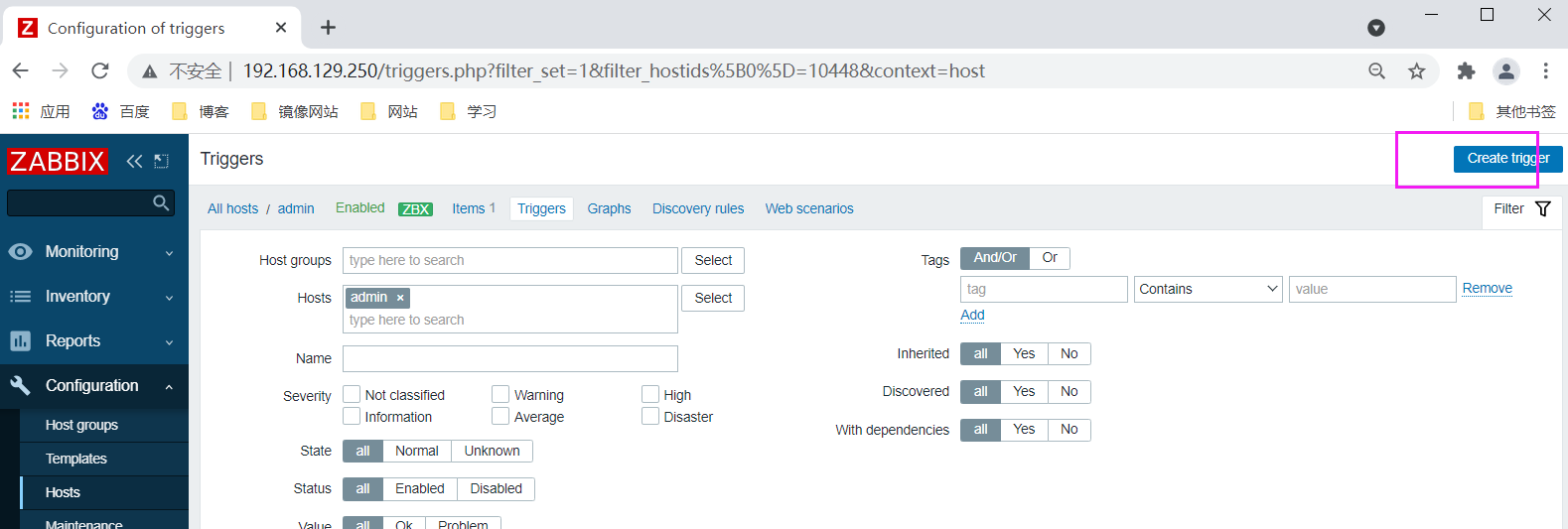
Create host


Create monitor item
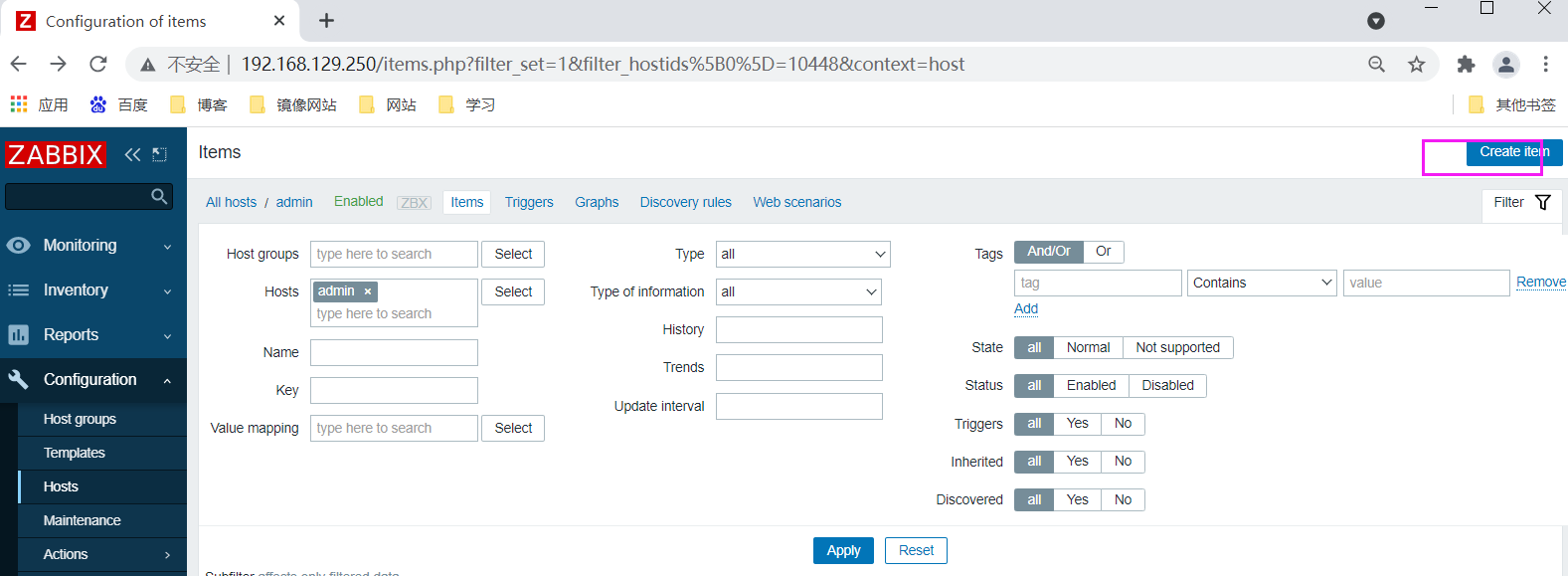


Create trigger




Add trigger

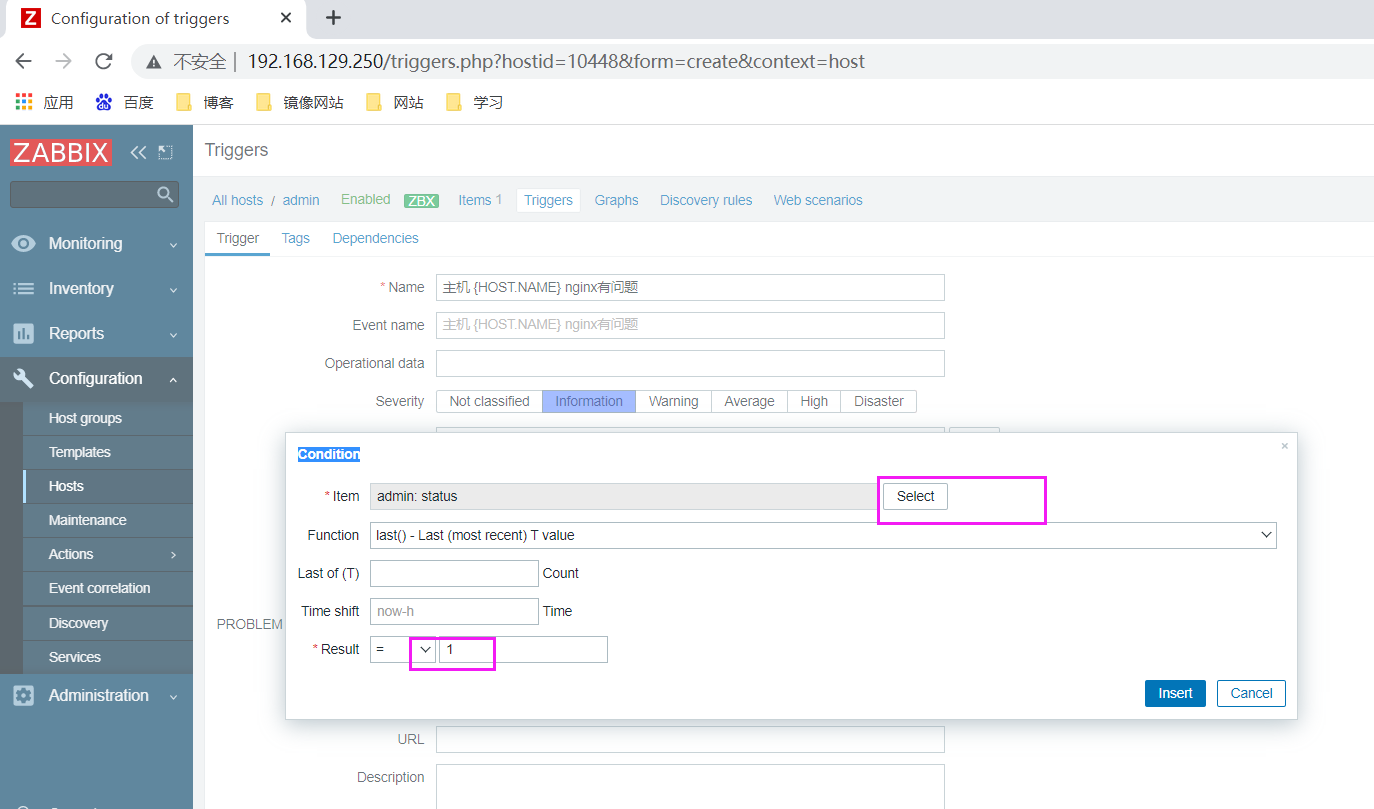


rewrite
Syntax: rewrite regex replacement flag;, For example:
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 break;
Here, $1 is used to refer to the matching content (. *. jpg), such as:
rewrite ^/bbs/(.*)$ http://www.idfsoft.com/index.html redirect;
As shown in the above example, the replacement can be a path or a URL
Common flag
| flag | effect |
|---|---|
| last | Basically, this flag is used to indicate the end of the current match and continue to match the next match, up to 10 to 20. Once the rewrite rule is completed, it will no longer be processed by other rewrite rules. Instead, the user agent will re request the rewritten URL and perform a similar process from the beginning |
| break | Abort rewriting and no longer continue matching. Once the rewriting of this rewriting rule is completed, the user agent will re initiate the request for the new URL and will no longer be checked by any rewriting rule in the current location |
| redirect | Return the new URL in the HTTP status 302 of temporary redirection |
| permanent | Return the new URL in permanently redirected HTTP status 301 |
The rewrite module is used to perform URL redirection. This mechanism is conducive to removing malicious URLs and search engine optimization (SEO)
break example 1
- break this rule will terminate upon completion of matching and will no longer match any subsequent rules
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@localhost html]# mkdir imgs
[root@localhost html]# ls
50x.html imgs index.html test
[root@localhost html]# ls images/
1.gif 2.webp
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.webp)$ /imgs/$1 break;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
Browser access test

break example 2
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.webp)$ https://www.linuxprobe.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/2653e3c945f3ca8b91108ccf35b8aa81.jpg-wh_651x-s_3754039934.jpg break;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
Browser access test

redirect example 1
- redirect returns 302 temporary redirection, and the browser address will display the URL address after the jump
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@localhost html]# mkdir imgs
[root@localhost html]# ls
404.html 50x.html imgs index.html
[root@localhost imgs]# ls
1.gif 2.webp
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.webp)$ http://images.baidu.com/ redirect;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
Browser access test

Example 1 of the combination of last and break
- last, after this rule is matched, continue to match the new location URI rule downward
- break this rule will terminate upon completion of matching and will no longer match any subsequent rules
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@localhost html]# mkdir imgs
[root@localhost html]# ls
404.html 50x.html imgs index.html
[root@localhost imgs]# ls
1.gif 2.webp
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.webp)$ /imgs/$1 last;
}
location /imgs {
rewrite ^/imgs/(.*\.webp)$ http://images.baidu.com/ last;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
Browser access
Find the page to access the second rule

Example 2 of the combination of last and break
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@localhost html]# mkdir imgs
[root@localhost html]# ls
404.html 50x.html imgs index.html
[root@localhost imgs]# ls
1.gif 2.webp
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.webp)$ /imgs/$1 break;
}
location /imgs {
rewrite ^/imgs/(.*\.webp)$ http://images.baidu.com/ last;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
Browser access
Find the page to access the first rule
redirect example
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.webp)$ /imgs/$1 redirect;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
The browser access status code becomes 302

permanent example
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /images {
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.webp)$ /imgs/$1 permanent;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
......
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
The browser access status code changes to 301

The syntax used by nginx is derived from the Perl compatible regular expression (PCRE) library. The basic syntax is as follows:
| identifier | significance |
|---|---|
| ^ | Must start with an entity after ^ |
| $ | Must end with an entity before $ |
| . | Match any character |
| [] | Matches any character in the specified character set |
| [^] | Matches any string that is not included in the specified character set |
| | | Match entities before or after |
| () | Grouping, forming a group of entities for matching, usually assisted by | |
Capture subexpressions. You can capture any text placed between (), such as:
^(hello|sir)$ //Result captured for string "hi sir": $1=hi=sir //These captured data can be used as variables later
if
Syntax: if (condition) {...}
Application scenario:
- server segment
- location segment
Common condition s
- Variable name (if the variable value is an empty string or starts with "0", it is false, and others are true)
- Comparison expressions with variables as operands (can be tested with comparison operators like =,! =)
- Pattern matching operation of regular expression
- ~: case sensitive pattern matching check
- ~*: case insensitive pattern matching check
- ! And! *: Reverse the above two tests
- Test the possibility that the specified path is a file (- f,! - f)
- Test the possibility that the specified path is a directory (- d,! - d)
- Test the existence of files (- e,! - e)
- Check whether the file has execution permission (- x,! - x)
Browser based separation case
if ($http_user_agent ~ Firefox) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /firefox/$1 break;
}
if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break;
}
if ($http_user_agent ~ Chrome) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /chrome/$1 break;
}
Anti theft chain case
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|jpeg|png)$ {
valid_referers none blocked www.idfsoft.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite ^/ http://www.idfsoft.com/403.html;
}
}