From[ http://blog.csdn.net/ab1322583838/article/details/52054260]
This blog has a clear explanation on color processing. It is also the place I should learn when I write a blog in the future.
I. Goals
Learning the use of Mat and the method of assigning initial values to Mat images
2. Function Description
Mat red_img(Size(), CV_8UC3, Scalar());
First parameter: Set the size of the image matrix
Second parameter: Set the type of image, CV_8UC3 refers to an 8-bit unsigned integer three-channel matrix
The third parameter: represents an array with four elements. This type is widely used in OpenCV to transfer pixel values. In this section, we will further use it to represent RGB color values (three parameters). If you do not use the fourth parameter, you do not need to define it.
Let's take an example, if we give the following color parameter expressions:
Scalar( a, b, c )
Then the RGB color values defined are: Red = c, Green = b, Blue= a
3. Program Code
#include "cv.h" // OpenCV File Header
#include "highgui.h"
#include "cvaux.h"
#include "cxcore.h"
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// Initialization of image matrix
Mat red_img(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 255));//Red image
Mat white_img(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(255));//White image
Mat black_img = Mat::zeros(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3);//Black image
// Re-assigning the channel of the image
Mat green_img = red_img.clone();//The purpose of this operation is to obtain pixels of the same size as red pictures.
green_img = Scalar(0, 255, 0);//Green image
namedWindow("red image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE | CV_WINDOW_FREERATIO);// Create a window
namedWindow("white image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE | CV_WINDOW_FREERATIO);// Create a window
namedWindow("black image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE | CV_WINDOW_FREERATIO);// Create a window
namedWindow("green image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE | CV_WINDOW_FREERATIO);// Create a window
imshow("red image", red_img);// Display pictures in Windows
imshow("white image", white_img);// Display pictures in Windows
imshow("black image", black_img);// Display pictures in Windows
imshow("green image", green_img);// Display pictures in Windows
waitKey(0);// Waiting for a button to close the program
}IV. Interpretation
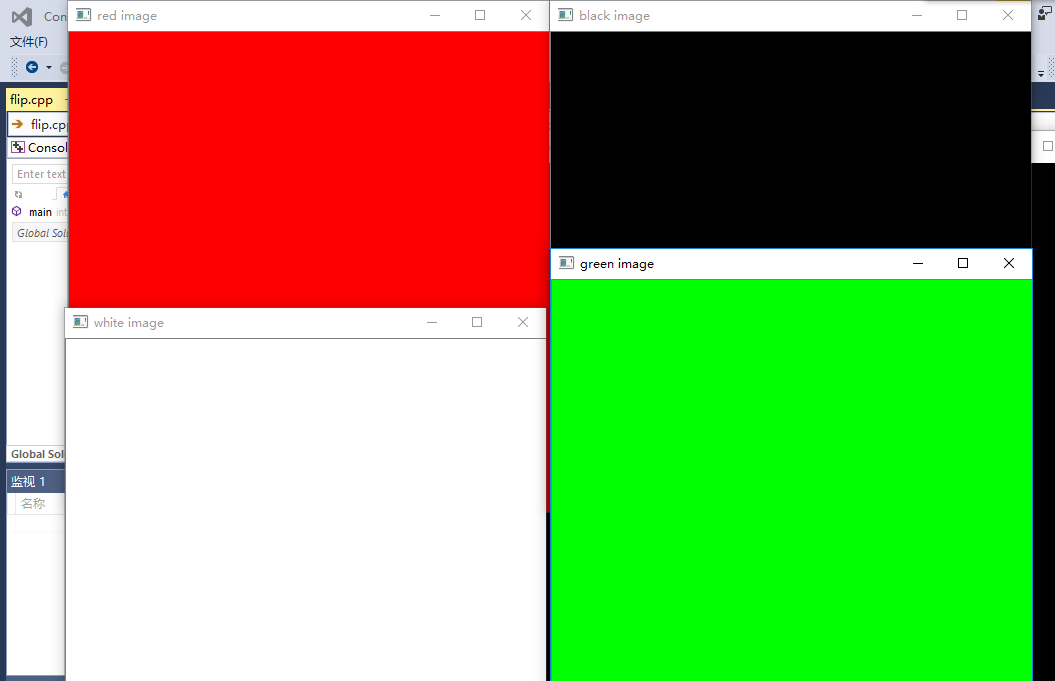
1. Red image
Mat red_img(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 255));2. White image
Mat white_img(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(255));Size(480, 480) is an image matrix that defines a 480 x 480. CV_8UC3 is an 8-bit unsigned integer three-channel matrix. Scalar::all(255) means that in these three channels, channel B is 255, channel G is 255, and channel R is 255.
3. Black image
Mat black_img = Mat::zeros(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3);zeros() denotes the initialization of a black image matrix with all values of 0.
It is equivalent to
Mat black_img(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0));
Mat black_img(Size(480, 480), CV_8UC3, Scalar(0,0,0));4. Green Image
Mat green_img = red_img.clone();
green_img = Scalar(0, 255, 0);//Green imageMat green_img = red_img.clone(); denotes that green_img is the same as red_img and is cloned by red_img.
green_img = Scalar(0, 255, 0); means to reassign the three channels, in which B channel is 0, G channel is 255, R channel is 0.
V. RESULTS
The results are as follows: