Optimize database model structure and modify query mode
Optimize database
The main purpose of optimizing the database here is to adapt to the query methods, such as in the second-hand car of melon seeds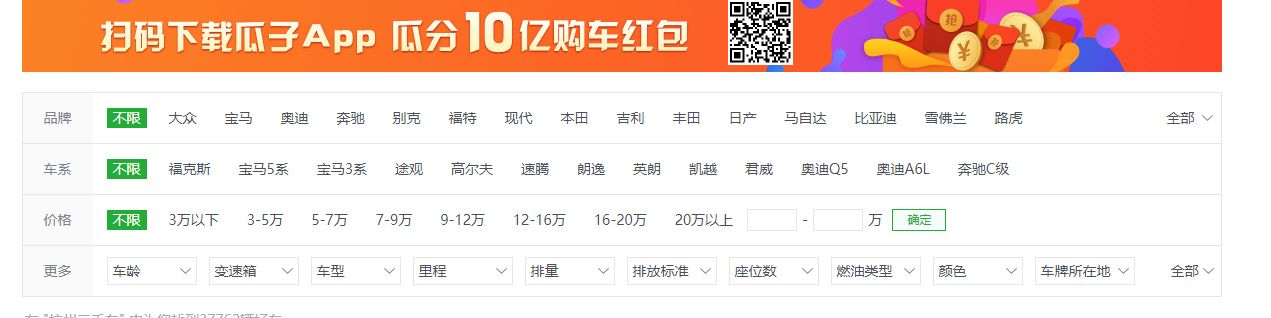
He inquires from the brand, car series and price. There may be some problems in the previous queries. First, there are duplicate brand data. Second, when he inquires about the car series, he cannot find the corresponding brand very well.
Then there are some problems in the later part, but now it's just a test, so modify this part first.
To complete the connection between the brand and the car series, you have to separate the previous brand table and the car series table to write an association table. Then the car series also needs to be associated with the car series table, so the modified models are as follows
from . import db
from datetime import datetime
from cars import constants
class BaseModel(object):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
is_delete=db.Column(db.Boolean,default=False)
create_time=db.Column(db.DATETIME,default=datetime.now)# create time
update_time=db.Column(db.DATETIME,default=datetime.now,onupdate=datetime.now)
#create user model
class User(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__='sc_users'
# id=db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True)
name=db.Column(db.String(10),unique=True,nullable=True)
password=db.Column(db.String(100),nullable=True)
phone=db.Column(db.String(11),nullable=False)
indentify =db.Column(db.String(18),nullable=True)
cars= db.relationship('Car',backref='user')
order=db.relationship('Order',backref='user')
def __repr__(self):
return self.phone
class Car(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__='sc_cars'
# id=db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True)
user_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('sc_users.id'))
brand_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('brand.id'))
price= db.Column(db.Integer,default=0,nullable=False)
car_age=db.Column(db.Integer) #age of the car
brand_style_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('brand_style.id'))#style of the car
car_gearbox=db.Column(db.Integer,default=0)#0 for hand,1 for auto
car_distance=db.Column(db.Integer)
car_displacement=db.Column(db.Float)
car_register_time=db.Column(db.DateTime)
car_num=db.Column(db.String(100))
car_color=db.Column(db.String(10))
car_oil_type=db.Column(db.String(10))
car_emission_standard=db.Column(db.String(10))
seat_num=db.Column(db.Integer)
transfer_time=db.Column(db.Integer)
inspect_annually=db.Column(db.String(10))
traffic_compulsory_insurance=db.Column(db.String(10))
commercial_insurance=db.Column(db.String(10))
images=db.relationship('Carimg',backref='img')
index_image_url=db.Column(db.String(100))
Car_is_collected_by=db.relationship('User',backref='one_car_to_many_users')
orders=db.relationship('Order',backref='orders')
def to_detail_dict(self):
new_dict={
'distance':self.car_distance,
'index_image_url':self.index_image_url
}
return new_dict
class Carimg(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__='car_img'
# id=db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True)
car_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('sc_cars.id'))
url=db.Column(db.String(100))# img
class Brand(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'brand'
# id=db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True)
brand_name=db.Column(db.String(20))
brand_style=db.relationship('Brand_style',backref='brand')
cars=db.relationship('Car',backref='brand')
def __repr__(self):
return self.brand_name
class Brand_style(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__='brand_style'
brand_style_name=db.Column(db.String(20))
brand_style_detail=db.Column(db.String(20))
brand_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('brand.id'))
cars = db.relationship('Car', backref='brand_car_style')
class outsideproperties(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__='engineparameter'
power_sunroof=db.Column(db.String(10))
panoramic_sunroof=db.Column(db.String(10))
Electric_suction_door=db.Column(db.String(10))
Induction_trunk=db.Column(db.String(10))
Rain_sensing_Wipers=db.Column(db.String(10))
rear_wiper=db.Column(db.String(10))
POWER_WINDOWS=db.Column(db.String(10))
ELECTRIC_ADJUSTING_KNOB_EXTERIOR_REAR_VISION_MIRROR=db.Column(db.String(10))
Rearview_mirror_heated=db.Column(db.String(10))
class Chassis_Brake(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'chassis_brake'
# id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True)
driving_mode = db.Column(db.String(15))#Driving mode
help_type = db.Column(db.String(15))#Assistance type
front_suspension_type = db.Column(db.String(15))#Front suspension type
rear_suspension_type = db.Column(db.String(15))#Rear suspension type
front_brake_type = db.Column(db.String(15))#Front brake type
rear_brake_type = db.Column(db.String(15))#Rear brake type
parking_brake_type = db.Column(db.String(15))#Parking brake type
front_tire_specification = db.Column(db.String(20))#Front tire specification
rear_tire_specification = db.Column(db.String(20))#Rear tire specification
class Engine(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'sc_engine'
displacement = db.Column(db.Float)
# Intake form
intake_form = db.Column(db.String(50))
# Cylinder
cylinder = db.Column(db.String(50))
# Maximum horsepower
max_horsepower = db.Column(db.Integer)
# Maximum torque
max_torque = db.Column(db.Integer)
# Fuel type
car_fuel = db.Column(db.String(10))
# Fuel code
fuel_num = db.Column(db.Integer)
# Fuel supply mode
fuel_method = db.Column(db.String(10))
# emission standard
emission_standard = db.Column(db.String(10))
class Basic_parameters(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'Basic_parameters'
# id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
certificate=db.Column(db.String(20))#Certificate brand and model
manufacturer = db.Column(db.String(20))#Manufacturer
level=db.Column(db.Integer)#level
engine = db.Column(db.String(20))#Engine
gearbox = db.Column(db.String(20))#Transmission case
body_structure = db.Column(db.String(20))#Body structure
size=db.Column(db.String(20))#Length * width * height (mm)
wheel_base=db.Column(db.Integer)#Wheelbase (mm)
luggage_compartment=db.Column(db.Integer)#Trunk volume (L)
curb_weight=db.Column(db.Integer)#Preparation quality (kg)
def __repr__(self):
return self.certificate
class Security(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'sc_security'
# id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
main_airbags = db.Column(db.String(15)) # Main and auxiliary airbags
anterior_airbags = db.Column(db.String(15)) # Front and rear side airbags
front_airbags = db.Column(db.String(15)) # Front and rear head airbags
tire = db.Column(db.String(15)) # Tire pressure
car_lock = db.Column(db.String(15)) # Vehicle central control lock
child_lock = db.Column(db.String(15)) # Child lock
key_lock = db.Column(db.String(15)) # Key lock
abs_lock = db.Column(db.String(15)) # ABS lock
esp_lock = db.Column(db.String(15)) # ESP lock
# car = db.relationship('Car', backref='brande')
def __repr__(self):
return 'sc_brand'
class Order(BaseModel,db.Model):
__tablename__='sc_order'
user_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('sc_users.id'))
car_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('sc_cars.id'))
order_time=db.Column(db.DateTime,default=datetime.now)
car_price=db.Column(db.Float)
server_charge=db.Column(db.Float)
You may need to delete the database and migrate it again. However, if it is an online project, it is recommended not to do so.
Change the query method to the current one.
@api.route('/cars',methods=['get'])
def car_list():
brand=request.args.get('brand')
print(brand)
carstyle=request.args.get('carstyle')
print(carstyle)
price=request.args.get('price')
ret_data_list=[]
if len(brand)==0 and len(carstyle)==0:
car_lists=models.Car.query.all()
for each in car_lists:
newdict=each.to_list_dict()
ret_data_list.append(newdict)
elif len(brand)==0 and len(carstyle)!=0:
car_lists=models.Car.query.all()
for each in car_lists:
if each.brand.brand_style==carstyle:
newdict=each.to_list_dict()
ret_data_list.append(newdict)
elif len(brand)!=0 and len(carstyle)==0:
car_lists=models.Car.query.all()
for each in car_lists:
if each.brand.brand_name==brand:
newdict=each.to_list_dict()
ret_data_list.append(newdict)
print(ret_data_list)
return jsonify(data=ret_data_list)
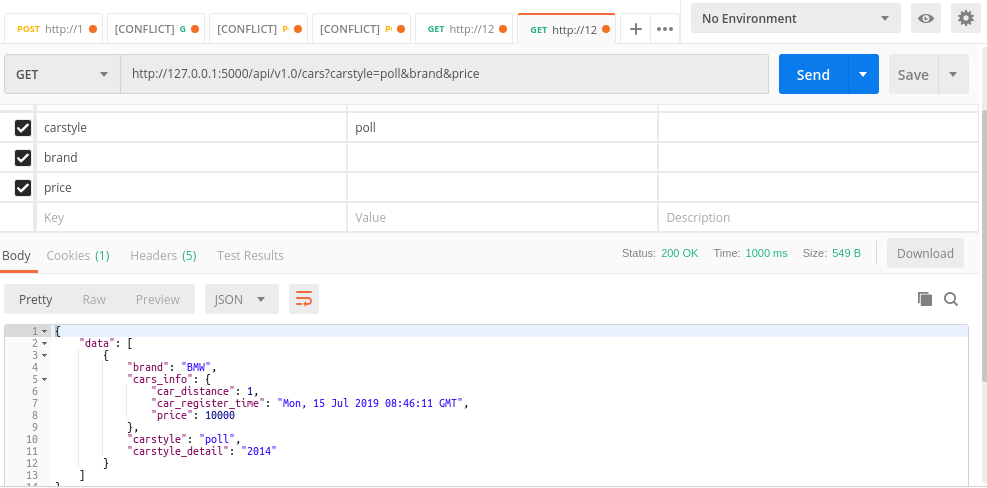
Query by brand model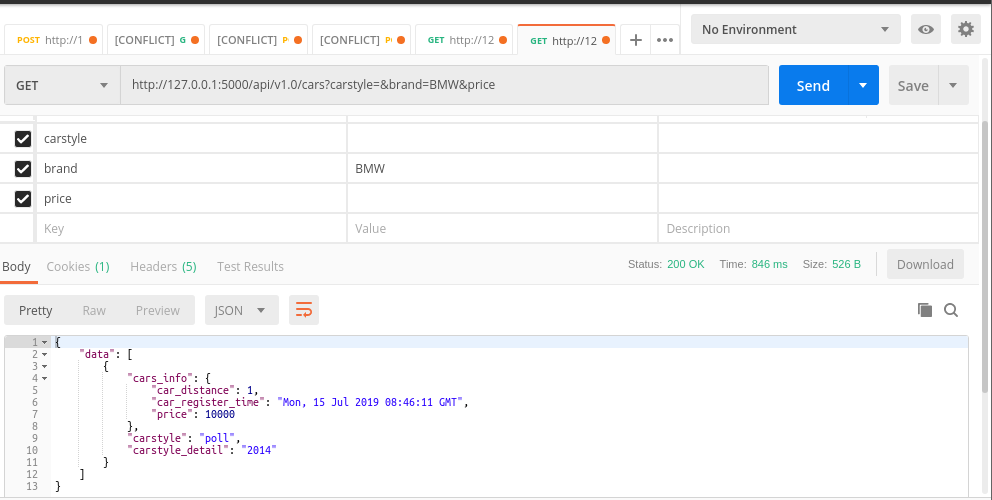
Query by brand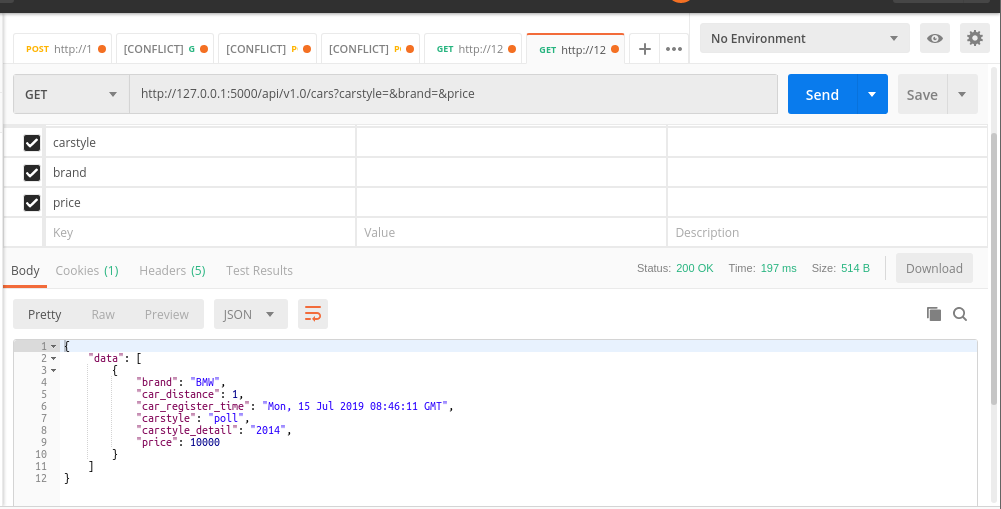
No query fields