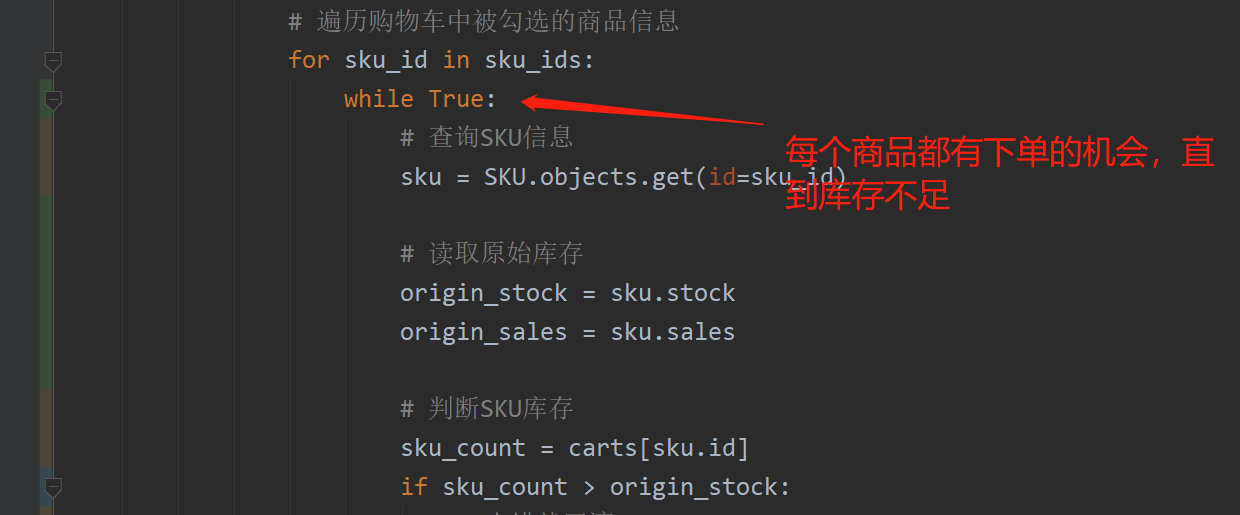
2.4 use optimistic lock to place orders concurrently
Important:
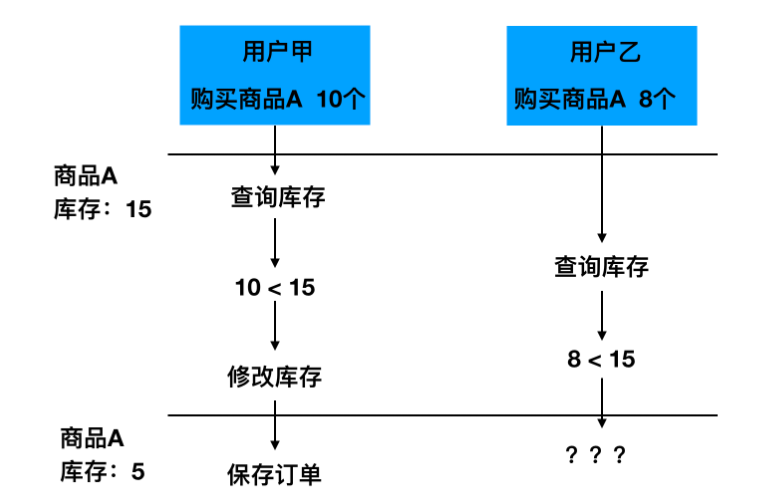
- When multiple users initiate an order request for the same commodity at the same time, first query the commodity inventory and then modify the commodity inventory, there will be resource competition, resulting in abnormal final results of inventory.
2.4.1. Concurrent order problem demonstration and solution
terms of settlement:
-
Pessimistic lock [low performance, generally not considered]
-
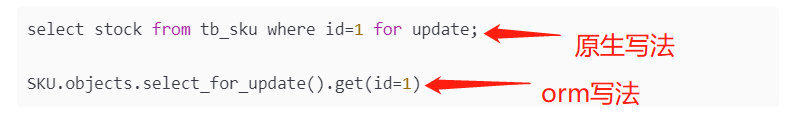
When querying a record, the database locks the record. After locking the record, others cannot operate. Use a syntax similar to the following
select stock from tb_sku where id=1 for update; SKU.objects.select_for_update().get(id=1)
- Pessimistic locks are similar to the mutex locks we add when competing for multi-threaded resources. They are prone to deadlock and are rarely used.
-
-
Optimistic lock
-
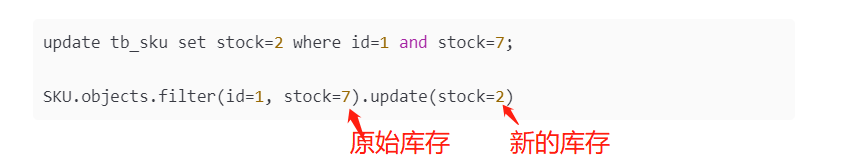
Optimistic locks are not real locks. They are used to determine whether the inventory at this time is the inventory found earlier when updating. If they are the same, it means that no one can modify and update the inventory. Otherwise, it means that others have robbed resources and will not update the inventory. Similar to the following operations
-
update tb_sku set stock=2 where id=1 and stock=7; SKU.objects.filter(id=1, stock=7).update(stock=2)
-
-
- Task queue [performance is good, and it's time to use second kill]
- Put the order placing logic into the task queue (e.g. celery), convert parallel to serial, and everyone queues up to place an order. For example, start the celery with only one process and process one order by one.
2.4.2. Use optimistic lock to place orders concurrently
reflection:
- What are the conditions for a successful order?
- First, the inventory is greater than the purchase quantity, and then the original inventory remains unchanged when the inventory and sales volume are updated.
Conclusion:
- Therefore, when the user's inventory is satisfied, if the original inventory changes when updating the inventory and sales volume, the user will continue to be given the opportunity to place orders.
class OrderCommitView(LoginRequiredJSONMixin, View):
"""Order submission"""
def post(self, request):
"""Save order information and order item information"""
# Get the information needed to save the current order
......
# Open a transaction explicitly
with transaction.atomic():
# Create a transaction savepoint
save_id = transaction.savepoint()
# Violent rollback
try:
# Save order basic information OrderInfo (I)
order = OrderInfo.objects.create(
order_id=order_id,
user=user,
address=address,
total_count=0,
total_amount=Decimal('0'),
freight=Decimal('10.00'),
pay_method=pay_method,
status=OrderInfo.ORDER_STATUS_ENUM['UNPAID'] if pay_method == OrderInfo.PAY_METHODS_ENUM['ALIPAY'] else
OrderInfo.ORDER_STATUS_ENUM['UNSEND']
)
# Read the checked item information in the shopping cart from redis
redis_conn = get_redis_connection('carts')
redis_cart = redis_conn.hgetall('carts_%s' % user.id)
selected = redis_conn.smembers('selected_%s' % user.id)
carts = {}
for sku_id in selected:
carts[int(sku_id)] = int(redis_cart[sku_id])
sku_ids = carts.keys()
# Traverse the checked item information in the shopping cart
for sku_id in sku_ids:
while True:
# Query SKU information
sku = SKU.objects.get(id=sku_id)
# Read original inventory
origin_stock = sku.stock
origin_sales = sku.sales
# Judge SKU inventory
sku_count = carts[sku.id]
if sku_count > origin_stock:
# Transaction rollback
transaction.savepoint_rollback(save_id)
return http.JsonResponse({'code': RETCODE.STOCKERR, 'errmsg': 'Insufficient inventory'})
# Analog delay
# import time
# time.sleep(5)
# SKU reduces inventory and increases sales
# sku.stock -= sku_count
# sku.sales += sku_count
# sku.save()
# Update inventory and sales volume
new_stock = origin_stock - sku_count
new_sales = origin_sales + sku_count
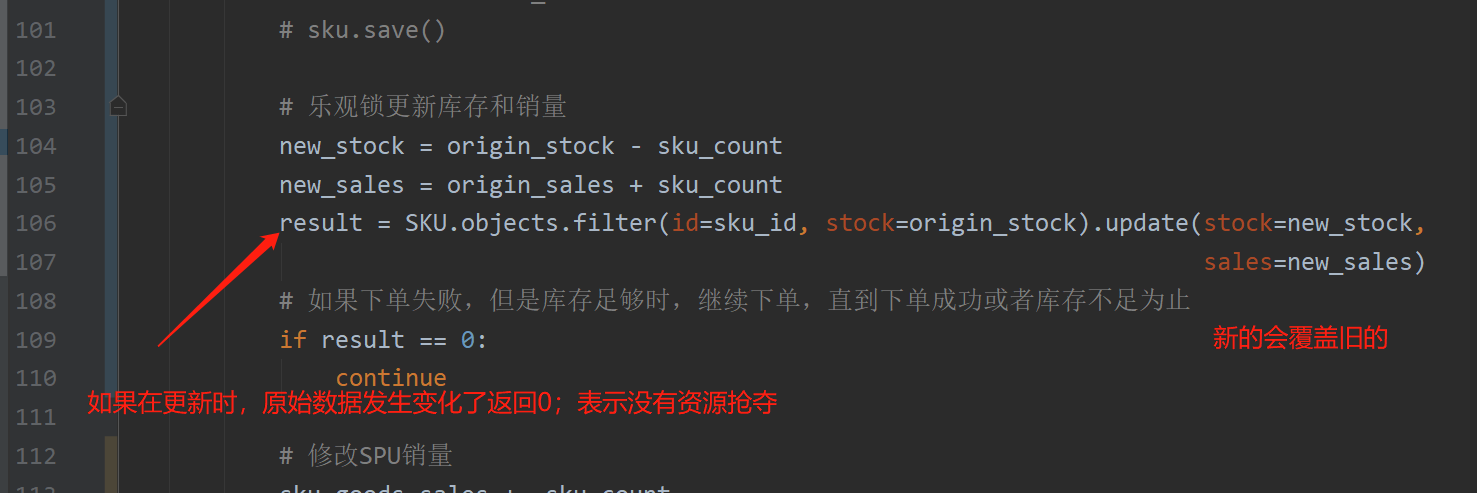
result = SKU.objects.filter(id=sku_id, stock=origin_stock).update(stock=new_stock, sales=new_sales)
# If the order fails but the inventory is sufficient, continue to place the order until the order is successful or the inventory is insufficient
if result == 0:
continue
# Modify SPU sales volume
sku.spu.sales += sku_count
sku.spu.save()
# Save order item information OrderGoods
OrderGoods.objects.create(
order=order,
sku=sku,
count=sku_count,
price=sku.price,
)
# Save the total price and total quantity in the commodity order
order.total_count += sku_count
order.total_amount += (sku_count * sku.price)
# If the order is successful or fails, it will jump out of the loop
break
# Add postage and save order information
order.total_amount += order.freight
order.save()
except Exception as e:
logger.error(e)
# Transaction rollback
transaction.savepoint_rollback(save_id)
return http.JsonResponse({'code': RETCODE.DBERR, 'errmsg': 'Order failed'})
# Save the order data successfully, and explicitly submit a transaction
transaction.savepoint_commit(save_id)
# Clear settled items in shopping cart
pl = redis_conn.pipeline()
pl.hdel('carts_%s' % user.id, *selected)
pl.srem('selected_%s' % user.id, *selected)
pl.execute()
# Response submit order results
return http.JsonResponse({'code': RETCODE.OK, 'errmsg': 'checkout success ', 'order_id': order.order_id})
2.4.3. MySQL transaction isolation level
-
Transaction isolation level refers to when one transaction can see the modified results after modifying the data in multiple transactions processing the same data.
-
There are four main transaction isolation levels for MySQL database:
- Serializable: serialization, the execution of a transaction. [low concurrency]
- Repeatable read: repeatable read. No matter whether other transactions modify and commit data, the data values seen in this transaction are always unaffected by other transactions.
- Read committed: read committed. After other transactions commit data modifications, this transaction can read the modified data values.
- Read uncommitted: read uncommitted. As long as other transactions modify data, even if uncommitted, this transaction can see the modified data value.
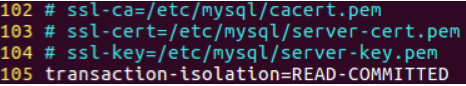
- MySQL database uses Repeatable read by default.
-
When using optimistic locks, if a transaction modifies the inventory and commits the transaction, other transactions should be able to read the modified data value. Therefore, the repeatable isolation level cannot be used. It should be modified to Read committed.
-
Modification method: [if permanently valid, directly modify the following configuration]
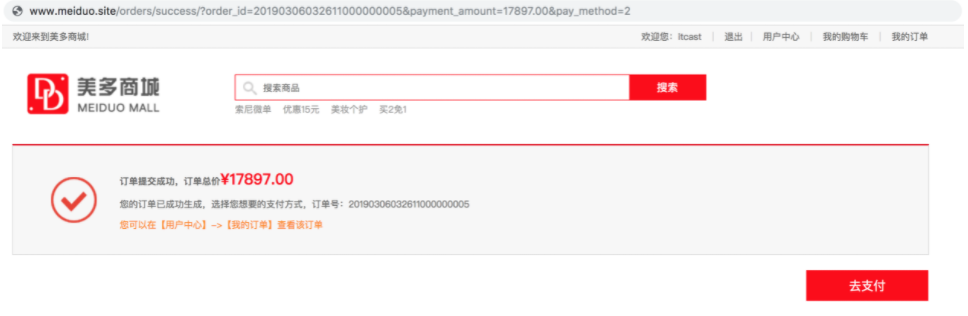
2.5 display the successful order submission page
Payment method: cash on delivery
Payment: Alipay
1. Request method
| option | programme |
|---|---|
| Request method | GET |
| Request address | /orders/success/ |
# Order submitted successfully
url(r'^orders/success/$', views.OrderSuccessView.as_view()),2. Request parameters:
nothing
3. Response result: HTML
order_success.html
4. Definition and implementation of back-end interface
class OrderSuccessView(LoginRequiredMixin, View):
"""Order submitted successfully"""
def get(self, request):
order_id = request.GET.get('order_id')
payment_amount = request.GET.get('payment_amount')
pay_method = request.GET.get('pay_method')
context = {
'order_id':order_id,
'payment_amount':payment_amount,
'pay_method':pay_method
}
return render(request, 'order_success.html', context)
5. Render the information of the successfully submitted order page
<div class="common_list_con clearfix">
<div class="order_success">
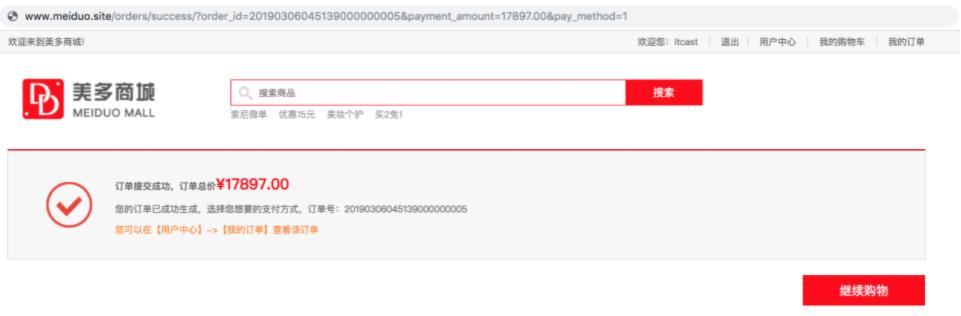
<p><b>Order submitted successfully, total order price<em>¥{{ payment_amount }}</em></b></p>
<p>Your order has been generated successfully. Select the payment method you want, order No.:{{ order_id }}</p>
<p><a href="{{ url('orders:info', args=(1, )) }}">You can click [user center]->[My order] view this order</a></p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="order_submit clearfix">
{% if pay_method == '1' %}
<a href="{{ url('contents:index') }}">Continue shopping</a>
{% else %}
<a @click="order_payment" class="payment">To pay</a>
{% endif %}
</div>