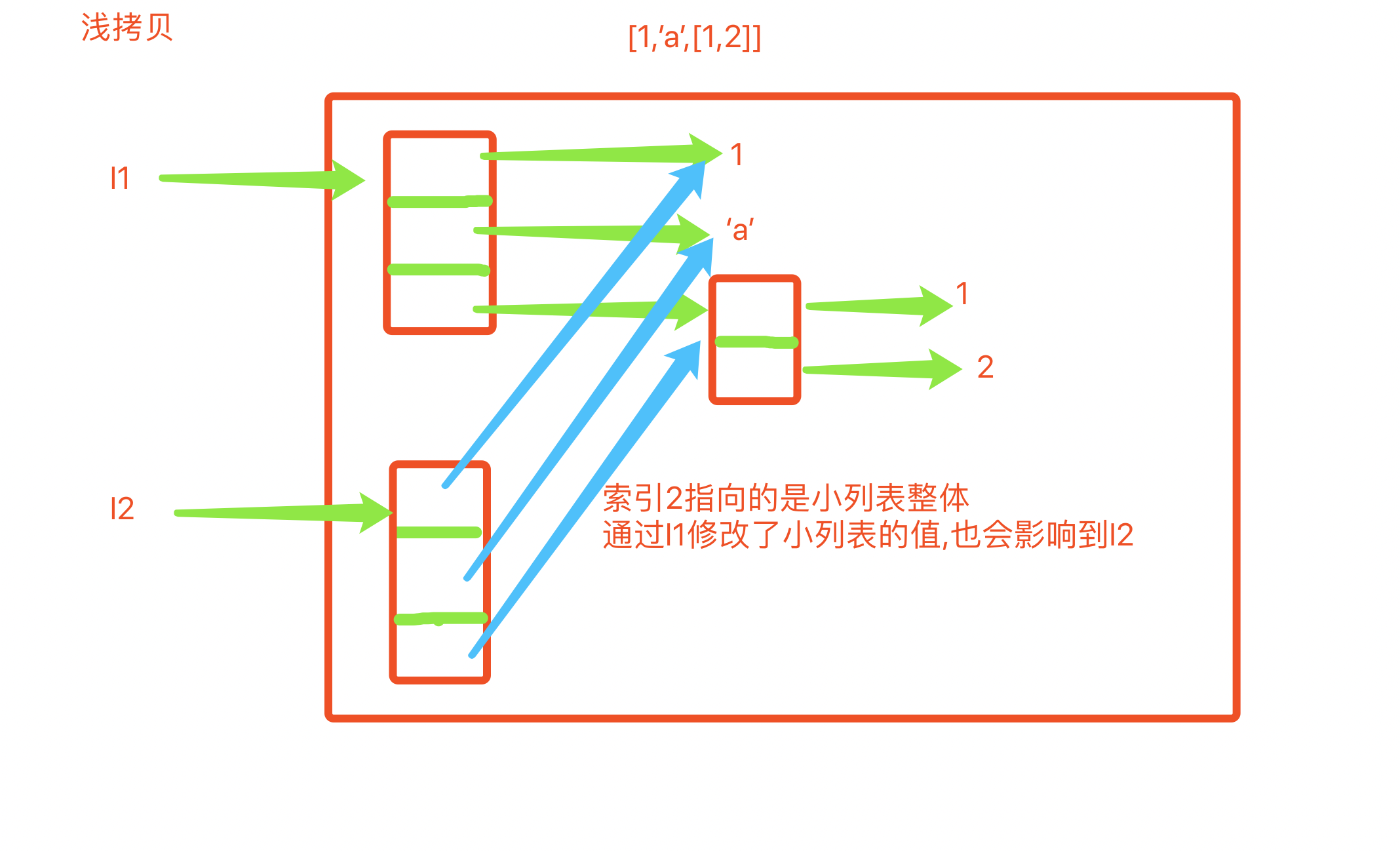
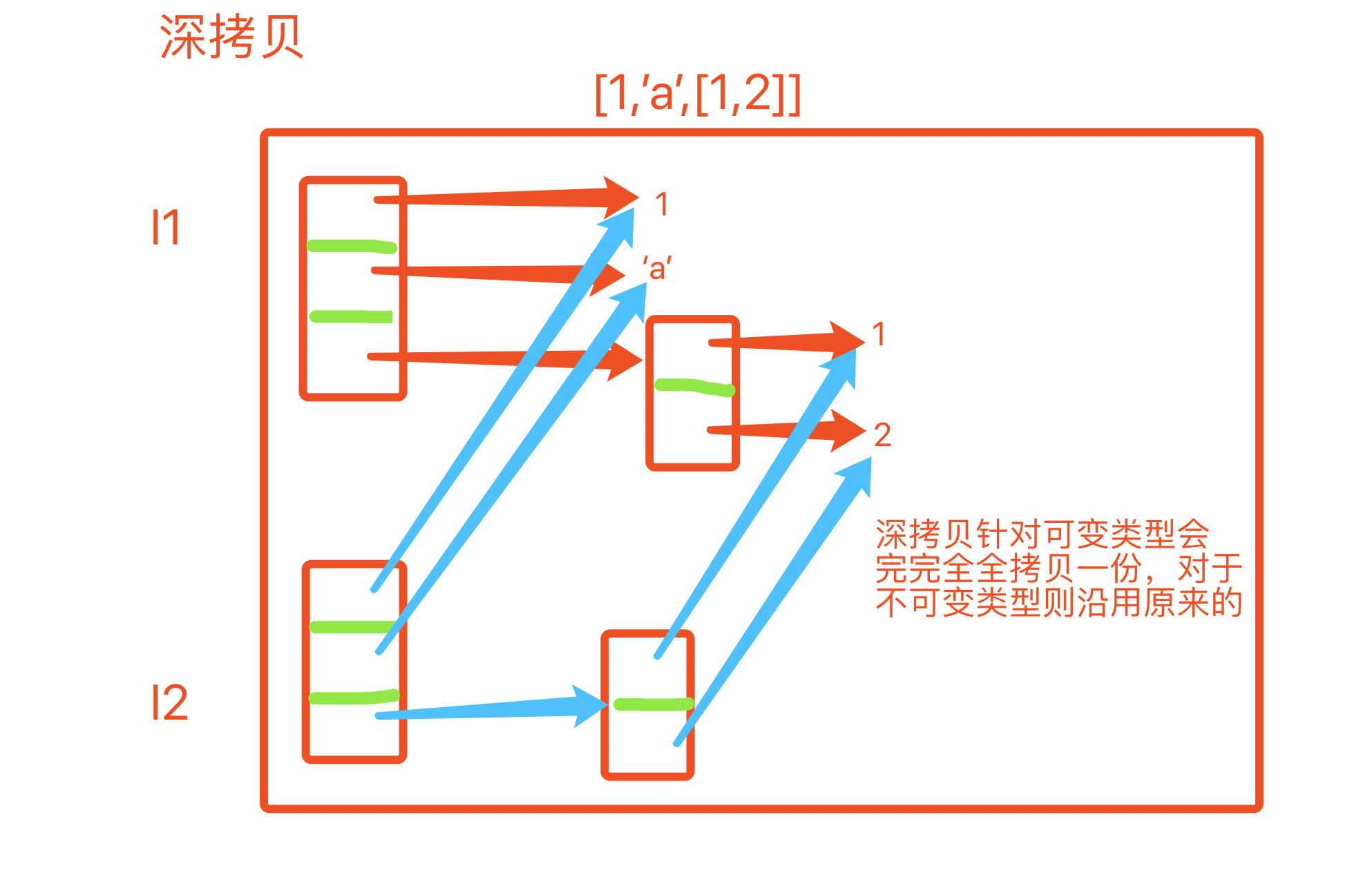
What is a bag?
A package is a folder that contains _init_ py files, so the purpose of creating a package is to organize files / modules with folders.
It should be emphasized that:
1. In Python 3, even if there is no _init_ py file under the package, the import package will still not report errors. In Python 2, the file must be under the package, otherwise the import package will report errors.
2. The purpose of creating packages is not to run, but to be imported and used. Remember, packages are only a form of modules, and the essence of packages is a module.
Why use packages
The essence of a package is a folder, so the only function of a folder is to organize the files. As more functions are written, we can't put all the functions into one file. So we use modules to organize the functions. As more modules are built, we need folders to organize the module files. To improve the structure and maintainability of programs
Matters needing attention:
Packet import can also be divided into import and from...import... two kinds, but no matter where it is, it must follow a principle when importing: Whatever points are brought in at the time of import, the left side of the points must be a package, otherwise it is illegal.
First import package:
Generate an execution file namespace first
Create the namespace of the _init_.py file under the package
2. Execute the code in the _init_ py file below the package to place the generated name in the _init_ py file namespace below the package
3. Get a name in the execution file that points to the _init_.py file namespace under the package
Developer Standing on Package: If you use absolute paths to manage your modules, it only needs to import modules in turn based on the path of the package forever.
User standing in the package: You must add the folder path where the package is located to the system path.
logging module
Logging Module: Recording
Logs are divided into five levels
logging.debug() #10
logging.info() #20
logging.warning() #30
logging.error() #40
logging.critical() #50
1.logger object: responsible for generating logs
2.filter object: filter logs (understand)
3.handler Object: Location of Control Log Output (File/Terminal)
4. Formmate object: specify the format of log content
logging Configuration Dictionary
logging Configuration Dictionary import os import logging.config # Define three log output formats to start with standard_format = '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]' \ '[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]' #among name by getlogger Designated name simple_format = '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s' # Define the end of log output format The values of the following two variables need to be modified manually logfile_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__) # log Catalogue of documents logfile_name = 'a3.log' # log file name # If there is no defined log directory, create one if not os.path.isdir(logfile_dir): os.mkdir(logfile_dir) # log Full path of file logfile_path = os.path.join(logfile_dir, logfile_name) # log Configuration Dictionary LOGGING_DIC = { 'version': 1, 'disable_existing_loggers': False, 'formatters': { 'standard': { 'format': standard_format }, 'simple': { 'format': simple_format }, }, 'filters': {}, # Filter logs 'handlers': { #Print logs to terminals 'console': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', # Print to screen 'formatter': 'simple' }, #Logs printed to files,collect info Logs above 'default': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # Save to file 'formatter': 'standard', 'filename': logfile_path, # log file 'maxBytes': 1024*1024*5, # Log size 5 M 'backupCount': 5, 'encoding': 'utf-8', # Log file encoding, no longer need to worry about Chinese log The code is out of order. }, }, 'loggers': { #logging.getLogger(__name__)Get it logger To configure '': { 'handlers': ['default', 'console'], # Here are the two definitions above. handler Add all, that is log Data is written to the file and printed to the screen. 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': True, # Up (higher) level Of logger)transmit }, # This is used by default when the key does not exist k:v To configure }, } # Configuration using log dictionary logging.config.dictConfig(LOGGING_DIC) # Configuration in Autoloading Dictionary logger1 = logging.getLogger('asajdjdskaj') logger1.debug('Good without impetuosity, hard work will bear fruit')
import os import logging.config # Define three log output formats to start with standard_format = '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]' \ '[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]' #among name by getlogger Designated name simple_format = '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s' # Define the end of log output format The values of the following two variables need to be modified manually logfile_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__) # log Catalogue of documents logfile_name = 'a3.log' # log file name # If there is no defined log directory, create one if not os.path.isdir(logfile_dir): os.mkdir(logfile_dir) # log Full path of file logfile_path = os.path.join(logfile_dir, logfile_name) # log Configuration Dictionary LOGGING_DIC = { 'version': 1, 'disable_existing_loggers': False, 'formatters': { 'standard': { 'format': standard_format }, 'simple': { 'format': simple_format }, }, 'filters': {}, # Filter logs 'handlers': { #Print logs to terminals 'console': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', # Print to screen 'formatter': 'simple' }, #Logs printed to files,collect info Logs above 'default': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # Save to file 'formatter': 'standard', 'filename': logfile_path, # log file 'maxBytes': 1024*1024*5, # Log size 5 M 'backupCount': 5, 'encoding': 'utf-8', # Log file encoding, no longer need to worry about Chinese log The code is out of order. }, }, 'loggers': { #logging.getLogger(__name__)Get it logger To configure '': { 'handlers': ['default', 'console'], # Here are the two definitions above. handler Add all, that is log Data is written to the file and printed to the screen. 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': True, # Up (higher) level Of logger)transmit }, # This is used by default when the key does not exist k:v To configure }, } # Configuration using log dictionary logging.config.dictConfig(LOGGING_DIC) # Configuration in Autoloading Dictionary logger1 = logging.getLogger('asajdjdskaj') logger1.debug('Good without impetuosity, hard work will bear fruit')