I. Creating Sequences
series can represent excel rows and columns
How to create it:
1. Using dictionaries, key is converted to index and value is converted to data.
2. Use lists
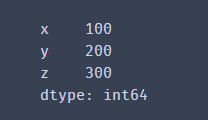
"Mode 1" s1=pd.Series()#Generate a sequence that represents rows and columns d={'x':100,'y':200,'z':300} s1=pd.Series(d)#Converting a dictionary into a sequence print(s1) "Mode 2" L1=[100,200,300] L2=['x','y','z'] s1=pd.Series(L1,index=L2)#Generate a sequence that represents rows and columns #perhaps s1=pd.Series([100,200,300],index=['x','y','z'])
Add the sequence to the dataframe
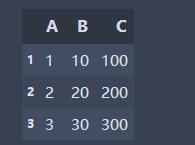
import pandas as pd s1=pd.Series([1,2,3],index=[1,2,3],name='A') s2=pd.Series([10,20,30],index=[1,2,3],name='B') s3=pd.Series([100,200,300],index=[1,2,3],name='C') df=pd.DataFrame({s1.name:s1,s2.name:s2,s3.name:s3}) df
II. Reading of Data Area
excel for operation at this time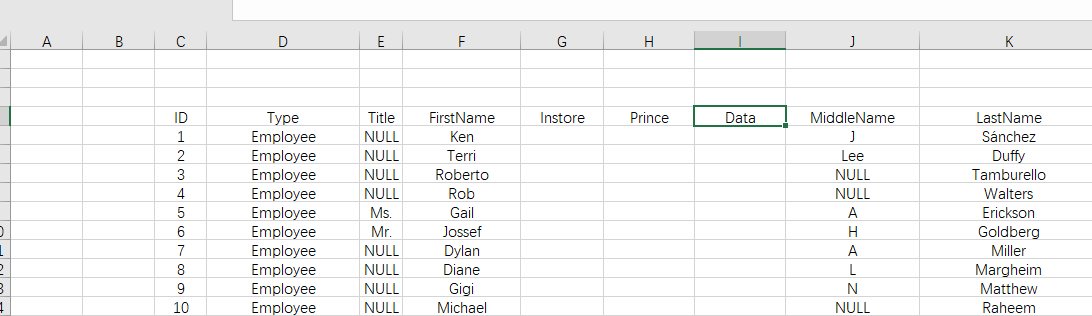
import pandas as pd import xlrd books=pd.read_excel('E:/ruanjianDM/people.xlsx',skiprows=3,usecols='C:I')#Skip the first three lines, C to column I books['ID'].at[0]=100 #books['ID'].at[index] specifies columns and rows books
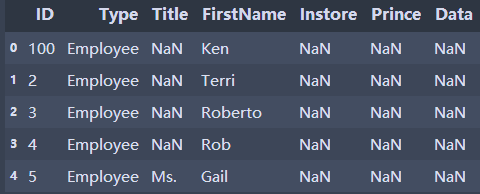
3. Automatic Filling
Simple filling
"1.Fill 1-n number" for i in books.index: books['ID'].at[i]=i+1 #Change the ID above to 1 "2.Fill in regular strings" #Direct padding can cause errors, setting Instor to str type books=pd.read_excel('E:/ruanjianDM/people.xlsx',skiprows=3,usecols='C:L',dtype={'ID':str,'Instore':str,'Date':str}) for i in books.index: books['Instore'].at[i]="Yes" if i%2==0 else "No" books.head()
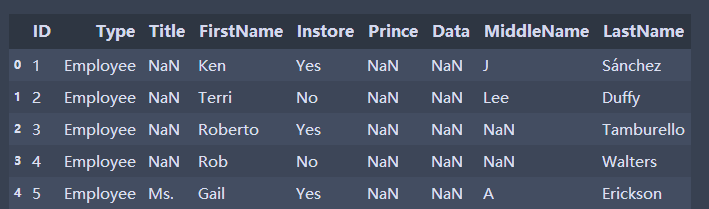
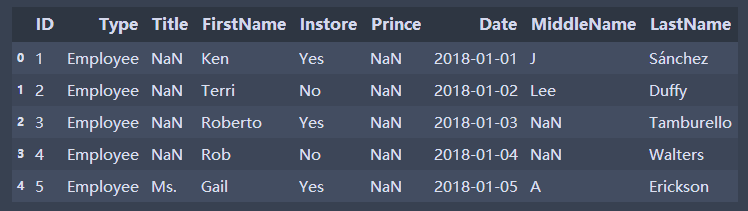
Fill in the date sequence
Date function: date(2018,1,1), date (year, month, day)
Time Delta (day = i) only has day, can only add date, minute, millisecond, hour, no month.
books.rename(columns={"Data":"Date"},inplace=True)#Reset Column Name from datetime import date,timedelta start=date(2018,1,1) for i in books.index: books['Date'].at[i]=start+timedelta(days=i)#On the basis of start, it increases or decreases one day, two days and three days in turn. #Increase one day books.head()
IV. Column Operation and Function Computation
The operation in Excel is a cell and the operation in pandas is a column.
Special case: do not want to start from scratch, calculate some of the lines
from numpy import random as nr books.Prince=nr.rand(books.shape[0],1) print(books.head()) for i in range(1,3):#Left closed right open interval, not 16 books['Prince'].at[i]=books['Prince'].at[i]*books['ID'].at[i] def add_2(x): return x+2 books['ID']=books['ID'].apply(add_2)#Write only the function name, no parentheses, ID column plus 2 print(books.head())
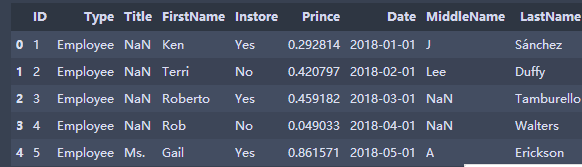
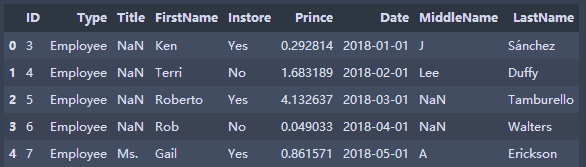
Five, sort
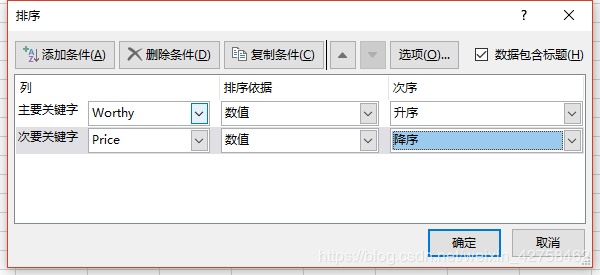
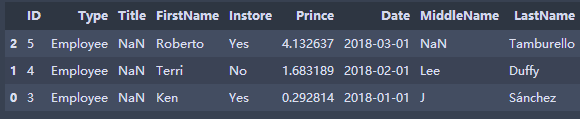
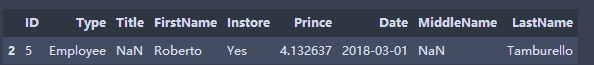
"Single Conditional Sorting" #books.sort_values(by='Prince',inplace=True)#The default is ascending order books.sort_values(by='Prince',ascending=False,inplace=True) books.head() "Multiple Conditional Sorting,Two conditions are considered to get the ranking result, which will not disturb the original row correspondence relationship." books.sort_values(by=['ID','Prince'],ascending=[False,True],inplace=True) books.head()
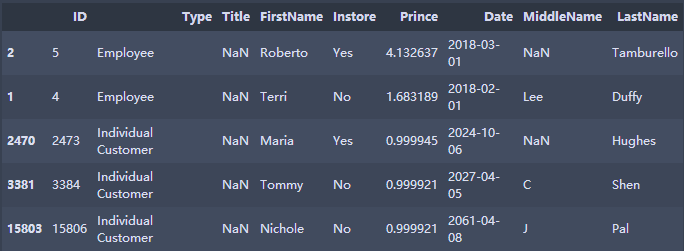
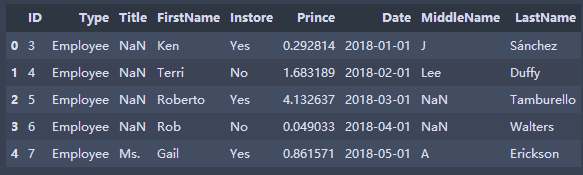
Screening filtration
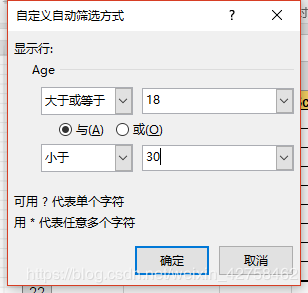
The statement of the two filter conditions can be understood as a=books.loc[books ['ID']. apply(ID_3_to_6)] first filters a part of the table, which is being filtered.
a.loc[books['Prince'].apply(Prince)]
"Define filter function" def ID_3_to_6(a): return 3<=a<6 def Prince(s): return 2<=s<=5 books.loc[books['ID'].apply(ID_3_to_6)]#Return TRUE if the condition is satisfied, Loc locates a line according to true and prints it. books.loc[books['ID'].apply(ID_3_to_6)].loc[books['Prince'].apply(Prince)]#Two screening conditions