1030 perfect sequence (25 points)
Given a positive integer sequence, and a positive integer p, let the maximum value of the sequence be m, and the minimum value be m. if M ≤ mp, then the sequence is a perfect sequence.
Now given the parameter p and some positive integers, please choose as many numbers as possible to form a perfect sequence.
Input format:
The first input line gives two positive integers N and p, where N (< 10 5) is the number of positive integers and p (< 10 9) is the given parameter. The second line gives N positive integers, each of which does not exceed 10 9.
Output format:
How many numbers can you choose to output in a row can be used to form a perfect sequence.
Input example:
10 8 2 3 20 4 5 1 6 7 8 9
Output example:
8
I always want to start from the minimum and maximum at the beginning, without thinking
Train of thought:
Two loops, one by one
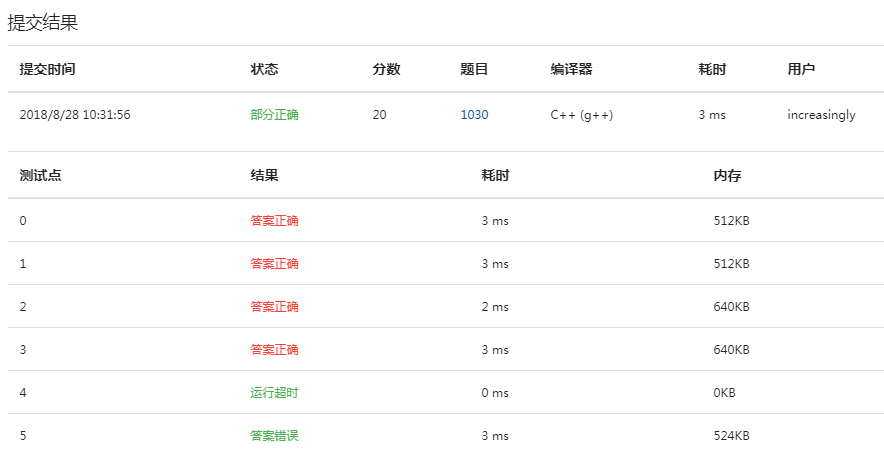
i find the minimum value from 1 - > n, j find the maximum value from i to n, and store the number of temp s until the equation is not satisfied and exit the cycle
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, p;//n is the number of input positive integers, p is the coefficient parameter
vector<int> num;
int temp;
cin >> n >> p;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> temp;
num.push_back(temp);
}
sort(num.begin(), num.end());//From small to large
int result = 0;
temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j < n; j++)
{
if (num[j] <= num[i] * p)
temp = j - i + 1;//Number of matches
else
break;
}
if (temp > result)
result = temp;
}
cout << result;
system("pause");
return 0;
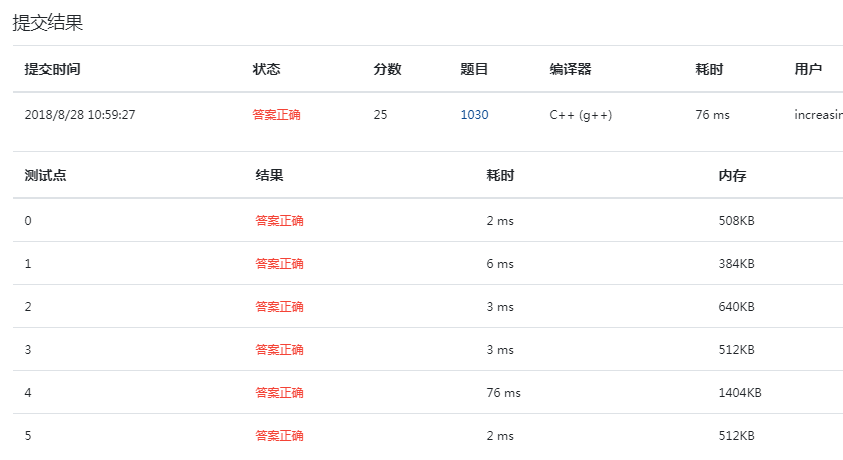
}
Test point 5, which should be a large number < = 10 ^ 9, in long long format
Run timeout Optimization:
Set the initialization j of the second for loop to i+result, starting from the maximum number of previously satisfied conditions
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
long long p;//n is the number of input positive integers, p is the coefficient parameter
vector<long long> num;
long long temp;
cin >> n >> p;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> temp;
num.push_back(temp);
}
sort(num.begin(), num.end());//From small to large
int result = 0;
temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + result; j < n; j++)
{
if (num[j] <= num[i] * p)
temp = j - i + 1;//Number of matches
else
break;
}
if (temp > result)
result = temp;
}
cout << result;
system("pause");
return 0;
}