Distributed full text search solution
1. Solution introduction
ElasticSearch is a distributed full-text search engine based on RESTful web interface.
The solution is to implement a distributed full-text search system based on three data systems: Mysql database, Hadoop Ecology (optional) and ElasticSearch search engine.
It mainly includes three modules: data access, data index and full-text search. Applicable to various search scenarios for various items.
1.1 three data systems
1.1.1 relational database
It is used for structured storage of goods, users and other data. Relational database supports OLTP[^1] operations (such as orders, settlement, etc.) with high transaction.
On line transaction processing, also known as transaction oriented processing
Primary selection: mysql database
1.1.2 hadoop ecology
Hadoop It is developed by the Apache foundation distributed system Infrastructure.
Hadoop implements a distributed file system (Hadoop Distributed File System), HDFS for short.
The core design of Hadoop framework is HDFS and MapReduce. HDFS provides storage for massive data, while MapReduce provides computing for massive data.
hadoop is the main carrier of data warehouse. In addition to backing up all versions of relational database, it also stores massive log data such as user behavior, click, exposure and interaction. hadoop supports OLAP[^2] operations such as data analysis and data mining, which is more scalable and stable than relational database.
On line analytical processing
Hive, a Hadoop based data warehouse The tool can map structured data files into a database table and provide simple sql query function.
HBase, a sub project of Hadoop, is a distributed, column oriented open source database.
Spark, a fast and universal computing engine specially designed for large-scale data processing, can run in parallel in Hadoop file system as a supplement to Hadoop.
1.1.3 search engine
Represented by elastic search and solr. Search engine is the most efficient way to obtain information. It has almost become the standard infrastructure of all kinds of websites and Applications (second only to database).
Elasticsearch is a Lucene based search server. It provides a distributed multi-user full-text search engine based on RESTful web interface. Elasticsearch is developed in Java and released as an open source under the Apache license terms. It is a popular enterprise search engine. Designed for cloud computing It can achieve real-time search, stable, reliable, fast and convenient installation and use.
1.2 ES based distributed search technology architecture
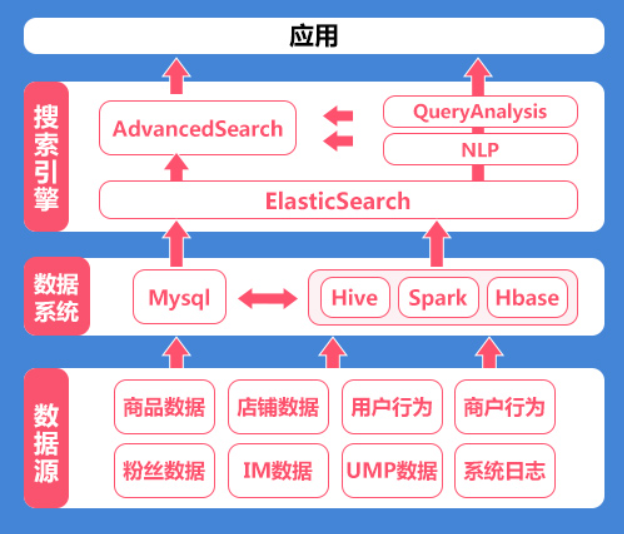
2. Software installation
2.1 installing JDK
ElasticSearch is developed in JAVA language, and JDK needs to be installed to run it.
JDK (Java Development Kit) is the core of the whole Java, including Java runtime environment, a pile of java tools and Java based class libraries (rt.jar).
2.1.1 download and install JDK
Download address https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
Installation: double click the software to open the installation interface
Click Change custom installation directory
Click next to install
Wait, the following interface appears, the installation is completed, and click close
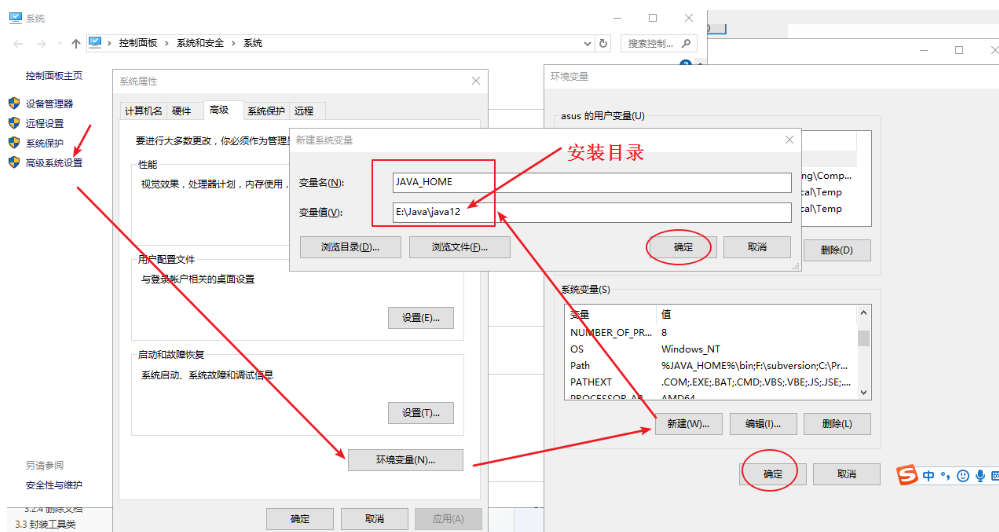
2.1.2 configuring environment variables
Configure JAVA_HOME environment variable
Configure Path environment variable
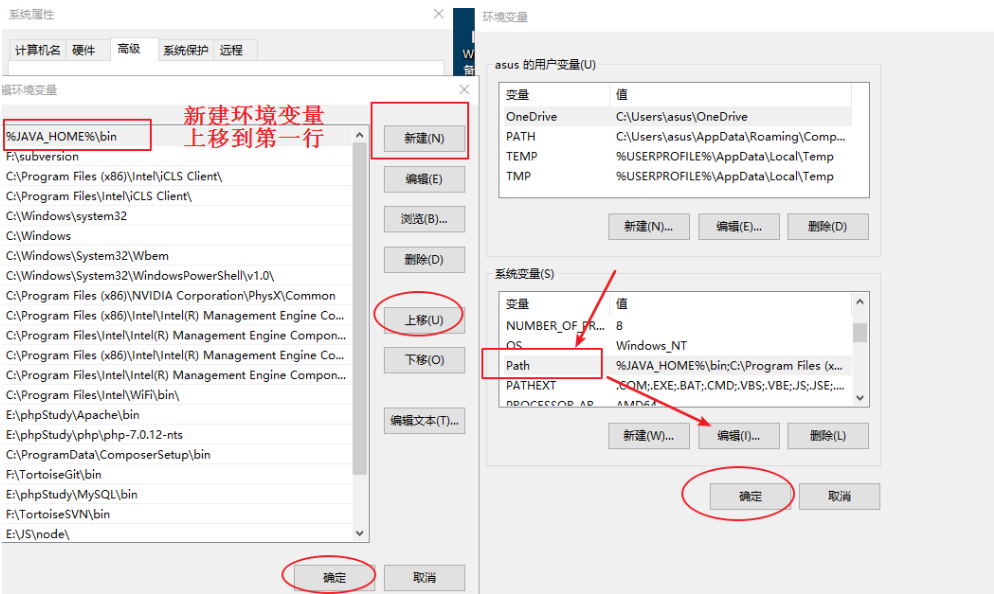
2.1.3 test - view JDK version
Open the command line window and enter java -version to view the JDK version
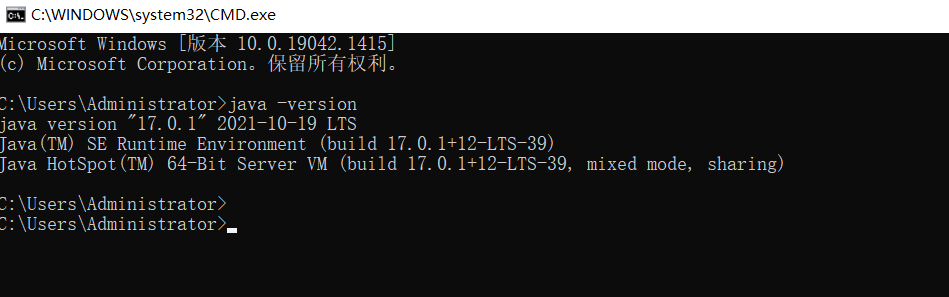
The above interface appears, indicating that the installation is successful.
2.2 installing Elasticsearch
Authoritative guide https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/index.html
2.2.1 download and installation
Download address https://www.elastic.co/downloads
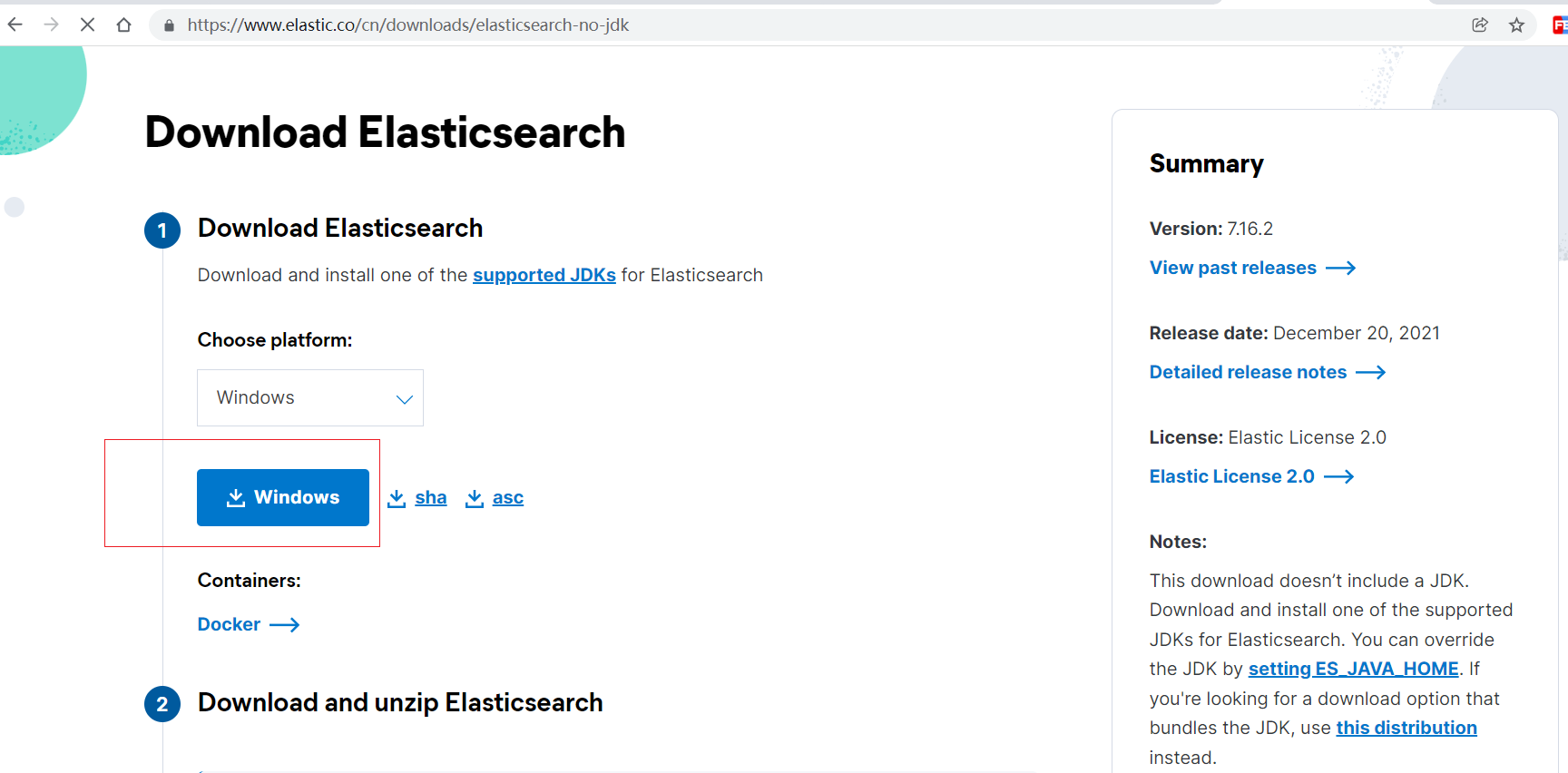
decompression
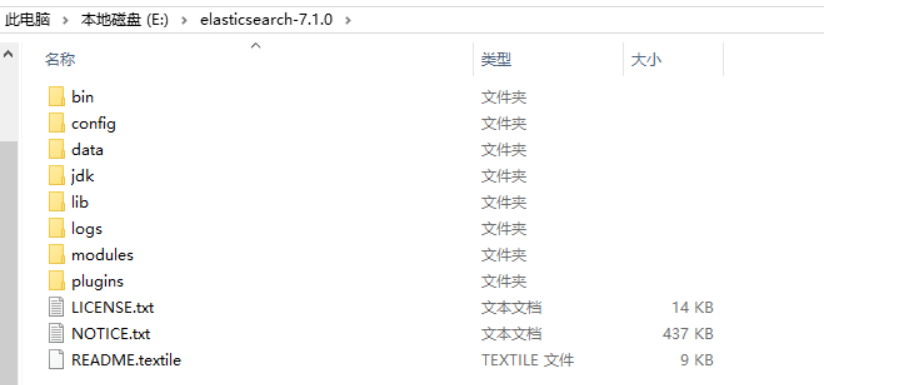
2.2.2 configuring Path environment variables
(bin directory)
2.2.3 start elasticsearch
Open a command line window and execute the command elasticsearch -d to start elasticsearch
Note: do not close the command line window.
Browser open http://localhost:9200
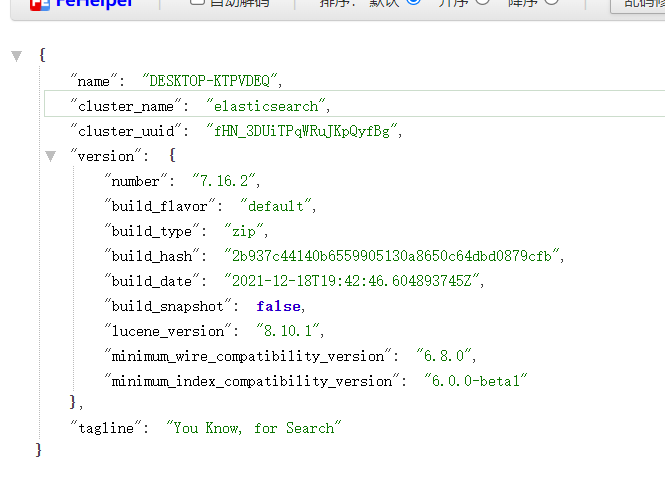
If the above interface appears, the startup is successful.
2.2.4 catalog interpretation
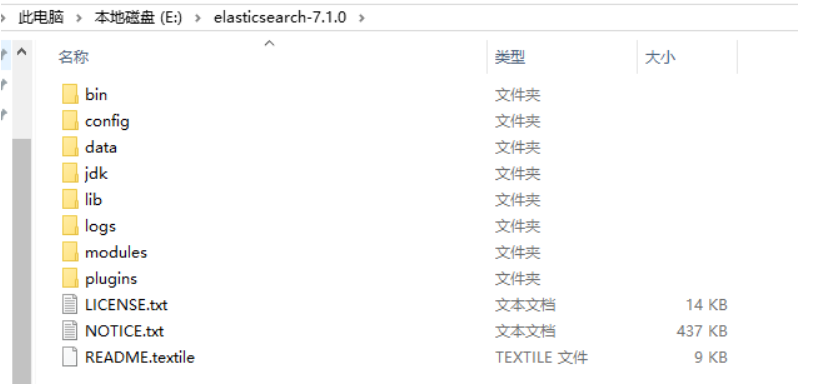
-
bin: startup file
-
config: configuration file
- log4j2.properties: log configuration file
- jvm.options: configuration of java virtual machine
- elasticsearch. Configuration file for YML: es
-
Data: index data directory
-
lib: Jar package of related class libraries
-
logs: log directory
-
Modules: function modules
-
plugins: plug-ins
. 2.5 (optional) install elasticsearch head
ElasticSearch head is a Web project for browsing and interacting with ElasticSearch clusters
GitHub hosting address: https://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head
Download and unzip:
Install: open the command line, switch to elasticsearch head directory, and execute the following command
npm install
Start: open the command line, switch to elasticsearch head directory, and execute the following command
npm run start
After successful startup, you can http://localhost:9100 Visit
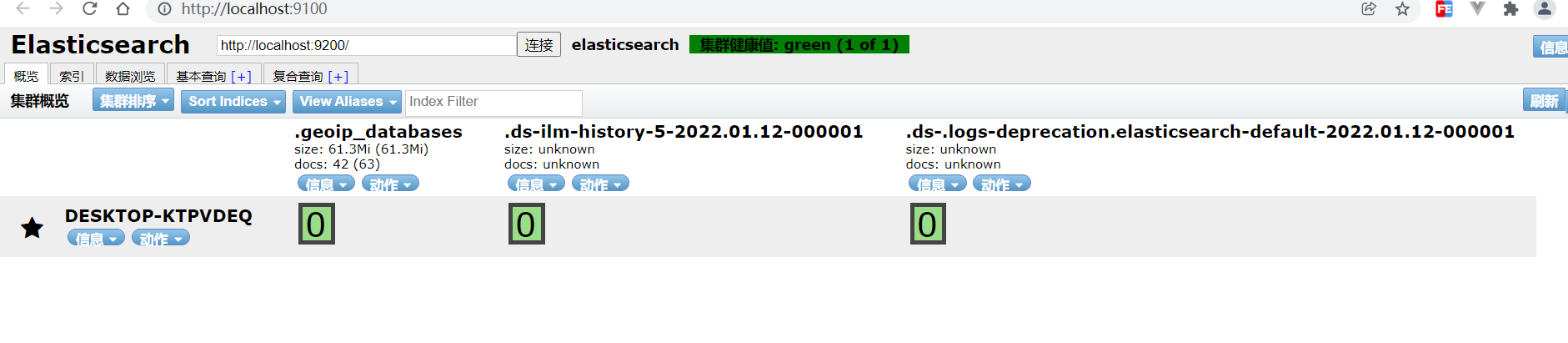
Due to cross domain (Elasticsearch is located on port 9200), configuration needs to be added: e: \ Elasticsearch-7.1.0 \ config \ Elasticsearch In YML
#Newly added configuration line http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
Restart
Access effect:
2.3 installing elasticsearch PHP
https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-php
Install using composer:
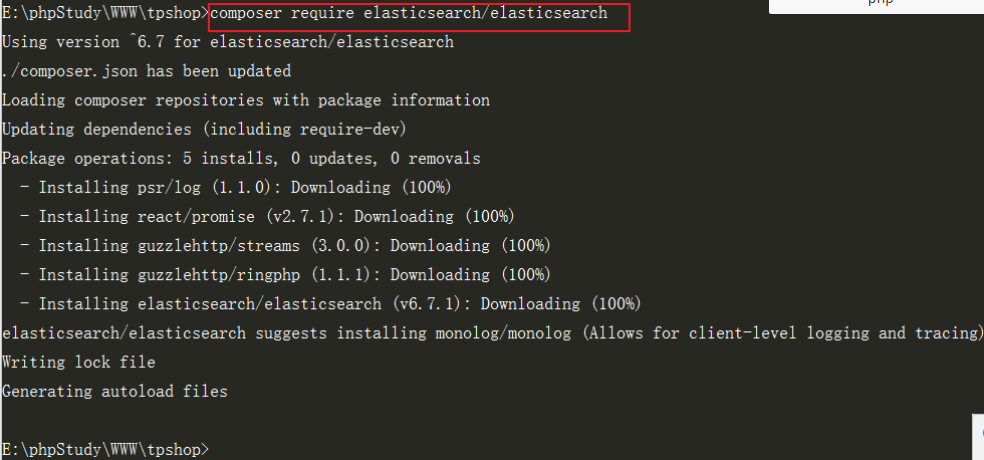
Under the project directory, execute the following command
composer require elasticsearch/elasticsearch
2.4 configuring PHP ini
Configure PHP Sys of ini_ temp_ dir
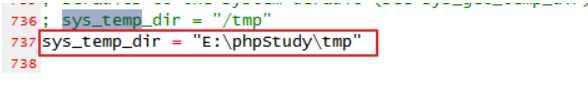
Otherwise, the following errors may occur during use

3.ElasticSearch basic usage
3.1 basic concepts
3.1.1 nodes and clusters
Elastic is essentially a distributed database that allows multiple servers to work together, and each server can run multiple elastic instances.
A single Elastic instance is called a node. A group of nodes form a cluster.
3.1.2 index
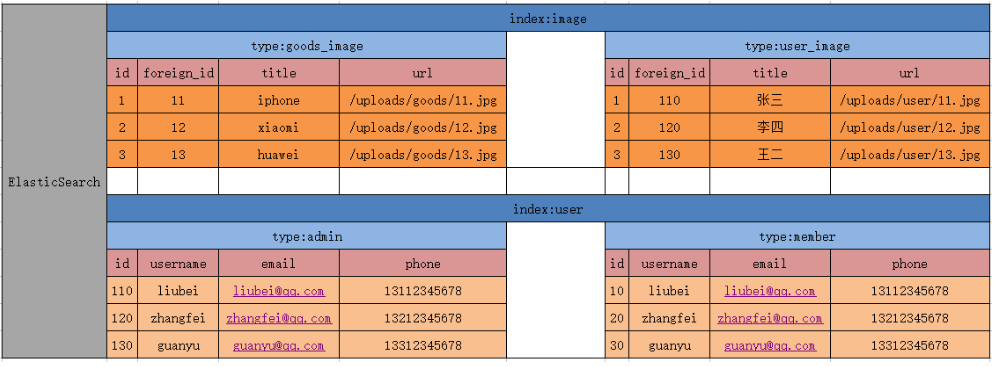
The behavior of storing data in elastic search is called Indexing
In elastic search, documents belong to one type, and these types exist in * * index * *
Analogy to traditional relational database:
Relational DB -> Databases -> Tables -> Rows -> Columns Elasticsearch -> Indices -> Types -> Documents -> Fields
Elasticsearch clusters can contain multiple indexes (databases)
Each index can contain multiple types (tables)
Each type contains multiple documents (lines)
Each document then contains multiple fields (columns).
3.2 basic use
3.2.1 index creation
$es = \Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder::create()->setHosts(['127.0.0.1:9200'])->build();
$params = [
'index' => 'test_index'
];
$r = $es->indices()->create($params);
dump($r);die;
Expected results:
array(3) {
["acknowledged"] => bool(true)
["shards_acknowledged"] => bool(true)
["index"] => string(10) "test_index"
}
3.2.2 add document (index document)
$es = \Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder::create()->setHosts(['127.0.0.1:9200'])->build();
$params = [
'index' => 'test_index',
'type' => 'test_type',
'id' => 100,
'body' => ['id'=>100, 'title'=>'PHP From introduction to mastery', 'author' => 'Zhang San']
];
$r = $es->index($params);
dump($r);die;
Expected results:
array(8) {
["_index"] => string(10) "test_index"
["_type"] => string(9) "test_type"
["_id"] => string(3) "100"
["_version"] => int(1)
["result"] => string(7) "created"
["_shards"] => array(3) {
["total"] => int(2)
["successful"] => int(1)
["failed"] => int(0)
}
["_seq_no"] => int(0)
["_primary_term"] => int(1)
}
3.2.3 modifying documents
$es = \Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder::create()->setHosts(['127.0.0.1:9200'])->build();
$params = [
'index' => 'test_index',
'type' => 'test_type',
'id' => 100,
'body' => [
'doc' => ['id'=>100, 'title'=>'ES From introduction to mastery', 'author' => 'Zhang San']
]
];
$r = $es->update($params);
dump($r);die;
Expected results:
array(8) {
["_index"] => string(10) "test_index"
["_type"] => string(9) "test_type"
["_id"] => string(3) "100"
["_version"] => int(2)
["result"] => string(7) "updated"
["_shards"] => array(3) {
["total"] => int(2)
["successful"] => int(1)
["failed"] => int(0)
}
["_seq_no"] => int(1)
["_primary_term"] => int(1)
}
3.2.4 deleting documents
$es = \Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder::create()->setHosts(['127.0.0.1:9200'])->build();
$params = [
'index' => 'test_index',
'type' => 'test_type',
'id' => 100,
];
$r = $es->delete($params);
dump($r);die;
Expected results:
array(8) {
["_index"] => string(10) "test_index"
["_type"] => string(9) "test_type"
["_id"] => string(3) "100"
["_version"] => int(3)
["result"] => string(7) "deleted"
["_shards"] => array(3) {
["total"] => int(2)
["successful"] => int(1)
["failed"] => int(0)
}
["_seq_no"] => int(2)
["_primary_term"] => int(1)
}
3.3 packaging tools
Tool class for encapsulating operations es: project directory / extensions / tools / ES / myelasticsearch php
<?php
namespace tools\es;
use Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder;
class MyElasticsearch
{
//ES client link
private $client;
/**
* Constructor
* MyElasticsearch constructor.
*/
public function __construct()
{
$params = array(
'127.0.0.1:9200'
);
$this->client = ClientBuilder::create()->setHosts($params)->build();
}
/**
* Determine whether the index exists
* @param string $index_name
* @return bool|mixed|string
*/
public function exists_index($index_name = 'test_ik')
{
$params = [
'index' => $index_name
];
try {
return $this->client->indices()->exists($params);
} catch (\Elasticsearch\Common\Exceptions\BadRequest400Exception $e) {
$msg = $e->getMessage();
$msg = json_decode($msg,true);
return $msg;
}
}
/**
* Create index
* @param string $index_name
* @return array|mixed|string
*/
public function create_index($index_name = 'test_ik') { // Can only be created once
$params = [
'index' => $index_name,
'body' => [
'settings' => [
'number_of_shards' => 5,
'number_of_replicas' => 0
]
]
];
try {
return $this->client->indices()->create($params);
} catch (\Elasticsearch\Common\Exceptions\BadRequest400Exception $e) {
$msg = $e->getMessage();
$msg = json_decode($msg,true);
return $msg;
}
}
/**
* Delete index
* @param string $index_name
* @return array
*/
public function delete_index($index_name = 'test_ik') {
$params = ['index' => $index_name];
$response = $this->client->indices()->delete($params);
return $response;
}
/**
* Add document
* @param $id
* @param $doc ['id'=>100, 'title'=>'phone']
* @param string $index_name
* @param string $type_name
* @return array
*/
public function add_doc($id,$doc,$index_name = 'test_ik',$type_name = 'goods') {
$params = [
'index' => $index_name,
'type' => $type_name,
'id' => $id,
'body' => $doc
];
$response = $this->client->index($params);
return $response;
}
/**
* Determine whether the document exists
* @param int $id
* @param string $index_name
* @param string $type_name
* @return array|bool
*/
public function exists_doc($id = 1,$index_name = 'test_ik',$type_name = 'goods') {
$params = [
'index' => $index_name,
'type' => $type_name,
'id' => $id
];
$response = $this->client->exists($params);
return $response;
}
/**
* Get document
* @param int $id
* @param string $index_name
* @param string $type_name
* @return array
*/
public function get_doc($id = 1,$index_name = 'test_ik',$type_name = 'goods') {
$params = [
'index' => $index_name,
'type' => $type_name,
'id' => $id
];
$response = $this->client->get($params);
return $response;
}
/**
* Update document
* @param int $id
* @param string $index_name
* @param string $type_name
* @param array $body ['doc' => ['title' => 'Apple iPhone X ']]
* @return array
*/
public function update_doc($id = 1,$index_name = 'test_ik',$type_name = 'goods', $body=[]) {
// You can add new fields flexibly. It's best not to add them indiscriminately
$params = [
'index' => $index_name,
'type' => $type_name,
'id' => $id,
'body' => $body
];
$response = $this->client->update($params);
return $response;
}
/**
* remove document
* @param int $id
* @param string $index_name
* @param string $type_name
* @return array
*/
public function delete_doc($id = 1,$index_name = 'test_ik',$type_name = 'goods') {
$params = [
'index' => $index_name,
'type' => $type_name,
'id' => $id
];
$response = $this->client->delete($params);
return $response;
}
/**
* Search documents (pagination, sorting, weight, filtering)
* @param string $index_name
* @param string $type_name
* @param array $body
* $body = [
'query' => [
'bool' => [
'should' => [
[
'match' => [
'cate_name' => [
'query' => $keywords,
'boost' => 4, // Great power
]
]
],
[
'match' => [
'goods_name' => [
'query' => $keywords,
'boost' => 3,
]
]
],
[
'match' => [
'goods_introduce' => [
'query' => $keywords,
'boost' => 2,
]
]
]
],
],
],
'sort' => ['id'=>['order'=>'desc']],
'from' => $from,
'size' => $size
];
* @return array
*/
public function search_doc($index_name = "test_ik",$type_name = "goods",$body=[]) {
$params = [
'index' => $index_name,
'type' => $type_name,
'body' => $body
];
$results = $this->client->search($params);
return $results;
}
}
4. Product search function
4.1 search rules
Full text search can be carried out for commodity name, commodity introduction and commodity classification according to keywords
4.2 create full volume index
Project directory / application / cli / controller / es php
<?php
namespace app\cli\controller;
use think\Controller;
use think\Request;
class Es extends Controller
{
/**
* Create a product index and import all product documents
* cd public
* php index.php /cli/Es/createAllGoodsDocs
*/
public function createAllGoodsDocs()
{
try{
//Instantiate ES tool class
$es = new \tools\es\MyElasticsearch();
//Create index
if($es->exists_index('goods_index')) $es->delete_index('goods_index');
$es->create_index('goods_index');
$i = 0;
while(true){
//Query commodity data and process 1000 pieces at a time
$goods = \app\common\model\Goods::with('category')->field('id,goods_name,goods_desc, goods_price,goods_logo,cate_id')->limit($i, 1000)->select();
if(empty($goods)){
//If the query result is empty, stop
break;
}
//Add document
foreach($goods as $v){
unset($v['cate_id']);
$es->add_doc($v['id'],$v, 'goods_index', 'goods_type');
}
$i += 1000;
}
die('success');
}catch (\Exception $e){
$msg = $e->getMessage();
die($msg);
}
}
}
Switch to the public directory and execute the command
php index.php /cli/Es/createAllGoodsDocs
Note: the encapsulated es tool class is used: project directory / extensions / tools / ES / myelasticsearch php
4.3 search
4.3.1 page section
Project directory / application / home / view / layout HTML, modify the search box form as follows:
<form action="{:url('home/goods/index')}" method="get" class="sui-form form-inline">
<!--searchAutoComplete-->
<div class="input-append">
<input type="text" id="autocomplete" class="input-error input-xxlarge" name="keywords" value="{$Request.param.keywords}" />
<button class="sui-btn btn-xlarge btn-danger" type="submit">search</button>
</div>
</form>
4.3.2 controller part
Project directory / application / home / controller / goods In PHP, modify the index as follows:
public function index($id=0)
{
//Receive parameters
$keywords = input('keywords');
if(empty($keywords)){
//Get the product list under the specified category
if(!preg_match('/^\d+$/', $id)){
$this->error('Parameter error');
}
//Query commodities under classification
$list = \app\common\model\Goods::where('cate_id', $id)->order('id desc')->paginate(10);
//Query classification name
$category_info = \app\common\model\Category::find($id);
$cate_name = $category_info['cate_name'];
}else{
try{
//Search from ES
$list = \app\home\logic\GoodsLogic::search();
$cate_name = $keywords;
}catch (\Exception $e){
$this->error('Server exception');
}
}
return view('index', ['list' => $list, 'cate_name' => $cate_name]);
}
4.3.3 search logic
Project directory / application / home / logic / goodlogic In PHP, the code is as follows
<?php
namespace app\home\logic;
use think\Controller;
class GoodsLogic extends Controller
{
public static function search(){
//Instantiate ES tool class
$es = new \tools\es\MyElasticsearch();
//Calculate paging conditions
$keywords = input('keywords');
$page = input('page', 1);
$page = $page < 1 ? 1 : $page;
$size = 10;
$from = ($page - 1) * $size;
//Assembly search parameter body
$body = [
'query' => [
'bool' => [
'should' => [
[ 'match' => [ 'cate_name' => [
'query' => $keywords,
'boost' => 4, // Great power
]]],
[ 'match' => [ 'goods_name' => [
'query' => $keywords,
'boost' => 3,
]]],
[ 'match' => [ 'goods_desc' => [
'query' => $keywords,
'boost' => 2,
]]],
],
],
],
'sort' => ['id'=>['order'=>'desc']],
'from' => $from,
'size' => $size
];
//Search
$results = $es->search_doc('goods_index', 'goods_type', $body);
//get data
$data = array_column($results['hits']['hits'], '_source');
$total = $results['hits']['total']['value'];
//Paging processing
$list = \tools\es\EsPage::paginate($data, $size, $total);
return $list;
}
}
4.3.4 ES paging class
Using the paging query method of the model for reference, encapsulate the paging class for ES search: project directory / extensions / tools / ES / espage php
<?php
namespace tools\es;
use think\Config;
class EsPage
{
public static function paginate($results, $listRows = null, $simple = false, $config = [])
{
if (is_int($simple)) {
$total = $simple;
$simple = false;
}else{
$total = null;
$simple = true;
}
if (is_array($listRows)) {
$config = array_merge(Config::get('paginate'), $listRows);
$listRows = $config['list_rows'];
} else {
$config = array_merge(Config::get('paginate'), $config);
$listRows = $listRows ?: $config['list_rows'];
}
/** @var Paginator $class */
$class = false !== strpos($config['type'], '\\') ? $config['type'] : '\\think\\paginator\\driver\\' . ucwords($config['type']);
$page = isset($config['page']) ? (int) $config['page'] : call_user_func([
$class,
'getCurrentPage',
], $config['var_page']);
$page = $page < 1 ? 1 : $page;
$config['path'] = isset($config['path']) ? $config['path'] : call_user_func([$class, 'getCurrentPath']);
return $class::make($results, $listRows, $page, $total, $simple, $config);
}
}
Commodity list page commodity classification display position
4.4 commodity document maintenance
After adding a new product, add the product document in ES
After updating the product, modify the product document in ES
After deleting the product, delete the product document in ES
Use the background test of MVC in admin / model / goods PHP
Use the front and back-end separation interface api test, which is written in common / model / goods PHP
Project directory / application / admin / model / goods In PHP, the init method code is as follows:
protected static function init()
{
//Instantiate ES tool class
$es = new \tools\es\MyElasticsearch();
//Set new callback
self::afterInsert(function($goods)use($es){
//Add document
$doc = $goods->visible(['id', 'goods_name', 'goods_desc', 'goods_price'])->toArray();
$doc['cate_name'] = $goods->category->cate_name;
$es->add_doc($goods->id, $doc, 'goods_index', 'goods_type');
});
//Set update callback
self::afterUpdate(function($goods)use($es){
//Modify document
$doc = $goods->visible(['id', 'goods_name', 'goods_desc', 'goods_price', 'cate_name'])->toArray();
$doc['cate_name'] = $goods->category->cate_name;
$body = ['doc' => $doc];
$es->update_doc($goods->id, 'goods_index', 'goods_type', $body);
});
//Set delete callback
self::afterDelete(function($goods)use($es){
//remove document
$es->delete_doc($goods->id, 'goods_index', 'goods_type');
});
}
5. Summary
Distributed full-text search solution: it is a distributed full-text search system based on Mysql database, Hadoop Ecology (optional) and ElasticSearch search engine.
Mysql database is used to structurally store project data.
Hadoop ecology is used to back up all versions of relational databases. It also stores massive log data such as user behavior, click, exposure and interaction for data analysis and processing.
ElasticSearch search search engine is used to index and full-text search the data provided by Mysql or Hadoop.
The core functions include full index creation, incremental index creation, real-time data synchronization (curd of documents), full-text search, etc.