
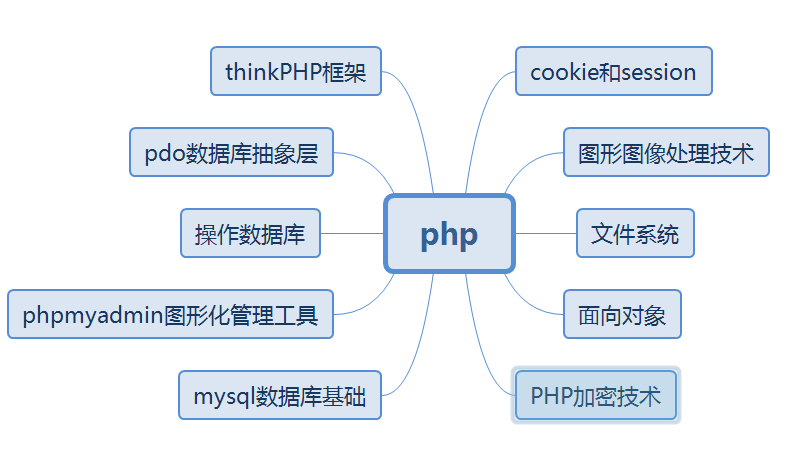
PHP and JavaScript, master JavaScript foundation, custom functions, process control statements, events, call JavaScript scripts, use JavaScript in PHP.
JavaScript, developed by Netscape, is an interpreted scripting language based on object and event driven and with security performance.
JavaScript Foundation, Data Types, Variables, Annotations
Data type, unll, undefined, object type, Boolean type, numerical type, string type.
Variable refers to a named storage unit that already exists in a program and a container for storing information.
abstract, continue, finally, instanceof, private, this class, final, in, package, synchronized, with char, false, import, null, switch, while catch, extends, implements, new, super, void case, else, goto, native, static, var byte, double, function, long, short, true break, do, for, interface, return, typeof boolean, default, float, int, public, throw
Custom function
Function function name ([parameter]){
return var;
}
Function name ();Process control statements:
Conditional statement
If (conditional expression){
Statement block
}
If (conditional expression)
{
Statement block 1;
}
else
{
Statement block 2;
}
Switch (expression or variable){
case Constant Expressions 1:
Statement block 1;
break;
case Constant Expressions 2:
Statement block 2;
break;
...
case Constant Expressions n:
Statement block n;
break;
default:
Statement block n+1;
break;
} <script language="javascript">
function check(){
var year1 = form.year.value;
if((year1%4==0&&(year1%100)!=0){}
}
</script>Loop statement
While (conditional expression){
Statement block
}
for (Initialization of cyclic variables; cyclic conditions; determination of the change value of cyclic variables){
Statement block;
}Jump statement, break statement terminates the cycle, continue statement jumps out of this cycle, into the next cycle.
Event
onclick mouse click event ondblclick mouse double-click event onmousedown mouse-down event Loosen the event after the onmouseup mouse is pressed Events when onmouseover mouse moves over an object Trigger event when onmousemove mouse moves On keypress keyboard press and release events onkeydown keyboard press event Events triggered when the onkeyup keyboard is pressed and released The onabort image is triggered when the user interrupts when it is downloaded Triggered when the content of the onload page is complete onresize browser window size changed This event is triggered when the current page of onunload is changed onblur loses focus onchange content changes onfocus gets focus onreset and onsubmit
Embedded JavaScript scripts
<script language="javascript"> ... </script> <input type="submit" name="Submit" value="Testing" onClick="check();"> <script src=url language="Javascript"></script>
<script language="javascript">
function check(){
if(myform.subject.value==""){
alert("The theme of the article should not be empty!!");myform.subject.focus();return false;
}
if(myform.content.value==""){
alert("Article content can not be empty!!");myform.content.focus();return false;
}
if(myform.author.value==""){
alert("The author can't be empty!!");myform.author.focus();return false;
}
alert("Successful verification!");
}
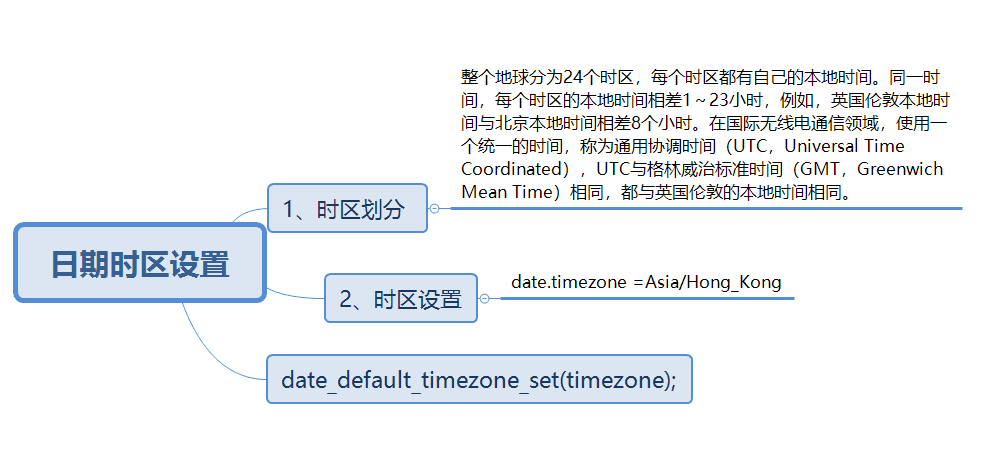
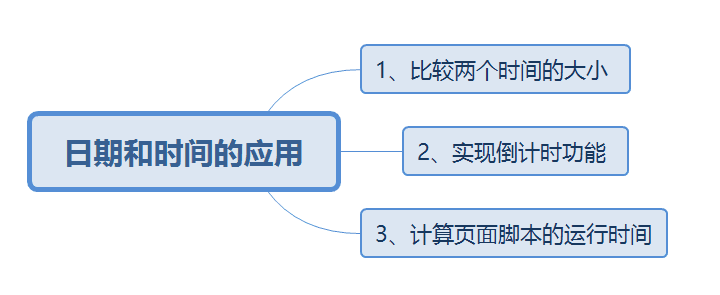
</script>System Time Zone Settings, PHP Date and Time Functions, Applications
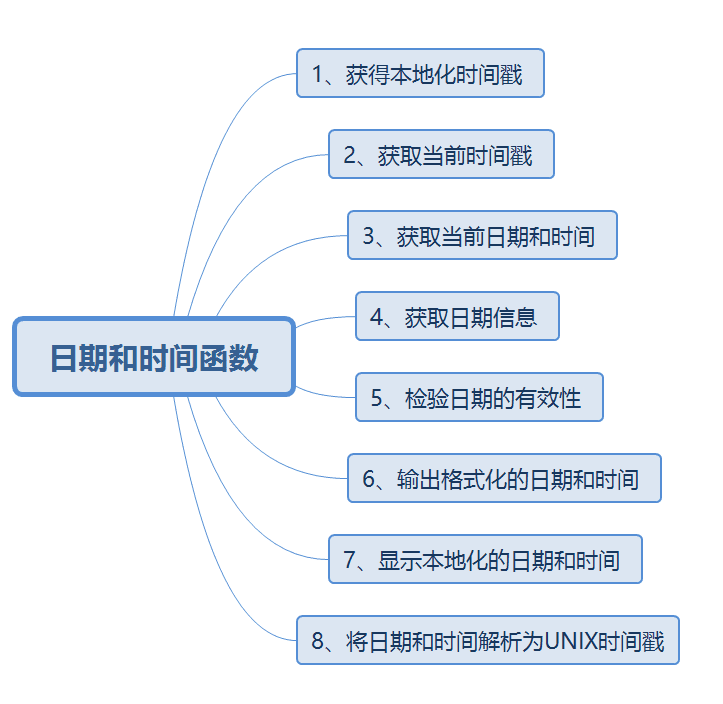
The mktime() function converts a time into a UNIX timestamp value
int mktime(int hour, int minute, int second, int month, int day, int year, int [is_dst] )
hour hours, minute minutes, second seconds, month months, day days, year years, is_dst is set to 1 at daylight saving time, not 0, uncertainty is -1
Get a timestamp
int time ( void )
Get the current date and time
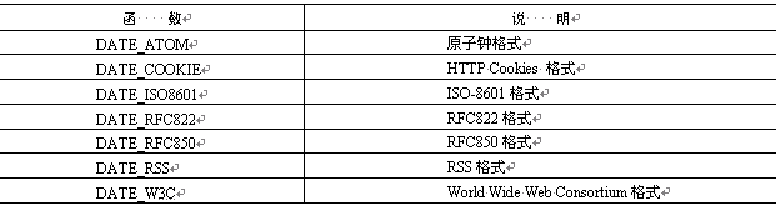
date(string format,int timestamp)
Get date information
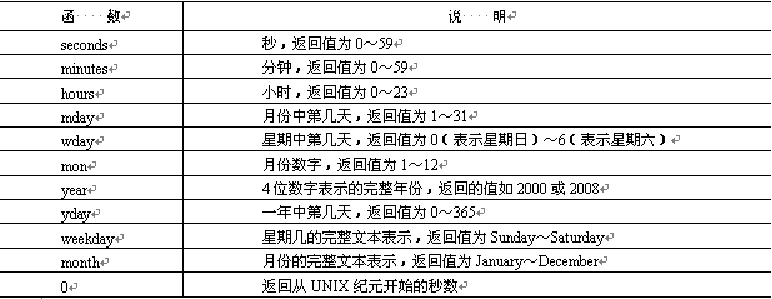
array getdate(int timestamp)
Validity of inspection date
bool checkdate(int month,int day,int year)
Output formatted date and time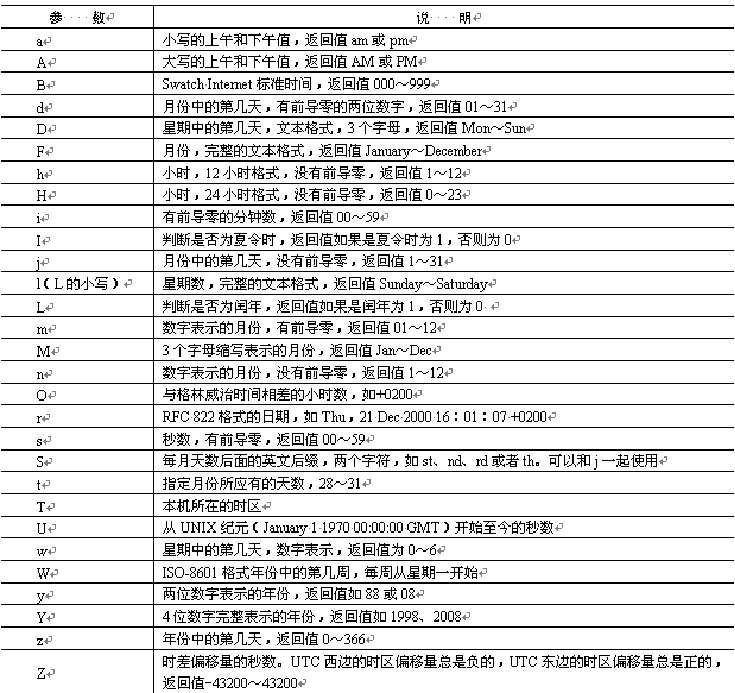
Y-m-d H:i:s
Display the date and time of localization
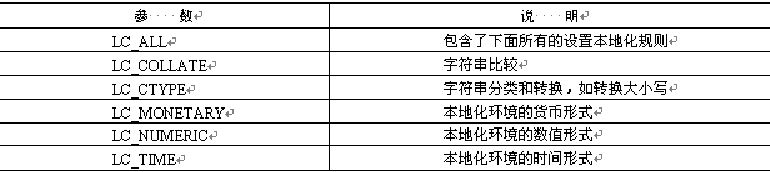
setlocale() function sets localization environment
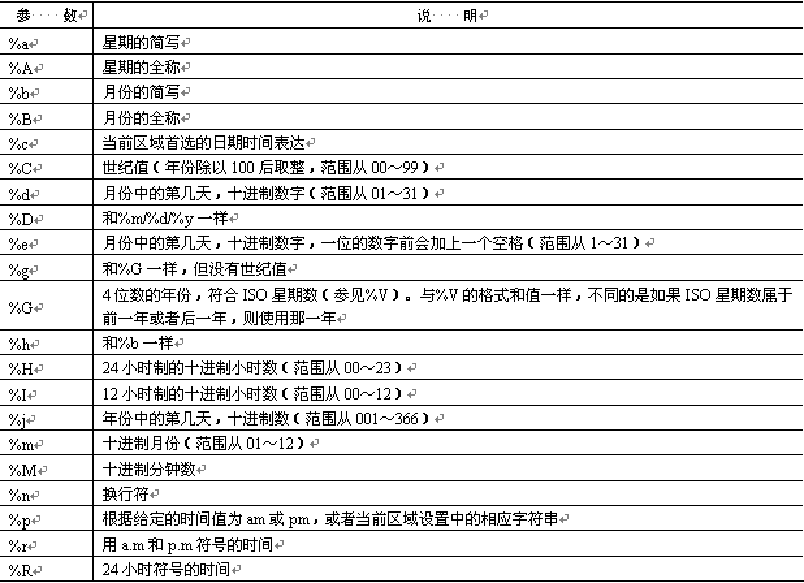
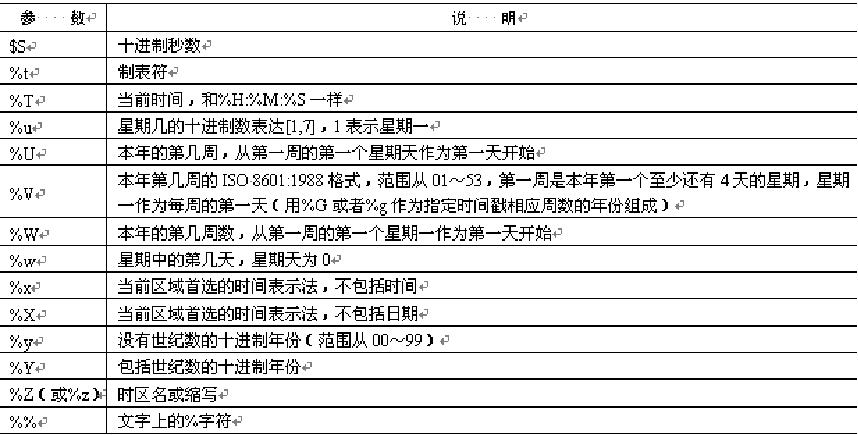
strftime() function formats output date and time
string setlocale(string category, string locale)
string strftime(string format, int timestamp)
Resolve date and time into UNIX timestamps
Int strtotime (string time [, int now]) parses the date and time of any English text into UNIX timestamps
Comparing time, we need to parse time into time stamp, strtotime() function.
<?php
$time1 = date("Y-m-d H:i:s");
$time2 = "2006-6-6 10:30:00";
echo "The time of variable 1 is:".$time1."<br>";
echo "The time of variable 2 is:".$time2."<p>";
if(strtotime($time1) - strtotime($time2) < 0){
echo "\$time1 Earlier than \$time2 ";
}else{
echo "\$time2 Earlier than $time1 ";
}
?><?PHP
$time1 = strtotime(date( "Y-m-d H:i:s"));
$time2 = strtotime("2010-5-2 12:10:00");
$time3 = strtotime("2014-2-4");
$sub1 = ceil(($time2 - $time1) / 3600); //60 * 60
$sub2 = ceil(($time3 - $time1) / 86400); //60 * 60 * 24
echo "There is still a holiday. $sub1 hour!!!" ;
echo "<p>";
echo "It's New Year's Day. $sub2 day!!!";
?> Calculate the running time of page scripts
string microtime(void)
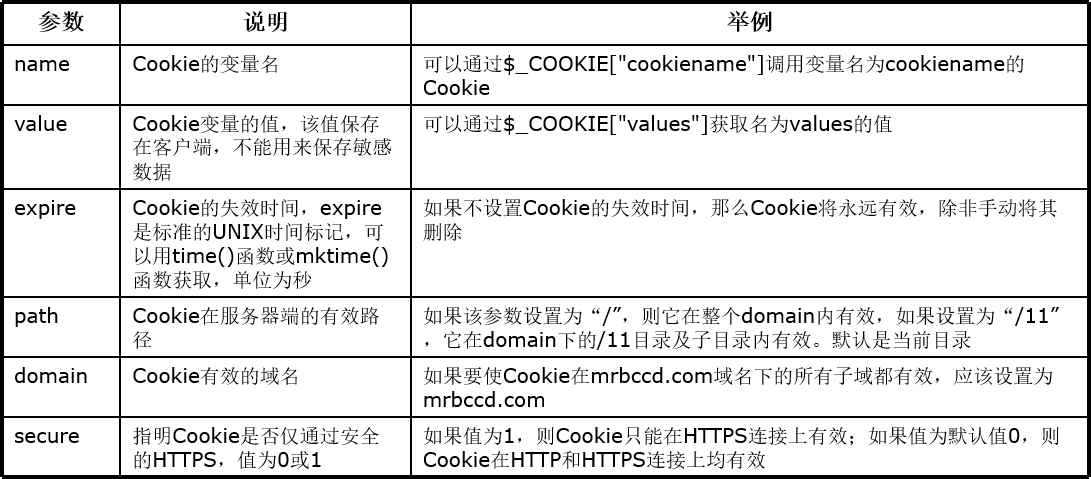
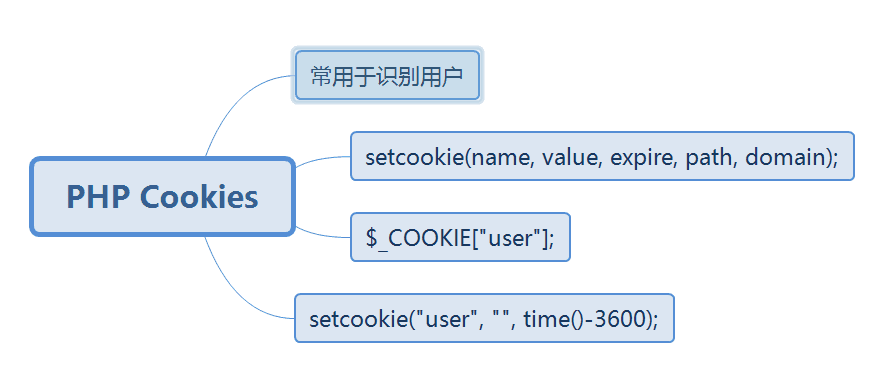
Using cookie s to differentiate different users
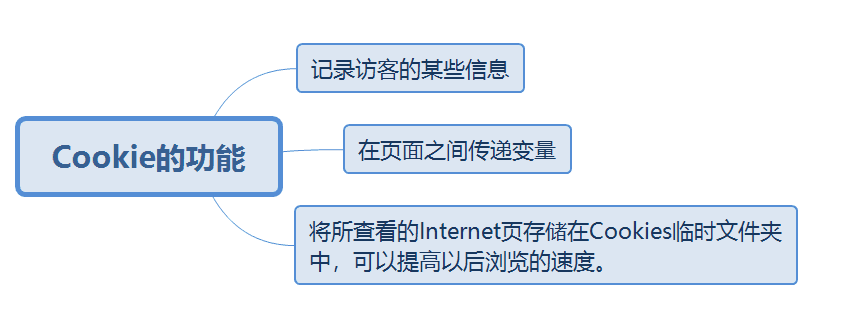
Cookie is a mechanism that stores data on the remote browser side and uses it to track and identify users.
The command format of the text file is as follows:
Username @ website address [number]. txt
Create cookie s:
bool setcookie(string name[,string value[,int expire[, string path[,string domain[,int secure]]]]])
<?php
setcookie("TMCookie","www.dashucoding.cn");
setcookie("TMCookie","www.dashucoding.cn", time()+60);
// Set the effective time to 60 seconds, directory "/ tm /", domain name
setcookie("TMCookie", $value, time() + 3600, "/tm/", ".dashucoding.cn", 1);
?>Read cookie
<?php
if(!isset($_COOKIE["visittime"])){
setcookie("visittime",date("y-m-d H:i:s"));
echo "Welcome to the first time";
}else{
setcookie("visittime",date("y-m-d H:i:s"), time()+60);
echo "Last visit".$_COOKIE["visittime"];
echo "<br>"
}
echo "This visit".date("y-m-d H:i:s");
?>Delete cookies: Delete cookies manually using the setcookie() function (Delete cookies manually in browsers)
setcookie("name","", time()-1);Browsers allow storage of up to 300 Cookie files, each supporting a maximum capacity of 4 KB, and each domain name supporting up to 20 cookies.
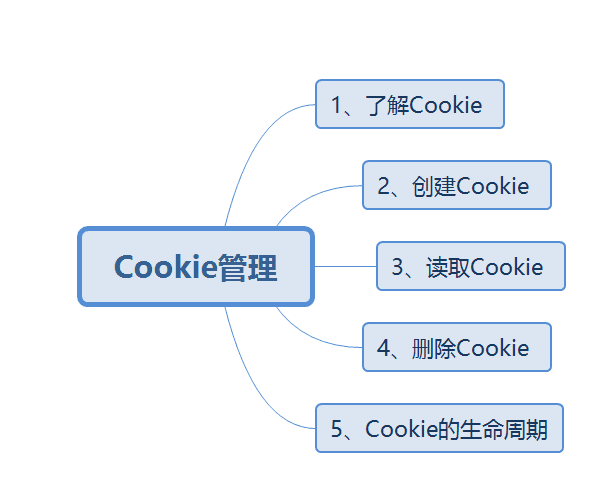
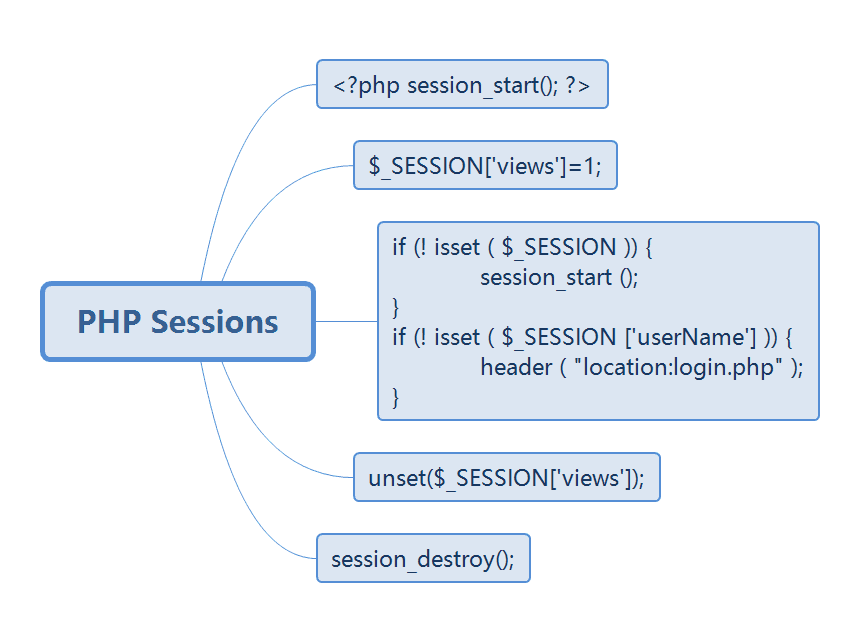
Start Session Register Session Use Session Delete Session
The session_start() function creates a session:
bool session_start(void)
Create a session through the session_register() function to create a variable for the session to implicitly start the session. With this function, the session_start() function is not called because hi implicitly calls the session_start() function.
Registration session:
<?php session_start(); //Start Session $_SESSION["admin"] = null; //Declare a variable named admin and assign a null value ?>
Using sessions:
<?php
if ( !empty ( $_SESSION['session_name'])) //Determine whether the Session session variable used to store user names is empty
$myvalue = $_SESSION['session_name'] ;//Assign the session variable to a variable $myvalue
?>
if (! isset ( $_SESSION )) {
session_start ();
}
if (! isset ( $_SESSION ['userName'] )) {
header ( "location:login.php" );
}
$userName = $_SESSION ['userName'];Delete session
Delete a single session, delete multiple sessions, and end the current session
Delete a single session
unset ( $_SESSION['user'] ) ;
Delete multiple sessions
$_SESSION = array() ;
End the current session
session_destroy() ;
Session setup time
Set Session's expiration time using session_set_cookie_params()
setcookie() function is used to set failure time for Session
<?php $time = 1*60; session_set_cookie_params($time); session_start(); $_SESSION[username] = "mr" ?>
<?php session_start(); $time=1*60; setcookie(session_name(), session_id(), time()+$time,"/"); $_SESSION['user']='mr'; ?>
Client prohibits Cookie:
Set session.use_trans_sid = 1 in the php.ini file Open the - enable-trans-sid option at compile time to allow PHP to automatically pass session_id across pages Hidden forms pass session_id
<form id="form1" name="form1" method="post" action="xx.php?<?=session_name();?>=<?=session_id();?>"> <?php $sess_name = session_name(); $sess_id = $_GET[$sess_name]; session_id($sess_id); session_start(); $_SESSION['admin']='mr'; ?>
Page a passes the value to page b:

Page a passes the value to Page b, Page c, Page d, etc. How to do?
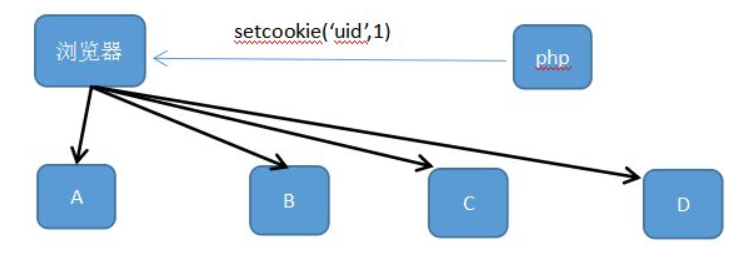
But cookie s are not safe, and it's dangerous if someone changes them.

Encryption. Using the hash function MD5:
MD5 (uid + a fixed random string)
if (! isset ( $_SESSION )) {
session_start ();
}
if (! isset ( $_SESSION ['userName'] )) {
header ( "location:login.php" );
}
$userName = $_SESSION ['userName'];Login partition
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312">
<title>Blog user login</title>
<style type="text/css">
<!--
.style1 {color: #FF0000}
-->
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script language="javascript">
function check(form){
if(form.user.value==""){
alert("enter one user name");form.user.focus();return false;
}
if(form.pwd.value==""){
alert("Please input a password");form.pwd.focus();return false;
}
form.submit();
}
</script>
<form name="form1" method="post" action="default.php">
<table width="521" height="394" border="0" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<td valign="top" background="images/login.jpg"><table width="521" border="0" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tr>
<td width="262" height="218"> </td>
<td width="259"> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td height="24" align="right">User name:</td>
<td height="24" align="left"><input name="user" type="text" id="user" size="20"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td height="24" align="right">dense Code:</td>
<td height="24" align="left"><input name="pwd" type="password" id="pwd" size="20"></td>
</tr>
<tr align="center">
<td height="24" colspan="2"><input type="submit" name="Submit" value="Submission" onClick="return check(form);">
<input type="reset" name="Submit2" value="Refill"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td height="76" align="right"><span class="style1">Super User: tsoft<br>
//Dense & nbsp; & nbsp; & nbsp; & nbsp; code: 111 & nbsp; & nbsp;;</span></td>
<td><span class="style1"> Ordinary users: zts<br>
dense Code: 000</span></td>
</tr>
</table></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html><?php
session_start();
$_SESSION[user]=$_POST[user];
$_SESSION[pwd]=$_POST[pwd];
if($_SESSION[user]==""){
echo "<script language='javascript'>alert('Please login the system through the right way!');history.back();</script>";
}
?>
<?php if($_SESSION[user]=="123" && $_SESSION[pwd]=="123456"){echo "Administrators";}else{echo "Ordinary users";}?><a href="safe.php">logoff</a>
<?php
session_start();
unset($_SESSION['user']);
unset($_SESSION['pwd']);
session_destroy();
header("location:index.php");
?>Session Advanced Applications
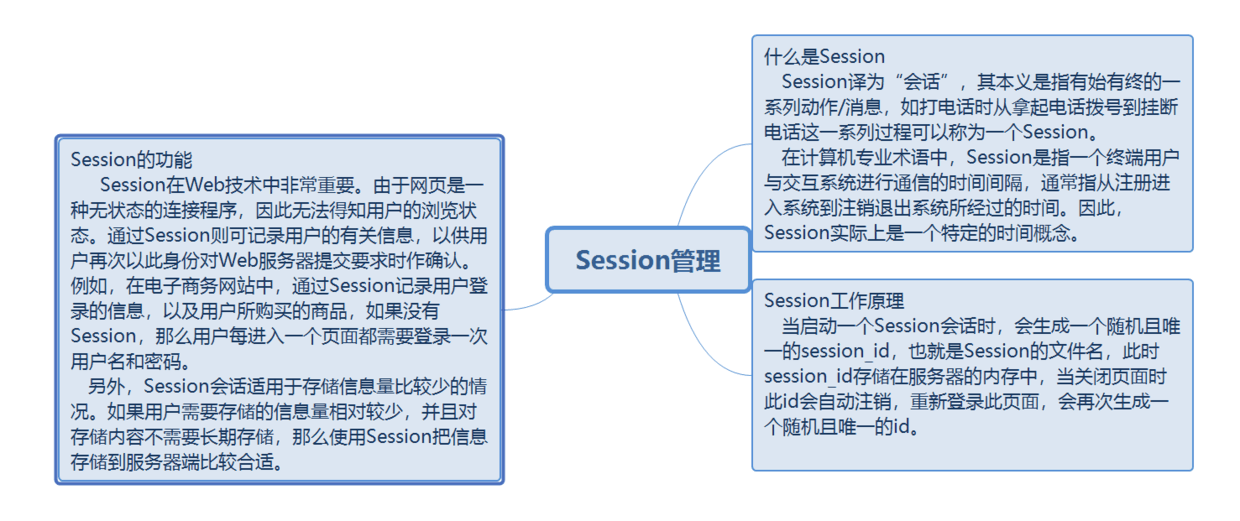
Session is to store session information on the server, and transmit the information of the client through session ID. At the same time, after the server receives session id, it provides relevant session information resources according to this ID.
Cookies are stored on the client side in the form of text files, which are managed and maintained through browsers.
If session is saved in a temporary directory, the security and efficiency of the server will be reduced. The session_save_path() function is used to solve the problem of session temporary files.
<?php $path="./tmp/'; session_save_path($path); session_start(); $_SESSION[username]=true; ?>
Session cache
string session_cache_limiter ( [string cache_limiter])
int session_cache_expire ( [int new_cache_expire])
Differences and summaries between cookie s and session s
Cookie is implemented by extending http protocol, including name, value, expiration time, path and domain. If the cookie does not set the time, it will be closed by browser. The cookie is generally stored in memory, not on the hard disk, set the time, and does not disappear with the browser's closure. The cookie is still valid beyond the set expiration time.
Session and session id, the way to save session ID can be cookie, cookie data stored in browser, session data placed on the server, cookie is not safe, session security, session will be saved in a certain time on the server, more access, will occupy the performance of the server, in view of reducing server performance, cookie should be used.
Browsers allow storage of up to 300 cookie files, each cookie file can not save more than 4 KB of data, many browsers limit a site to save up to 20 cookies, each domain name supports up to 20 cookies. If it exceeds, the browser will automatically delete the cookie file.
Sign-in information and other important information are stored in session, but not in cookie. It's easy to lose in session, so when session is lost, if the cookie is still in the validity period we set, we can take the value out of the cookie and put it into session again.
<sessionState timeout="5" mode="InProc" />
<sessionState timeout="2" mode="StateServer" />
cookie Establishment of validity period
httpCookie.Expires = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(2);
//Do you have permission to access this page?
if (Request.Cookies["httpCookie"] != null)
{
Session["admin"] = Request.Cookies["httpCookie"].Values["admin"].ToString();
}
if (Session["admin"] == null)
{
this.ClientScript.RegisterStartupScript(this.GetType(), "", "<script>alert('Please login again');location.href='logins.aspx'</script>");
}Is Session still available after PHP disables Cookie? Yes.
Remind users that cookie s must be opened before logging in.
Set "session.use_trans_sid = 1" in the php.ini configuration file, or turn on the "enable-trans-sid" option at compile time to allow PHP to automatically pass Session ID across pages.
Pass the value manually through the URL and hide the form to pass the Session ID.
Save the Session ID in the form of files, databases, etc., and call it manually during the cross-page process.
Use of COOKIE and SESSION
Create cookie values:
// Function Settings Cookie
Setcookie("Identifying key values","Cookie value","Effective time","Effective scope / Represents that the current website is good for use");
// Assignment Settings Cookie
$_COOKIE['Identifying key values'] = "Cookie value";Modify the Cookie value:
// Function Settings Cookie
Setcookie("Identifying key values","Cookie New value","New effective time","New effective scopes");
// Assignment Settings Cookie
$_COOKIE['Identifying key values'] = "Cookie New value";Delete cookie values:
// Function Settings Cookie
Setcookie("Identifying key values","Null value",time()-1);View Cookie values:
// View all Cookie values var_dump($_COOKIE); // View specific Cookie values var_dump($_COOKIE['Key value']);
Give an example:
<?php
// Increase Cookie
// Set Cookie function method setCookie();
setCookie("test1","test1");
// Setting Cookie Assignment Method
$_COOKIE['test2'] = "test2";
// Modify Cookie
// Modify Cookie setCookie()
setCookie("test1","test1->test3");
// Modified Cookie Assignment Method
$_COOKIE["test2"] = "test2->test4";
// Query all Cookie values
var_dump($_COOKIE);
// The query key value is the value of test2
var_dump($_COOKIE['test2']);
// Delete the value whose key value is test1
setCookie("test1","",time()-1);
// Set test2 value to null
$_COOKIE['test2'] = "";
var_dump($_COOKIE);After setting or modifying cookies with setcookie, the first refresh page print cookies will not produce results, only generate cookie files, the second refresh will only obtain new or modified values, and use $_COOKIE to add or modify values, after the first request can obtain results.
When setting cookie is used to delete cookie values, the first deletion is only to delete files. After refreshing the page, the corresponding cookie values have been deleted.
All setcookie functions do not produce results for the first time, and for the second time, data using the $_COOKIE operation will be available for the first time.
SESSION session control
Session content is usually stored in the server as a file. Cookie stores the Seion_id value of the key value "PHPSESSID", and the session file stored in the server will be cleared automatically after 30 minutes.
Add session:
$_SESSION['session Key value'] = "session value";
Modify session:
$_SESSION['session Key value'] = "session New value";
View session values:
// View all session s var_dump($_SESSION); // View key values separately var_dump($_SESSION['test']);
Delete session:
// Delete session value, but retain data type $_session['session Key value'] = array(); // Delete session_id in cookie s $session_id = session_name(); setCookie($session_id,"",time()-1); // Release all $_SESSION variables that are currently created in memory session_unset(); // Delete the session file corresponding to the current user and release session_id session_destroy();
Use examples:
<?php
// Open session
session_start();
// Increase session
$_SESSION['test'] = "session content";
$_SESSION['test1'] = "session content";
// var_dump($_SESSION['test']);
// Modify session
$_SESSION['test'] = "session Modify content";
// var_dump($_SESSION['test']);
// View all session s
var_dump($_SESSION);
// View the Session value of the key value test separately
var_dump($_SESSION['test']);
// Delete session
// Delete session variable values
// $_SESSION['test'] = array();
// Deleting all SESSION s is generally used for exit operations
// 1 to expire SESSIONID in client COOKIE
// $session_id = Session_name();
// setcookie($session_id,"",time()-1);
// Release all $_SESSION variables that are currently created in memory, without deleting the session file and without releasing the corresponding session_id
// session_unset();
// Delete the session file corresponding to the current user and release session_id, but the contents of the $_SESSION variable remain in memory
session_destroy();
var_dump($_SESSION);The difference between cookie and session:
Storage Location, Quantity and Size Limitations, Content Distinction, Path Distinction
Session value has no size limit, but too much will lead to server pressure, content, cookie saves string, session saves data is the object.

session implementation, storage

session_id Gets / Sets the Current Session ID
session_id ([ string $id ] ) : string
cookie usage in php
Cookies are stored in client browsers. cookies are part of http headers. when requesting pages through browsers, they are sent in the form of http headers. when requesting pages, the value of cookies is obtained through PHP.
Set cookie:
bool setcookie( string name,[string value],[int expire],[string path],[string domain]);
Name: cookie name
Value: cookie value
Expire: expire time
Path is a valid path on the server side
Domain: A valid domain name for cookie s
Example:
setcookie('text','text',time()+3600*12,'/','www.test.com');Get cookie:
$cookieValue ='';
if (isset($_COOKIE['text'])) //First, determine if the cookie has been set
{
$cookieValue = $_COOKIE['text'];
}Destroy cookie s:
setcookie("user", "", time()-3600);Summary:
Session Advanced Applications
Session temporary file, session cache, session database storage
Temporary file session_save_path() stores session temporary files, which can alleviate the problem of server efficiency degradation caused by temporary file storage.
<?php $path="./tmp/"; session_save_path($path); session_start(); $_SESSION[username] = true; ?>
Session cache
Session cache completion uses session_cache_limiter() function
string session_cache_limiter ( [string cache_limiter])
session_cache_expire() function, cache time setting
int session_cache_expire ( [int new_cache_expire])
Example:
<?php
session_cache_limiter('private');
$cache_limit = session_cache_limiter(); // Open Client Cache
session_cache_expire(30);
$cache_expire = session_cache_expire(); // Setting client cache time
session_start();
?>Session database storage
session_set_save_handler() function in PHP
bool session_set_save_handler ( string open, string close, string read, string write, string destroy, string gc)
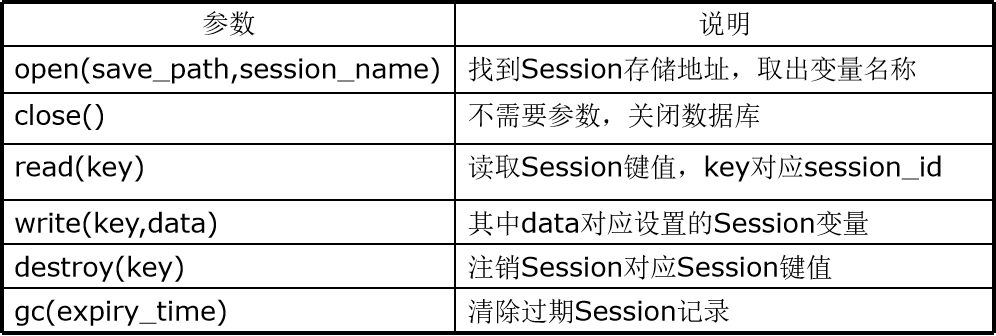
Encapsulate session_open() function to connect to database
function _session_open($save_path,$session_name)
{
global $handle;
$handle = mysql_connect('localhost','root','root') or die('Failure of database connection'); //Connect to MySQL database
mysql_select_db('db_database11',$handle) or die('There is no library name in the database'); //Find the database
return(true);
}Encapsulate session_close() function to close database connection
function _session_close()
{
global $handle;
mysql_close($handle);
return(true);
} Encapsulating session_read() function
function _session_read($key)
{
global $handle; //Global variable $handle connects to database
$time = time(); //Set the current time
$sql = "select session_data from tb_session where session_key = '$key' and session_time > $time";
$result = mysql_query($sql,$handle);
$row = mysql_fetch_array($result);
if ($row){
return($row['session_data']); //Returns the Session name and content
}else{
return(false);
}
}Encapsulating session_write() function
function _session_write($key,$data)
{
global $handle;
$time = 60*60; //Setting failure time
$lapse_time = time() + $time; //Get UNIX timestamp $sql = "select session_data from tb_session where session_key ='$key'and session_time > $lapse_time";
$result = mysql_query($sql,$handle);
if (mysql_num_rows($result) == 0 ) { //No result
$sql = "insert into tb_session values('$key','$data',$lapse_time)";//Insert database sql statement
$result = mysql_query($sql,$handle);
}else{
$sql = "update tb_session set session_key = '$key',session_data = '$data',session_time = $lapse_time where session_key = '$key'"; //Modify the database SQL statement $result = mysql_query($sql,$handle);
}
return($result);
} Encapsulating session_destroy() function
function _session_destroy($key)
{
global $handle;
$sql = "delete from tb_session where session_key = '$key'"; //Delete database sql statements
$result = mysql_query($sql,$handle);
return($result);
}Encapsulating session_gc() function
function _session_gc($expiry_time)
{
global $handle;
$lapse_time = time(); //Assign the parameter $expiry_time to the current timestamp
$sql = "delete from tb_session where expiry_time < $lapse_time"; //Delete database sql statements
$result = mysql_query($sql,$handle);
return($result);
}afterword
Well, welcome to leave a message in the message area, and share your experience and experience with you.
Thank you for learning today's content. If you think this article is helpful to you, you are welcome to share it with more friends. Thank you.
Thank! Thank you for your attention! Your sincere appreciation is the greatest driving force for my progress!

