Headline and Replace
I. replace
Definition: after taking out the maximum element, put a new element [the total number in the heap has not changed]
The implementation methods are as follows: 1. Extract max, then add, two operations of O(log n);
2. You can directly replace the heap top element and then Sift Down, one O(log n) operation.
Code implementation: MaxHeap.java
public class MaxHeap<E extends Comparable<E>> {
private Array<E> data;
public MaxHeap(int capacity){
data = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public MaxHeap(){
data = new Array<>();
}
public MaxHeap(E[] arr){
data = new Array<>(arr);
for(int i = parent(arr.length - 1) ; i >= 0 ; i --)
siftDown(i);
}
// Returns the number of elements in the heap
public int size(){
return data.getSize();
}
// Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the heap is empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return data.isEmpty();
}
// Returns the index of the parent node of the element represented by an index in the array representation of a complete binary tree
private int parent(int index){
if(index == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index-0 doesn't have parent.");
return (index - 1) / 2;
}
// Returns the index of the left child node of the element represented by an index in the array representation of a complete binary tree
private int leftChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 1;
}
// Returns the index of the right child node of the element represented by an index in the array representation of a complete binary tree
private int rightChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 2;
}
// Add elements to the heap
public void add(E e){
data.addLast(e);
siftUp(data.getSize() - 1);
}
private void siftUp(int k){
while(k > 0 && data.get(parent(k)).compareTo(data.get(k)) < 0 ){
data.swap(k, parent(k));
k = parent(k);
}
}
// Look at the largest element in the heap
public E findMax(){
if(data.getSize() == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not findMax when heap is empty.");
return data.get(0);
}
// Take out the largest element in the heap
public E extractMax(){
E ret = findMax();
data.swap(0, data.getSize() - 1);
data.removeLast();
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}
private void siftDown(int k){
while(leftChild(k) < data.getSize()){
int j = leftChild(k); // In this cycle, data[k] and data[j] exchange positions
if( j + 1 < data.getSize() &&
data.get(j + 1).compareTo(data.get(j)) > 0 )
j ++;
// data[j] is the maximum of leftChild and rightChild
if(data.get(k).compareTo(data.get(j)) >= 0 )
break;
data.swap(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
// Take out the largest element in the heap and replace it with element E (new code)
public E replace(E e){
E ret = findMax();
data.set(0, e);
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}
}
II. Repalce
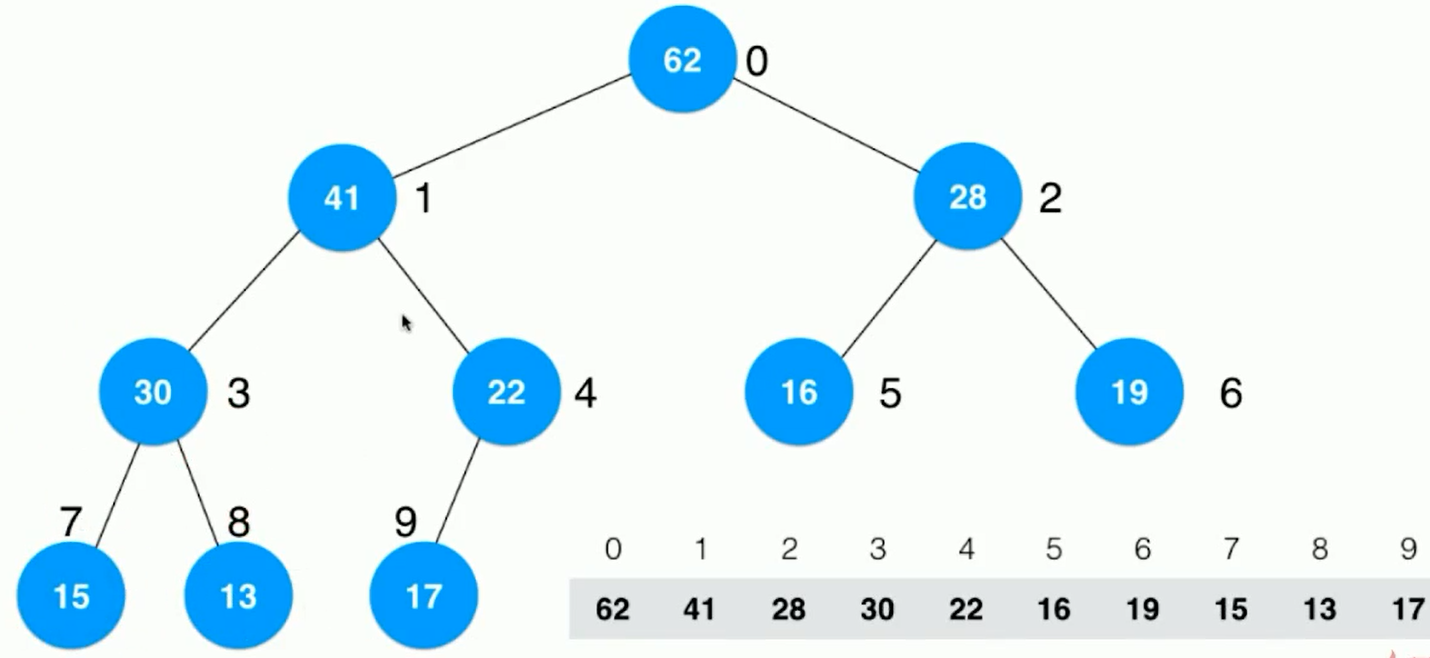
Definition: organize any array into a heap shape;
Method: treat the current array as a complete binary tree, starting from the last non leaf node, that is, 22 in the figure.
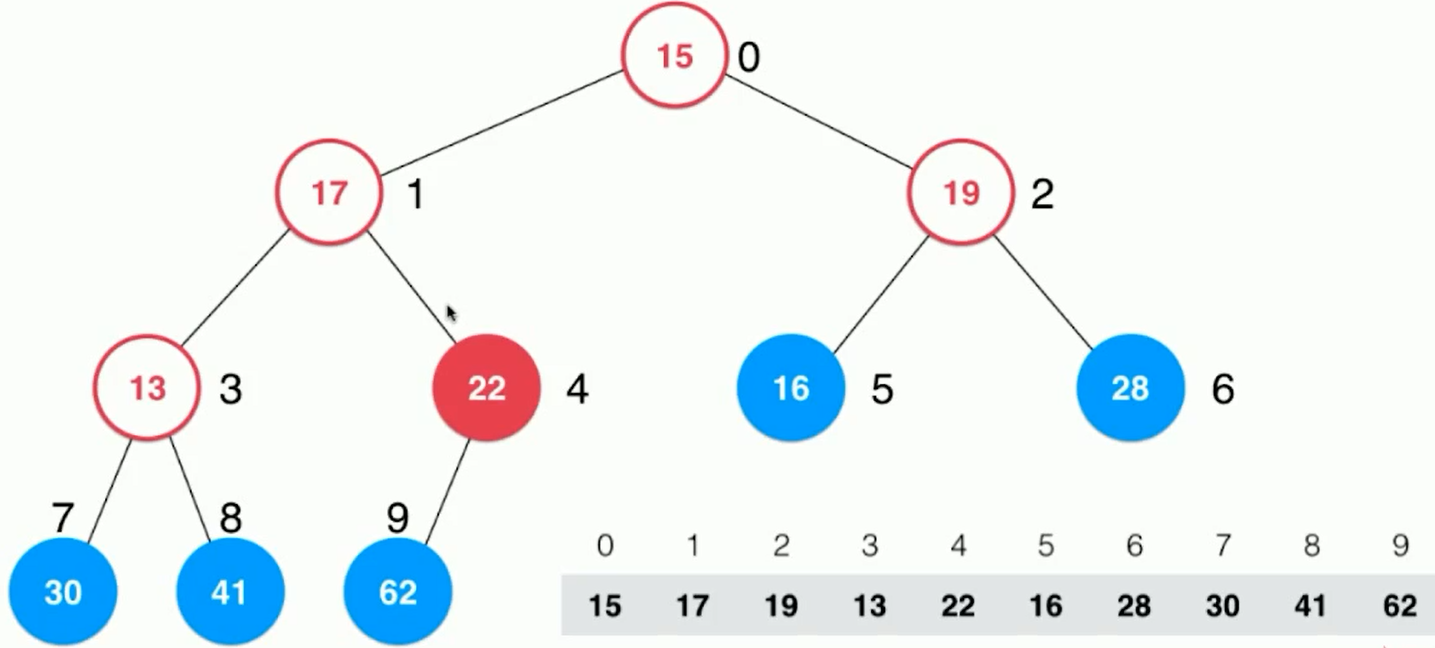
From 22 onwards, continue sinking operation
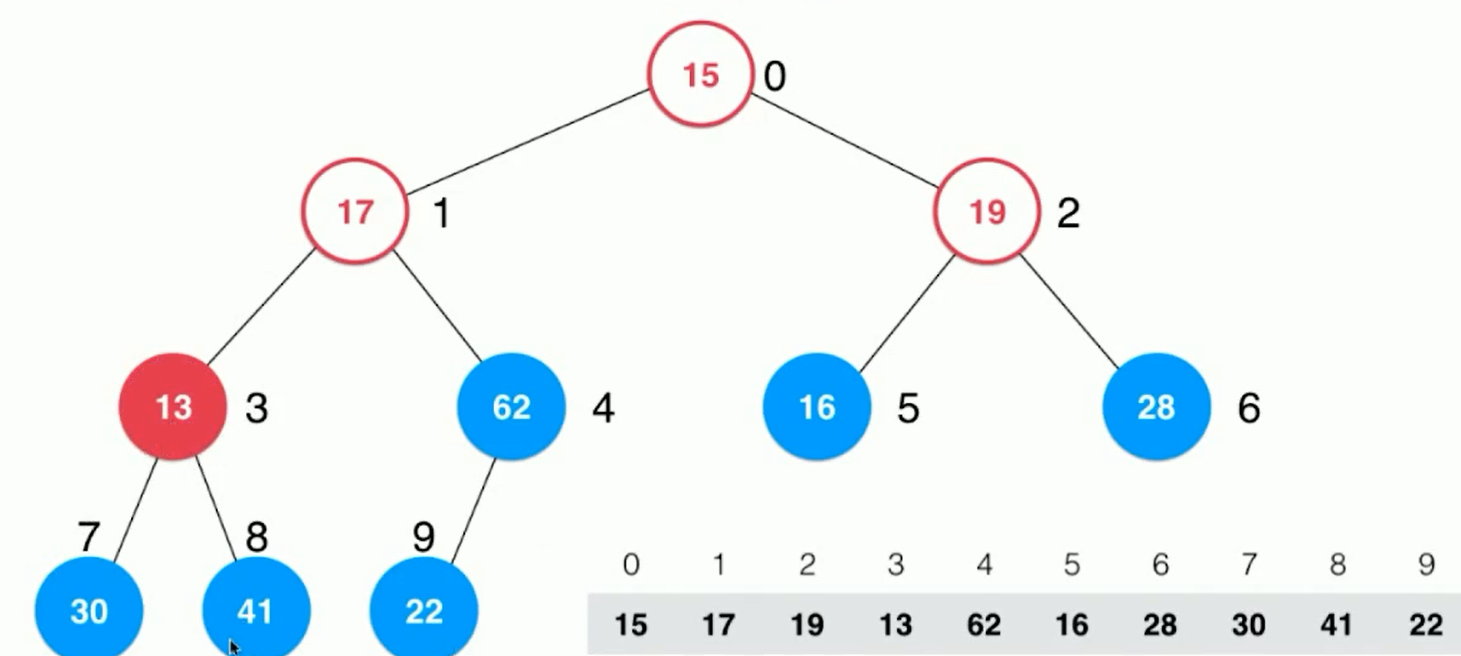
Index 3 is 13, which is sinking, exchanging 41 and 13;
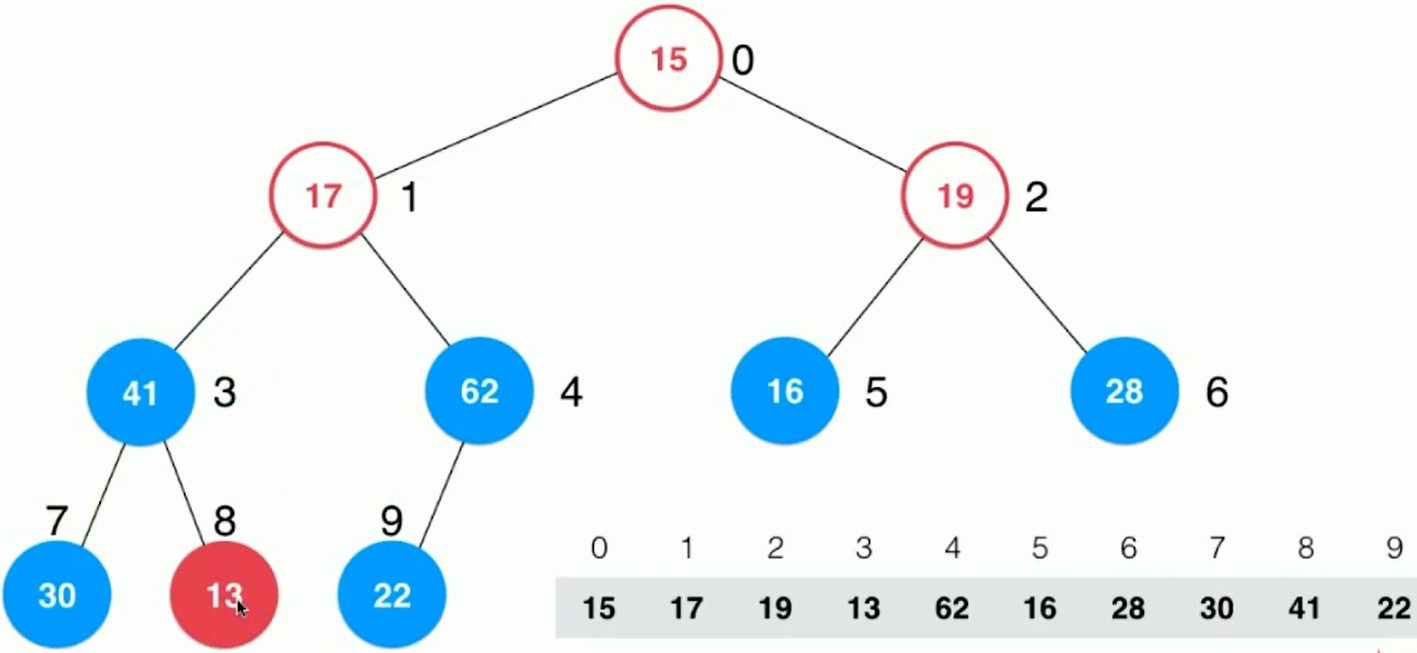
Index 2 is 19, sink it
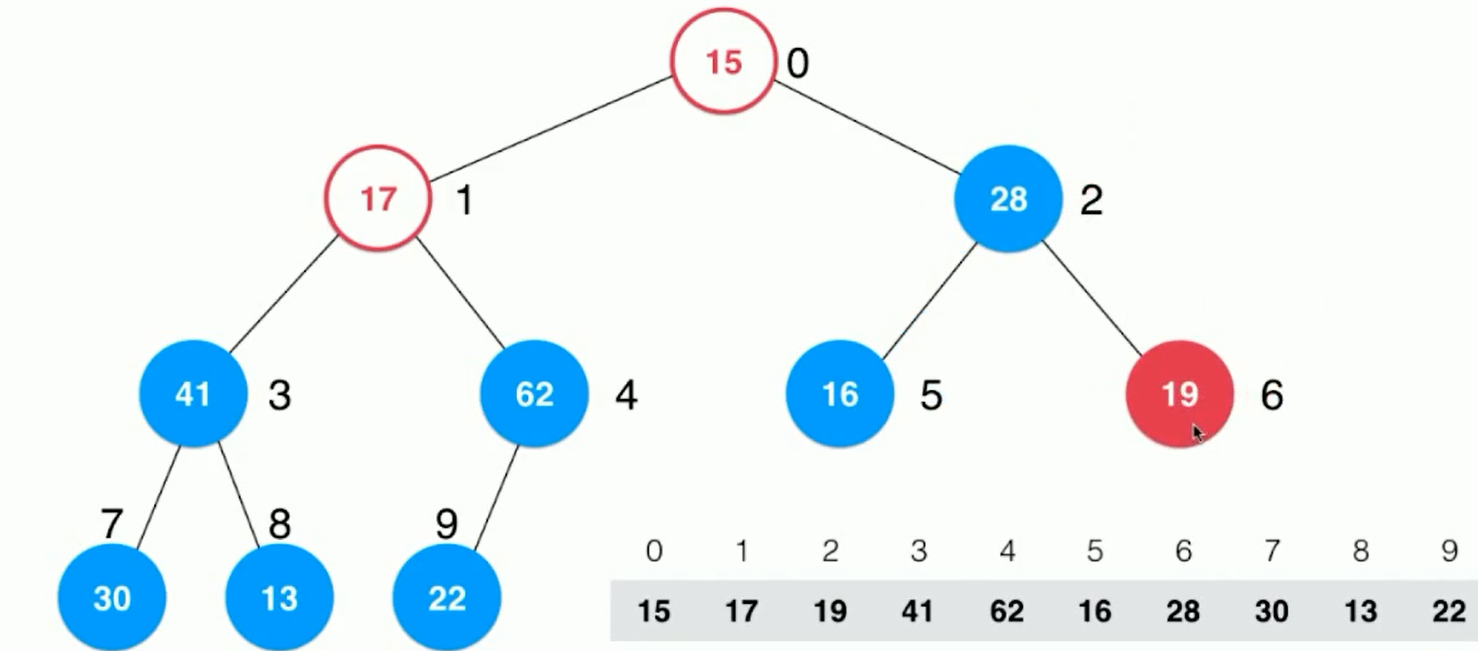
Continue to sink the index 1 and 0 to get the final binary tree.
The complexity of the algorithm is as follows:
N elements are inserted into an empty heap one by one. The algorithm complexity is O(nlog n).
With heaify, the algorithm complexity is O(n)
Code implementation heap ify: Array.java
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// Constructor, passing in the capacity of the Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// Parameterless constructor, capacity of default array capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
public Array(E[] arr){ //New code
data = (E[])new Object[arr.length];
for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++)
data[i] = arr[i];
size = arr.length;
}
// Get the capacity of an array
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// Get the number of elements in the array
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// Returns whether the array is empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// Insert a new element e in the index index
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// Add a new element after all elements
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// Add a new element before all elements
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// Get elements of index location
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// Change the element of index location to e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// Find if there is element e in the array
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Finds the index of element e in the array, and returns - 1 if element e does not exist.
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// Delete the element at index position from the array, and return the deleted element
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// Delete the first element from the array, return the deleted element
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// Delete the last element from the array, return the deleted element
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// Remove element e from array
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
public void swap(int i, int j){
if(i < 0 || i >= size || j < 0 || j >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index is illegal.");
E t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// Change the capacity of array space to newCapacity
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}
MaxHeap.java
public class MaxHeap<E extends Comparable<E>> {
private Array<E> data;
public MaxHeap(int capacity){
data = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public MaxHeap(){ //New code
data = new Array<>();
}
public MaxHeap(E[] arr){
data = new Array<>(arr);
for(int i = parent(arr.length - 1) ; i >= 0 ; i --)
// From the last non leaf node to the root node traversal
siftDown(i); //Sinking operation
}
// Returns the number of elements in the heap
public int size(){
return data.getSize();
}
// Returns a Boolean value indicating whether the heap is empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return data.isEmpty();
}
// Returns the index of the parent node of the element represented by an index in the array representation of a complete binary tree
private int parent(int index){
if(index == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index-0 doesn't have parent.");
return (index - 1) / 2;
}
// Returns the index of the left child node of the element represented by an index in the array representation of a complete binary tree
private int leftChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 1;
}
// Returns the index of the right child node of the element represented by an index in the array representation of a complete binary tree
private int rightChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 2;
}
// Add elements to the heap
public void add(E e){
data.addLast(e);
siftUp(data.getSize() - 1);
}
private void siftUp(int k){
while(k > 0 && data.get(parent(k)).compareTo(data.get(k)) < 0 ){
data.swap(k, parent(k));
k = parent(k);
}
}
// Look at the largest element in the heap
public E findMax(){
if(data.getSize() == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not findMax when heap is empty.");
return data.get(0);
}
// Take out the largest element in the heap
public E extractMax(){
E ret = findMax();
data.swap(0, data.getSize() - 1);
data.removeLast();
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}
private void siftDown(int k){
while(leftChild(k) < data.getSize()){
int j = leftChild(k); // In this cycle, data[k] and data[j] exchange positions
if( j + 1 < data.getSize() &&
data.get(j + 1).compareTo(data.get(j)) > 0 )
j ++;
// data[j] is the maximum of leftChild and rightChild
if(data.get(k).compareTo(data.get(j)) >= 0 )
break;
data.swap(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
// Take out the largest element in the heap and replace it with element E (new code)
public E replace(E e){
E ret = findMax();
data.set(0, e);
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}
}
Test time complexity:
Main.java
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
//test
private static double testHeap(Integer[] testData, boolean isHeapify){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
MaxHeap<Integer> maxHeap;
if(isHeapify)
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>(testData);
else{
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>();
for(int num: testData)
maxHeap.add(num);
}
int[] arr = new int[testData.length];
for(int i = 0 ; i < testData.length ; i ++)
arr[i] = maxHeap.extractMax();
for(int i = 1 ; i < testData.length ; i ++)
if(arr[i-1] < arr[i])
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Error");
System.out.println("Test MaxHeap completed.");
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1000000;
Random random = new Random();
Integer[] testData = new Integer[n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
testData[i] = random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
double time1 = testHeap(testData, false);
System.out.println("Without heapify: " + time1 + " s");
double time2 = testHeap(testData, true);
System.out.println("With heapify: " + time2 + " s");
}
}
Output:
