1, Reference link
Alibaba open source mirror station OPSX mirror station Alibaba cloud developer community
2, Introduction to PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is a free software object relational database management system (ORDBMS) with complete characteristics. It is an object relational database management system based on POSTGRES version 4.2 developed by the computer department of the University of California. Many of the leading concepts of POSTGRES appeared in the commercial website database only later. PostgreSQL supports most SQL standards and provides many other modern features, such as complex queries, foreign keys, triggers, views, transaction integrity, multi version concurrency control, etc. Similarly, PostgreSQL can be extended in many ways, such as by adding new data types, functions, operators, aggregation functions, index methods, process languages, etc. In addition, because of the flexible license, anyone can use, modify and distribute PostgreSQL for free for any purpose. (—— PostgreSQL_ Baidu Encyclopedia)
3, PostgreSQL installation
< font color = Red > this experiment is based on CentOS 7.9 system for demonstration operation < / font >
[root@postgresql ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
Installation preparation
Modify host name # hostnamectl set-hostname prostgresql Turn off the firewall # systemctl stop firewalld # systemctl disable firewalld close SELinux safe mode # setenforce 0 # getenforce Configure network information and test connectivity vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens32 Mainly modify the following parameter information. BOOTPROTO=static ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.200.25 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.200.1 DNS1=192.168.200.1 Press:wq Save and exit. Restart the network card # systemctl restart network # ping bing.com Configuring alicloud CentOS YUM Source, speed up image access and download Reference link: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45392321/article/details/121450443 # yum clean all # yum makecache # yum repolist Upgrade system🆙 # yum update inspect postgresql Installed # rpm -qa | grep postgre inspect PostgreSQL Installation position # rpm -qal | grep postgres newly added postgres User group # groupadd postgres newly added postgres User and set this postgres User belongs to the created postgres User group # useradd -g postgres postgres modify postgres User password [root@postgresql ~]# passwd postgres Changing password for user postgres. New password: BAD PASSWORD: The password is a palindrome Retype new password: passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. [root@postgresql ~]# Restart the system reboot
1. Query and install PostgreSQL server
yum list | grep postgresql-server yum install -y postgresql-server.x86_64
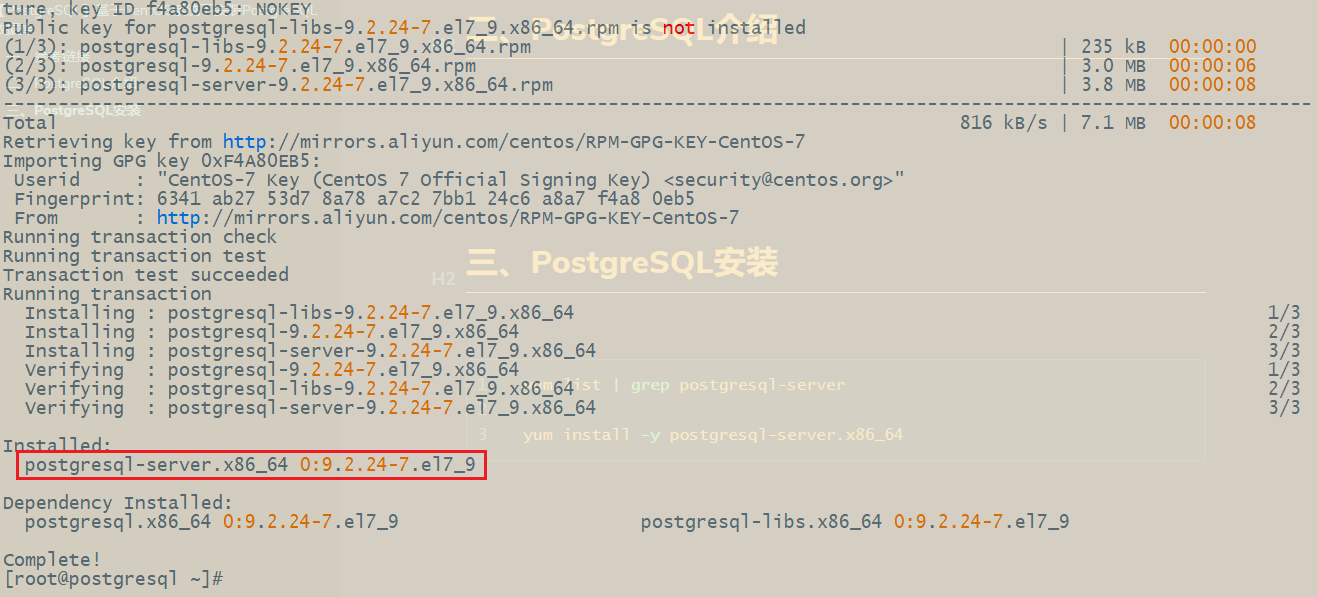
2. Initialize PostgreSQL server database
<font color=red>service postgresql initdb</font>
# service postgresql initdb Hint: the preferred way to do this is now "postgresql-setup initdb" Initializing database ... OK
3. Start the postgresql service and set the startup self startup
systemctl start postgresql systemctl enable postgresql
4. View postgresql service status
systemctl status postgresql
5. View service process information
[root@postgresql ~]# ps -ef | grep postgres postgres 1405 1 0 16:05 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/postgres -D /var/lib/pgsql/data -p 5432 postgres 1406 1405 0 16:05 ? 00:00:00 postgres: logger process postgres 1408 1405 0 16:05 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer process postgres 1409 1405 0 16:05 ? 00:00:00 postgres: writer process postgres 1410 1405 0 16:05 ? 00:00:00 postgres: wal writer process postgres 1411 1405 0 16:05 ? 00:00:00 postgres: autovacuum launcher process postgres 1412 1405 0 16:05 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector process root 1440 1131 0 16:07 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto postgres [root@postgresql ~]#
6. Check whether the postgresql service port is enabled
# ss -tunpl | grep postgres
tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:5432 *:* users:(("postgres",pid=1349,fd=4))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:5432 [::]:* users:(("postgres",pid=1349,fd=3))
[root@postgresql ~]# # netstat -tunpl | grep 5432 tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:5432 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1349/postgres tcp6 0 0 ::1:5432 :::* LISTEN 1349/postgres
4, Test connection
1. Switch postgres users
[root@postgresql ~]# su postgres [postgres@postgresql root]$
2. Connect database
[root@postgresql ~]# su postgres
[postgres@postgresql root]$ psql -U postgres
could not change directory to "/root"
psql (9.2.24)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=#
# Use \ l to view existing databases:
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+-----------+---------+-------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
template0 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(3 rows)
postgres=#
# After entering the command line tool, you can use \ help to view the syntax of each command
postgres-# \help3. Create database
# Create a runoobdb database postgres=# CREATE DATABASE xybdiy; CREATE DATABASE postgres=# # Use \ c + database name to enter the database postgres=# \c xybdiy You are now connected to database "xybdiy" as user "postgres". xybdiy=#
4. Create table
# A table is created. The table name is COMPANY table. The primary key is ID. NOT NULL means that the field is not allowed to contain NULL values
xybdiy=# CREATE TABLE COMPANY(
xybdiy(# ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
xybdiy(# NAME TEXT NOT NULL,
xybdiy(# AGE INT NOT NULL,
xybdiy(# ADDRESS CHAR(50),
xybdiy(# SALARY REAL
xybdiy(# );
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE / PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "company_pkey" for table "company"
CREATE TABLE
# Use the \ d command to see if the table was created successfully
xybdiy=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+---------+-------+----------
public | company | table | postgres
(1 row)
xybdiy=# CREATE TABLE DEPARTMENT(
xybdiy(# ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
xybdiy(# DEPT CHAR(50) NOT NULL,
xybdiy(# EMP_ID INT NOT NULL
xybdiy(# );
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE / PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "department_pkey" for table "department"
CREATE TABLE
xybdiy=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------
public | company | table | postgres
public | department | table | postgres
(2 rows)
xybdiy=# 5, Modify profile
1. Modify the configuration file of postgresql
# vim /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf # Modify listening IP listen_addresses = '*' # Open log collector logging_collector = on # Set log directory log_directory = 'pg_log'
2. Modify pg_hba.conf service connection configuration file
# vim /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf 77 # TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD 78 79 # "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only 80 local all all trust 81 # IPv4 local connections: 82 host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust 83 host all all 0.0.0.0/0 trust 84 # IPv6 local connections: 85 host all all ::1/128 md5
3. Restart postgresql service
# systemctl restart postgresql
5, Test remote connection
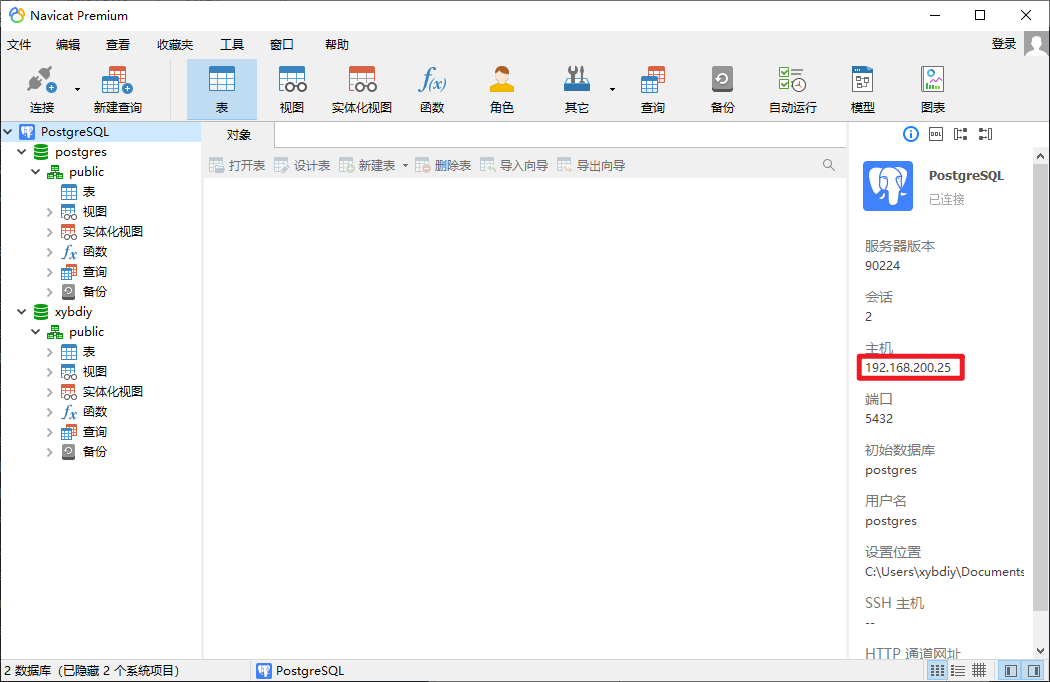
Test connection

After the test is successful, connect

Connection successful
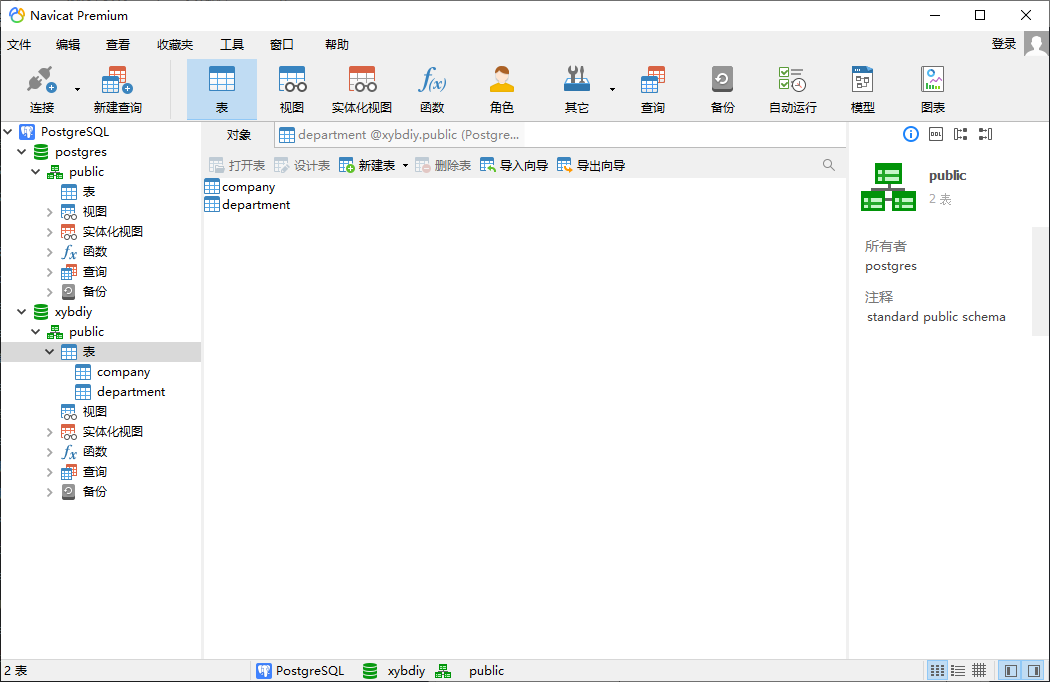
So far, the installation of PostgreSQ database is completed.