Reference link: UDP based server and client_ C language Chinese network
1, IP address, port, communication protocol
1. IP address
Computers in the network use IP addresses for unique identification.
2. Port number
Port number is an integer number label of application programs in the computer, which is used to distinguish different applications.
0 ~ 1024 are reserved port numbers used by the system;
0 ~ 65535 are valid port numbers;
1024 ~ 65535 the range that can be used when customizing the port number.
3. Communication protocol
Communication protocol is the rule of network communication, which is divided into TCP and UDP protocols.
First: TCP protocol
Chinese Name: TCP (control transmission protocol)
Protocol Description: TCP is a connection oriented, reliable and byte stream based transport layer communication protocol
For example: it is similar to making a phone call. Only when both parties are connected can they have a dialogue
Features: Although the efficiency is low, the data transmission is safe.
Second: UDP protocol
Chinese Name: UDP (datagram protocol)
Protocol Description: UDP is a connectionless transport layer communication protocol
For example: similar to sending SMS, there is no need for both parties to establish a connection, but the transmission data is small, and the size of datagram is limited to Within 64K.
Features: high efficiency, but the data transmission is unsafe and easy to lose packets.
2, Three elements of network programming
Different IP addresses
Same port number
Same agreement
3, UDP programming
UDP uses datagrams for data transmission.
There is no distinction between client and server, only sender and receiver.
Both start first, neither party will report an error, but there will be data packet loss.
And the sent content size must be within 64K.
Self practice:
Development tool: QtCreate
Practice content: echo server / client based on UDP
1. Project directory:
2. Server side code
//Input / output header file
#include <stdio.h>
//socket header file
#include <winsock2.h>
//ws2_32.lib Library
#pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
// ! Define buf size
#define BUFF_SIZE 100
//main function entry
int main()
{
// Initialize dll library
// 1. Define structure
WSADATA wsaData;
// 2. Set socket version and storage structure
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsaData);
//Create socket
SOCKET sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
// Define socket structure
sockaddr_in servAddr;
// Assign all bytes to 0
memset(&servAddr, 0, sizeof (servAddr));
// Set protocol
servAddr.sin_family = PF_INET;
// Set IP address
servAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
// Set port
servAddr.sin_port = htons(1234);
// Binding socket interface information
bind(sock, (SOCKADDR*)&servAddr, sizeof (SOCKADDR));
// Receive client messages
// 1. Obtain client IP address information
SOCKADDR clntAddr;
// 2. Define buffer size
int nSize = sizeof (SOCKADDR);
char buffer_c[BUFF_SIZE] = {0};
while(1)
{
char buffer_s[BUFF_SIZE] = {0};
//Send message to client
printf("server:");
gets(buffer_s);
// Send message to client
//sock, buffer address, data length, optional parameters, client address, client size
sendto(sock, buffer_s, strlen(buffer_s), 0, &clntAddr, nSize);
// 3. Receive client message data
int strLen = recvfrom(sock, buffer_c, BUFF_SIZE, 0, &clntAddr, &nSize);
buffer_c[strLen] = 0;
printf("Message from client: %s\n", buffer_c);
}
//Close socket
closesocket(sock);
//Resources occupied by closing socket binding and contacting socket socket
WSACleanup();
return 0;
}
3. Client code
//Input / output header file
#include <stdio.h>
//sock header file
#include <winsock2.h>
//Add lib Library
#pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
//Macro definition BUFF size
#define BUFF_SIZE 100
//Main function program entry
int main()
{
//Initialize DLl
WSADATA wsaData;
//Bind sock version and storage address
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
//Create socket
SOCKET sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
//Define socket content
sockaddr_in sockadd;
//Define all bytes as 0
memset(&sockadd, 0, sizeof (sockadd));
//Define protocol
sockadd.sin_family = PF_INET;
//Define IP address
sockadd.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
//Define port
sockadd.sin_port = htons(1234);
//Bind socket
//Send message to server
//1. Create a server socket
sockaddr fromAddr;
int addlen = sizeof (fromAddr);
char buffer_s[BUFF_SIZE];
//Receive messages from the server
while (1) {
//client input message buffer
char buffer_c[BUFF_SIZE] = {0};
printf("client:");
gets(buffer_c);
sendto(sock, buffer_c, strlen(buffer_c), 0,
(struct sockaddr*)&sockadd, sizeof (sockadd));
//Receive server data information
int strLen = recvfrom(sock, buffer_s, BUFF_SIZE, 0,
&fromAddr, &addlen);
buffer_s[strLen] = 0;
printf("Message from server :%s\n", buffer_s);
}
//Close socket
closesocket(sock);
//Contact socket binding and socket resource occupation
WSACleanup();
return 0;
}
4. Operation results
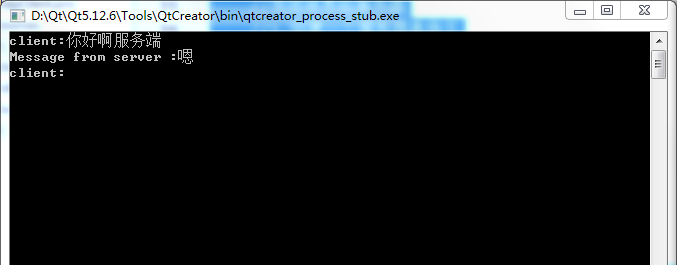
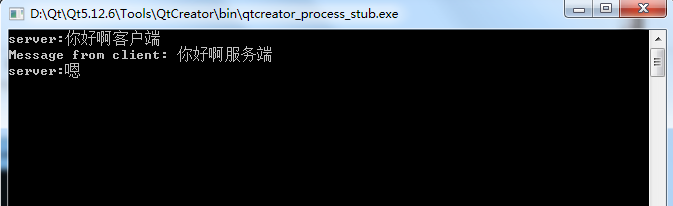
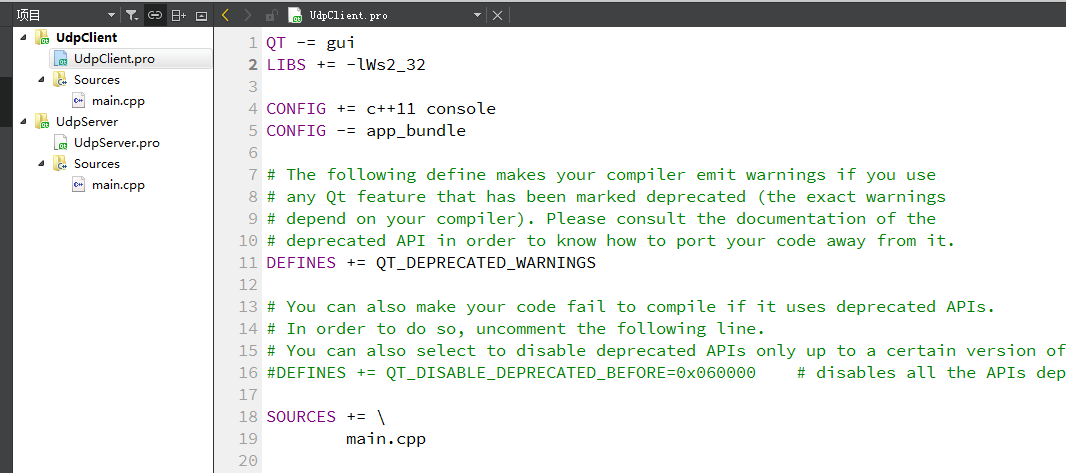
5. pro file
LIBS += -lWs2_32
6. A little problem
There is a small problem with this code. The code is modified based on the client return code in the beginning link. Then the two-way communication is barely realized, but the communication process is not smooth.