Reactor defines "reactor" as an event driven mechanism. The difference from ordinary function calls is that the application does not actively call an API to complete processing. On the contrary, reactor reverses the event processing process. The application needs to provide corresponding interfaces and register with reactor. If corresponding events occur, reactor will actively call the interfaces registered by the application, which are also called "callback functions".
Reactor mode is a common mode for processing concurrent io. It is used for synchronous io. The central idea is to register all IO events to be processed on a central IO multiplexer, and the main thread / process is blocked on the multiplexer; Once an IO event arrives or is ready (file descriptor or socket can be read or written), the multiplexer returns and distributes the corresponding IO event registered in advance to the corresponding processor.
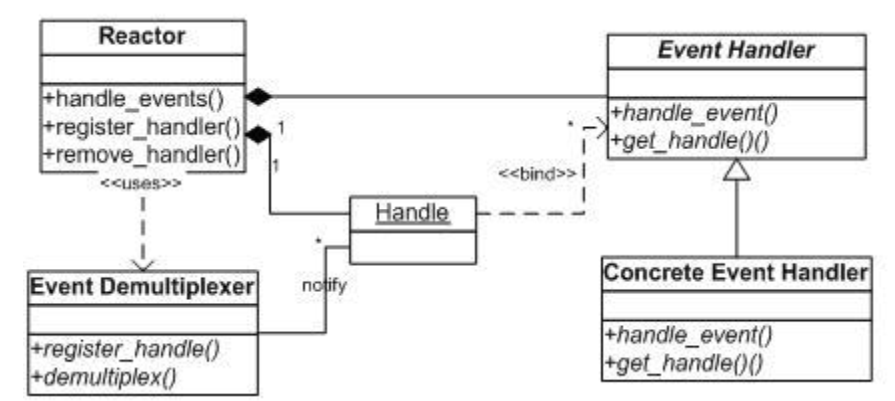
Three important components of the Reactor model
- Multiplexer: provided by the operating system. On linux, it is generally called by select, poll, epoll and other systems;
- Event distributor: divide the ready events returned from the multiplexer into the corresponding processing functions;
- Event handler: a handler function responsible for handling specific events.
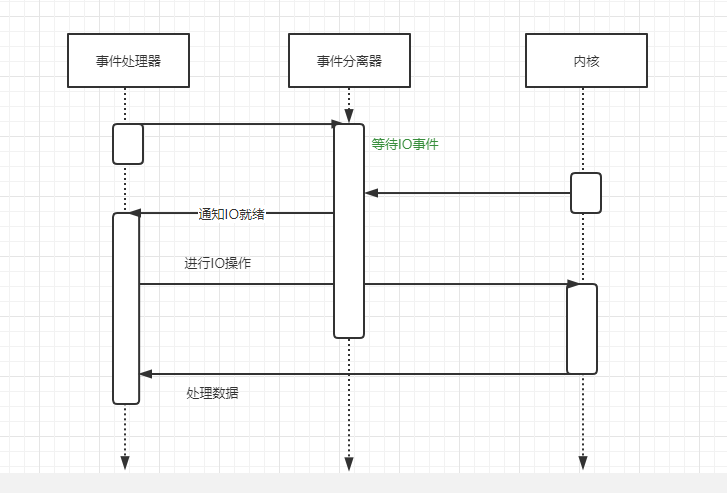
Specific operation process:
- Register the read ready event and the corresponding event processor;
- Event separator waits for events;
- When the event arrives, activate the separator, and the separator calls the processor corresponding to the event;
- The event processor completes the actual operation, processes the read data, registers a new event, and then returns the control right;
Advantages of Reactor
- The response is fast and does not have to be blocked by a single synchronization time, although the Reactor itself is still synchronized;
- The programming is relatively simple, which can avoid complex multithreading and synchronization problems to the greatest extent, and avoid the switching overhead of multithreading / process;
- Scalability, which can easily make full use of CPU resources by increasing the number of Reactor instances;
- Reusability: reactor framework itself is independent of specific event processing logic and has high reusability;
The development efficiency of the Reactor model is higher than that of the direct use of IO reuse. It is usually single threaded. The design goal is to use all the resources of one CPU, but it also has the additional advantage that the mutually exclusive access of shared resources can not be considered in each event processing.
code implementation
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 4096
#define MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS 1024
#define SERVER_PORT 8888
typedef int NCALLBACK(int ,int, void*);
struct ntyevent {
int fd;
int events;
void *arg;
int (*callback)(int fd, int events, void *arg);
int status;
char buffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int length;
long last_active;
};
struct ntyreactor {
int epfd;
struct ntyevent *events;
};
int recv_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg);
int send_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg);
//Set event
void nty_event_set(struct ntyevent *ev, int fd, NCALLBACK callback, void *arg) {
ev->fd = fd;
ev->callback = callback;
ev->events = 0;
ev->arg = arg;
ev->last_active = time(NULL);
return;
}
//Add event
int nty_event_add(int epfd, int events, struct ntyevent *ev) {
struct epoll_event ep_ev = {0, {0}};
ep_ev.data.ptr = ev;
ep_ev.events = ev->events = events;
int op;
if (ev->status == 1) {
op = EPOLL_CTL_MOD;
} else {
op = EPOLL_CTL_ADD;
ev->status = 1;
}
if (epoll_ctl(epfd, op, ev->fd, &ep_ev) < 0) {
printf("event add failed [fd=%d], events[%d]\n", ev->fd, events);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
//Delete event
int nty_event_del(int epfd, struct ntyevent *ev) {
struct epoll_event ep_ev = {0, {0}};
if (ev->status != 1) {
return -1;
}
ep_ev.data.ptr = ev;
ev->status = 0;
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, ev->fd, &ep_ev);
return 0;
}int recv_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg) {
struct ntyreactor *reactor = (struct ntyreactor *)arg;
struct ntyevent *ev = reactor->events + fd;
int len = recv(fd, ev->buffer, BUFFER_LENGTH, 0);
nty_event_del(reactor->epfd, ev);
if (len > 0) {
ev->length = len;
ev->buffer[len] = '\0';
printf("C[%d]:%s\n", fd, ev->buffer);
nty_event_set(ev, fd, send_cb, reactor);
nty_event_add(reactor->epfd, EPOLLOUT, ev);
} else if (len == 0) {
close(ev->fd);
printf("[fd=%d] pos[%ld], closed\n", fd, ev - reactor->events);
} else {
close(ev->fd);
printf("recv[fd=%d] error[%d]:%s\n", fd, errno, strerror(errno));
}
return len;
}
int send_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg) {
struct ntyreactor *reactor = (struct ntyreactor *)arg;
struct ntyevent *ev = reactor->events + fd;
int len = send(fd, ev->buffer, ev->length, 0);
if (len > 0) {
printf("send[fd=%d], [%d]%s\n", fd, len, ev->buffer);
nty_event_del(reactor->epfd, ev);
nty_event_set(ev, fd, recv_cb, reactor);
nty_event_add(reactor->epfd, EPOLLIN, ev);
} else {
close(ev->fd);
nty_event_del(reactor->epfd, ev);
printf("send[fd=%d] error %s\n", fd, strerror(errno));
}
return len;
}
int accept_cb(int fd, int events, void *arg) {
struct ntyreactor *reactor = (struct ntyreactor *)arg;
if (reactor == NULL) return -1;
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(client_addr);
int clientfd;
if ((clientfd = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &len)) == -1) {
if (errno != EAGAIN && errno != EINTR) {
}
printf("accept: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
int i = 0;
do {
for (i = 3; i < MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS; i++) {
if (reactor->events[i].status == 0) {
break;
}
}
if (i == MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS) {
printf("%s: connect limit[%d]\n", __func__, MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS);
break;
}
int flag = 0;
if ((flag = fcntl(clientfd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK)) < 0) {
printf("%s: fcntl nonblocking failed, %d\n", __func__, MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS);
break;
}
nty_event_set(&reactor->events[clientfd], clientfd, recv_cb, reactor);
nty_event_add(reactor->epfd, EPOLLIN, &reactor->events[clientfd]);
} while (0);
printf("new connect [%s:%d][time:%ld], pos[%d]\n",
inet_ntoa(client_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(client_addr.sin_port),
reactor->events[i].last_active, i);
return 0;
}int init_sock(short port) {
int fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
memset(&server_addr, 0, sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
bind(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
if (listen(fd, 20) < 0) {
printf("listen failed : %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return fd;
}
int ntyreactor_init(struct ntyreactor *reactor) {
if (reactor == NULL) return -1;
memset(reactor, 0, sizeof(struct ntyreactor));
reactor->epfd = epoll_create(1);
if (reactor->epfd <= 0) {
printf("create epfd in %s err %s\n", __func__, strerror(errno));
return -2;
}
reactor->events =
(struct ntyevent *)malloc((MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS) * sizeof(struct ntyevent));
if (reactor->events == NULL) {
printf("create epfd in %s err %s\n", __func__, strerror(errno));
close(reactor->epfd);
return -3;
}
}
int ntyreactor_destory(struct ntyreactor *reactor) {
close(reactor->epfd);
free(reactor->events);
}
int ntyreactor_addlistener(struct ntyreactor *reactor, int sockfd,
NCALLBACK *acceptor) {
if (reactor == NULL) return -1;
if (reactor->events == NULL) return -1;
nty_event_set(&reactor->events[sockfd], sockfd, acceptor, reactor);
nty_event_add(reactor->epfd, EPOLLIN, &reactor->events[sockfd]);
return 0;
}
int ntyreactor_run(struct ntyreactor *reactor) {
if (reactor == NULL) return -1;
if (reactor->epfd < 0) return -1;
if (reactor->events == NULL) return -1;
struct epoll_event events[MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS + 1];
int checkpos = 0, i;
while (1) {
long now = time(NULL);
for (i = 0; i < 100; i++, checkpos++) {
if (checkpos == MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS) {
checkpos = 0;
}
if (reactor->events[checkpos].status != 1) {
continue;
}
long duration = now - reactor->events[checkpos].last_active;
if (duration >= 60) {
close(reactor->events[checkpos].fd);
printf("[fd=%d] timeout\n", reactor->events[checkpos].fd);
nty_event_del(reactor->epfd, &reactor->events[checkpos]);
}
}
int nready = epoll_wait(reactor->epfd, events, MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS, 1000);
if (nready < 0) {
printf("epoll_wait error, exit\n");
continue;
}
for (i = 0; i < nready; i++) {
struct ntyevent *ev = (struct ntyevent *)events[i].data.ptr;
if ((events[i].events & EPOLLIN) && (ev->events & EPOLLIN)) {
ev->callback(ev->fd, events[i].events, ev->arg);
}
if ((events[i].events & EPOLLOUT) && (ev->events & EPOLLOUT)) {
ev->callback(ev->fd, events[i].events, ev->arg);
}
}
}
}int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
unsigned short port = SERVER_PORT;
if (argc == 2) {
port = atoi(argv[1]);
}
int sockfd = init_sock(port);
struct ntyreactor *reactor =
(struct ntyreactor *)malloc(sizeof(struct ntyreactor));
ntyreactor_init(reactor);
ntyreactor_addlistener(reactor, sockfd, accept_cb);
ntyreactor_run(reactor);
ntyreactor_destory(reactor);
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}