Install Redis
Download package
On the official website https://redis.io/download install
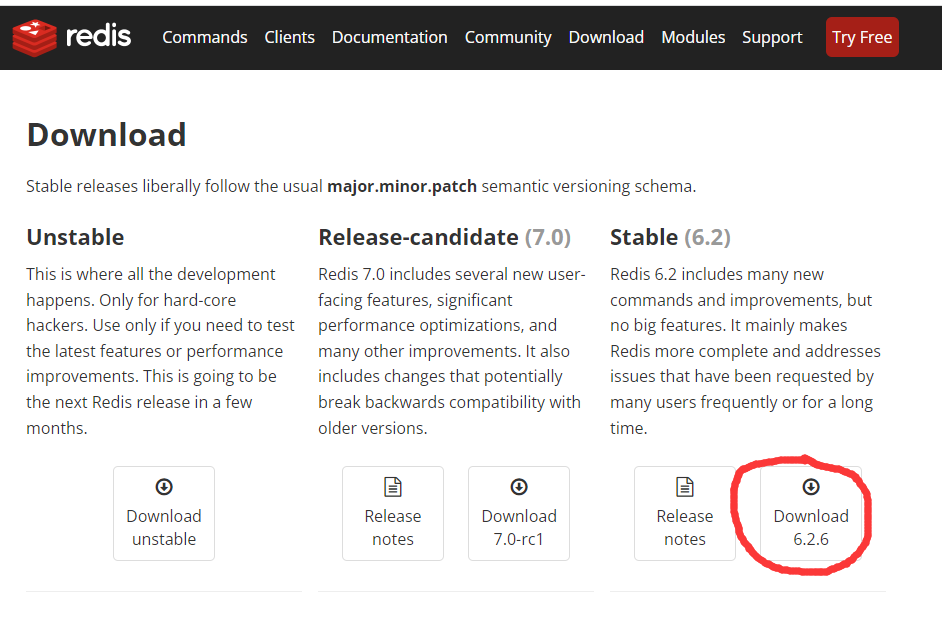
Download redis-6.2.6 tar. GZ file
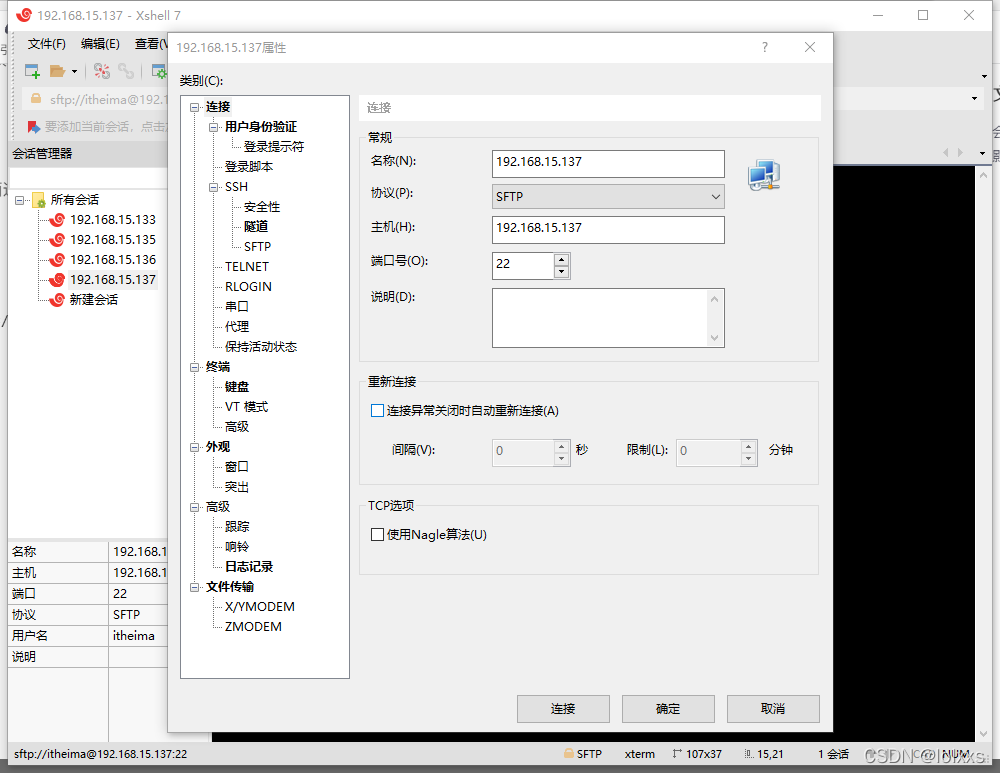
Use Xshell to transfer files into the virtual machine
Using sftp protocol, the host ip is the ip address in ens33 in ifconfig on the command line. For the first time, you need to enter the virtual machine login account root and password
Unzip and compile
tar -zxvf redis-6.2.6.tar.gz mv redis-6.2.6 /usr/local/redis cd /usr/local/redis make && make install
Modify configuration
vi /usr/local/redis/redis.conf
The modification configuration is as follows. When modifying, you can use / the string to search, such as / bind, to quickly find in vi
bind 0.0.0.0#Unrestricted access to ip and remote connections protected-mode no
Enter (colon): w to save
Start Redis
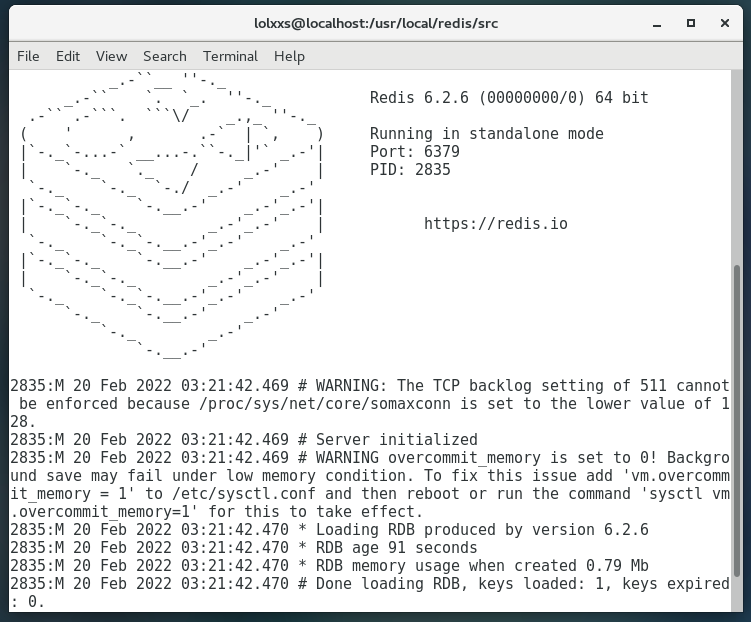
cd /usr/local/redis/src redis-server ../redis.conf #Start redis according to the configuration
If the following occurs, the startup is successful
Connect to Redis using RedisDesktopManager
If there is a problem, there are two possibilities: one is that the above configuration has not been modified successfully, and the other is that the firewall needs to be closed or the filtering rules need to be set as follows
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6379/tcp --permanent #--permanent is permanently open firewall-cmd --reload #service crond reload firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports #View all open ports
Master slave replication setup
prepare
First, duplicate redis twice, that is, a total of three redis. Build one master and two slaves. In order to simplify the construction of three instances on the same virtual machine
cp -r /usr/local/redis /usr/local/redis-slave cp -r /usr/local/redis /usr/local/redis-slave2
-r means recursive replication. Because there are directories under redis, you must - r recursive replication
Host configuration
Modify the following items in the configuration file
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6379 protected-mode no #Set to unprotected mode requirepass 123456 #Set the password required to connect to redis
Slave configuration
Slave 1
Modify the following items in the configuration file
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6380 #Different ports protected-mode no requirepass 123456 masterauth 123456 #Set the password for the slave service to connect to the master replicaof 127.0.0.1 6379 #Specify the local machine as the slave, and configure the address of the connected host
Slave 2
Modify the following items in the configuration file
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6381 #Different ports protected-mode no requirepass 123456 masterauth 123456 #Set the password for the slave service to connect to the master replicaof 127.0.0.1 6379 #Specify the local machine as the slave, and configure the address of the connected host
start-up
Use the command to connect two redis automatically and synchronize data. Use RedisDesktopManager to connect two redis to see data synchronization. Remember to add a password when connecting, because the password has been set in the above configuration.
Start the command according to the configuration file as follows
/usr/local/redis/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis/redis.conf /usr/local/redis-slave/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis-slave/redis.conf /usr/local/redis-slave2/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis-slave2/redis.conf
The following log on the primary server indicates that the connection is successful
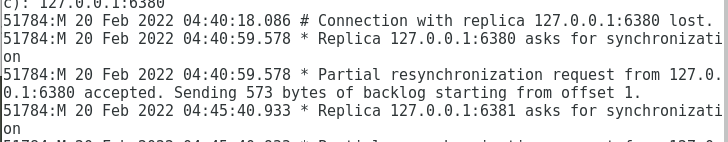
Sentry Switch Setup
Modify configuration
Modify sentinel. In the three redis folders just copied Conf configuration, in which only sentinel sentinel is configured to know the IP and port of the primary redis. By communicating with the primary redis, sentinel sentinel will know that multiple sentinels will communicate with each other through the secondary redis and the primary redis.
sentinel1
port:26379 protected-mode:no #Turn off protected mode for external access sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.231.130 6379 2 #Specify the IP address and port of the host, and specify that when two sentinels think the host is hung, the host will be switched for disaster recovery. sentinel auth-pass mymaster 123456 #Redis needs to provide a password if requirepass is enabled. sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 3000 #It is set here that if the host does not respond for several seconds, it is considered offline snetinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1 #During active / standby switching, the maximum number of slave s that synchronize the new master at the same time is set to 1 by default. sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000 #The timeout for failover is set to three minutes here
sentinel2
port:26380 protected-mode:no #Turn off protected mode for external access sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.231.130 6379 2 #Specify the IP address and port of the host, and specify that when two sentinels think the host is hung, the host will be switched for disaster recovery. sentinel auth-pass mymaster 123456 #Redis needs to provide a password if requirepass is enabled. sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 3000 #It is set here that if the host does not respond for several seconds, it is considered offline snetinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1 #During active / standby switching, the maximum number of slave s that synchronize the new master at the same time is set to 1 by default. sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000 #The timeout for failover is set to three minutes here
sentinel3
port:26381 protected-mode:no #Turn off protected mode for external access sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.231.130 6379 2 #Specify the IP address and port of the host, and specify that when two sentinels think the host is hung, the host will be switched for disaster recovery. sentinel auth-pass mymaster 123456 #Redis needs to provide a password if requirepass is enabled. sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 3000 #It is set here that if the host does not respond for several seconds, it is considered offline snetinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1 #During active / standby switching, the maximum number of slave s that synchronize the new master at the same time is set to 1 by default. sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000 #The timeout for failover is set to three minutes here
Turn off the master redis and observe the master-slave switch
Turn off primary redis
redis-cli -p 6379 auth 123456 #Enter password verification info replication #View master-slave replication information shutdown #Turn off redis
Restart redis later
/usr/local/redis/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis/redis.conf
Check the main redis information again to see if it has been switched
redis-cli -p 6379 auth 123456 #Enter password verification info replication #View master-slave replication information
If not, check sentinel info
redis-cli -p 26379 info sentinel #View sentinel information
My is always displayed as 1 at the beginning, so I can't automatically switch between master and slave
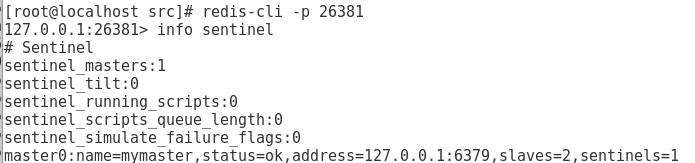
At this time, sentinel The sentinel my id 981e49fbf1483aa3ec28bacc7ed11 of conf is annotated or changed to three different IDs. Otherwise, the three IDS will be one by default. Restart and repeat the above steps to see the master-slave switching
Redis cluster deployment
Redis cluster needs at least three nodes, and each node has at least one backup node, so it needs at least six nodes, that is, three master and three slave
prepare
Copy redis three more times
cp -r /usr/local/redis /usr/local/redis-slave3 cp -r /usr/local/redis /usr/local/redis-slave4 cp -r /usr/local/redis /usr/local/redis-slave5
After modifying the configuration file, there are six redis files as follows
| main | from |
|---|---|
| redis | redis-slave |
| redis-slave2 | redis-slave3 |
| redis-slave4 | redis-slave5 |
Modify configuration
Redis.redis Conf file
redis
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6379 protected-mode no #Set to unprotected mode requirepass 123456 #Set the password required to connect to redis
redis-slave
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6380 #Different ports protected-mode no requirepass 123456 masterauth 123456 #Set the password for the slave service to connect to the master replicaof 127.0.0.1 6379 #Specify the local machine as the slave, and configure the address of the connected host
redis-slave2
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6381 protected-mode no #Set to unprotected mode requirepass 123456 #Set the password required to connect to redis
redis-slave3
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6382 #Different ports protected-mode no requirepass 123456 masterauth 123456 #Set the password for the slave service to connect to the master replicaof 127.0.0.1 6381 #Specify the local machine as the slave, and configure the address of the connected host
redis-slave4
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6383 protected-mode no #Set to unprotected mode requirepass 123456 #Set the password required to connect to redis
redis-slave5
bind 0.0.0.0 port 6384 #Different ports protected-mode no requirepass 123456 masterauth 123456 #Set the password for the slave service to connect to the master replicaof 127.0.0.1 6383 #Specify the local machine as the slave, and configure the address of the connected host
Start 6 redis servers
/usr/local/redis/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis/redis.conf /usr/local/redis-slave/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis-slave/redis.conf /usr/local/redis-slave2/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis-slave2/redis.conf /usr/local/redis-slave3/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis-slave3/redis.conf /usr/local/redis-slave4/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis-slave4/redis.conf /usr/local/redis-slave5/src/redis-server /usr/local/redis-slave5/redis.conf
Install ruby environment
yum install ruby gem install redis-6.2.6.gem #Consistent with your own redis version
gem install redis-6.2.6.gem appears

That is, the network is not good. If the installation is successful, use redis trib The RB command changes six servers into a cluster
Create cluster
redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 127.0.0.1:6379 127.0.0.1:6380 127.0.0.1:6381 127.0.0.1:6382 127.0.0.1:6383 127.0.0.1:6384