Programming Realization of Simplex Method (Part I)
I. Basic concepts
1. Standard Form of Linear Programming Problem
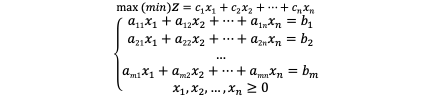
2. Simplex Method for Linear Programming (Table)
https://baike.baidu.com/item/simplex method/8580570?fr=aladdin
3. Artificial Variable Method
https://baike.baidu.com/item/artificial variable method/16629814?fr=aladdin
------------------
2. python Programming of Simplex Method
Step1: Establishing Simplex Table Classes
class Table(object): def __init__(self,X_num,B_num,z0,Xbase,bound): #Initialization function self.X_num=X_num #Number of variables self.B_num=B_num #Number of constraints self.z0=z0 #objective function self.check=[] #Inspection Number self.Xbase=Xbase #Base variable self.bound=bound #Constraints, including right-hand constants self.flag=0 #The type of solution, 0 is (temporarily) insoluble, 1 is the only optimal solution, 2 is the infinite number of optimal solutions.
Step2: Iterative Function
def Iteration(self): #Iterative function lim=100 #Maximum number of iterations (to prevent infinite iterations without solutions) while(lim>0): self.check=[] for i in range(self.X_num): #Calculate the number of tests temp=0 for j in range(self.B_num): temp+=self.bound[j][i]*self.z0[self.Xbase[j]] self.check.append(self.z0[i]-temp) self.IsEnd() #Judging whether the iteration is over if self.flag>0: #If there is a solution, the iteration ends. break else: #Otherwise, base transformation is performed. self.BaseChange(1) lim-=1
Step3: Judging Iterative Termination Function
def IsEnd(self): #Check whether the optimal solution is optimal and whether the optimal solution is unique self.flag=1 zero=0 for i in range(self.X_num): if self.check[i]>0: #Non-optimal solution with test number greater than 0 self.flag=0 break if abs(self.check[i])<0.00001: #Because M takes 1000, there is a slight error in the calculation of the test number. zero+=1 if zero>self.B_num: self.flag=2 #The number of zeros in the test number is greater than the number of cardinal variables, and there are infinite optimal solutions.
Step4: Base Transform
def BaseChange(self,model): #Base transformation if model==1: [i,j,main]=self.FindMain() #Simplex Method: Finding Main Elements else: [i,j,main]=self.FindMain2() #Dual Simplex Method: Finding Main Elements self.Xbase[i]=j #Replacement of base variables for t in range(self.X_num+1): #Transform the row of the base variable self.bound[i][t]=self.bound[i][t]/main for k in range(self.B_num): #Transform other rows if k!=i: times=self.bound[k][j] for t in range(self.X_num+1): temp=self.bound[i][t]*times self.bound[k][t]=self.bound[k][t]-temp
def FindMain(self): #Finding the Main Element j=self.check.index(max(self.check)) #Get the maximum value serial number in the number of tests theta=[] for i in range(self.B_num): if self.bound[i][j]==0: #When the dividend is 0, give its theta a sufficiently large value th=1000 else: th=self.bound[i][self.X_num]/self.bound[i][j] if th<0: #When theta < 0, give it a sufficiently large value th=10000 theta.append(th) i=theta.index(min(theta)) #Get the minimum value serial number in the number of tests and replace it with main=self.bound[i][j] return [i,j,main]