Project summary of grain College
1. Project introduction
1.1 business model adopted
B2C mode (Business To Customer member mode)
Merchants to users, this mode is to make a large number of videos with their own copyright and put them on their own platform, so that users can pay monthly or annual fees. This model is simple and fast. It can develop rapidly as long as you concentrate on recording a large number of videos. It was hot because of lynda's sky high financing. However, in China, due to the weak awareness of copyright protection, easy reproduction of educational content and many competitors with massive free resources, it is difficult to obtain a decent cash flow
1.2 functional modules
Grain college is a B2C Online vocational skills education system, which is divided into foreground user system and background operation platform
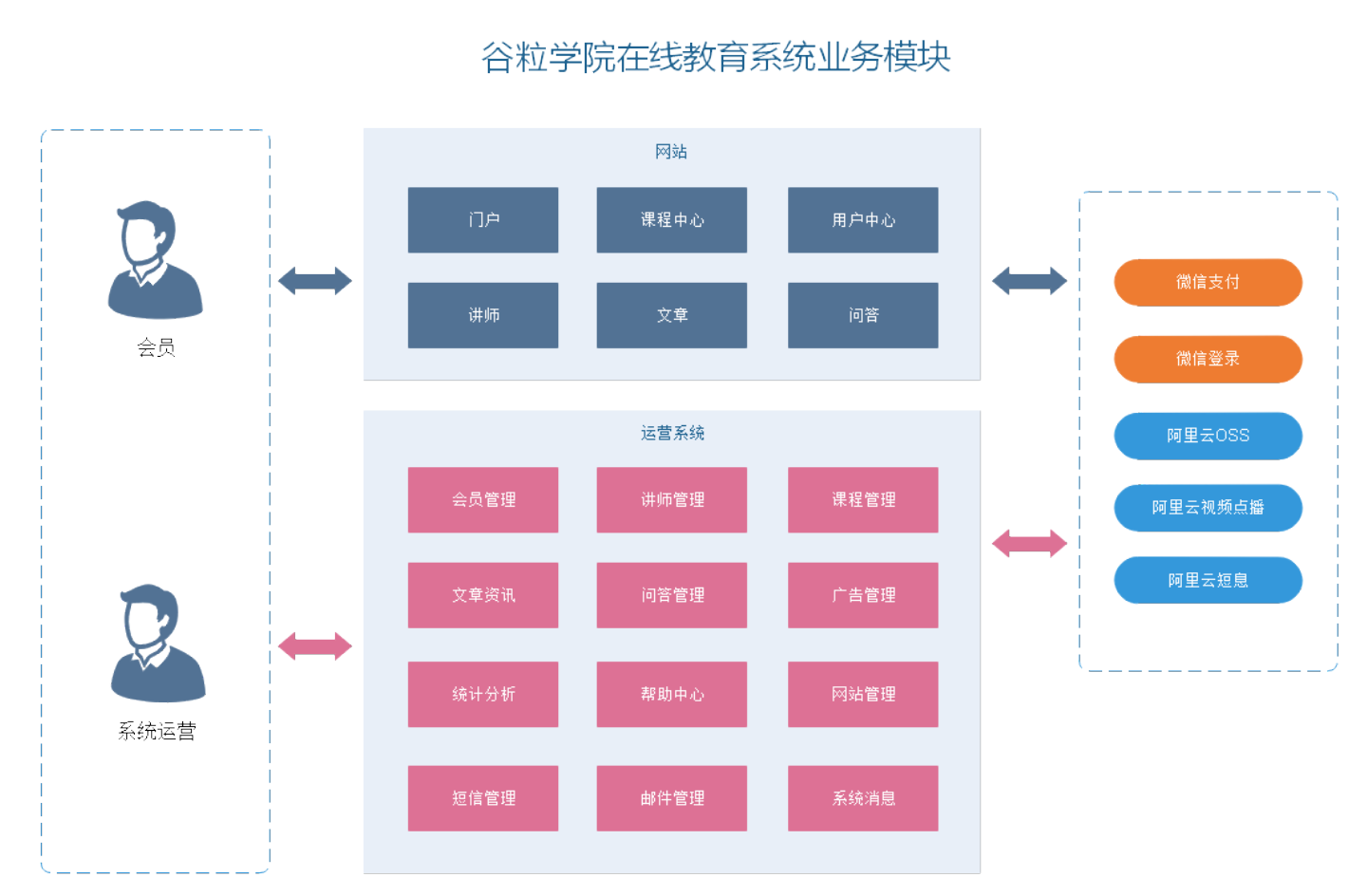

1.3 adopted technology

2. Mybatis plus related configuration
2.1 configuring paging plug-ins
You can create a new mybatis plus configuration class MyBatisPlusConfig under the config package for unified management:
//Make it a configuration class
@Configuration
//Turn on transaction management
@EnableTransactionManagement
//Specify the package where the interface to become the implementation class is located, and then all interfaces under the package will generate corresponding implementation classes after compilation (the same as adding @ Mapper to each class)
@MapperScan("com.atguigu.eduservice.mapper")
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
//Configuring paging plug-ins
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.H2));
return interceptor;
}
}
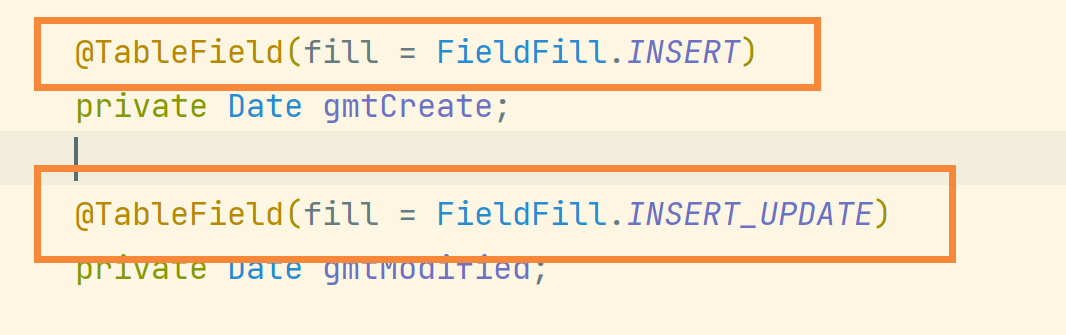
2.2 automatic filling
Create a new MyMetaObjectHandler class to implement the MetaObjectHandler interface:
//Inject into spring
@Component
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
//Auto fill on insertion
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
//Property name, not field name
this.setFieldValByName("gmtCreate", new Date(), metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("gmtModified", new Date(), metaObject);
}
//Auto fill on update
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
this.setFieldValByName("gmtModified", new Date(), metaObject);
}
}
Annotate the fields that need to be automatically populated:
2.3 code generator
public class CodeGenerator {
@Test
public void run() {
// 1. Create code generator
AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator();
// 2. Global configuration
GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig();
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
//Project path
gc.setOutputDir("D:\\guli_parent\\service\\service_edu" + "/src/main/java");
gc.setAuthor("xppll");
//Open Explorer after build
gc.setOpen(false);
//Whether the file is overwritten during regeneration
gc.setFileOverride(false);
//UserServie
gc.setServiceName("%sService"); //Remove the initial I of the Service interface
//Primary key policy
gc.setIdType(IdType.ID_WORKER_STR);
//Defines the date type in the generated entity class
gc.setDateType(DateType.ONLY_DATE);
//Turn on Swagger2 mode
gc.setSwagger2(true);
mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc);
// 3. Data source configuration
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/guli?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8");
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dsc.setUsername("root");
dsc.setPassword("root");
dsc.setDbType(DbType.MYSQL);
mpg.setDataSource(dsc);
// 4. Package configuration
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
//Module name
pc.setModuleName("eduservice");
//Package com atguigu. eduservice
pc.setParent("com.atguigu");
//Package com atguigu. eduservice. controller
pc.setController("controller");
pc.setEntity("entity");
pc.setService("service");
pc.setMapper("mapper");
mpg.setPackageInfo(pc);
// 5. Policy configuration
StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig();
strategy.setInclude("edu_course", "edu_course_description", "edu_chapter", "edu_video");
//Naming policy for mapping database tables to entities
strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
//Remove table prefix when generating entities
strategy.setTablePrefix(pc.getModuleName() + "_");
//Naming policy for mapping database table fields to entities
strategy.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
// lombok model @ accessories (chain = true) setter chain operation
strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true);
//restful api style controller
strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true);
//Hump to hyphen in url
strategy.setControllerMappingHyphenStyle(true);
mpg.setStrategy(strategy);
// 6. Execute
mpg.execute();
}
}
3.Swagger configuration
Introduce Swagger related dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<scope>provided </scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<scope>provided </scope>
</dependency
You can create a new Swagger configuration class SwaggerConfig under the config package for unified management:
/**
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/11/29 14:56
*/
@Configuration //Configuration class
@EnableSwagger2 //swagger annotation
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket webApiConfig() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.groupName("webApi")
.apiInfo(webApiInfo())
.select()
.paths(Predicates.not(PathSelectors.regex("/admin/.*")))
.paths(Predicates.not(PathSelectors.regex("/error.*")))
.build();
}
private ApiInfo webApiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("website-Course Center API file")
.description("This document describes the microservice interface definition of the course center")
.version("1.0")
.contact(new Contact("Helen", "http://atguigu.com",
"55317332@qq.com"))
.build();
}
}
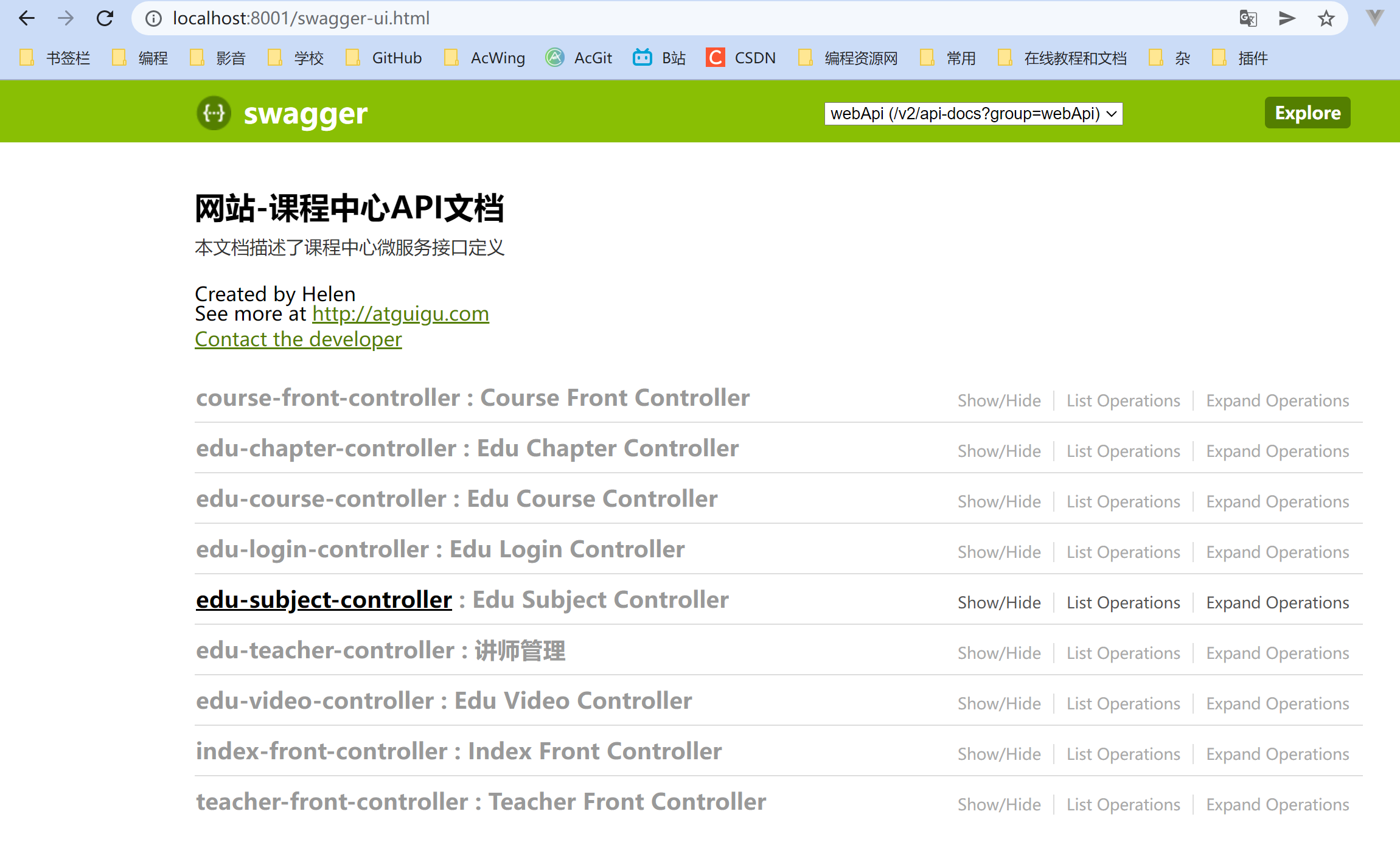
Accessing the edu module, you can see:
4. Unified return data format
In the project, we will package the response into json return. Generally, we will unify the data format of all interfaces to make the data operation of the front end (IOS, Android, web) more consistent and easy. Generally, the unified return data format has no fixed format, as long as it can clearly describe the returned data status and the specific data to be returned. However, it usually includes status code, return message and data
4.1 unified result return class
Create a unified result return class R under the commonutils package
/**
* Define classes that uniformly return results
*/
@Data
public class R {
//Notes for swagger
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Is it successful")
private Boolean success;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Return code")
private Integer code;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Return message")
private String message;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Return data")
private Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<String, Object>();
//Construction method private
public R() {
}
//Successful static method
public static R ok() {
R r = new R();
r.setSuccess(true);
r.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS);
r.setMessage("success");
return r;
}
//Failed static method
public static R error(){
R r = new R();
r.setSuccess(false);
r.setCode(ResultCode.ERROR);
r.setMessage("fail");
return r;
}
//this is returned for chain programming, such as r.ok() code(). message()
public R success(Boolean success) {
this.setSuccess(success);
return this;
}
public R message(String message) {
this.setMessage(message);
return this;
}
public R code(Integer code) {
this.setCode(code);
return this;
}
public R data(String key, Object value) {
this.data.put(key, value);
return this;
}
public R data(Map<String, Object> map) {
this.setData(map);
return this;
}
}
4.2 unified definition of return code
There are many ways here. Here are two:
1. Create interface definition return code
public interface ResultCode {
public static Integer SUCCESS = 20000;
public static Integer ERROR = 20001;
}
2. Create an enumeration class to define the return code
public enum ErrorCode {
PARAMS_ERROR(10001, "Parameter error"),
ACCOUNT_PWD_NOT_EXIST(10002, "User name or password does not exist"),
TOKEN_ERROR(10003, "token wrongful"),
ACCOUNT_EXIST(10004, "Account already exists"),
NO_PERMISSION(70001, "No access"),
SESSION_TIME_OUT(90001, "session time out"),
NO_LOGIN(90002, "Not logged in");
private int code;
private String msg;
ErrorCode(int code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
//get,set method
}
5. Unified exception handling
5.1 create a unified exception handler
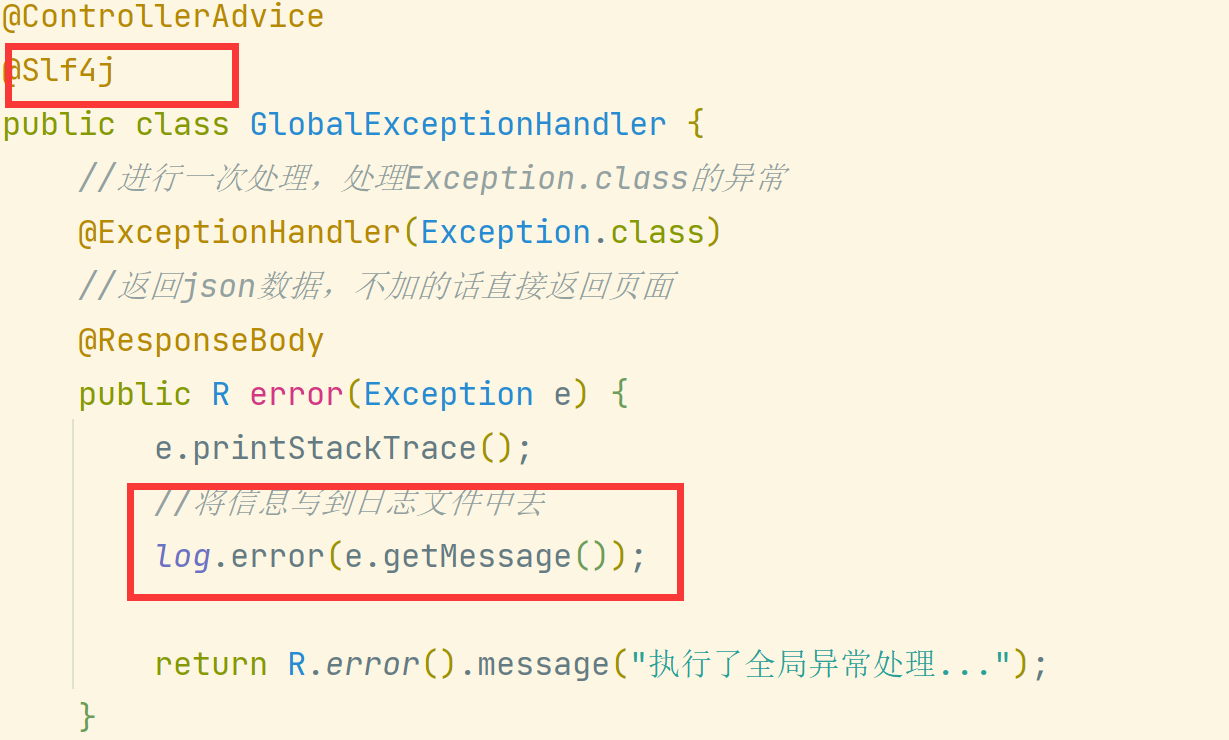
Create a unified exception handling class GlobalExceptionHandler under the handler package:
/**
* Unified exception handling class
*
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/11/29 19:11
*/
//Intercept the method with @ Controller, and the implementation of AOP
@ControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
//Process once to handle exception Class exception
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
//Return json data and directly return to the page without adding
@ResponseBody
public R error(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//Write the information to the log file
log.error(e.getMessage());
return R.error().message("Global exception handling was performed...");
}
}
You can also handle specific exceptions:
//Add a specific exception method
@ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class)
@ResponseBody
public R error(ArithmeticException e){
e.printStackTrace();
return R.error().message("A specific exception was executed");
}
5.2 custom exception handling
Create a custom exception class GuliException under the handler package:
/**
* Custom exception
* Need to inherit RuntimeException
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/11/29 20:09
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class GuliException extends RuntimeException {
//Status code
private Integer code;
//Abnormal information
private String msg;
}
Handling custom exceptions:
//Add custom exception
//You need to throw it manually
@ExceptionHandler(GuliException.class)
@ResponseBody
public R error(GuliException e){
log.error(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
//Pass in self-defined parameters
return R.error().code(e.getCode()).message(e.getMsg());
}
Chestnuts: throw them manually
@GetMapping("findAll")
public R list(){
try {
int a = 10/0;
}catch(Exception e) {
throw new GuliException(20003,"Custom exception occurred");
}
List<EduTeacher> list = teacherService.list(null);
return R.ok().data("items",list);
}
6. Unified log processing
6.1 configuring log levels
The behavior of the Logger is hierarchical. As shown in the following table: OFF, fat, ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG and ALL. By default, the log level printed by spring boot from the console is only INFO or above. The log level can be configured:
# Set log level logging.level.root=WARN
This configuration method can only print logs on the console
6.2 Logback log
spring boot uses Logback internally as the framework for log implementation
Configure logback logs
Note: you need to delete application Other log configurations in properties
Create logback spring. Net in resources XML (the name as like as two peas!)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="10 seconds">
<!-- The log level is from low to high TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < FATAL,If set to WARN,Is lower than WARN No information will be output -->
<!-- scan:When this property is set to true If the configuration file changes, it will be reloaded. The default value is true -->
<!-- scanPeriod:Set the time interval for monitoring whether the configuration file is modified. If no time unit is given, the default unit is milliseconds. When scan by true This property takes effect when. The default interval is 1 minute. -->
<!-- debug:When this property is set to true When, it will be printed out logback Internal log information, real-time viewing logback Running status. The default value is false. -->
<contextName>logback</contextName>
<!-- name The value of is the name of the variable, value The value defined by the variable. Values defined by are inserted into the logger In context. After defining variables, you can make“ ${}"To use variables. -->
<property name="log.path" value="D:/guli_1010/edu" />
<!-- Color log -->
<!-- Configure format variables: CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN Color log format -->
<!-- magenta:Magenta -->
<!-- boldMagenta:Coarse red-->
<!-- cyan:Cyan -->
<!-- white:white -->
<!-- magenta:Magenta -->
<property name="CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN"
value="%yellow(%date{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}) |%highlight(%-5level) |%blue(%thread) |%blue(%file:%line) |%green(%logger) |%cyan(%msg%n)"/>
<!--Output to console-->
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!--This log appender It is used for development. Only the lowest level is configured. The log level output from the console is log information greater than or equal to this level-->
<!-- For example, if you configure INFO Level, even if other locations are configured DEBUG Level logs will not be output -->
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter">
<level>INFO</level>
</filter>
<encoder>
<Pattern>${CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN}</Pattern>
<!-- Set character set -->
<charset>UTF-8</charset>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--output to a file-->
<!-- Time scrolling output level by INFO journal -->
<appender name="INFO_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<!-- The path and file name of the log file being recorded -->
<file>${log.path}/log_info.log</file>
<!--Log file output format-->
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
<charset>UTF-8</charset>
</encoder>
<!-- The rolling strategy of the logger, recording by date and by size -->
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!-- Daily log archive path and format -->
<fileNamePattern>${log.path}/info/log-info-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.log</fileNamePattern>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>100MB</maxFileSize>
</timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
<!--Log file retention days-->
<maxHistory>15</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<!-- This log file only records info Rank -->
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>INFO</level>
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<!-- Time scrolling output level by WARN journal -->
<appender name="WARN_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<!-- The path and file name of the log file being recorded -->
<file>${log.path}/log_warn.log</file>
<!--Log file output format-->
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
<charset>UTF-8</charset> <!-- Set character set here -->
</encoder>
<!-- The rolling strategy of the logger, recording by date and by size -->
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${log.path}/warn/log-warn-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.log</fileNamePattern>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>100MB</maxFileSize>
</timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
<!--Log file retention days-->
<maxHistory>15</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<!-- This log file only records warn Rank -->
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>warn</level>
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<!-- Time scrolling output level by ERROR journal -->
<appender name="ERROR_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<!-- The path and file name of the log file being recorded -->
<file>${log.path}/log_error.log</file>
<!--Log file output format-->
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
<charset>UTF-8</charset> <!-- Set character set here -->
</encoder>
<!-- The rolling strategy of the logger, recording by date and by size -->
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${log.path}/error/log-error-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.log</fileNamePattern>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>100MB</maxFileSize>
</timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
<!--Log file retention days-->
<maxHistory>15</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<!-- This log file only records ERROR Rank -->
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>ERROR</level>
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<!--
<logger>Used to set the log printing level of a package or a specific class, and specify<appender>.
<logger>Only one name Properties,
An optional level And an optional addtivity Properties.
name:Used to specify that this logger A package or a specific class of constraints.
level:Used to set the print level, regardless of case: TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, ALL and OFF,
If this property is not set, the current logger Will inherit the level of the superior.
-->
<!--
use mybatis When I was young, sql Statement is debug It will not print until next, and here we only configure it info,So I want to see sql Statement, there are two operations:
First handle<root level="INFO">Change to<root level="DEBUG">This will print sql,But there will be a lot of other messages in the log
The second is to give it alone mapper Directory configuration under DEBUG Mode, the code is as follows, which is configured in this way sql The statement will print, and others are normal DEBUG Level:
-->
<!--development environment :Print Console -->
<springProfile name="dev">
<!--You can output data in a project debug Logs, including mybatis of sql journal-->
<logger name="com.guli" level="INFO" />
<!--
root Node is a required node. It is used to specify the most basic log output level. There is only one node level attribute
level:Used to set the printing level, regardless of case: TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, ALL and OFF,The default is DEBUG
Can contain zero or more appender Element.
-->
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE" />
<appender-ref ref="INFO_FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="WARN_FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="ERROR_FILE" />
</root>
</springProfile>
<!--production environment :output to a file-->
<springProfile name="pro">
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE" />
<appender-ref ref="DEBUG_FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="INFO_FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="ERROR_FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="WARN_FILE" />
</root>
</springProfile>
</configuration>
6.3 output error log to file
for instance:
- Add annotation on class in GlobalExceptionHandler @Slf4j
- Exception output statement: log error(e.getMessage());
7. Integrate Alibaba cloud OSS
SpringBoot integrates alicloud OSS
8. Integrate EasyExcel
SpringBoot integrates EasyExcel
9. Integrate Alibaba cloud video on demand
SpringBoot integrates Alibaba cloud video on demand
10. Integrate JWT single sign on
For detailed knowledge of JWT, please refer to: JWT integrates Springboot
10.1 single sign on
There are three common ways of single sign on:
- Implementation of session broadcast mechanism
- Implementation using cookie+reids
- Using token to implement

10.2 introducing dependencies
<dependencies>
<!-- JWT-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
10.3 create JWT tool class
/**
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/12/8 13:49
*/
public class JwtUtils {
//token expiration time
public static final long EXPIRE = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24;
//Secret key
public static final String APP_SECRET = "ukc8BDbRigUDaY6pZFfWus2jZWLPHO";
/**
* Get token
*
* @param id User id
* @param nickname User nickname
* @return
*/
public static String getJwtToken(String id, String nickname) {
String JwtToken = Jwts.builder()
//Set jwt header information
.setHeaderParam("typ", "JWT")
.setHeaderParam("alg", "HS256")
//Set classification
.setSubject("guli-user")
//Set issuing time
.setIssuedAt(new Date())
//Set expiration time = current time + expiration time after how long
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + EXPIRE))
//Set the token body part to store user information
.claim("id", id)
.claim("nickname", nickname)
//Set issuing algorithm + secret key
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS256, APP_SECRET)
.compact();
return JwtToken;
}
/**
* Judge whether the token exists and is valid
*
* @param jwtToken
* @return
*/
public static boolean checkToken(String jwtToken) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(jwtToken)) return false;
try {
//Verify whether the token is a valid token
Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(APP_SECRET).parseClaimsJws(jwtToken);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Judge whether the token exists and is valid
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
public static boolean checkToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
String jwtToken = request.getHeader("token");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(jwtToken)) return false;
Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(APP_SECRET).parseClaimsJws(jwtToken);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Get the user id according to the token
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
public static String getMemberIdByJwtToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String jwtToken = request.getHeader("token");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(jwtToken)) return "";
Jws<Claims> claimsJws = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(APP_SECRET).parseClaimsJws(jwtToken);
Claims claims = claimsJws.getBody();
return (String) claims.get("id");
}
}
10.4 information received and transmitted by the packaging front end
Login information:
@Data
public class UcentMemberVo {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "cell-phone number")
private String mobile;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "password")
private String password;
}
Registration information:
@Data
public class RegisterVo {
private String nickname;
private String mobile;
private String password;
private String code;
}
10.5 controller layer
There are three main interfaces:
- Sign in
- register
- After successful login, the user information is obtained according to the token for front-end display
/**
* Membership table front controller
*
* @author xppll
* @since 2021-12-08
*/
@CrossOrigin
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/educenter/member")
public class UcenterMemberController {
@Autowired
private UcenterMemberService memberService;
/**
* Sign in
*
* @param member Receive data from front-end login
* @return Return to R
*/
@PostMapping("login")
public R loginUser(@RequestBody UcentMemberVo member) {
//Return the token and generate it using jwt
String token = memberService.login(member);
return R.ok().data("token", token);
}
/**
* register
*
* @param registerVo Receive data from front-end registration
* @return Return to R
*/
@PostMapping("register")
public R registerUser(@RequestBody RegisterVo registerVo) {
memberService.register(registerVo);
return R.ok();
}
/**
* Obtain user information according to the token for front-end display
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("getMemberInfo")
public R getMemberInfo(HttpServletRequest request) {
//Call the jwt tool class, get the header information according to the request object, and return the user id
String memberId = JwtUtils.getMemberIdByJwtToken(request);
UcentMemberVo member = memberService.getLoginInfo(memberId);
return R.ok().data("userInfo", member);
}
}
10.6 service layer
/**
* Membership table service implementation class
*
* @author xppll
* @since 2021-12-08
*/
@Service
public class UcenterMemberServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UcenterMemberMapper, UcenterMember> implements UcenterMemberService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
/**
* Sign in
*
* @param member Parameters transmitted by the front end
* @return Return token
*/
@Override
public String login(UcentMemberVo member) {
//Get login phone number and password
String mobile = member.getMobile();
String password = member.getPassword();
//1. One of the two is empty, login failed!
if (StringUtils.isBlank(mobile) || StringUtils.isBlank(password)) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "Mobile number and password cannot be empty, login failed!");
}
//2. Judge whether the mobile phone number exists
LambdaQueryWrapper<UcenterMember> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(UcenterMember::getMobile, mobile);
UcenterMember mobileMember = baseMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper);
if (mobileMember == null) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "Mobile number does not exist, login failed!");
}
//3. Judge whether the password is correct
//The database password is encrypted
//The input password needs to be encrypted in comparison
if (!MD5.encrypt(password).equals(mobileMember.getPassword())) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "Password error, login failed!");
}
//4. Judge whether the user is banned (seal number)
if (mobileMember.getIsDisabled()) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "User has been forbidden to log in, login failed!");
}
//Call JWT tool class to generate token
//Pass in id, nickname
return JwtUtils.getJwtToken(mobileMember.getId(), mobileMember.getNickname());
}
//register
@Override
public void register(RegisterVo registerVo) {
//Verification Code
String code = registerVo.getCode();
//cell-phone number
String mobile = registerVo.getMobile();
//nickname
String nickname = registerVo.getNickname();
//password
String password = registerVo.getPassword();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(mobile) || StringUtils.isBlank(code)
|| StringUtils.isBlank(nickname) || StringUtils.isBlank(password)) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "The passed in parameter cannot be empty!, login has failed");
}
//Retrieve the verification code from redis
String redisCode = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(mobile);
//Judge whether the verification code is invalid
if (StringUtils.isBlank(redisCode)) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "Verification code is invalid!, login has failed");
}
//Determine whether the verification code is correct
if (!code.equals(redisCode)) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "Verification code error!,login has failed");
}
//Judge whether the mobile phone number has been registered
LambdaQueryWrapper<UcenterMember> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(UcenterMember::getMobile, mobile);
Integer count = baseMapper.selectCount(queryWrapper);
if (count > 0) {
throw new GuliException(20001, "The mobile phone number has been registered! login has failed");
}
//Add to database
UcenterMember member = new UcenterMember();
member.setMobile(mobile);
member.setNickname(nickname);
//The password needs to be encrypted
member.setPassword(MD5.encrypt(password));
member.setIsDisabled(false);
member.setAvatar("https://xppll.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/2021/12/08/dde5b98fe9dca6b6076file.png");
baseMapper.insert(member);
}
//Get the information according to the id and send it to the front end
@Override
public UcentMemberVo getLoginInfo(String memberId) {
UcenterMember member = baseMapper.selectById(memberId);
UcentMemberVo ucentMemberVo = new UcentMemberVo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(member, ucentMemberVo);
return ucentMemberVo;
}
}
11. Integrate Alibaba cloud SMS
The SMS function is implemented here in order to complete user registration
11.1 preparation
First, you need to open Alibaba cloud SMS service
When importing dependencies:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-java-sdk-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
11.2 specific implementation
controller layer:
/**
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/12/8 19:52
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/edumsm/msm")
public class MsmController {
@Autowired
private MsmService msmService;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> reditemplate;
//Method of sending short message through mobile phone number
@GetMapping("send/{phone}")
public R sendMsm(@PathVariable("phone") String phone) {
//1. Obtain the verification code from redis. If it is obtained, it will be returned directly
String code = reditemplate.opsForValue().get(phone);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(code)) {
return R.ok();
}
//2. Call the tool class to generate a four digit random number and pass it to Alibaba cloud for sending
code = RandomUtil.getFourBitRandom();
Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("code", code);
//3. Call the method in the service to send SMS
boolean isSend = msmService.send(param, phone);
if (isSend) {
//4. After successful sending, put the successfully sent verification code into redis and set the effective time
reditemplate.opsForValue().set(phone, code, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return R.ok();
} else {
//5. Send failed, return failure information
return R.error().message("SMS sending failed!");
}
}
}
service layer:
/**
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/12/8 19:53
*/
@Service
public class MsmServiceImpl implements MsmService {
/**
* Send SMS
* @param param The verification code sent by alicloud is required
* @param phone cell-phone number
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean send(Map<String, Object> param, String phone) {
//If the mobile phone number is empty, false is returned
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(phone)) return false;
//Region node, id, key
DefaultProfile profile =
DefaultProfile.getProfile("default", "xxx", "xxx");
IAcsClient client = new DefaultAcsClient(profile);
//Set relevant parameters
CommonRequest request = new CommonRequest();
request.setSysMethod(MethodType.POST);
request.setSysDomain("dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com");
request.setSysVersion("2017-05-25");
request.setSysAction("SendSms");
//Set sending related parameters
//cell-phone number
request.putQueryParameter("PhoneNumbers", phone);
//"Signature name" applied in Alibaba cloud“
request.putQueryParameter("SignName", "My grain online education website");
//"Template CODE" applied by Alibaba cloud
request.putQueryParameter("TemplateCode", "SMS_xxxxx");
//Verification Code
request.putQueryParameter("TemplateParam", JSONObject.toJSONString(param));
//send out
try {
CommonResponse response = client.getCommonResponse(request);
System.out.println(response.getData());
return response.getHttpResponse().isSuccess();
} catch (ClientException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
}
12. Integrate wechat scanning login
SpringBoot integrates wechat login
13. Regularly count the number of registered people every day
13.1 database tables and entity classes
Database table statistics_daily:
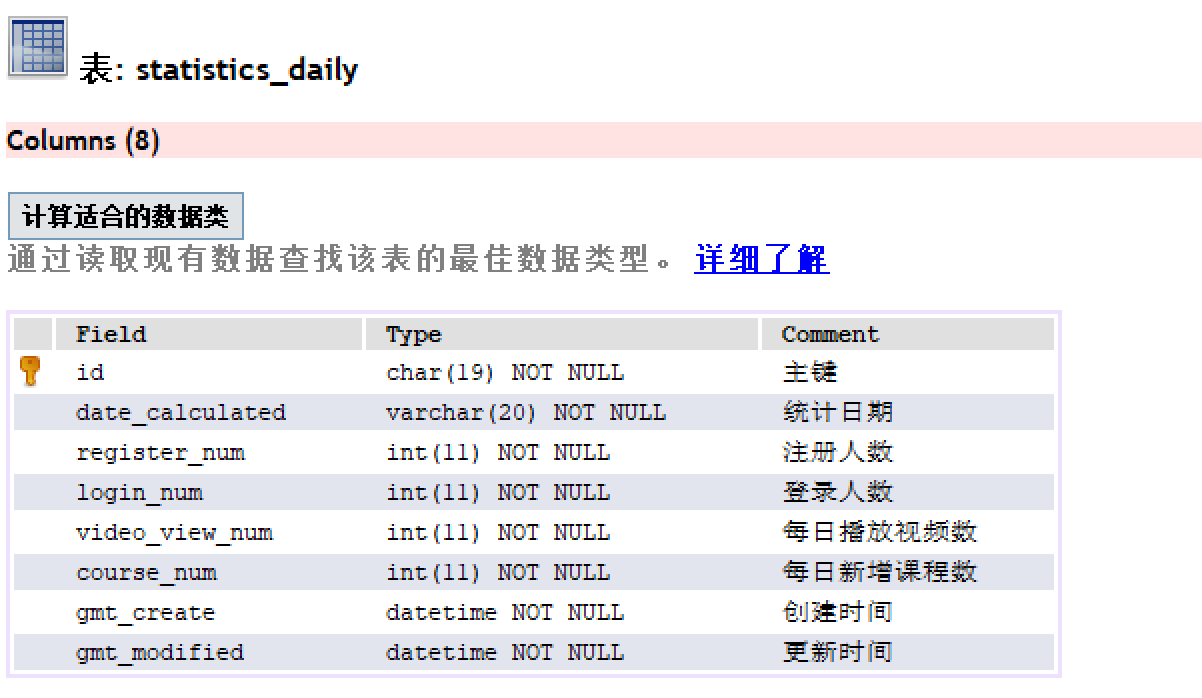
Corresponding entity class:
/**
* Website statistics daily data
*
* @author xppll
* @since 2021-12-16
*/
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false)
@Accessors(chain = true)
@ApiModel(value="StatisticsDaily object", description="Website statistics daily data")
public class StatisticsDaily implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Primary key")
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.ID_WORKER_STR)
private String id;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Statistical date")
private String dateCalculated;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Number of registrants")
private Integer registerNum;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Number of login")
private Integer loginNum;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Number of videos played per day")
private Integer videoViewNum;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Number of new courses per day")
private Integer courseNum;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Creation time")
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date gmtCreate;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Update time")
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date gmtModified;
}
13.2 implementation interface
In service_ The UCenter module creates an interface to count the number of registered people on a certain day:
controller layer:
//Query the number of registrants on a certain day
@GetMapping("countRegister/{day}")
public R countRegister(@PathVariable("day") String day){
Integer count=memberService.countRegisterDay(day);
return R.ok().data("countRegister",count);
}
service layer:
@Override
public Integer countRegisterDay(String day) {
return baseMapper.countRegisterDay(day);
}
mapper layer:
<!--Query the number of registrants on a certain day-->
<select id="countRegisterDay" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM ucenter_member uc
WHERE DATE(uc.gmt_create) = #{day}
</select>
13.3 remote call
In service_ The statistics module creates a remote call interface:
Under the client package, the UcenterClient interface:
/**
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/12/16 22:38
*/
@Component
@FeignClient("service-ucenter")
public interface UcenterClient {
//Query the number of registrants on a certain day
@GetMapping("/educenter/member/countRegister/{day}")
public R countRegister(@PathVariable("day") String day);
}
controller layer:
//Count the number of registrants on a certain day and generate statistics
@PostMapping("registerCount/{day}")
public R registerCount(@PathVariable("day") String day){
staService.registerCount(day);
return R.ok();
}
service layer:
@Service
public class StatisticsDailyServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<StatisticsDailyMapper, StatisticsDaily> implements StatisticsDailyService {
@Autowired
private UcenterClient ucenterClient;
@Override
public void registerCount(String day) {
//First delete the database records of that day, and then rewrite the addition to prevent adding multiple records
LambdaQueryWrapper<StatisticsDaily> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(StatisticsDaily::getDateCalculated, day);
baseMapper.delete(queryWrapper);
//Remote call to get the number of registrants on a certain day
R register = ucenterClient.countRegister(day);
Integer count = (Integer) register.getData().get("countRegister");
//Add the obtained data to the database and statistical analysis table
StatisticsDaily sta = new StatisticsDaily();
//Number of registrants
sta.setRegisterNum(count);
//Statistical date
sta.setDateCalculated(day);
//Daily video playback
sta.setVideoViewNum(RandomUtils.nextInt(100, 200));
//Daily login number
sta.setLoginNum(RandomUtils.nextInt(100, 200));
//Number of new courses per day
sta.setCourseNum(RandomUtils.nextInt(100, 200));
baseMapper.insert(sta);
}
}
13.4 scheduled tasks
Recommend a website that can generate cron expressions for the required scheduled tasks: Online Cron expression builder (qqe2.com)
Create a scheduled task class using cron expression:
/**
* @author xppll
* @date 2021/12/17 13:31
*/
@Component
public class ScheduledTask {
@Autowired
private StatisticsDailyService staService;
/**
* At 1 a.m. every day, query and add the data of the previous day
*/
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 1 * * ?")
public void task(){
staService.registerCount(DateUtil.formatDate(DateUtil.addDays(new Date(),-1)));
}
}
The date conversion tool class DateUtil here:
/**
* Date operation tool class
*
* @author qy
* @since 1.0
*/
public class DateUtil {
private static final String dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd";
/**
* format date
*
* @param date
* @return
*/
public static String formatDate(Date date) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(dateFormat);
return sdf.format(date);
}
/**
* Add amount days to date.
*
* @param date Date processed, non null
* @param amount The number of days to add may be negative
*/
public static Date addDays(Date date, int amount) {
Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
now.setTime(date);
now.set(Calendar.DATE, now.get(Calendar.DATE) + amount);
return now.getTime();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(DateUtil.formatDate(new Date()));
System.out.println(DateUtil.formatDate(DateUtil.addDays(new Date(), -1)));
}
}
14. Integrate wechat payment
SpringBoot integrates wechat payment
15. Authority management module
To be added
16. gateway
For details on the use of gateway in microservices, please refer to: [spring cloud] learning notes -p4 (Gateway service Gateway)
16.1 preparation
Create an API gateway module (Gateway Service):
Introduce related dependencies:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atguigu</groupId>
<artifactId>common_utils</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--gson-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Service call-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
16.2 writing basic configuration and routing rules
# Service port server.port=8222 # service name spring.application.name=service-gateway # nacos service address spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848 #Discover routes using services spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.enabled=true #Service route name lowercase #spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.lower-case-service-id=true #Routing id, user-defined, as long as it is unique spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].id=service-acl #The destination address lb of the route is load balancing, followed by the service name spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].uri=lb://service-acl #Routing assertion is to judge whether the request meets the conditions of routing rules spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].predicates= Path=/*/acl/** #Configure service edu service spring.cloud.gateway.routes[1].id=service-edu spring.cloud.gateway.routes[1].uri=lb://service-edu spring.cloud.gateway.routes[1].predicates= Path=/eduservice/** #Configuring the service UCenter service spring.cloud.gateway.routes[2].id=service-ucenter spring.cloud.gateway.routes[2].uri=lb://service-ucenter spring.cloud.gateway.routes[2].predicates= Path=/ucenterservice/** #Configuring the service UCenter service spring.cloud.gateway.routes[3].id=service-cms spring.cloud.gateway.routes[3].uri=lb://service-cms spring.cloud.gateway.routes[3].predicates= Path=/cmsservice/** spring.cloud.gateway.routes[4].id=service-msm spring.cloud.gateway.routes[4].uri=lb://service-msm spring.cloud.gateway.routes[4].predicates= Path=/edumsm/** spring.cloud.gateway.routes[5].id=service-order spring.cloud.gateway.routes[5].uri=lb://service-order spring.cloud.gateway.routes[5].predicates= Path=/orderservice/** spring.cloud.gateway.routes[6].id=service-order spring.cloud.gateway.routes[6].uri=lb://service-order spring.cloud.gateway.routes[6].predicates= Path=/orderservice/** spring.cloud.gateway.routes[7].id=service-oss spring.cloud.gateway.routes[7].uri=lb://service-oss spring.cloud.gateway.routes[7].predicates= Path=/eduoss/** spring.cloud.gateway.routes[8].id=service-statistic spring.cloud.gateway.routes[8].uri=lb://service-statistic spring.cloud.gateway.routes[8].predicates= Path=/staservice/** spring.cloud.gateway.routes[9].id=service-vod spring.cloud.gateway.routes[9].uri=lb://service-vod spring.cloud.gateway.routes[9].predicates= Path=/eduvod/** spring.cloud.gateway.routes[10].id=service-edu spring.cloud.gateway.routes[10].uri=lb://service-edu spring.cloud.gateway.routes[10].predicates= Path=/eduuser/** spring.redis.host=192.168.75.130 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.database= 0 spring.redis.timeout=1800000 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=20 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1 #Maximum blocking waiting time (negative number means no limit) spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=5 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
16.3 gateway to solve cross domain problems
Here, we use the gateway to solve the cross domain problem, so we don't need to use nginx+@CrossOrigin to solve the cross domain problem:
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig {
@Bean
public CorsWebFilter corsFilter() {
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
//Allowed cross domain ajax request mode
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
//Which websites are allowed to cross domain requests, here * is all
config.addAllowedOrigin("*");
//Header allowed in request
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource(new PathPatternParser());
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
return new CorsWebFilter(source);
}
}
16.4 Filter usage
To create a global Filter class, you need to implement the GlobalFilter interface to uniformly handle member login and external services that are not allowed to access:
/**
* Global Filter, which uniformly handles member login and external services that are not allowed to access
*
* @author qy
* @since 2019-11-21
*/
@Component
public class AuthGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
private AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
//Get request parameters
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
String path = request.getURI().getPath();
//The api interface of grain college, the verification user must log in
if (antPathMatcher.match("/api/**/auth/**", path)) {
List<String> tokenList = request.getHeaders().get("token");
//token Null, not logged in, blocking request
if (null == tokenList) {
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
return out(response);
} else {
//Intercept request
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
return out(response);
}
}
//Internal service interface, external access is not allowed
if (antPathMatcher.match("/**/inner/**", path)) {
//Intercept request
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
return out(response);
}
//Release
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
private Mono<Void> out(ServerHttpResponse response) {
JsonObject message = new JsonObject();
message.addProperty("success", false);
message.addProperty("code", 28004);
message.addProperty("data", "Authentication failed");
byte[] bits = message.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
DataBuffer buffer = response.bufferFactory().wrap(bits);
//response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
//Specify the code, otherwise Chinese garbled code will appear in the browser
response.getHeaders().add("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
return response.writeWith(Mono.just(buffer));
}
}
16.5 custom exception handling
When the service gateway calls the service, there may be some exceptions or the service is unavailable. The error information returned by the service gateway is unfriendly. We need to override the processing and create an exception handling class ErrorHandlerConfig:
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class})
public class ErrorHandlerConfig {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
public ErrorHandlerConfig(ServerProperties serverProperties,
ResourceProperties resourceProperties,
ObjectProvider<List<ViewResolver>> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer,
ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList);
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
}
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public ErrorWebExceptionHandler errorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
JsonExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = new JsonExceptionHandler(
errorAttributes,
this.resourceProperties,
this.serverProperties.getError(),
this.applicationContext);
exceptionHandler.setViewResolvers(this.viewResolvers);
exceptionHandler.setMessageWriters(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getWriters());
exceptionHandler.setMessageReaders(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getReaders());
return exceptionHandler;
}
}
JsonExceptionHandler:
/**
* Custom exception handling
*
* <p>In case of exception, JSON is used instead of HTML exception information < p >
/
public class JsonExceptionHandler extends DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler {
public JsonExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ResourceProperties resourceProperties,
ErrorProperties errorProperties, ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
super(errorAttributes, resourceProperties, errorProperties, applicationContext);
}
/**
* Get exception properties
*/
@Override
protected Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("success", false);
map.put("code", 20005);
map.put("message", "Gateway failed");
map.put("data", null);
return map;
}
/**
* Specifies that the response processing method is JSON processing method
*
* @param errorAttributes
*/
@Override
protected RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getRoutingFunction(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return RouterFunctions.route(RequestPredicates.all(), this::renderErrorResponse);
}
/**
* Get the corresponding HttpStatus according to the code
*
* @param errorAttributes
*/
@Override
protected int getHttpStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes) {
return 200;
}
}
17.Redis cache
The home page data is cached through Redis. The Redis cache configuration class RedisConfig:
//Enable cache
@EnableCaching
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory
factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key serialization method
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value serialization
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap serialization
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//Solve the problem of query cache conversion exception
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// Configure serialization (solve the problem of garbled code), and the expiration time is 600 seconds
RedisCacheConfiguration config =
RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
Used to query teachers:
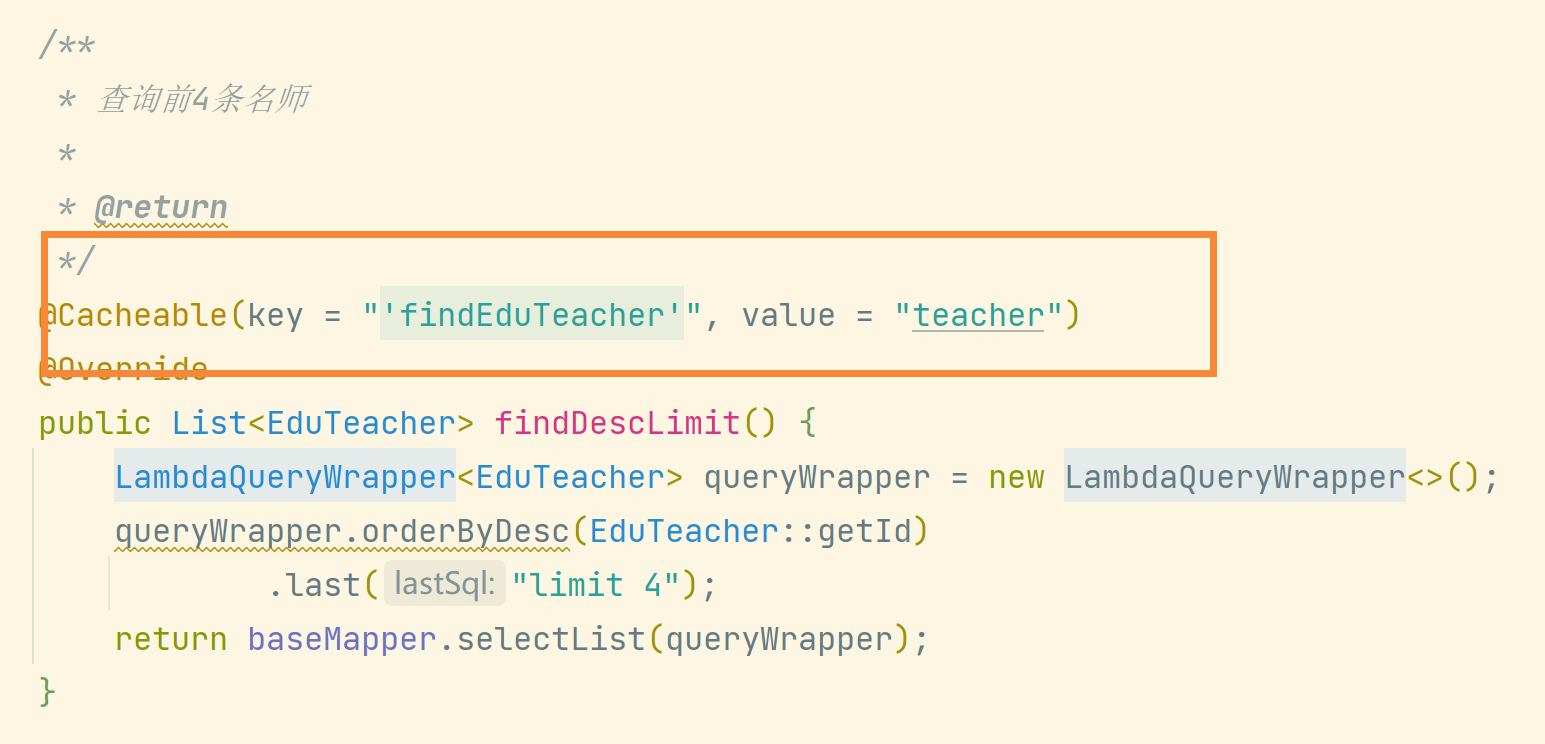
18. Project summary
Online education system is divided into foreground website system, background operation platform and B2C mode.
The microservice technology architecture is used, and the front and rear ends are developed separately:
- The main technical architecture of the backend is: springboot + springcloud + mybatis Plus + httpclient + MySQL + Maven + easyexcel + nginx
- The architecture of the front end is: node js + Vue. js +element-ui+NUXT+ECharts
- Other middleware involved include Redis, Alibaba cloud OSS and Alibaba cloud video on demand
- In the business, ECharts is used for chart display, EasyExcel is used to complete classification, batch addition and registration, and JWT is used for distributed single sign on
The system is divided into two parts: foreground user system and background management system:
- The foreground user system includes: home page, courses, famous teachers, Q & A and articles
- The background management system includes: Lecturer management, course classification management, course management, statistical analysis, Banner management, order management, authority management and other functions
