Introduction to agent mode
- Proxy mode: provide an avatar for an object to control access to the object. That is, the target object is accessed through the proxy object
- The advantage is that on the basis of the realization of the target object, additional function operations can be enhanced, that is, the function of the target object can be extended
- The proxied object can be a remote object, an object with high creation cost or an object requiring security control
- The proxy mode has different forms, mainly including three kinds of static proxy, dynamic proxy (JDK proxy, interface proxy) and Cglib proxy (it can dynamically create objects in memory without implementing interfaces. It belongs to the category of dynamic proxy)
Static proxy
When using a static proxy, you need to define an interface or parent class. The proxy object (i.e. the target object) and the proxy object implement the same interface or inherit the same parent class together
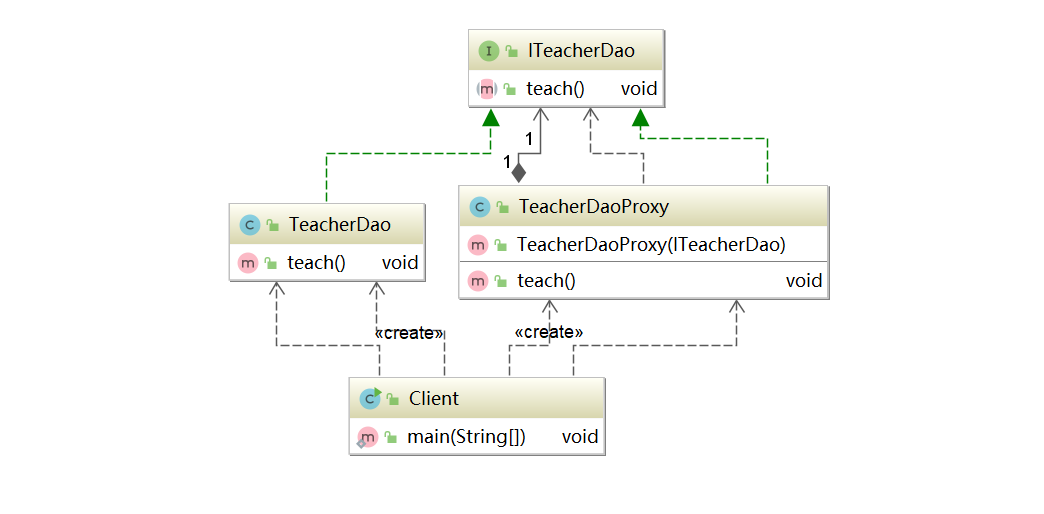
- Define an interface: ITeacherDao
- The target object TeacherDAO implements the interface ITeacherDAO
- Using the static proxy method, you need to implement ITeacherDAO in the proxy object TeacherDAOProxy
- When called, the target object is called by calling the method of the proxy object
- The proxy object and the target object should implement the same interface, and then call the method of the target object by calling the same method
//Interface
public interface ITeacherDao {
void teach(); // Teaching methods
}
public class TeacherDao implements ITeacherDao {
@Override
public void teach() {
System.out.println(" In the course of teaching.....");
}
}
//Proxy object, static proxy
public class TeacherDaoProxy implements ITeacherDao{
private ITeacherDao target; // Target object, aggregated through interface
//constructor
public TeacherDaoProxy(ITeacherDao target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public void teach() {
System.out.println("Start agent to complete some operations..... ");//method
target.teach();
System.out.println("Submit.....");//method
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create target object (proxied object)
TeacherDao teacherDao = new TeacherDao();
//Create a proxy object and pass the proxy object to the proxy object at the same time
TeacherDaoProxy teacherDaoProxy = new TeacherDaoProxy(teacherDao);
//Through the proxy object, call the method of the proxy object
//That is, the method of the proxy object is executed, and the proxy object calls the method of the target object
teacherDaoProxy.teach();
}
}
advantage
- Without modifying the function of the target object, the target function can be extended through the proxy object
shortcoming - Because the proxy object needs to implement the same interface as the target object, there will be many proxy classes
- Once a method is added to the interface, both the target object and the proxy object must be maintained
Dynamic agent
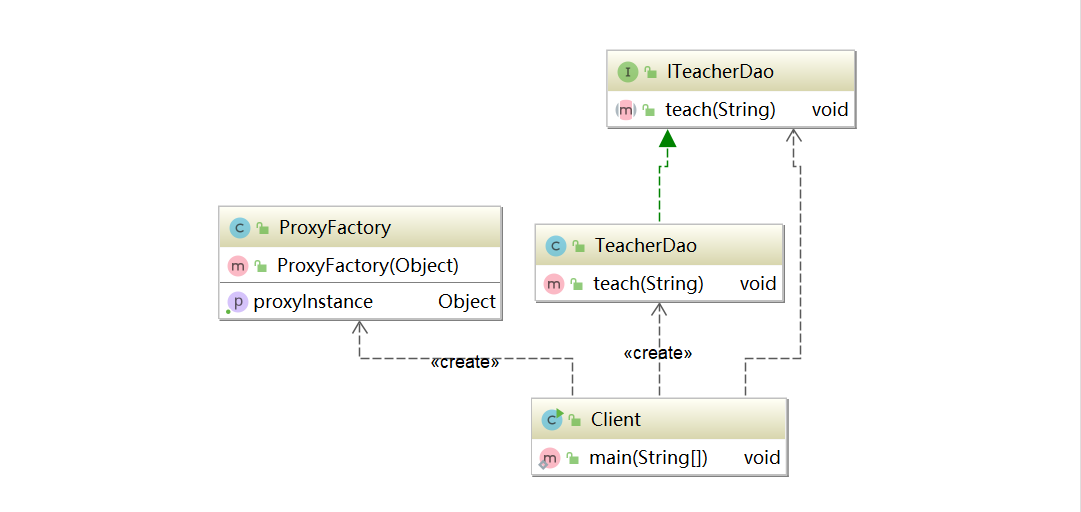
- The proxy object does not need to implement the interface, but the target object needs to implement the interface, otherwise the dynamic proxy cannot be used
- The generation of proxy object is to dynamically build proxy object in memory by using JDK API
- Dynamic agent is also called JDK agent and interface agent
JDK dynamic proxy application instance
API for generating proxy objects in JDK
- Package of proxy class: Java lang.reflect. Proxy
- The JDK implementation agent only needs to use the newProxyInstance method, but this method needs to receive three parameters. The complete writing method is: static object newProxyInstance (classiloader loader, class <? > [] interfaces, invocationhandler h)
//Interface
public interface ITeacherDao {
void teach(String name); // Training Methods
}
public class TeacherDao implements ITeacherDao {
@Override
public void teach(String name) {
System.out.println(name+" In Teaching.... ");
}
}
public class ProxyFactory {
//Maintain a target Object, Object
private Object target;
//Constructor to initialize the target
public ProxyFactory(Object target) { this.target = target; }
//Generate a proxy object for the target object
public Object getProxyInstance() {
/*
* public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h)
* 1. ClassLoader loader : Specifies the class loader used by the current target object, and the method to get the loader is fixed
* 2. Class<?>[] interfaces: The interface type implemented by the target object, and use the generic method to confirm the type
* 3. InvocationHandler h : In event processing, when executing the method of the target object, the event processor method will be triggered, and the currently executed target object method will be passed in as a parameter
*/
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("JDK Agent start~~");
//The reflection mechanism calls the method of the target object
Object returnVal = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("JDK Agent submission");
return returnVal;
}
});
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create target object
ITeacherDao target = new TeacherDao();
//Create a proxy object for the target object, which can be converted to ITeacherDao
ITeacherDao proxyInstance = (ITeacherDao)new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
// proxyInstance=class com. sun. proxy.$ Proxy objects are dynamically generated in proxy0 memory
System.out.println("proxyInstance=" + proxyInstance.getClass());
//Call the method of the target object through the proxy object
//proxyInstance.teach();
proxyInstance.teach(" tom ");
}
}
Cglib proxy application instance
- Both static proxy and JDK proxy modes require the target object to implement an interface, but sometimes the target object is only a separate object and does not implement any interface. At this time, the target object subclass can be used to implement the proxy, which is Cglib proxy
- Cglib agent is also called subclass agent. It constructs a subclass object in memory to expand the function of the target object. Some books also attribute cglib agent to dynamic agent.
- Cglib is a powerful and high-performance code generation package, which can extend java classes and implement java interfaces at run time It is widely used by many AOP frameworks, such as Spring AOP, to implement method interception
- How to select agent mode in AOP programming:
- The target object needs to implement the interface and use JDK proxy
- The target object does not need to implement the interface and uses Cglib proxy
- The bottom layer of Cglib package is to convert bytecode and generate new classes by using bytecode processing framework ASM
If you use eclipse, you need to add the following jar packages

- Dynamically build subclasses in memory. Note that the class of the agent cannot be final, otherwise an error Java. Net will be reported lang.IlegalArgumentException
- If the method of the target object is final/static, it will not be intercepted, that is, additional business methods of the target object will not be executed
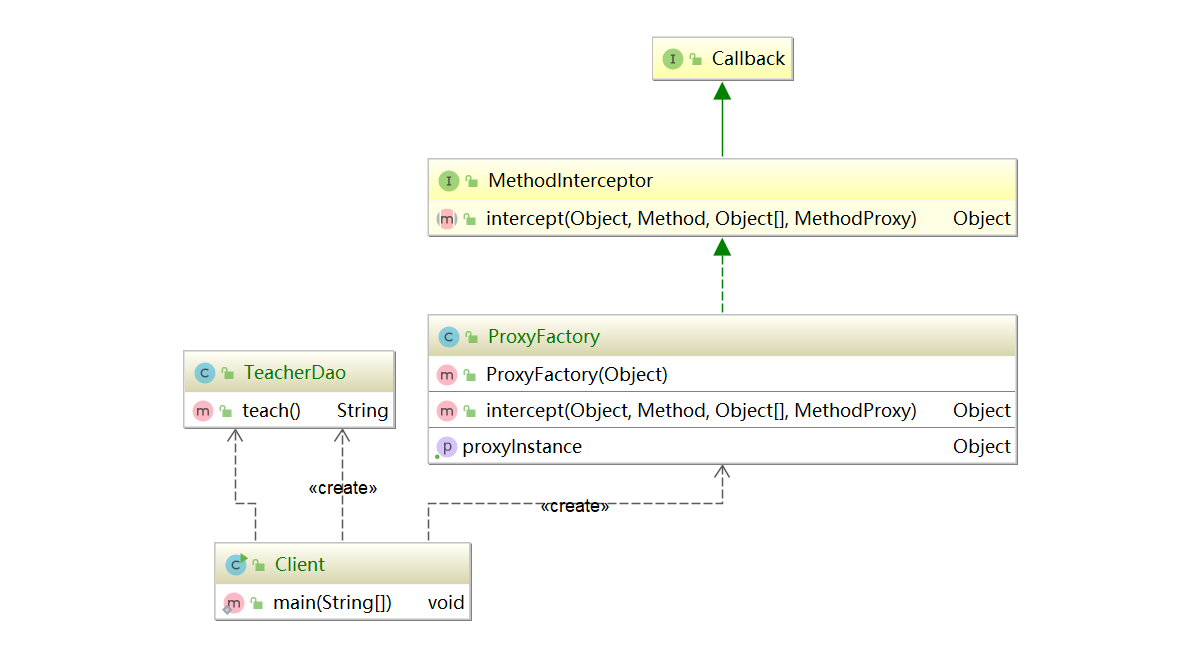
- getProxyInstance creates a proxy object for the target object target
//Returns a proxy object: the proxy object of the target object
public Object getProxyInstance() {
//1. Create a tool class
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//2. Set parent class
enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
//3. Set callback function
enhancer.setCallback(this);
//4. Create a subclass object, that is, a proxy object
return enhancer.create();
}
- Override the intercept method to call the proxy object (target object) method
//Overriding the intercept method will call the method of the target object
@Override
public Object intercept(Object arg0, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy arg3) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Cglib proxy pattern ~~ start");
Object returnVal = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("Cglib proxy pattern ~~ Submit");
return returnVal;
}
idea import pom dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
</dependency>
public class TeacherDao {
public String teach() {
System.out.println(" Yes, I am cglib Proxy, no need to implement interface ");
return "hello";
}
}
public class ProxyFactory implements MethodInterceptor {
//Maintain a target object
private Object target;
//Constructor, passing in an object to be represented
public ProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//Returns a proxy object: the proxy object of the target object
public Object getProxyInstance() {
//1. Create a tool class
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//2. Set parent class
enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
//3. Set callback function
enhancer.setCallback(this);
//4. Create a subclass object, that is, a proxy object
return enhancer.create();
}
//Overriding the intercept method will call the method of the target object
@Override
public Object intercept(Object arg0, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy arg3) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Cglib proxy pattern ~~ start");
Object returnVal = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("Cglib proxy pattern ~~ Submit");
return returnVal;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//Create target object
TeacherDao target = new TeacherDao();
//Gets the proxy object and passes the target object to the proxy object
TeacherDao proxyInstance = (TeacherDao)new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
//Execute the method of the proxy object and trigger the concept method to call the target object
String res = proxyInstance.teach();
System.out.println("res=" + res);
}
}
Several common agent models introduce one or more variants
Firewall agent
The intranet penetrates the firewall through the agent to realize the access to the public network.
Cache agent
For example, when requesting resources such as picture files, go to the cache agent first. If you get the resources, ok. If you can't get the resources, go to the public network or database, and then cache.
Remote agent
The local representative of the remote object, through which the remote object can be called as a local object. Remote agents communicate information with real remote objects through the network.
Synchronization agent
It is mainly used in multithreaded programming to complete the synchronization between multithreads