1. requests
In Python 3, you can use urllib Request and requests for web page crawling.
- The urllib library is built into python and does not need to be installed
- The requests library is a third-party library and needs to be installed by yourself
1.1 installation command
pip install requests
1.2 basic methods of requests
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| requests.request() | Construct a request to support the basic method of the following methods |
| requests.get() | GET HTML web page, corresponding to HTTP GET |
| requests.head() | Get the header information of the HTML web page, corresponding to the HTTP HEAD |
| requests.post() | The method of submitting POST requests to web pages, corresponding to HTTP POST |
| requests.put() | The method of submitting PUT requests to HTML web pages, corresponding to HTTP PUT |
| requests.putch() | Submit a local modification request to an HTML web page, corresponding to the HTTP PATCH |
| requests.delete() | Submit a DELETE request to the HTML page, corresponding to the HTTP DELETE |
Official Chinese tutorial address
2. Beautiful Soup
2.1 installation command
pip install beautifulsoup4
3. Import library
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
4. Actual combat - novel crawling
Target site: https://www.52bqg.net/
First, check out the robots Txt file: https://www.52bqg.net/robots.txt

You can see that except js and css files, other contents are allowed to crawl
4.1 get web content
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
if __name__ == '__main__':
target = "https://www.52bqg.net / "# target website
response = requests.get(url=target) # Get web content
print(response.text) # Print information
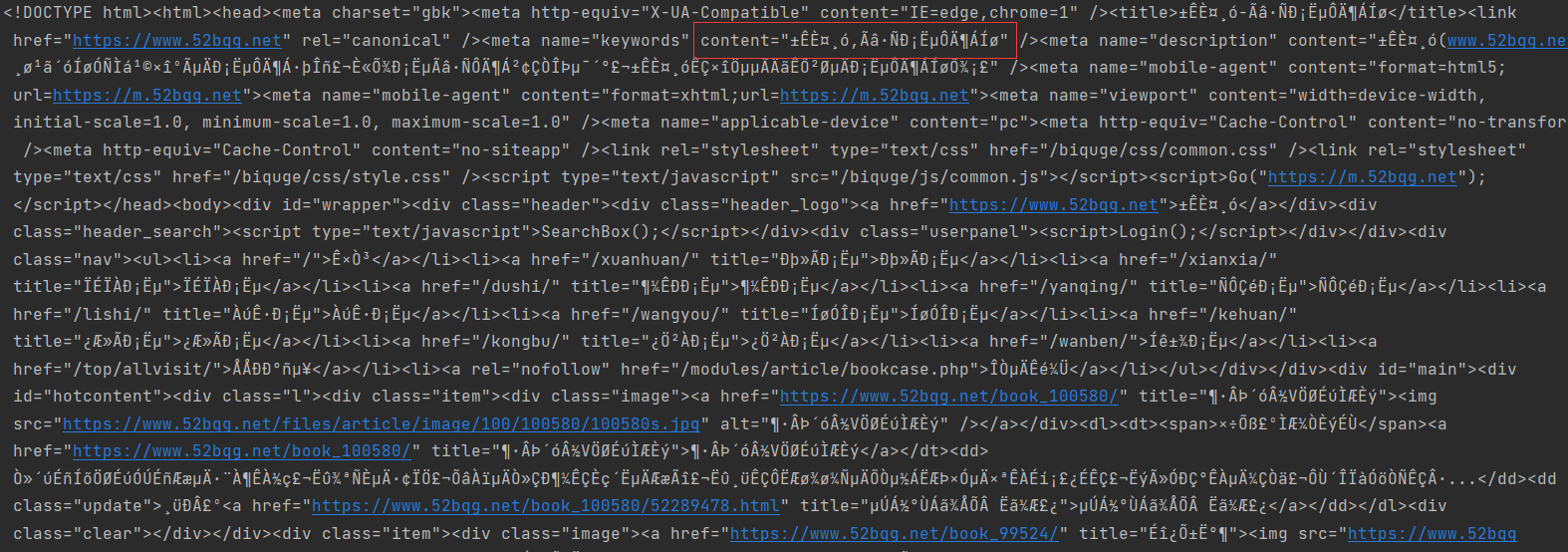
The printed content is as follows:
4.1. 1 decoding problem
It can be seen that there are many problems in the current content, and the crawled content needs to be transcoded. Right click Check (F12) in the website to view the page structure. There will be a meta tag in the head tag. Specify the encoding format used by the current page and decode it through the corresponding encoding format.
response.encoding = "gbk"

4.1. 2 automatic decoding
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding # Automatic transcoding
4.2 get the required content
Get a chapter of the novel and try to get it: https://www.52bqg.net/book_121653/43348470.html
As follows, the content of the novel is the object to climb

Use the following code to get the text information of the web page
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
if __name__ == '__main__':
target = "https://www.52bqg.net/book_121653/43348470.html "# target site
response = requests.get(url=target) # Get web content
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding # Automatic transcoding
print(response.text) # Print information

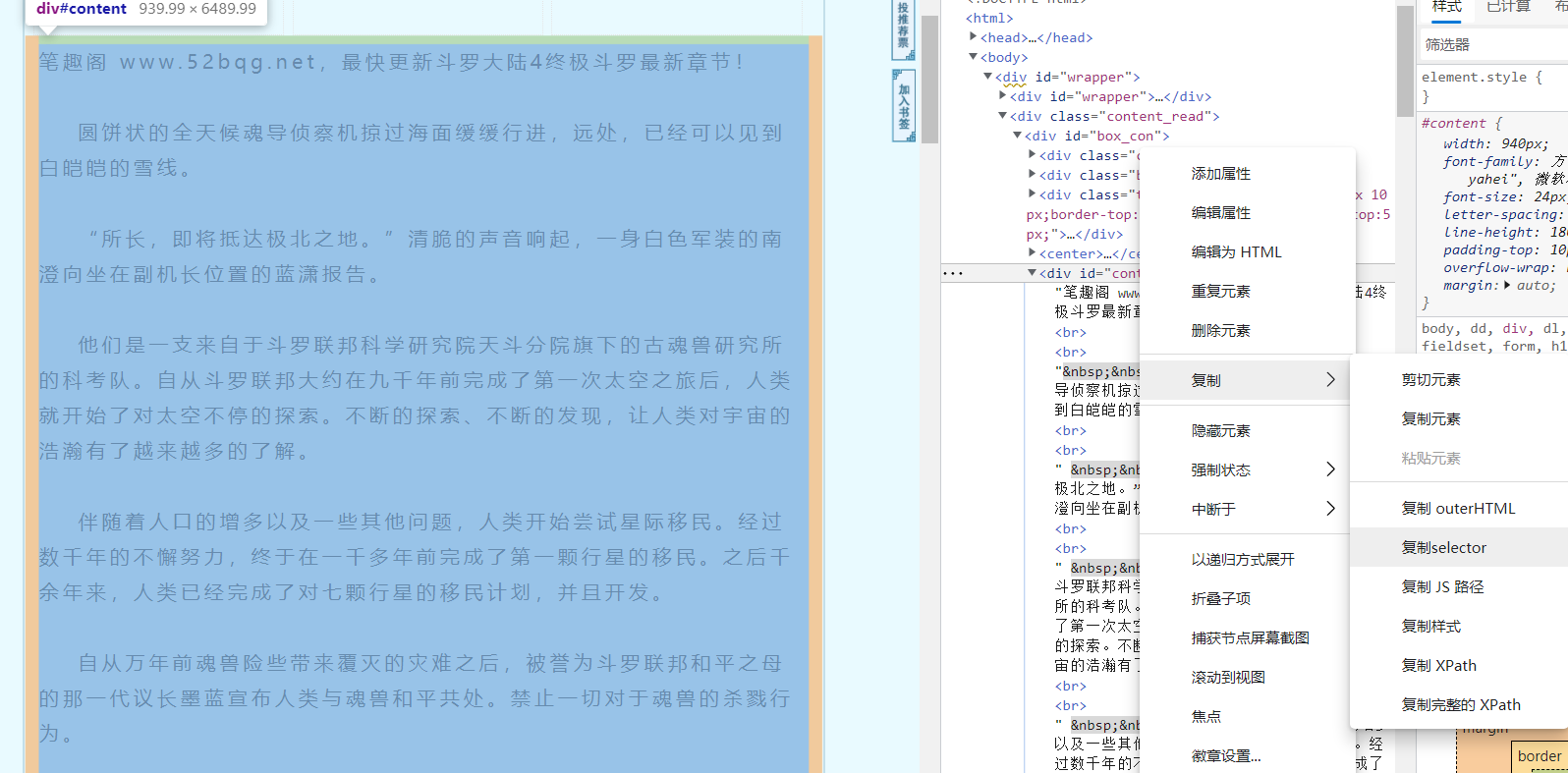
From the web page structure, we can see that the content we need is actually contained in labels, but now the content we get is text, and the corresponding content cannot be obtained through labels. At this time, we need Beautiful Soup to analyze it
Steps:
-
First create a Beautiful Soup object. The parameters in the BeautifulSoup function are the html information we have obtained.
-
find_all method to obtain all xxx tags with class attribute xxx in html information. (find multiple and regular labels)
td = Soup.find_all('td', class_='even') # Get td tags for all class attributes find_all method - The first parameter is the tag name obtained - Second parameter class_Is the attribute of the tag (why not class But class_,Because python in class Is a keyword. In order to prevent conflicts, it is used here class_Represents the of the label class Properties, class_Followed by the attribute value. -
select method to obtain the value under the corresponding path (find the one with the determined path)
Soup.select('#intro > p:nth-child(2)') # obtain#Intro > P: nth child (2) contents under the path
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
if __name__ == '__main__':
target = "https://www.52bqg.net/book_121653/43348470.html "# target site
response = requests.get(url=target) # Get web content
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding # Automatic transcoding
html = response.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, features="html.parser") # Create a beautiful soup object
info = soup.select('#content')
print(info)

It can be seen from the results that what is currently obtained is a list. After extracting the matching results, use the text attribute to extract the text content, so as to filter out the < br > tags. Then use the replace method to replace the space with carriage return for segmentation.
  stay html Used to represent spaces in
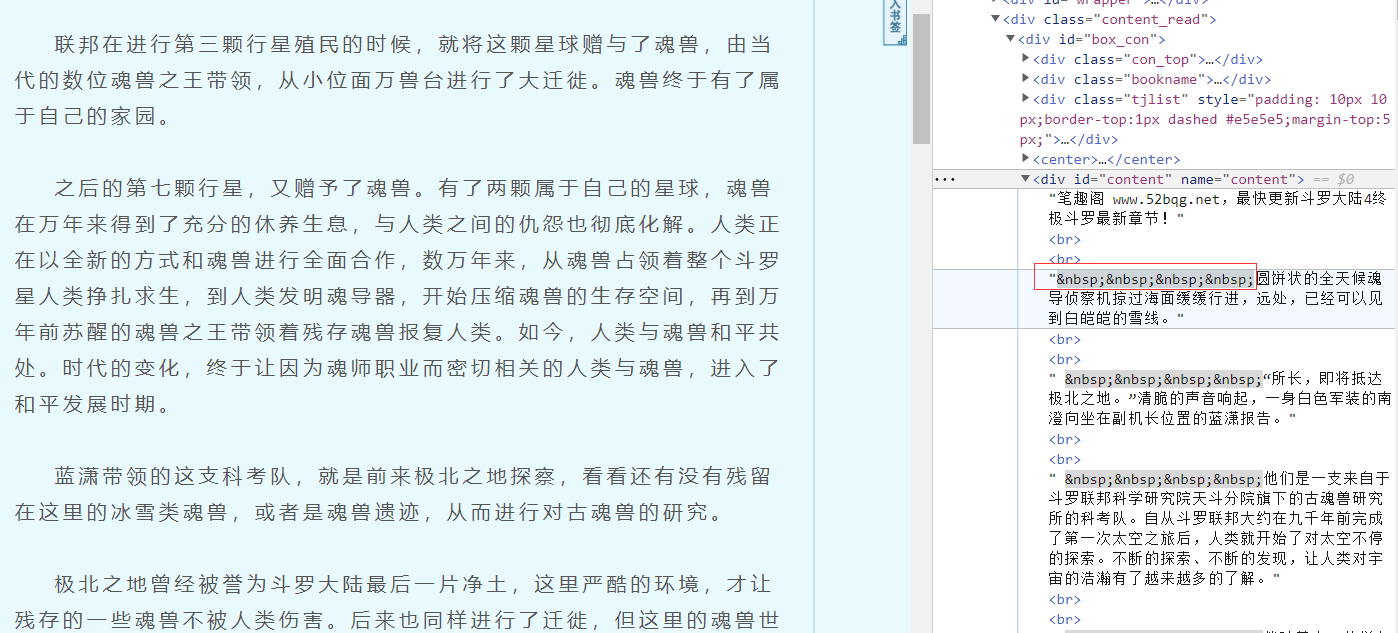
The code of the extracted content is as follows:
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, features="html.parser")
info = soup.select('#content')
content = info[0].text.replace('\xa0'*8, '\n\n')
print(content)
4.2. 1. Acquisition of label path
The path obtained in the above steps is #content
info = soup.select('#content')