Circular linked list
I. Summary:
Circular linked list is a special case relative to single linked list, which assigns the next field of the last node to the head node (Figure 1 is a single linked list, Figure 2 is a circular linked list).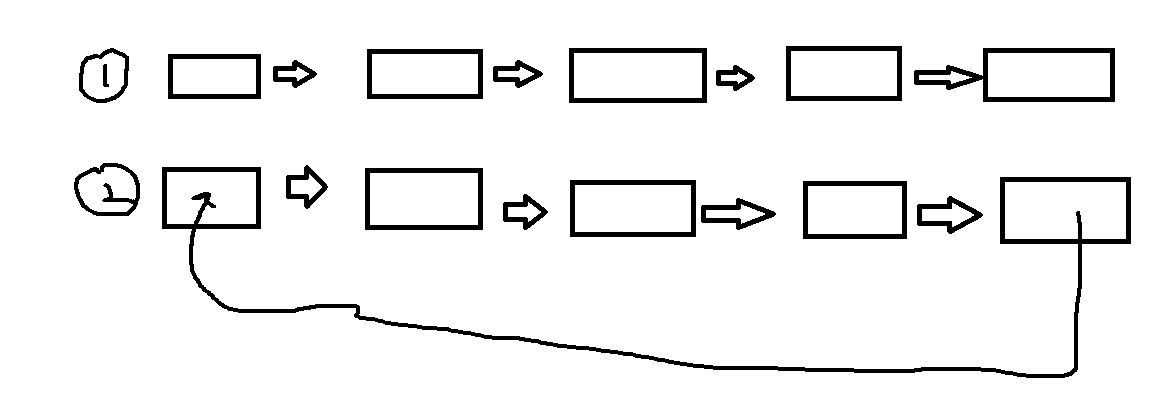
Comparisons of Level Cyclic List and Single List
The characteristic of circular linked list is that it does not need to increase the storage, but only changes the way of linking the table slightly, which makes the table processing more convenient and flexible. There is no None field in the circular list. When traversal operation is involved, its termination condition is no longer to judge whether P or p->next is None as a non-circular list, but whether they are equal to a specified pointer, such as head pointer or tail pointer. (2) In a single linked list, starting from a known node, only the node and its subsequent nodes can be accessed, and other nodes before the node can not be found. In a single-loop list, all nodes in the list can be accessed from any node. This advantage makes some operations easy to implement on a single-loop list.
2. Implementation code:
(1) Establishing nodes:
class Node():
"""
//Establishing Nodes
"""
def __init__(self,date):
self.date=date
self.next=Node
(2) Establish a circular list with header nodes:
Judging whether the circular list is empty
def is_empty(self):
"""Judging whether the list is empty"""
return self.__head==None
Finding the Length of Circulating Link List
def length(self):
"""
//Finding the Length of Chain List
"""
if self.is_empty():
return 0
else:
count=1
cur=self.__head
while cur.next!=self.__head:
count+=1
cur=cur.next
return count
Finding the Length of Circulating Link List
def travel(self):
cur=self.__head
if self.is_empty():
print("The list is empty and cannot be traversed")
else:
while cur!=self.__head:
print(str(cur.date),end=" ")
cur=cur.next
print(str(cur.date))#Used to traverse the last node
This line of code should pay attention to the last line, not less, otherwise it can not output the last node, because cur== self. head can not enter the last node when scanning in the while loop, so it needs to be output separately.
Insert nodes from scratch:
def HeadInsert(self,num):
"""
//Head insertion node
"""
node=Node(num)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head=node
node.next=node
else:
cur=self.__head
while cur.next!=self.__head:
cur=cur.next
node.next=self.__head
self.__head=node
cur.next=self.__head
Insert nodes from the tail:
def TailInsert(self,num):
"""
//Tail insertion node
"""
node=Node(num)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head=node
node.next=self.__head
else:
cur=self.__head
while cur.next!=self.__head:
cur=cur.next
node.next=self.__head
cur.next=node
Index insertion:
def NodeInsert(self,index,num):
"""Adding elements at specified locations"""
#Point to the address of self. head, which is not a header element
# For the next element, so Preis the next element
if index <= 0:
#Think of it as head insertion.
self.HeadInsert(num)
elif index > (self.length()-1):
self.TailInsert(num)
else:
pre_cur = self.__head
count = 0
while count < (index-1):
count+=1
pre_cur = pre_cur.next
node = Node(num)
node.next = pre_cur.next
pre_cur.next = node
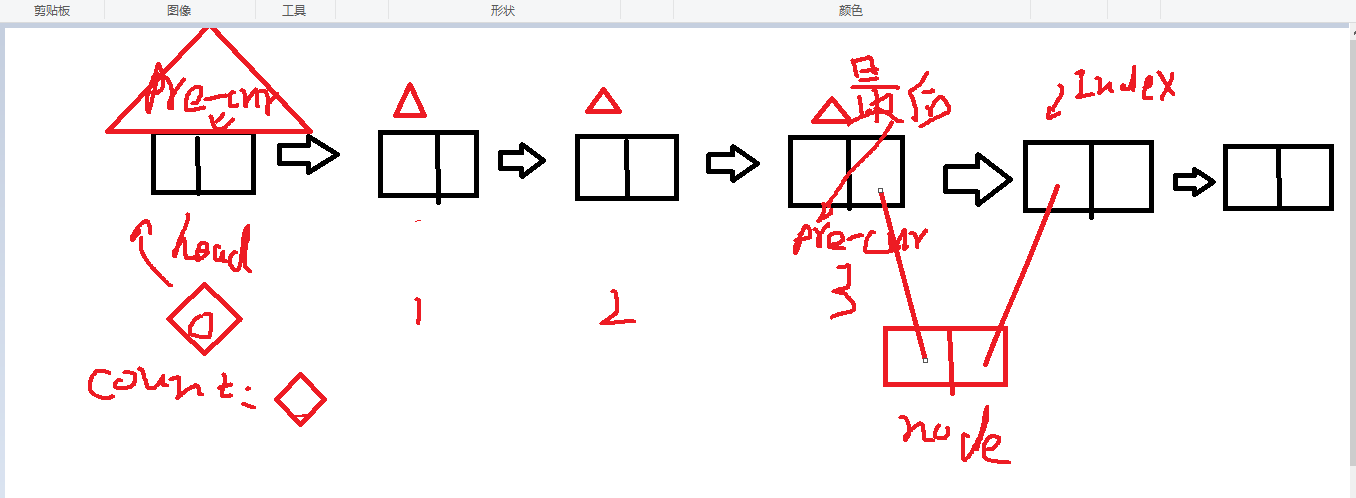
Complete code:
import random
class Node():
"""
//Establishing Nodes
"""
def __init__(self,date):
self.date=date
self.next=None
class LinkNode():
def __init__(self,node=None):
self.__head=node
if node:
node.next=self.__head #Establish a loop head node
def is_empty(self):
"""Judging whether the list is empty"""
return self.__head==None
def length(self):
"""
//Finding the Length of Chain List
"""
if self.is_empty():
return 0
count=1
cur=self.__head
while cur.next!=self.__head:
count+=1
cur=cur.next
return count
def travel(self):
"""Traversing the entire list"""
if self.is_empty():
return
#Creating a cursor equals the starting node
cur = self.__head
while cur.next != self.__head:
print(cur.date,end=" ")
cur = cur.next
print(cur.date,end="\n")
def HeadInsert(self,num):
"""
//Head insertion node
"""
node=Node(num)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head=node
node.next=node
else:
cur=self.__head
while cur.next!=self.__head:
cur=cur.next
node.next=self.__head
self.__head=node
cur.next=self.__head
def TailInsert(self,num):
"""
//Tail insertion node
"""
node=Node(num)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head=node
node.next=self.__head
else:
cur=self.__head
while cur.next!=self.__head:
cur=cur.next
cur.next=node
node.next=self.__head
def NodeInsert(self,index,num):
"""Adding elements at specified locations"""
#Point to the address of self. head, which is not a header element
# For the next element, so Preis the next element
if index <= 0:
#Think of it as head insertion.
self.HeadInsert(num)
elif index > (self.length()-1):
self.TailInsert(num)
else:
pre_cur = self.__head
count = 0
while count < (index-1):
count+=1
pre_cur = pre_cur.next
node = Node(num)
node.next = pre_cur.next
pre_cur.next = node
a=LinkNode()
for i in range(6):
a.TailInsert(random.randint(0,10))#Random insertion of six numbers
a.travel()
a.NodeInsert(5,100)
a.travel()