book
Alicloud disk acquisition, invalid in 2025
Use notes in combination with videos on station B. compare nice < Python learning alliance >
Some frameworks:
1. Sketch framework
2.pyspider
3.cola framework (distributed)
Reptile first step
import urllib.request
response = urllib.request.urlopen('http://placekitten.com/g/500/600')
cat_img = response.read()
with open('cat.jpg','wb') as f:
f.write(cat_img)
Note that f is followed by a colon, not a semicolon. At first, I thought it was a colon, but an error was reported
urlopen(string) # Returns an Object urllib--URL handing modules urllib.request for opening and reading URLs urllib.error containing the exceptions raised by urllib.request urllib.parse for parsing URLs urllib.robotparser for parsing robots.txt files
Reptile song
write file
r : Read the file. If the file does not exist, an error will be reported w: Write the file. If the file does not exist, it will be created first and then written, and the original file will be overwritten a : If the file does not exist, it will be created first and then written, but the original file will not be overwritten, but appended to the end of the file rb,wb: Respectively r,w Similar, but used to read and write binaries r+ : It is readable and writable. If the file does not exist, an error will be reported, and it will be overwritten during write operation w+ : It is readable and writable. If the file does not exist, it will be created first and will be overwritten a+ : It is readable and writable. The file does not exist. It is created first and will not be overwritten. It is appended at the end
urllib
regular expression
. Matches any character except newline \w Match letters or numbers or underscores \s Match any whitespace \d Match number \n Match a newline character \t Match a tab ^ Start of matching string $ Matches the end of the string \W Match non alphanumeric underscores \D Match non numeric \S Match non whitespace a | b Matching letters a Or character b () Match expressions in parentheses [...] Matches the characters in the character group [^...] Matches all characters except those in the character group
Quantifier: controls the number of occurrences of metacharacters
* Repeat zero or more times
+ Repeat one or more times
? Repeat zero or once
{n} repeat n second
{n,} repeat n Times or more
{n,m} repeat n reach m second
Greedy matching && Inert matching .* Greedy matching .*? Inert matching
Example of inert matching
# Parse data
obj = re.compile(r'<li>.*?<div class="item">.*?<span class="title">(?P<name>.*?)</span>'
r'.*?<p class="">.*?<br>(?P<year>.*?) .*?<span class="rating_num" '
r'property="v:average">(?P<score>.*?)</span>.*?'
r'<span>(?P<num>.*?)Human evaluation</span>',re.S)
BS4 parsing
PIP3 install beautiful soup4 installation
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = "https://umei.cc/bizhitupian/weimeibizhi/"
resp = requests.get(url)
resp.encoding = 'utf-8'
main_page = BeautifulSoup(resp.text, "html.parser")
alist = main_page.find("div", class_="TypeList").find_all("a")
for a in alist:
href = "https://umei. CC "+ A.get (" href ") # directly get the value of the attribute
# print(href)
# Get the source code of the sub page
child_page_resp = requests.get(href)
child_page_resp.encoding = 'utf-8'
child_page_text = child_page_resp.text
# Get the download path of the picture from the sub page
child_page = BeautifulSoup(child_page_text, "html.parser")
p = child_page.find("p", align="center")
img = p.find("img")
print(img.get("src"))
Note that if the print(href) above is not spliced, you will get: / bizhitupian / weimeibizhi / 225260 Htm is not a complete link in the video, so you need to splice the link address of the picture here, otherwise it will be in request Get (href) will report an error, because the request needs a URL to parse, but in fact, the obtained href is not a complete URL, but:

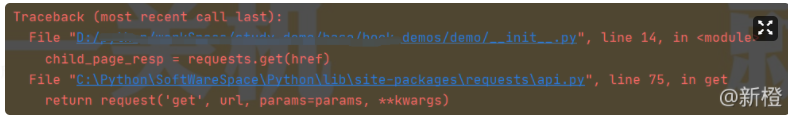
The screenshot of the error report is as follows. The psychological shadow is really great. I also went to see the api source code of request.... However, I don't quite understand
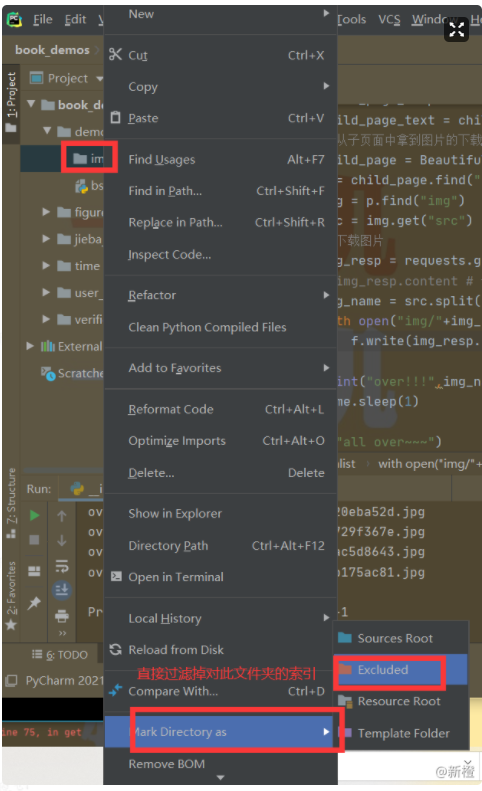
When there are many downloaded files, it is recommended to set the folder for downloading resources to red; The setting method is as follows:
xpath
xpath is a language for searching content in xml documents, and html is a subset of xml
The lxml module command pip install lxml needs to be installed
text() get text
// It means offspring
* Arbitrary node
./ current node
xpath The order of starts with 1
res = tree.xpath("/html/body/ol/li/a[@href='dapao']/text()") # [@xxx=xxx] # Attribute filtering
# Get attribute value: @ attribute
import requests
from lxml import etree
url = "https://beijing.zbj.com/search/f/?kw=sass"
resp = requests.get(url)
# analysis
html = etree.HTML(resp.text)
divs = html.xpath("/html/body/div[6]/div/div/div[2]/div[5]/div/div")
for div in divs: # Information of each service provider
price = div.xpath("./div/div/a[2]/div[2]/div[1]/span[1]/text()")[0].strip("¥")
title = "sass".join(div.xpath("./div/div/a[2]/div[2]/div[2]/p/text()"))
com_name = div.xpath("./div/div/a[1]/div[1]/p/text()") # [0] put it in the list
print(com_name)
Processing cookies
import requests
# conversation
session = requests.session()
data = {
"loginName": "xxxxxxxx",
"password": "xxxxxxxxx"
}
# Sign in
url = "https://passport.17k.com/login/"
sp = session.post(url, data=data)
resp = session.get('https://user.17k.com/ck/author/shelf?page=1&appKey=2406394919')
print(resp.json())
/* or */
resp = request.get("https://user.17k.com/ck/author/shelf?page=1&appKey=2406394919",headers={
"Cookie":"abbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb"
})
Handling of anti-theft chain
Search for video address (check element – > vedio) – but here is the real-time page video address,
# 1. Get contId
# 2. Get the JSON - > srcurl returned by vedioStatus
# 3. Adjust the contents of srcurl
# 4. Download Video
# refer: it's a traceability to find the requested URL
import requests
url = "https://www.pearvideo.com/video_1742368"
contId = url.split("_")[1] # With "" Split "" Subsequent number 1742368
videoStatusUrl = f"https://www.pearvideo.com/videoStatus.jsp?contId={contId}&mrd=0.5467768006452396"
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/94.0.4606.71 Safari/537.36 Edg/94.0.992.38",
# Anti theft chain: traceability. Who is the upper level of the current request
"Referer": url
}
resp = requests.get(videoStatusUrl, headers=headers)
dic = resp.json()
srcUrl = dic['videoInfo']['videos']['srcUrl']
systemTime = dic['systemTime']
# https://video.pearvideo.com/mp4/adshort/20210924/1633438051634-15773028_adpkg-ad_hd.mp4
# src="https://video.pearvideo.com/mp4/adshort/20210924/cont-1742368-15773028_adpkg-ad_hd.mp4"
srcUrl = srcUrl.replace(systemTime,f"cont-{contId}")
print(srcUrl)
# Download Video
with open("a.pm4",mode="wb") as f:
f.write(requests.get(srcUrl).content)
Netease cloud comment crawling comprehensive case
Find the correct request (remember to refresh the page)
Click to get the information in json format
Set breakpoint
Keep asking until we get to the place we need
Next, you need to find out where the encrypted code is
You can use Ctrl + F to find keywords. The previously requested data are params and encSecKey. You can also find the location of the encrypted code
The other is to observe where the request data of the stack has changed, resulting in data encryption, which can also be located at the same location
Click one stack by one and observe the changes in the data
/*Requested parameters*/ csrf_token: "" cursor: "-1" offset: "0" orderType: "1" pageNo: "1" pageSize: "20" rid: "R_SO_4_1417862046" threadId: "R_SO_4_1417862046"
You can set breakpoints and run step by step until data changes are observed
Keep looking
These two strings return the same value on the console, so they are fixed and written to death when simulating encryption.
To get the above long things, first find the stack of the first call, then set the breakpoint at send, and then click refresh to directly jump to the encrypted statement, as shown in the figure below. At this time, go to the console to print and get the things you need.
Get i and encSecKey
# 1.Unencrypted parameters found # window. Arsea (parameter, xxx,xxx)\
# 2. Try to encrypt the parameters (refer to Netease logic), params - > enctext, encseckey - > encseckey
# 3. Request to Netease and get the comment information
'''
Process encryption
function() {
function a(a = 16) { # Returns a 16 bit random string
var d, e, b = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789", c = "";
for (d = 0; a > d; d += 1) # 16 cycles
e = Math.random() * b.length, # Random number 1.2345
e = Math.floor(e), # Rounding
c += b.charAt(e); # Go to xxx position b in the string
return c
}
function b(a, b) { # a is the content to be encrypted
var c = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse(b) # b is the key
, d = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse("0102030405060708")
, e = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse(a) # e is data
, f = CryptoJS.AES.encrypt(e, c, { # c encrypted key
iv: d, # Offset
mode: CryptoJS.mode.CBC # Mode: CBC
});
return f.toString()
}
function c(a, b, c) { # c does not generate random numbers
var d, e;
return setMaxDigits(131),
d = new RSAKeyPair(b,"",c),
e = encryptedString(d, a)
}
function d(d, e, f, g) { d:data e:010001 f:Very long g:0CoJUm6Qyw8W8jud
var h = {} # Empty object
, i = a(16); # i is a 16 bit random value. Set i to a fixed value
return h.encText = b(d, g),
h.encText = b(h.encText, i),
h.encSecKey = c(i, e, f),
h
/* The above three lines are equivalent to - >
* h.encText = b(d,g) # g Is the key
* h.encText = b(h.encText, i) # The returned params I is also the key
* h.encSecKey = c(i,e,f) # The result is that the encSecKey e and f are fixed, so i is also fixed at this time, which means that the returned encSecKey is also fixed
* return h
* Double encryption:
* Data + G = > b = > first encryption + I = > b = params
*/
}
function e(a, b, d, e) {
var f = {};
return f.encText = c(a + e, b, d),
f
}
window.asrsea = d,
window.ecnonasr = e
}();
'''
import requests
import json
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from base64 import b64encode
url = "https://music.163.com/weapi/comment/resource/comments/get?csrf_token="
# The method of request is post
data = {
"csrf_token": "",
"cursor": "-1",
"offset": "0",
"orderType": "1",
"pageNo": "1",
"pageSize": "20",
"rid": "R_SO_4_1417862046",
"threadId": "R_SO_4_1417862046"
}
# Serving d
f = "00e0b509f6259df8642dbc35662901477df22677ec152b5ff68ace615bb7b725152b3ab17a876aea8a5aa76d2e417629ec4ee341f56135fccf695280104e0312ecbda92557c93870114af6c9d05c4f7f0c3685b7a46bee255932575cce10b424d813cfe4875d3e82047b97ddef52741d546b8e289dc6935b3ece0462db0a22b8e7"
g = "0CoJUm6Qyw8W8jud"
e = "010001"
i = "d8YcSIZJWOho8lxf" # Manually fixed - > random in other people's functions
def get_encSecKey(): # Because i is fixed, encSecKey is fixed, and the result of c() function is fixed
return "abad643b9dfb5ab1456db763d10c39f633729bec3edc4f22a433772d0eb1a0b6dcf44a22d734565b7525c0e32a3b930ff1ac79a2cbade5b91bf9a9887bd3fa04b0468a4f450cdfcf41afb00402272fc860ff21960eee003e3f7b29f1066a6385dd53f33a647c5ef7c83377d2ce4bd44e0e72cdd753a559a327327ecbd5d5080b"
# Convert it into a multiple of 16 to serve the encryption algorithm below
def to_16(data):
pad = 16 - len(data) % 16
data += chr(pad) * pad
return data
# Encryption process
def enc_params(data, key): # Encryption process
iv = "0102030405060708"
data = to_16(data)
aes = AES.new(key=key.encode("utf-8"), IV=iv.encode("utf-8"), mode=AES.MODE_CBC) # Create encryptor
bs = aes.encrypt(data.encode("utf-8")) # The length of encrypted content must be a multiple of 16
ans = str(b64encode(bs), "utf-8")
return ans # Convert to string return
# Encrypt parameters
def get_params(data): # By default, a string is received here
first = enc_params(data, g)
second = enc_params(first, i)
return second # params is returned
# Send request,
resp = requests.post(url, data={
"params": get_params(json.dumps(data)),
"encSecKey": get_encSecKey()
})
print(resp.text)
Improvement of reptile efficiency
Multithreading
A process is a resource unit, and each process must have at least one thread Thread is the execution unit Each program starts with a main thread by default
"""
Single threaded demo case
result:
func 0
func 1
func 2
func 3
func 4
main 0
main 1
main 2
main 3
main 4
"""
# def func():
# for i in range(5):
# print("func", i)
#
#
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# func()
# for i in range(5):
# print("main", i)
# Multithreading (two methods)
# from threading import Thread
# one
# def func():
# for i in range(1000):
# print("func ", i)
#
#
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# t = Thread(target=func()) # Create a thread and schedule tasks for the thread
# t.start() # The multithreading state is the working state, and the specific execution time is determined by the CPU
# for i in range(1000):
# print("main ", i)
# two
class MyThread(Thread):
def run(self): # Fixed - > when a thread is executed, run() is executed
for i in range(1000):
print("Child thread ", i)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = MyThread()
# t.run() #Method call -- single thread
t.start() #Open thread
for i in range(1000):
print("Main thread ", i)
The child thread and the main thread sometimes execute at the same time. This is multithreading
After a thread is created, it only represents that it is in a working state, not immediate execution. The specific execution time depends on the CPU
Multi process
from multiprocessing import Process
def func():
for i in range(1000):
print("Subprocess ", i)
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = Process(target=func())
p.start()
for i in range(1000):
print("Main process ", i)
Thread pool & process pool
# Thread pool: open up some threads at one time. Our users directly submit tasks to the thread pool, and the scheduling of thread tasks is handed over to the thread pool to complete
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, ProcessPoolExecutor
def fn(name):
for i in range(1000):
print(name,i)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create thread pool
with ThreadPoolExecutor(50) as t:
for i in range(100):
t.submit(fn, name=f"thread {i}")
# Wait until all the tasks in the thread pool have been executed before continuing to execute (guard)
print(123)
json.dump() and JSON The difference between dumps()
json.dumps() is a process of converting python objects into JSON objects, which generates strings.
json.dump() converts python objects into JSON objects to generate an fp file stream, which is related to files.
import json
x = {'name':'Have a guess','age':19,'city':'Sichuan'}
#Encoding python into json strings with dumps
y = json.dumps(x)
print(y)
i = json.dumps(x,separators=(',',':'))
print(i)
"""
Output results
{"name": "\u4f60\u731c", "age": 19, "city": "\u56db\u5ddd"}
{"name":"\u4f60\u731c","age":19,"city":"\u56db\u5ddd"}
"""
#### Verification code - Super Eagle
```python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding:utf-8
import requests
from hashlib import md5
class Chaojiying_Client(object):
def __init__(self, username, password, soft_id):
self.username = username
password = password.encode('utf8')
self.password = md5(password).hexdigest()
self.soft_id = soft_id
self.base_params = {
'user': self.username,
'pass2': self.password,
'softid': self.soft_id,
}
self.headers = {
'Connection': 'Keep-Alive',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident/4.0)',
}
def PostPic(self, im, codetype):
"""
im: Picture byte
codetype: Topic type reference http://www.chaojiying.com/price.html
"""
params = {
'codetype': codetype,
}
params.update(self.base_params)
files = {'userfile': ('ccc.jpg', im)}
r = requests.post('http://upload.chaojiying.net/Upload/Processing.php', data=params, files=files,
headers=self.headers)
return r.json()
def ReportError(self, im_id):
"""
im_id:Pictures of wrong topics ID
"""
params = {
'id': im_id,
}
params.update(self.base_params)
r = requests.post('http://upload.chaojiying.net/Upload/ReportError.php', data=params, headers=self.headers)
return r.json()
if __name__ == '__main__':
chaojiying = Chaojiying_Client('xxxxxx', 'xxxxx', '924155') # The user center > > software ID generates a replacement 96001
im = open('code.png', 'rb').read() # Local image file path to replace a.jpg. Sometimes WIN system needs to//
print(chaojiying.PostPic(im, 1902)) # 1902 verification code type official website > > price system version 3.4 + print should be added ()
Super Eagle deal with super Eagle
from selenium.webdriver import Chrome
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import time
from chaojiying import Chaojiying_Client
web = Chrome()
web.get("http://www.chaojiying.com/user/login/")
# Processing verification code
img = web.find_element(By.XPATH, '/html/body/div[3]/div/div[3]/div[1]/form/div/img').screenshot_as_png
chaojiying = Chaojiying_Client('xxxx', 'xxxxx', '924155')
dic = chaojiying.PostPic(img, 1902)
verify_code = dic['pic_str']
# Fill in the user name, password and verification code into the page
web.find_element(By.XPATH,'/html/body/div[3]/div/div[3]/div[1]/form/p[1]/input').send_keys("xxxx")
web.find_element(By.XPATH,'/html/body/div[3]/div/div[3]/div[1]/form/p[2]/input').send_keys("xxxx")
web.find_element(By.XPATH,'/html/body/div[3]/div/div[3]/div[1]/form/p[3]/input').send_keys(verify_code)
time.sleep(5)
# Click login
web.find_element(By.XPATH,'/html/body/div[3]/div/div[3]/div[1]/form/p[4]/input').click()
Process 12306 login
Image recognition of ghost animals
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
# Initialize super Eagle
chaojiying = Chaojiying_Client('2xxxxg', '1xxxxx', '924155')
verify_img = web.find_elelment(By.XPATH,'xxx').screenshot_as_png
# Super Eagle identification verification code
dic = chaojiyiing.PostPic(verify_img,9004)
result = dic['pic_str'] # x1,y1|x2,y2
rs_list = result.split("|")
for rs in rs_list: # x1,y1
p_temp = rs.split(",")
x = int(p_temp[0])
y = int(p_temp[1])
# To make the mouse move with a certain position
ActionChains(web).move_to_element_with_offset(verify_img,x,y).click().perform() # Take the picture as the reference point, offset x, y
Prevent programs from being recognized
opt = Options()
opt.add_argument('--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled')
from selenium.webdriver import Chrome
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import time
# What if the program is recognized?
opt = Options()
opt.add_argument('--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled')
web = Chrome(options=opt)
web.get("https://kyfw.12306.cn/otn/resources/login.html")
time.sleep(2)
web.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="toolbar_Div"]/div[2]/div[2]/ul/li[2]/a').click()
time.sleep(3)
# Fill in the user name, password and verification code into the page
web.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="J-userName"]').send_keys("18574779087")
web.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="J-password"]').send_keys("1844733921wqf")
time.sleep(5)
# Click login
web.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="J-login"]').click()
time.sleep(5)
# Drag
btn = web.find_element(By.XPATH,'//*[@id="nc_1_n1z"]')
ActionChains(web).drag_and_drop_by_offset(btn, 300, 0).perform()
time.sleep(60)
actual combat
agent
Send the request through a third-party machine
Free agent IP https://www.zdaye.com/Free/ Free agent IP http://ip.yqie.com/ipproxy.htm 66 Free agent network http://www.66ip.cn/ 89 Free agent http://www.89ip.cn/ Worry free agent http://www.data5u.com/ Cloud agent http://www.ip3366.net/ Fast agent https://www.kuaidaili.com/free/ Speed exclusive agent http://www.superfastip.com/ HTTP agent IP https://www.xicidaili.com/wt/ Xiaoshu agent http://www.xsdaili.com Shiraz free agent IP http://www.xiladaili.com/ Xiaohuan HTTP agent https://ip.ihuan.me/ Whole network agent IP http://www.goubanjia.com/ Feilong agent IP http://www.feilongip.com/
import requests
proxies = {
"https": "https://58.209.234.8:3389"
}
resp = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com", proxies=proxies, verify=False)
resp.encoding = 'utf-8'
print(resp.text)
report errors
SSLError certificate error
requests.exceptions.SSLError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='www.baidu.com', port=443)
reason
SSL certificate error
http Too many connections are not closed.
After some inquiry, it is found that the error is due to the following:
http The number of connections exceeds the maximum limit. By default, the number of connections is Keep-alive Therefore, the server maintains too many connections and cannot create new connections.
1,ip Sealed
2,The program request is too fast.
resolvent
link
(1)time.sleep()
(2)close SSL verification verify=False
response = requests.get(fpath_or_url,headers=headers,stream=True, verify=False)
(3) requests The default is keep-alive Yes, it may not be released. Add parameters headers={'Connection':'close'}
# The TODO ssl certificate reports an error. The parameter verify=False. Meanwhile, requests are kept alive by default. It may not be released. Add the parameter
sess = requests.Session()
sess.mount('http://', HTTPAdapter(max_retries=3))
sess.mount('https://', HTTPAdapter(max_retries=3))
sess.keep_alive = False # Close redundant connections
text = requests.get(self.target_img_url, headers=headers, stream=True, verify=False, timeout=(5,5)) # The timeout of connect and read is an array
with open(img_files_path, 'wb') as file:
for i in text.iter_content(1024 * 10):
file.write(i)
text.close() # Close, it's important to make sure you don't have too many links
Event loop is closed
When creating a collaboration process, no error will be reported. RuntimeError: Event loop is closed
Error reporting reason:
aiohttp is used internally_ Proctorbasepipetransport: when the program exits to release memory, it automatically calls its del method, resulting in a secondary shutdown event loop. General Co process procedures will not be used_ Proctorbasepipetransport, so asyncio Run () still works. And this only happens on Windows.
terms of settlement:
Add asyncio Change run (getcatalog (URL)) to
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(getCatalog(url)) #getCatalog(url) is the name of the main function of the coroutine
Write at the end:
Video crawling and selenium's notes are still private letters. I don't want to toss
Crawler's code is generally time-effective. Sometimes the previously written code may not work when it is used by itself, so we need to master its core points, principles and methods to successfully crawl to legitimate data. Also remember that reptiles should be used for legitimate purposes~