Python asynchronous framework - Sanic
brief introduction
Sanic is a python 3.7 + Web server and Web framework (sanic is not just a framework, it is also a Web server) designed to improve performance. It allows the use of async/await syntax added in Python 3.5, which makes your code effectively avoid blocking, so as to improve the response speed.
Sanic (including Vibora, which claims to be several times faster than other frameworks and more than twice faster than competitor sanic) is somewhat similar to flash, but different.
start
1 new project
The project name is sanic_pro
Create a new python package in this directory:
config: configuration system file server: service utils: Other tools
2 project configuration
In the asynchronous framework, there are many asynchronous orm. In sanic, there are sanicdb, etc. sanicdb uses native SQL statements. In this column, tortoise ORM similar to Django ORM framework is used. For details, see https://tortoise.github.io/
pip install sanic pip install tortoise-orm[aiomysql]
Create a new settings.py file in the config directory, which is the main configuration file path of the project
**Note: the database used in this column is MariaDB, which is a version derived from MySQL. Please refer to the official website for details**
from pathlib import Path
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent
# ============================== ProjectConfig start ==============================
# to get a string like this run:
# openssl rand -hex 32
SECRET_KEY = ''
TITLE = 'recharge_platform'
# =============================== ProjectConfig end ===============================
# ================================== MySQL start ==================================
default_user = '' # Database user
default_host = '' # Database ip
default_port = 3306 # Database port
default_password = '' # Database password
default_database = '' # database
TORTOISE_ORM = {
'connections': {
'default': {
'engine': 'tortoise.backends.mysql',
'credentials': {
'host': default_host,
'port': default_port,
'user': default_user,
'password': default_password,
'database': default_database,
}
},
},
'apps': {
'default': {
'models': [
'aerich.models',
],
'default_connection': 'default',
},
},
'use_tz': False,
'timezone': 'Asia/Shanghai'
}
# ================================== MySQL end ====================================
# =============================== RedisConfig start ===============================
REDIS_HOST = ''
REDIS_PORT = 6379
REDIS_PASSWD = ''
REDIS_SYS_DB = 1
REDIS_NAME = ''
REDIS = {
'host': REDIS_HOST,
'port': REDIS_PORT,
'password': REDIS_PASSWD,
'db': REDIS_SYS_DB
}
# ================================ RedisConfig end ================================
Here, we use aerich to manage the database
pip install aerich
Create the migration directory and initialize the database link
aerich init -t config.settings.TORTOISE_ORM
After executing the above command, a migrations directory and an aero.ini file will be generated in the same directory as config, which is used to store the database migration history
3. Create a new service
Create a new base in the config directory_ model.py
from tortoise import models, fields
class DBBaseModel(models.Model):
class Meta:
abstract = True
id = fields.IntField(pk=True, allows_generated=True)
create_time = fields.DatetimeField(auto_now_add=True, null=True, description='Creation time')
update_time = fields.DatetimeField(auto_now=True, null=True, description='Update time')
Create a python package in the server directory and name it app_system, and create models.py in this directory
from tortoise import fields
from config.base_model import DBBaseModel
class Zoning(DBBaseModel):
class Meta:
table = 'sys_zoning'
table_description = 'administrative division'
code = fields.CharField(max_length=64, null=False, description='Administrative division code')
name = fields.CharField(max_length=64, null=False, description='Name of administrative division')
short = fields.CharField(max_length=32, null=True, default=None, description='Administrative abbreviation')
level = fields.IntField(null=False, default=-1, description='Grade')
area = fields.DecimalField(max_digits=16, decimal_places=4, default=0, description='the measure of area')
longitude = fields.DecimalField(max_digits=16, decimal_places=13, default=0, description='longitude')
latitude = fields.DecimalField(max_digits=16, decimal_places=13, default=0, description='latitude')
coordinates = fields.TextField(null=True, description='Coordinate set')
serial = fields.IntField(null=True, default=None, description='Serial number')
z_list = fields.TextField(null=True, description='Regional hierarchy')
is_active = fields.SmallIntField(default=1, description='state')
parent = fields.ForeignKeyField('default.Zoning',
null=True,
on_delete=fields.SET_NULL,
description='Parent node')
class Projects(DBBaseModel):
class Meta:
table = 'sys_projects'
table_description = 'Project information'
name = fields.CharField(max_length=128, null=False, description='name')
app_key = fields.CharField(max_length=64, unique=True, null=False, description='project key')
describe = fields.TextField(null=True, description='Project introduction')
image = fields.TextField(null=True, description='Project picture')
is_active = fields.SmallIntField(default=1, description='state')
zoning = fields.ForeignKeyField('default.Zoning',
null=True,
on_delete=fields.SET_NULL,
description='administrative division')
class Account(DBBaseModel):
class Meta:
table = 'sys_account'
table_description = 'User information'
username = fields.CharField(max_length=64, unique=True, null=False, description='user name')
password = fields.CharField(max_length=256, null=False, description='password')
telephone = fields.CharField(max_length=64, unique=True, null=False, description='cell-phone number')
real_name = fields.CharField(max_length=64, null=False, description='User name')
is_superuser = fields.SmallIntField(default=1, description='Is it super tube')
is_active = fields.SmallIntField(default=1, description='state')
email = fields.CharField(max_length=64, null=True, default=None, description='mailbox')
address = fields.CharField(max_length=256, null=True, default=None, description='Contact address')
longitude = fields.DecimalField(max_digits=16, decimal_places=13, default=0, description='longitude')
latitude = fields.DecimalField(max_digits=16, decimal_places=13, default=0, description='latitude')
z_list = fields.TextField(null=True, default=None, description='Regional hierarchy')
project = fields.ForeignKeyField('default.Projects',
null=True,
on_delete=fields.SET_NULL,
description='Project')
zoning = fields.ForeignKeyField('default.Zoning',
null=True,
on_delete=fields.SET_NULL,
description='administrative division')
...
Modify settings.py file
.....
'apps': {
'default': {
'models': [
'aerich.models',
'server.app_system.models',
],
'default_connection': 'default',
},
},
....
The first migration uses the following command for database initialization
aerich init-db
After executing this command, the default directory will be generated in migrations, which is the default database configuration migration version file. If multiple databases are configured, the corresponding directory will be created. Now the corresponding data table has been generated in the database.
If the data table is modified, use the following command to migrate the database
# Generate migration file aerich migrate --name drop_column # Execute migration file aerich upgrade
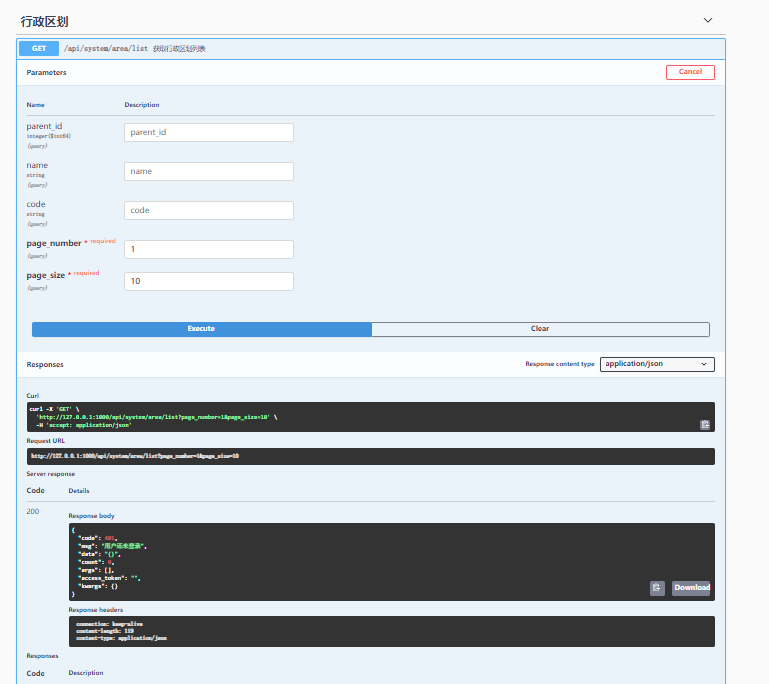
Create new views under system_ area.py
from sanic import Blueprint
from server.app_system.models import Zoning
from utils.helper import return_result
area_router = Blueprint('administrative division', url_prefix='/area')
@area_router.get('/list')
async def area_list(request):
parent_id = request.args.get('parent_id')
code = request.args.get('code')
name = request.args.get('name')
page_size = int(request.args.get('page_size', '10'))
page_number = int(request.args.get('page_number', '1'))
offset = (page_number - 1) * page_size
zoning_info = Zoning.filter()
if parent_id:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(id=parent_id)
if code:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(code__contains=code)
if name:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(name__contains=name)
res = await zoning_info.select_related(
'parent__name', 'parent__code'
).offset(offset).limit(page_size).values()
count = await zoning_info.select_related('parent__name', 'parent__code').count()
return return_result(data=res, count=count)
__init__.py
from sanic import Blueprint
from .views_area import area_router
auth_blue_group = Blueprint.group(auth_router)
sys_blue_group = Blueprint.group(
area_router,
url_prefix='/system'
)
During data serialization, some data types do not support serialization, so some modified data needs to be processed
Create helper.py file under utils
import json as public_json
from decimal import Decimal
from datetime import datetime, date
from sanic.response import json as sanic_json
# Process data that cannot be serialized
class DateEncoder(public_json.JSONEncoder):
def default(self, obj):
if isinstance(obj, datetime):
return obj.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
elif isinstance(obj, date):
return obj.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
elif isinstance(obj, Decimal):
return str(Decimal(obj))
else:
return public_json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj)
def data_json_str(data):
if not isinstance(data, str):
return public_json.dumps(data, cls=DateEncoder)
else:
return data
def data_json_dict(data):
if isinstance(data, str):
return public_json.loads(data)
else:
return data
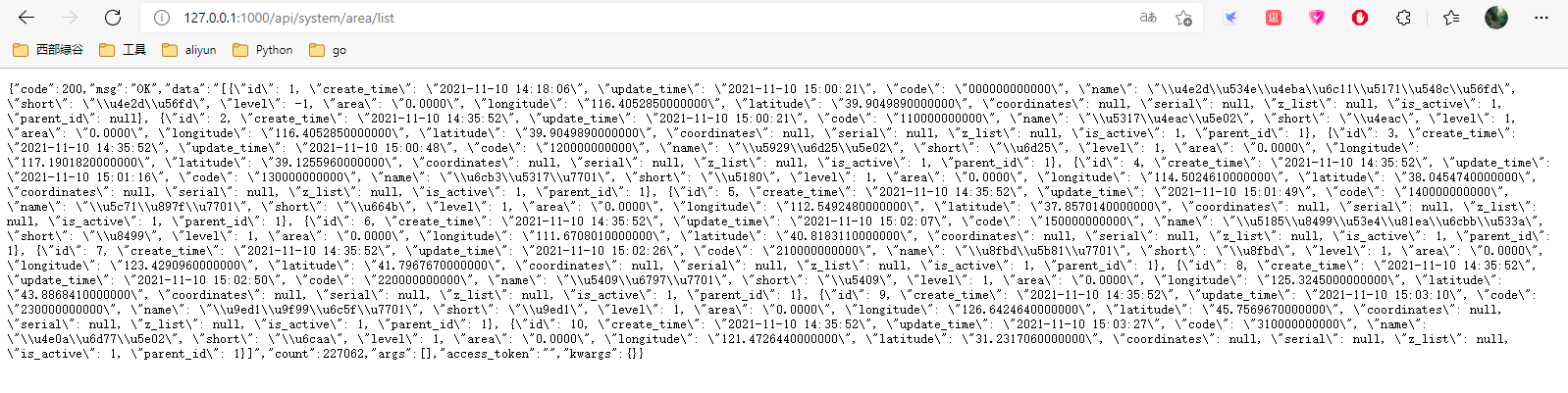
def return_result(code: int = 200, msg: str = 'OK', data=None, count: int = 0, access_token: str = '', *args, **kwargs):
if data is None:
data = {}
return sanic_json({
'code': code,
'msg': msg,
'data': data_json_str(data),
'count': count,
'args': args,
'access_token': access_token,
'kwargs': kwargs
})
In the server directory__ init__.py file add the following content
from config.settings import TORTOISE_ORM
from sanic import Sanic
from server.app_system import auth_blue_group, sys_blue_group
from tortoise.contrib.sanic import register_tortoise
app = Sanic(name='recharge_platform')
app.blueprint(sys_blue_group, url_prefix='/api')
# database
register_tortoise(
app=app,
config=TORTOISE_ORM,
generate_schemas=False
)
Create the manager.py file in the project root directory
from server import app
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(port=1000, auto_reload=True, debug=False)
Run the manager.py file


In FastAPI, there is a complete api document. Sanic uses sanic_openapi can also be implemented
pip install sanic_openapi
Modify serve__ init__. Py file
from config.settings import TORTOISE_ORM
from sanic_openapi import swagger_blueprint, openapi3_blueprint
from sanic import Sanic
from server.app_system import auth_blue_group, sys_blue_group
from tortoise.contrib.sanic import register_tortoise
app = Sanic(name='recharge_platform')
# Interface documentation
# http://127.0.0.1:1000/swagger
app.blueprint(swagger_blueprint)
# app.blueprint(openapi3_blueprint)
app.blueprint(auth_blue_group)
app.blueprint(sys_blue_group, url_prefix='/api')
# database
register_tortoise(
app=app,
config=TORTOISE_ORM,
generate_schemas=False
)
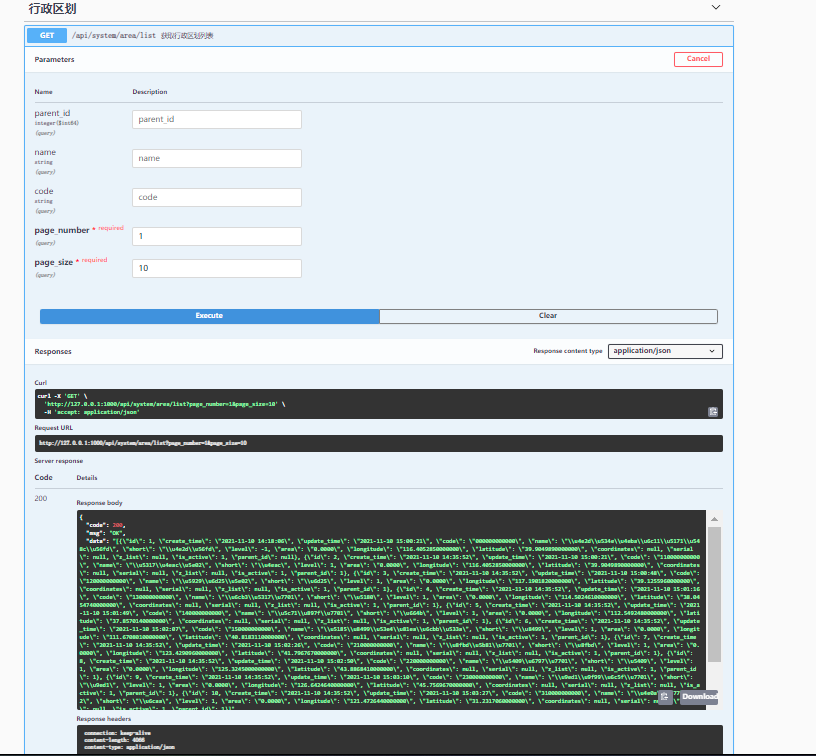
Modify app_system.views_area.py file
Note: note the parameter type here
@area_router.get('/list')
@doc.summary('Get list of administrative divisions')
@doc.consumes({'page_number': '1'}, {'page_size': '10'}, location='query', required=True, )
@doc.consumes({'parent_id': int}, {'name': str}, {'code': str}, location='query')
async def area_list(request):
parent_id = request.args.get('parent_id')
code = request.args.get('code')
name = request.args.get('name')
page_size = int(request.args.get('page_size', '10'))
page_number = int(request.args.get('page_number', '1'))
offset = (page_number - 1) * page_size
zoning_info = Zoning.filter()
if parent_id:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(id=parent_id)
if code:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(code__contains=code)
if name:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(name__contains=name)
res = await zoning_info.select_related(
'parent__name', 'parent__code'
).offset(offset).limit(page_size).values()
count = await zoning_info.select_related('parent__name', 'parent__code').count()
return return_result(data=res, count=count)
4 authentication
Sanic has many methods for interface authentication (login authentication). See for details https://github.com/mekicha/awesome-sanic/blob/master/README.md#authentication
Create a new account under config_ Conf.py file
import hashlib
import jwt
from config.settings import SECRET_KEY, TITLE
from config.database_pool.redis_pool import RedisPool
from functools import wraps
from utils.helper import return_result
# Generate password
def make_password(password):
pass_str = password + hashlib.new('sha256', SECRET_KEY.encode()).hexdigest()
encryption = hashlib.new('md5', pass_str.encode()).hexdigest()
return encryption
# Verify password
def check_password(login_pass, user_pass):
encryption = make_password(login_pass)
if encryption == user_pass:
return True
else:
return False
# Generate token
def create_token(user_name, user_id):
payload = {
'sub': user_id,
'user_name': user_name
}
herder = {
'key': SECRET_KEY,
'title': TITLE,
}
token = jwt.encode(
payload=payload,
key=SECRET_KEY,
headers=herder,
algorithm='HS256'
)
return token
# Validate token
def check_token(token, user_id):
if not user_id or not token:
return False
try:
payload_data = jwt.decode(
jwt=token,
key=SECRET_KEY,
algorithms=['HS256']
)
if payload_data.get('sub') != user_id:
return False
else:
return True
except jwt.exceptions.InvalidTokenError:
return False
# Interface authentication
def protected(wrapped):
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
async def decorated_function(request, *args, **kwargs):
try:
token = request.ctx.token
user_id = request.ctx.user.get('id')
is_authenticated = check_token(user_id=user_id, token=token)
if is_authenticated:
_redis = RedisPool(db=0)
user_token = await _redis.get_redis_info(_key=str(user_id))
if token == user_token:
response = await func(request, *args, **kwargs)
return response
else:
return return_result(code=401, msg='User login has expired, please login again')
else:
return return_result(code=401, msg='User login has expired, please login again')
except Exception as e:
return return_result(code=401, msg='The user is not logged in')
return decorated_function
return decorator(wrapped)
if __name__ == '__main__':
_token = create_token('user', 1)
data = jwt.decode(
jwt=_token,
key=SECRET_KEY,
algorithms=['HS256']
)
print(data, type(data))
Modify app_system.views_area.py file
@area_router.get('/list')
@doc.summary('Get list of administrative divisions')
@doc.consumes({'page_number': '1'}, {'page_size': '10'}, location='query', required=True, )
@doc.consumes({'parent_id': int}, {'name': str}, {'code': str}, location='query')
@protected
async def area_list(request):
parent_id = request.args.get('parent_id')
code = request.args.get('code')
name = request.args.get('name')
page_size = int(request.args.get('page_size', '10'))
page_number = int(request.args.get('page_number', '1'))
offset = (page_number - 1) * page_size
zoning_info = Zoning.filter()
if parent_id:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(id=parent_id)
if code:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(code__contains=code)
if name:
zoning_info = zoning_info.filter(name__contains=name)
res = await zoning_info.select_related(
'parent__name', 'parent__code'
).offset(offset).limit(page_size).values()
count = await zoning_info.select_related('parent__name', 'parent__code').count()
return return_result(data=res, count=count)