Hello, I'm brother Chen
Today, I'd like to introduce a library that can obtain the current system information - psutil
Using psutil library, we can obtain some information of the system, such as cpu, memory utilization, etc., so that we can view the current system usage. Collecting these information in real time can achieve the purpose of real-time monitoring the system.
psutil Library
The installation of psutil is simple
pip install psutil
What system information can the psutil library get?
psutil What are the effects 1.Memory usage 2.Disk usage 3.cpu Utilization rate 4.Network interface sending and receiving traffic 5.Get current network speed 6.Current system process ...
The following is a demonstration through a specific code case
Memory usage
import psutil
#Memory
mem = psutil.virtual_memory()
# Total system memory
zj = float(mem.total) / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
# The system has used memory
ysy = float(mem.used) / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
# System free memory
kx = float(mem.free) / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
print('Total system memory:%d.4GB' % zj)
print('The system has used memory:%d.4GB' % ysy)
print('System free memory:%d.4GB' % kx)

Get the current system total memory, used memory, and free memory
The memory obtained here is in bytes, so it needs to be converted to G by dividing by 1024. The same is true below, so the explanation will not be repeated.
Get system cpu Information
#Display all logical information of cpu print(psutil.cpu_times(percpu=True)) # View information about the logical number of CPUs print(u"logic CPU number: %s" % psutil.cpu_count()) # View information about the physical number of CPUs print(u"Physics CPU number: %s" % psutil.cpu_count(logical=False)) #CPU utilization cpu = (str(psutil.cpu_percent(1))) + '%' print(u"cup Utilization rate: %s" % cpu)
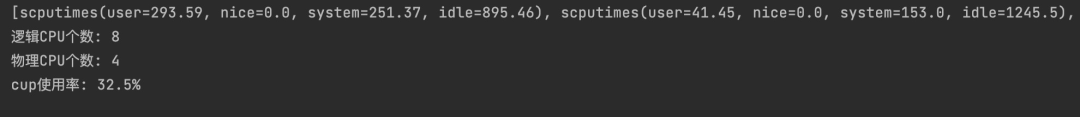
Obtain the cpu information, the number of local CPUs (including the number of logical CPUs and physical CPUs), and the current cpu utilization (obtain it every 1 second to view the real-time cpu utilization)
System disk usage
part = psutil.disk_partitions()
for i in part:
print(i)
dk = psutil.disk_usage('/')
print(dk)
#Total disk
total = dk.total / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
used = dk.used / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
free = dk.free / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
print('System total disk:%d.3GB' % total)
print('The disk is already used by the system:%d.3GB' % used)
print('System free disk:%d.3GB' % free)
print(u"Disk utilization: %s%%" % dk.percent)
# Get the total number of io disks and read and write information
print(psutil.disk_io_counters())
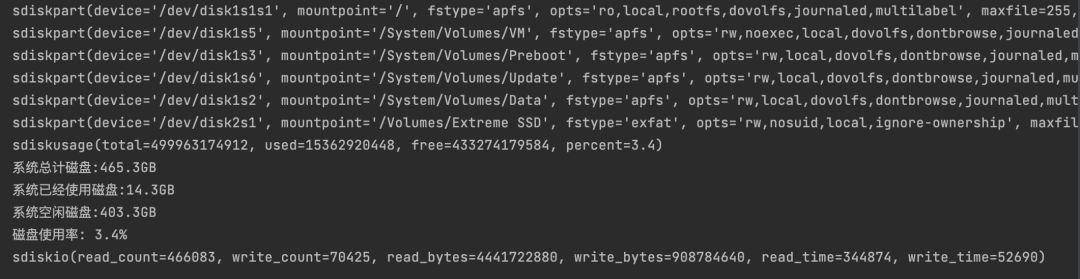
The first few lines are the disk information that the current system can access
In the first line, mountpoint = '/' indicates the current local default disk
In line 6, mountpoint = '/ Volumes/Extreme SSD', indicating an external solid-state mobile hard disk
Here, take the local disk mountpoint = '/' as an example to check the disk usage (total capacity, used capacity, free capacity and utilization rate)
The meaning of each field in the last line is as follows:
"""
read_count read IO number
write_count write IO number
read_bytes read IO Number of bytes
write_bytes write IO Number of bytes
read_time Disk read time
write_time Disk write time
"""
Get system network card information
# Get total network IO information
print(psutil.net_io_counters())
# Send packet
print("Send data bytes:", psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent,"bytes")
#Receive packet
print("Receive data bytes:",psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv,"bytes")
# Output information of each network interface
net_counter = psutil.net_io_counters(pernic=True)
for i in net_counter:
print("network card:"+i+" ,Network card information:",net_counter[i])
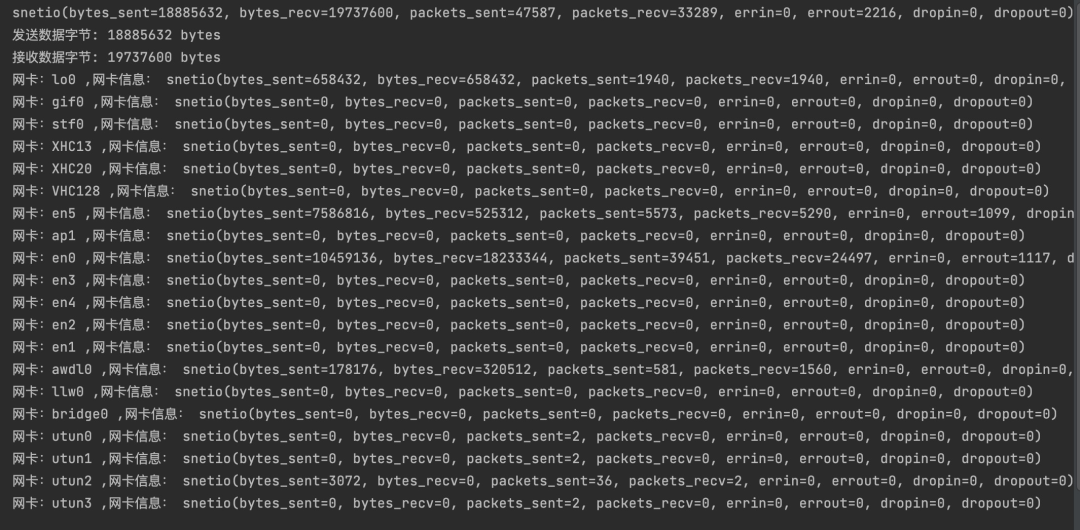
You can get which network cards exist in the current machine and the traffic sent and received
Check whether the local network card is consistent in the terminal
mac and linux system commands: ifconfig
window system command: ipconfig
Some screenshots are as follows:
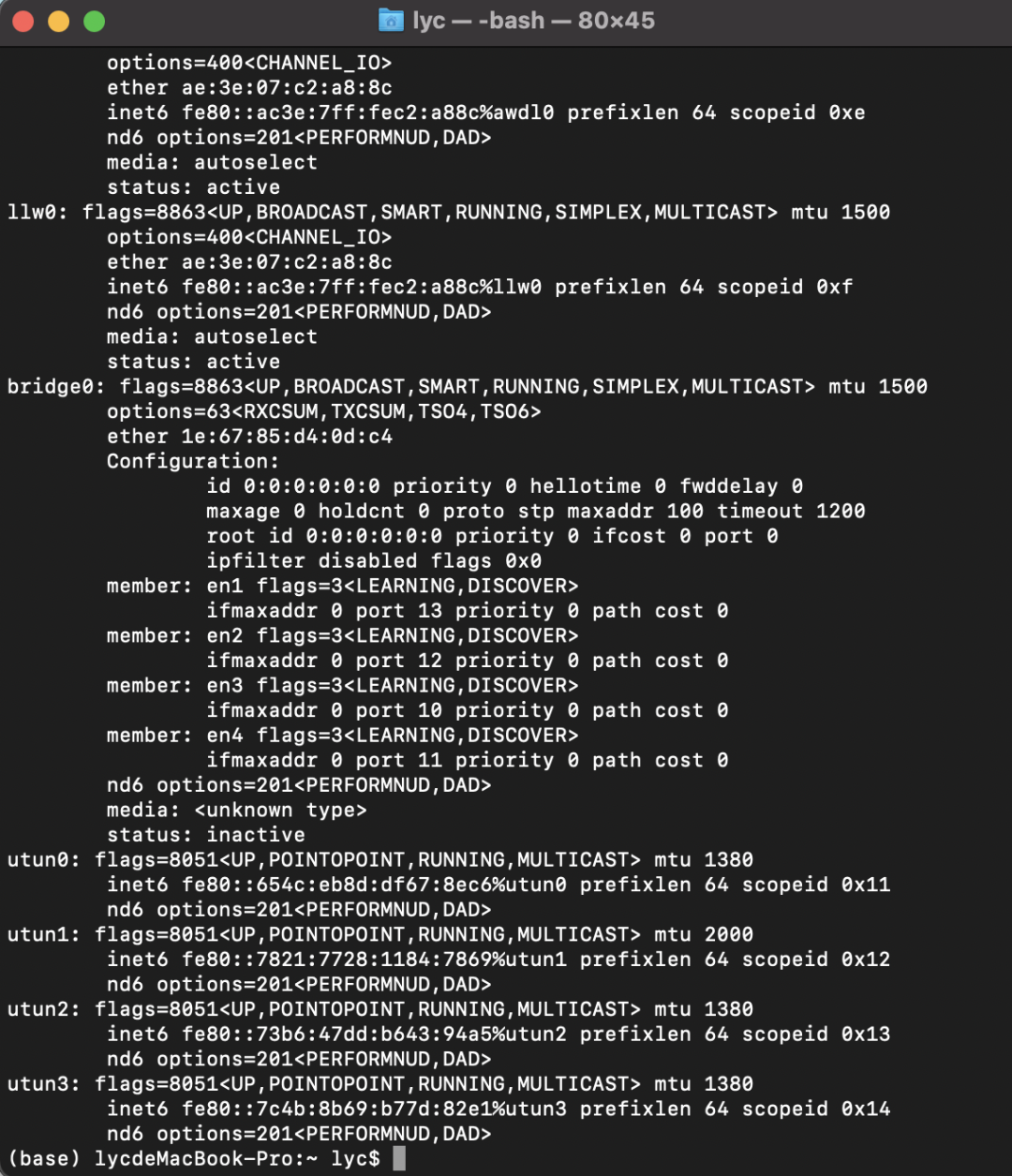
You can see that the network card data obtained by the program is consistent with that obtained by the local terminal
Get current network speed
Obtain the current network speed by obtaining the traffic sent and received by the network card through the above program
s1 = psutil.net_io_counters(pernic=True)['en0']
time.sleep(1)
s2 = psutil.net_io_counters(pernic=True)['en0']
result = s2.bytes_recv - s1.bytes_recv
print(str('%d' % (result / 1024)) + 'kb/s')
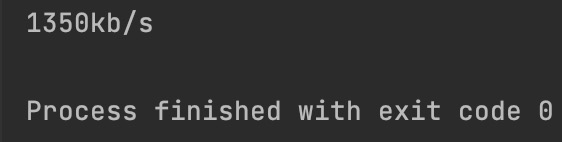
['en0'] in the code means to obtain the data of en0 network card, because the network card of chenge's local machine is en0
Finally, you can see the current network speed
Executing the code every 1 second can obtain the network speed in real time
Other functions
# System Up Time
# Convert to natural time format
print(datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(psutil.boot_time ()).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H: %M: %S"))
#Get current system user login information
users = psutil.users()
for i in users:
print(i)
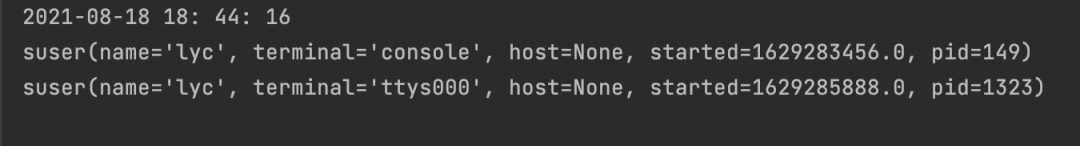
You can get the startup time of the machine and the current user
That's all for today's article
If you have any questions, please leave a message below~
last
1. This paper introduces in detail how python obtains system information (memory, disk, cpu, etc.) through psutil
2. This article is only for readers to learn and use, not for other purposes!