1, dictionary
Create dictionary
- A dictionary is another variable container model and can store any type of object
- Each key value pair of the dictionary is separated by a colon (:), each pair is separated by a comma (,), and the whole dictionary is included in curly braces ({}).
- Key must be unique, but value is not required
- Value can take any data type, but the key must be immutable, such as string, number or tuple
#format d = {key1 : value1, key2 : value2 } #Example dict = {'Alice': '2341', 'Beth': '9102', 'Cecil': '3258'} dict1 = { 'abc': 456 } dict2 = { 'abc': 123, 98.6: 37 }
ACCESS Dictionary
dict = {'Name': 'python', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'} print ("dict['Name']: ", dict['Name']) print ("dict['Age']: ", dict['Age']) ''' dict['Name']: python dict['Age']: 7 '''
- If you use a key that is not in the dictionary to access the data, the output error is as follows
dict = {'Name': 'python', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'} print ("dict['Alice']: ", dict['Alice']) Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 5, in <module> print ("dict['Alice']: ", dict['Alice']) KeyError: 'Alice'
Modify dictionary
dict = {'Name': 'python', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'} dict['Age'] = 8 # Update Age dict['School'] = "LG" # Add information print ("dict['Age']: ", dict['Age'])#dict['Age']: 8 print ("dict['School']: ", dict['School'])#dict['School']: LG
Delete dictionary element
dict = {'Name': 'Runoob', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'} del dict['Name'] # Delete key 'Name' dict.clear() # Empty dictionary del dict # Delete dictionary print ("dict['Age']: ", dict['Age']) print ("dict['School']: ", dict['School']) Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 9, in <module> print ("dict['Age']: ", dict['Age']) TypeError: 'type' object is not subscriptable #An exception was thrown. The dictionary no longer exists after del operation.
- Two occurrences of the same key are not allowed. If the same key is assigned twice during creation, the latter value will be remembered.
dict = {'Name': 'python', 'Age': 7, 'Name': 'LG'} print ("dict['Name']: ", dict['Name'])#dict['Name']: LG
- Keys must be immutable, so they can be numbers, strings, or tuples, not lists
dict = {['Name']: 'Runoob', 'Age': 7} print ("dict['Name']: ", dict['Name']) Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 3, in <module> dict = {['Name']: 'Runoob', 'Age': 7} TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
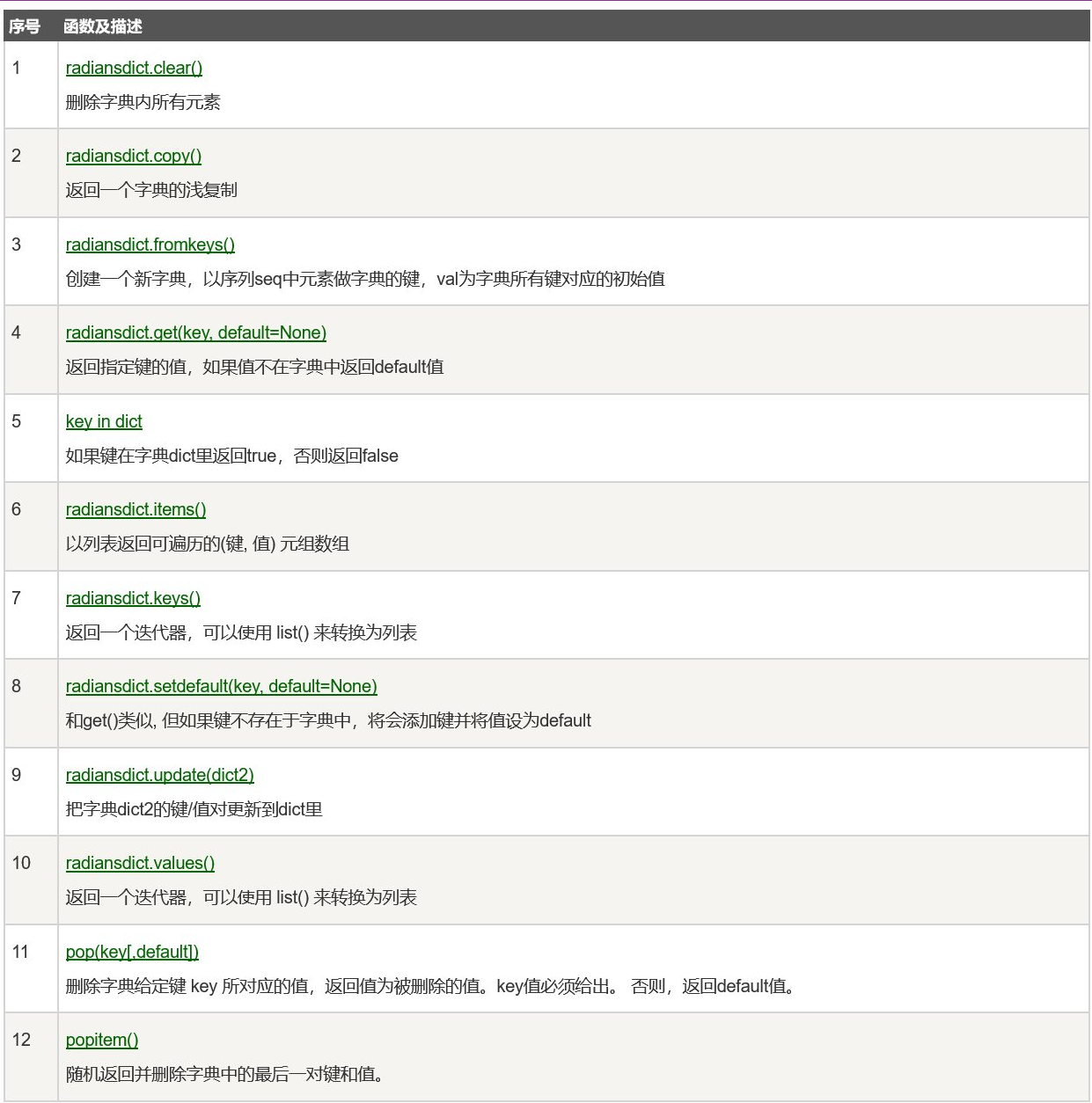
Dictionary built-in functions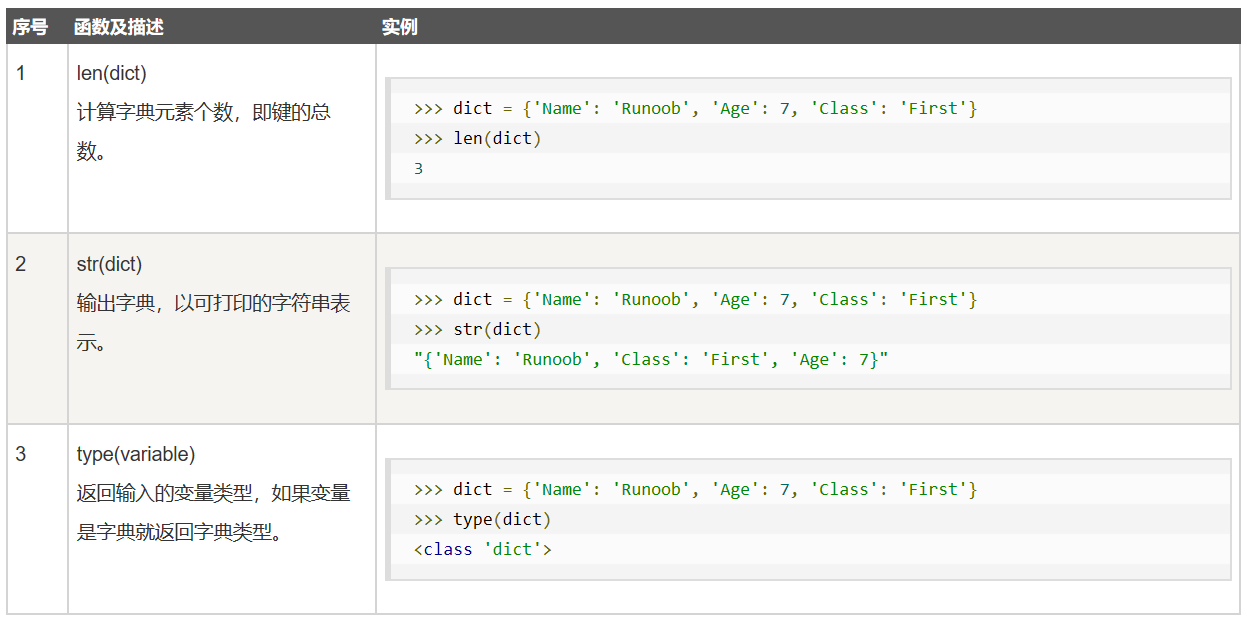 Dictionary built in method
Dictionary built in method
Assignment and copying of dictionaries
- Assignment reference - b = A: both a and b point to the same object
- Shallow copy - b = a.copy(): A and b parent objects are independent objects, but their child objects still point to unified objects (references).
- Deep copy - b = copy.deep copy (a): completely copies the parent object and its children, and the parent object and its children of a and b, both of which are completely independent.
import copy a = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b']] #Original object b = a #Assignment, reference to passed object c = copy.copy(a) #Object copy d = copy.deepcopy(a) #Object copy a.append(5) #Modify object a a[4].append('c') #Modify the array object of ['a ','b'] in object a print( 'a = ', a ) #a = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c'], 5] print( 'b = ', b ) #b = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c'], 5] print( 'c = ', c ) #c = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b', 'c']] print( 'd = ', d ) #d = [1, 2, 3, 4, ['a', 'b']]
Dictionary sorting
- Sorting by key
d = {'d1':2, 'd2':4, 'd4':1,'d3':3,} for k in sorted(d): print(k,d[k]) ''' d1 2 d2 4 d3 3 d4 1 '''
- Sorting by value: getitem
d = {'d1':2, 'd2':4, 'd4':1,'d3':3,} for k in sorted(d,key=d.__getitem__): print(k,d[k]) ''' d4 1 d1 2 d3 3 d2 4 '''
- Reverse: reverse=True
d = {'d1':2, 'd2':4, 'd4':1,'d3':3,} for k in sorted(d,key=d.__getitem__,reverse=True): print(k,d[k]) '''d2 4 d3 3 d1 2 d4 1 '''
- Sort dict items
d = {'d1':2, 'd2':4, 'd4':1,'d3':3,} res = sorted(d.items(),key=lambda d:d[1],reverse=True) print(res) # [('d2', 4), ('d3', 3), ('d1', 2), ('d4', 1)]
2, set
- A set is an unordered sequence of distinct elements
- You can create a collection using curly braces {} or the set() function
- To create an empty set, you must use set() instead of {}; {} is used to create an empty dictionary
basket = {'apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'pear', 'orange', 'banana'} print(basket) # De duplication function {'orange', 'banana', 'pear', 'apple'}
- Quickly determine whether an element is in a set
>> 'orange' in basket True >>> 'crabgrass' in basket False
- Operation between two sets
>>> a = set('abracadabra') >>> b = set('alacazam') >>> a {'a', 'r', 'b', 'c', 'd'} >>> a - b # Elements contained in set a but not contained in set b {'r', 'd', 'b'} >>> a | b # All elements contained in set a or b {'a', 'c', 'r', 'd', 'b', 'm', 'z', 'l'} >>> a & b # Elements contained in sets a and b {'a', 'c'} >>> a ^ b # Elements different from a and b {'r', 'd', 'b', 'm', 'z', 'l'}
Additive elements
- S.add (x) --- add element X to set s, and do nothing if the element already exists
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao")) >>> thisset.add("Facebook") >>> print(thisset) {'Taobao', 'Facebook', 'Google', 'Runoob'}
- S.update (x) -- add elements, and parameters can be lists, tuples, dictionaries, etc.
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao")) >>> thisset.update({1,3}) >>> print(thisset) {1, 3, 'Google', 'Taobao', 'Runoob'} >>> thisset.update([1,4],[5,6]) >>> print(thisset) {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'Google', 'Taobao', 'Runoob'}
Removing Elements
- s.remove (x) --- remove element x from set s. if the element does not exist, an error will occur.
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao")) >>> thisset.remove("Taobao") >>> print(thisset) {'Google', 'Runoob'} >>> thisset.remove("Facebook") # No error will occur Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> KeyError: 'Facebook'
- S.discard (x) -- another method is to remove the elements from the collection, and if the elements do not exist, no errors will occur.
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao")) >>> thisset.discard("Facebook") # No no error >>> print(thisset) {'Taobao', 'Google', 'Runoob'}
- s.pop() -- set to randomly delete an element in the collection
thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao", "Facebook"))
x = thisset.pop()
print(x)
'''
$ python3 test.py
Runoob
The results of multiple tests are different
'''- In interactive mode, pop is the first element of the deleted collection (the first element of the sorted collection)
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao", "Facebook")) >>> thisset.pop() 'Facebook' >>> print(thisset) {'Google', 'Taobao', 'Runoob'}
- len(s) --- count the number of set elements
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao")) >>> len(thisset) 3
- s.clear() -- empty set
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao")) >>> thisset.clear() >>> print(thisset) set()
- x in s -- judge whether an element exists in a set
>>>thisset = set(("Google", "Runoob", "Taobao")) >>> "Runoob" in thisset True >>> "Facebook" in thisset False
Collection built-in method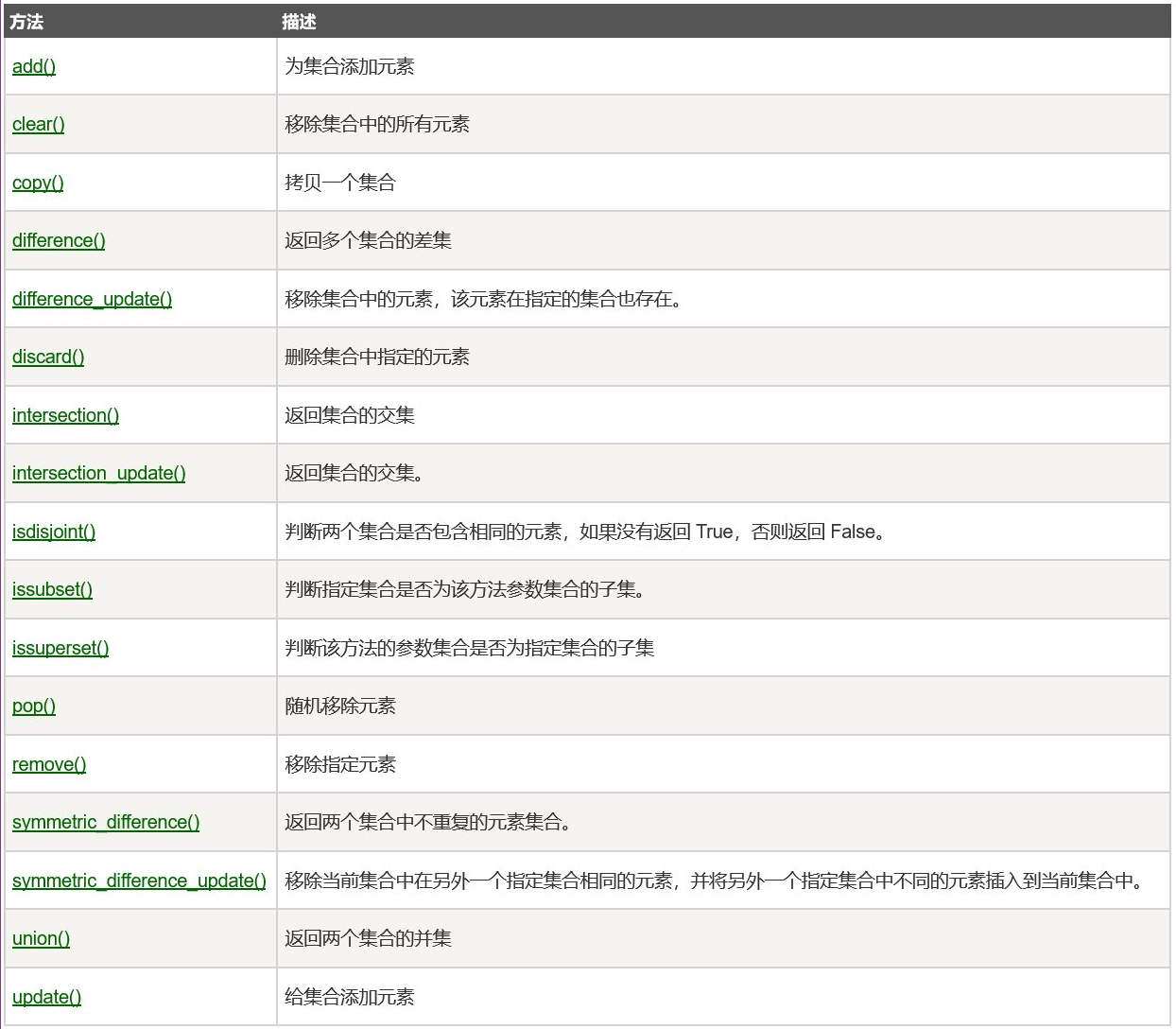
Reference
- https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-set.html
- https://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-dictionary.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/kilometerwine/p/9712329.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/faithfu/p/10825965.html