1, System environment
Assuming that you have an offline server with CentOS system installed, you can only load data through U SB flash disk or intranet transmission. Here is how to install Python environment using Intranet environment.
System: CentOS 7.5 one thousand eight hundred and four
2, Environment configuration
1. Configure SSH environment
FTP or SSH can be used to transfer files over the intranet. Now SSH is generally used. Because it is more secure, the first step is to configure the SSH environment of CentOS.
Usually, the full version of CentOS distribution includes SSH environment by default. If it is not included in your system, you need to use USB flash disk to copy SSH RPM installation package, which is the basis of everything. If you already have SSH, you can start configuration directly.
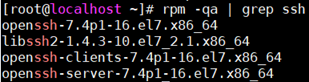
(1) Confirm whether the SSH service exists
rpm –qa | grep ssh
If an SSH environment already exists, the following results are displayed:
(2) modify SSH service configuration
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Modify the following configurations:
Port 22 # Port of SSH service PermitRootLogin yes # Allow root user login PasswordAuthentication yes # Allow password login
(3) Restart SSH service
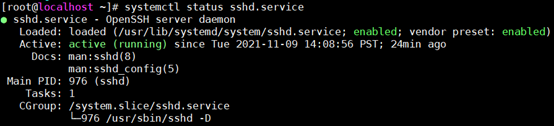
After modification, restart the SSH service and check the service status:
systemctl restart sshd.service systemctl status sshd.service
The following results will be obtained:
(4) configure firewall
First, confirm whether the firewall is on:
fireall-cmd --state # running is displayed when the firewall is turned on firewall-cmd –-zone=public –query-port=22/tcp # Check whether port 22 used by SSH service is open. yes is displayed if it is open, otherwise no is displayed
If port 22 is not open, do the following to open the port:
firewall-cmd –-zone=public –add_port=22/tcp --permanent # Permanently add port 22 to the firewall whitelist firewall-cmd --reload # Reload firewall rules firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-port=22/tcp # Confirm port opening
If the port is open, the following results are displayed:

At this time, you can log in to the system through putty, XShell, SecureCRT, MobaXterm and other clients.
2. Install dependent Libraries
(1) Install zlib
Because our CentOS is an offline environment, we can't directly use the yum install command or wget command to obtain the software package, so we need to download the source code of zlib to the Windows system first, and then upload SFTP to CentOS.
Go to sourceforge to download the source code of zlib at:
https://nchc.dl.sourceforge.net/project/libpng/zlib/1.2.11/zlib-1.2.11.tar.gz
After uploading to cenos (assuming uploading to / home / [username] / downloads directory), unzip the source code first:
tar -zxvf zlib-1.2.11.tar.gz
Configure installation path:
cd zlib-1.2.11/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/zlib
Compile and install:
make && make install
To build a shared library:
make clean ./configure --shared make test make install cp zutil.h /usr/local/include/ cp zutil.c /usr/local/include/
Finally, write the zlib library to the path of the dynamic library:
echo "/usr/local/zlib/lib" >> /etc/ld.so.conf ldconfig -v
(2) Install libffi
First, download the libffi source package at:
https://hub.fastgit.org/libffi/libffi/archive/refs/tags/v3.4.2.tar.gz
After downloading, upload it to the / home/[Username]/Downloads directory of CentOS (the same below), and extract the file:
tar -zxvf libffi-3.4.2.tar.gz
Next, set the installation path:
cd libffi-3.4.2/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/libffi
Compile and install:
make && make install
Finally, add the libffi library to the dynamic link library:
echo "/usr/local/libffi/lib" >> /etc/ld.so.conf ldconfig -v
(3) Install bzip2
First, download the bzip2 source code at:
https://sourceware.org/pub/bzip2/bzip2-1.0.8.tar.gz
After downloading, upload to the / home/[Username]/Downloads directory of CentOS, and extract the file:
tar -zxvf bzip2-1.0.8.tar.gz
Specify to link the source code compilation to the dynamic link library, and then compile and install:
cd bzip2-1.0.8/ make -f Makefile-libbz2_so make && make install
(4) Install openssl
First, download the openssl source code at:
https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.1.1l.tar.gz
tar -zxvf openssl-1.1.1l.tar.gz
Configure installation directory:
cd openssl-1.1.1l/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/openssl
Compile and install:
make && make install
(5) Install ncurses
Download the ncurses source code at:
https://invisible-island.net/datafiles/release/ncurses.tar.gz
tar -zxvf ncurses.tar.gz
Configure installation directory:
cd ncurses-6.3/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/ncurses
Compile and install:
make && make install
(6) Install sqlite
Download sqlite source code at:
https://www.sqlite.org/2021/sqlite-autoconf-3370000.tar.gz
tar -zxvf sqlite-autoconf-3370000.tar.gz
Configure installation directory:
cd sqlite-autoconf-3370000/ ./configure # Use the default configuration
Compile and install:
make && make install
(7) Install readline
Download the readline source code at:
http://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/readline/readline-8.0.tar.gz
tar -zxvf readline-8.0.tar.gz
Configure installation directory:
cd readline-8.0/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/readline
Compile and install:
make && make install
(8) Install tk
To install tk, you need to install tcl first. Download the tcl source code at:
https://nchc.dl.sourceforge.net/project/tcl/Tcl/8.6.12/tcl8.6.12-src.tar.gz
tar -zxvf tcl8.6.12-src.tar.gz
Configure installation directory:
cd tcl8.6.12/unix/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/tcl
Compile and install:
make && make install
Download tk source code at:
https://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/tcl/tk8.6.12-src.tar.gz
tar -zxvf tk8.6.12-src.tar.gz
Configure installation directory:
cd tk8.6.12/unix/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/tk
Compile and install:
make && make install
(9) Install git
Download Git source code at:
https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/software/scm/git/git-2.34.1.tar.gz
tar -zxvf git-2.34.1.tar.gz
Configure installation directory:
cd git-2.34.1/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/git
Compile and install:
make && make install
3, Install Python
1. Download Python 3.8 12 source code
Due to the slow speed of foreign sources, you can download Python source code from domestic images. Download address:
http://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/python/3.8.12/Python-3.8.12.tgz
After downloading, upload to / home/[Username]/Downloads /python directory of CentOS.
2. Unzip and set the installation address
tar -zxvf Python-3.8.12.tgz cd Python-3.8.12/ ./configure prefix=/usr/local/python3
3. Compile and install
make && make install
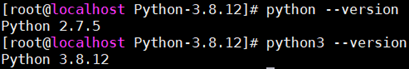
4. Add soft connection
ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/python3.8 /usr/bin/python3 ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/pip3.8 /usr/bin/pip3
[note] since the default Python version of CentOS 7 system is version 2.7, in order not to conflict with the system environment, the soft connection of Python 3.8 is named python3. If you want to use Python 3.8 environment later, you must enter python3, as shown in the following figure.