Conversion related methods - eval

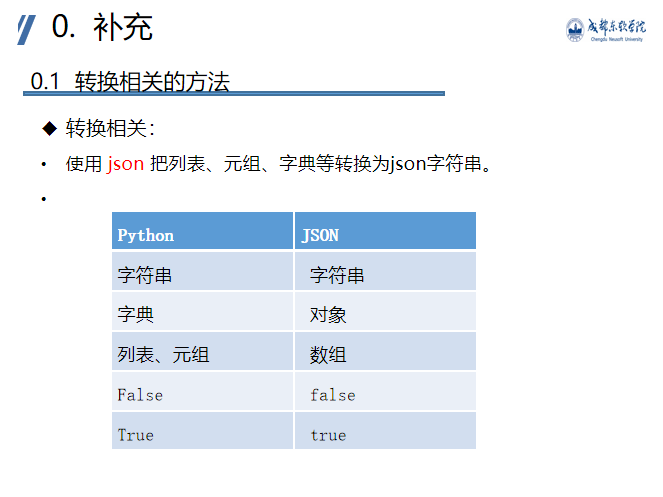
Transformation related methods - json



Basic grammar outline of function
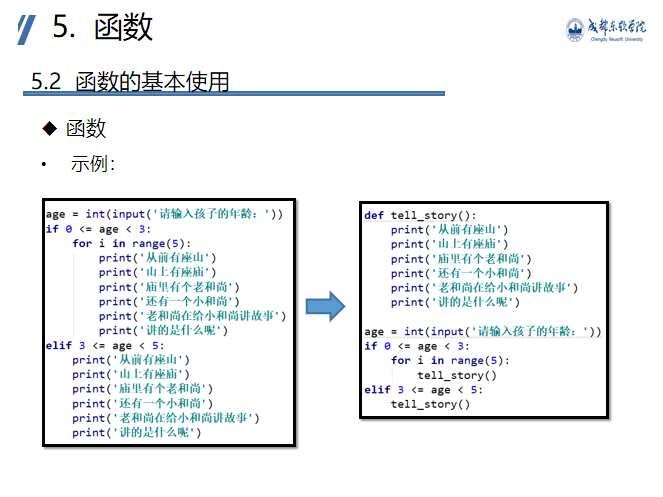
Function concept

Example:
Title:


Parameters of function


Error prone questions:
1)

2)
a=1: keyword parameter
*args: variable position parameter
**args: variable keyword parameter
def f1(a,*b,c=1,**d):
The keyword parameter (a=1,**args) is after the location parameter (* args)
C is right

Return value of function
If a function has no return value, its return is None.
If return is not written, it means that there is no return value

There is no return type and multiple values can be returned:
An example is to return the quotient and remainder of a/b


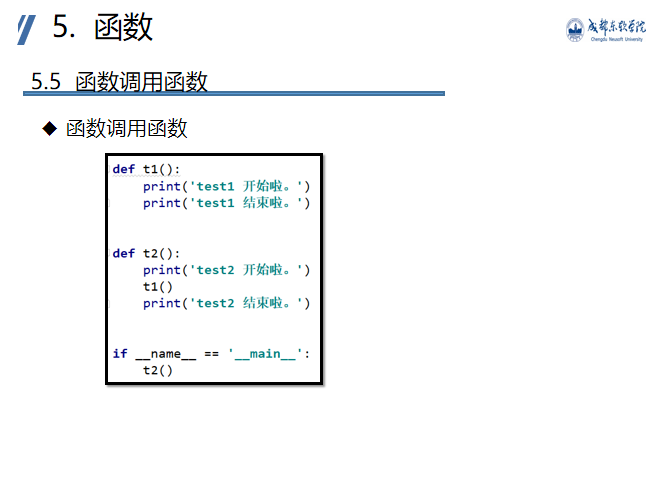
Function call function
Recursive function

Exercise 1 - sum all integers between [n, m)
#1
#Define a function to find the sum of all integers between [n, m).
a= int(input("Please enter the first number"))
b=int(input("Please enter the first number"))
def add(n, m):
count = 0
for i in range(n,m - 1):
count += i
return count
print(add(a,b))
Exercise 2 - factoring n
#2
#Define a function to find the factorial of n.
n=int(input("Please enter a number"))
def factor(n):
count=1
for i in range(1,n+1,1):
count*=i
return count
print(factor(n))
Exercise 3 - sum factorials
#3
#Calculate the sum of factorials. For example, m = 6 1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5! + 6!.
n=int(input("Please enter a number"))
def factor(n):
count=1
for i in range(1,n+1,1):
count*=i
return count
def sum1(n):
sum1 = 0
for i in range(1,n+1,1):
sum1 += factor(i)
return sum1
print(sum1(n))
Local and global variables

Code example:

To view local and global variables:

In python, only functions can split scopes:
Only local variables are defined in the function, and others are global variables

Function Comments

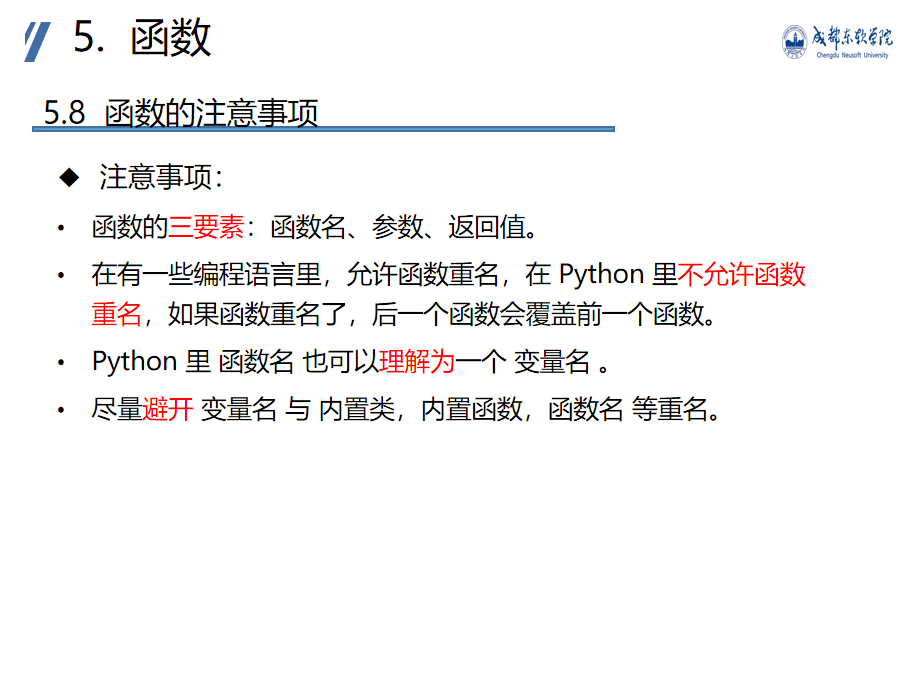
Function considerations
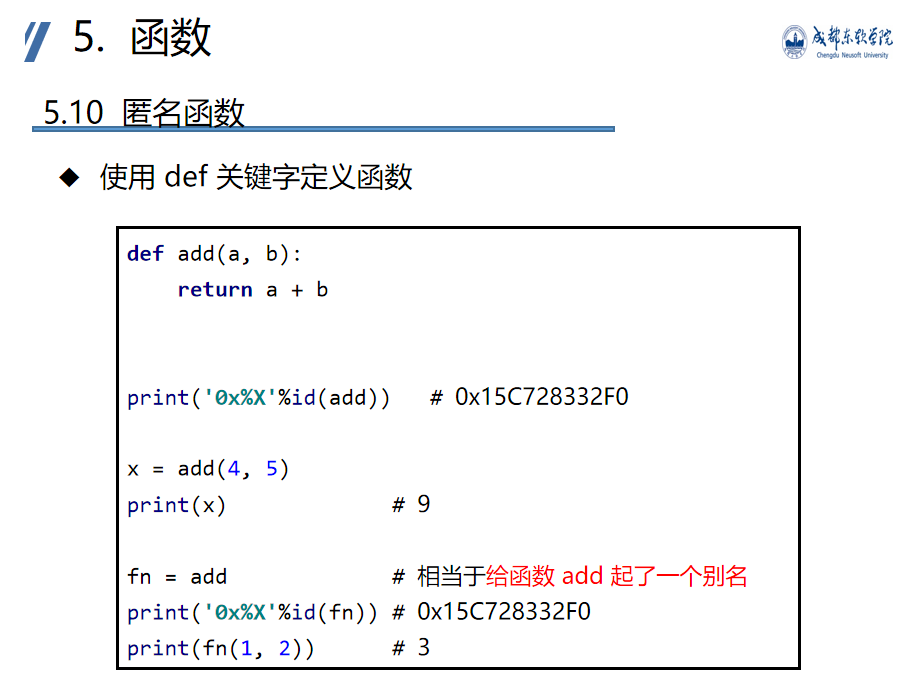
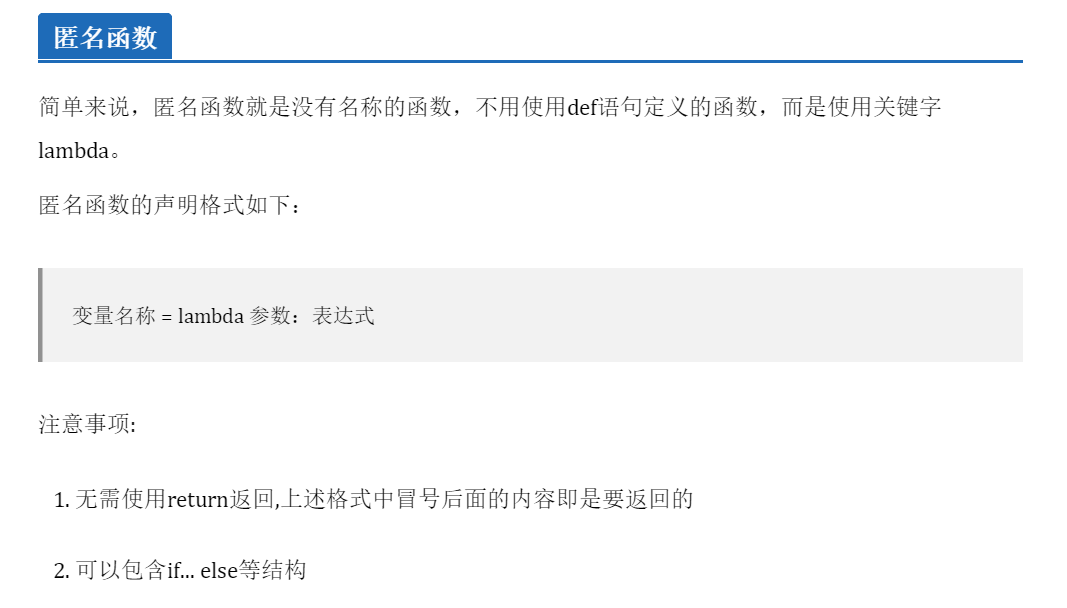
Anonymous function


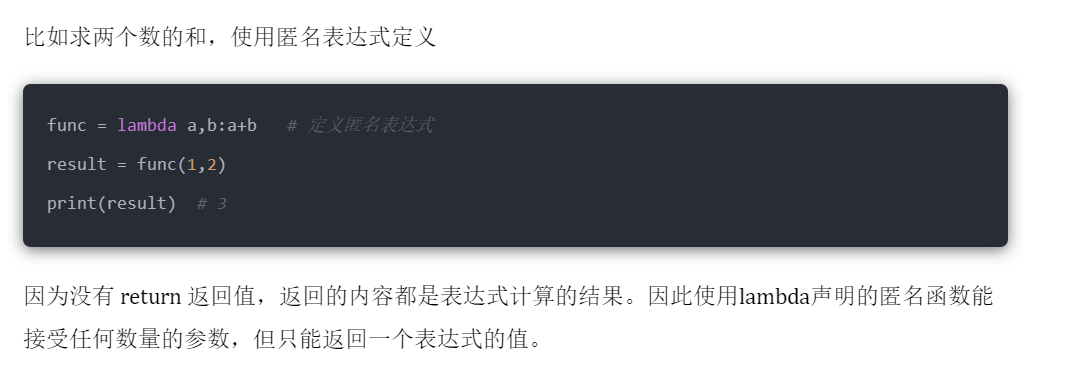
Example:

list1 = [{"a": 10, "b": 20}, {"a": 20, "b": 20}, {"a": 50, "b": 20}, {"a": 6, "b": 20}, {"a": 9, "b": 20}]
# a in that list is the largest
max_value = max(list1, key=lambda x: x["a"])
print(max_value)
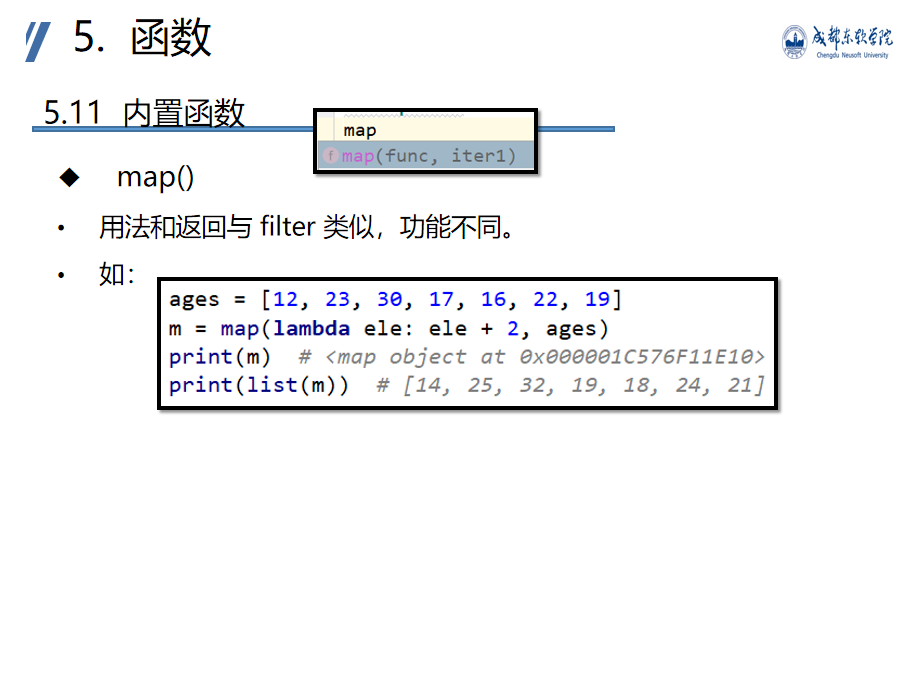
Built in function
Anonymous functions are used in built-in functions and built-in classes
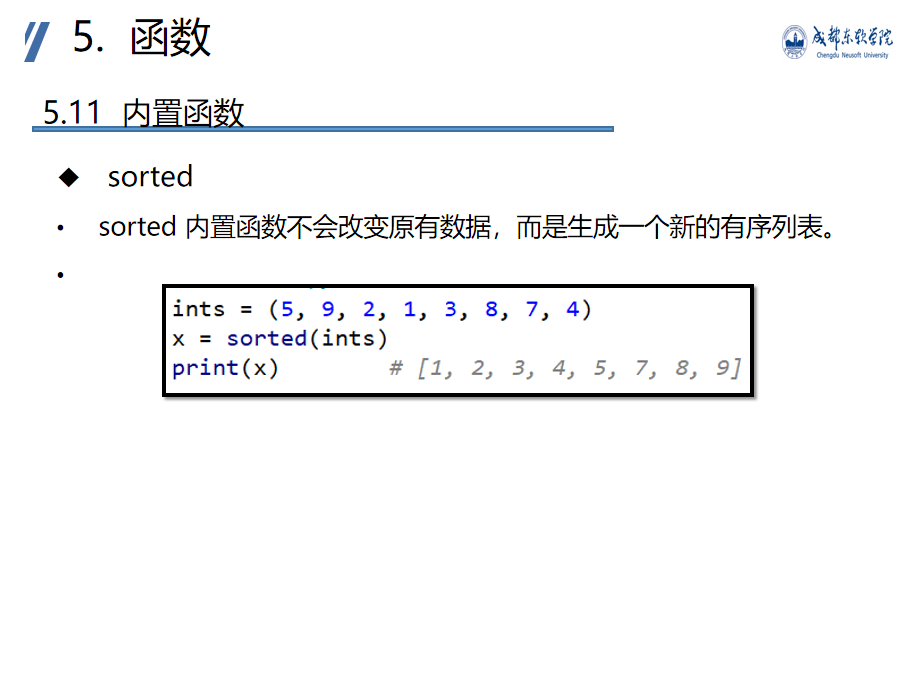
sorted(Iterable, key= None, reverse = False)
Iterable: sort rule (sort function). Within sorted, each element in the iteratable object will be passed to the parameters of this function. Sort according to the result of function operation
Reverse: whether it is in reverse order. True: reverse order False: positive order key: anonymous functions can be used
Example:
Now there is a dictionary {Xiao Hong: 20, Xiao Ming: 18, Xiao Yu: 19, Xiao Xue: 22, Xiao Dong: 17}, which is sorted by age
dict1 = {'Xiao Hong':20,'Xiao Ming':18,'Small fish':19,'light snow':22,'Xiaodong':17}
order_dict = sorted(dict1.items(),key=lambda s:s[1])
print(dict(order_dict))
# order_dict is a list [('xiaodong ', 17), ('xiaoming', 18), ('xiaoyu ', 19), ('xiaohong', 20), ('xiaoxue ', 22)], so it needs to be converted into a dictionary
In the above case, the key uses the anonymous function to formulate the sorting conditions, that is, the return value of lambda is the sorting condition, and the default is ascending
Example 2;
# Sort by quantity
goods = [('Anti hair loss Shampoo', 60, 3), ('Plaid Shirt', 156, 1), ('Jeans', 99, 7), ('sneakers', 299, 2)]
goods = sorted(goods, key=lambda g: g[2], reverse=True) # Set to descending order
print(goods)
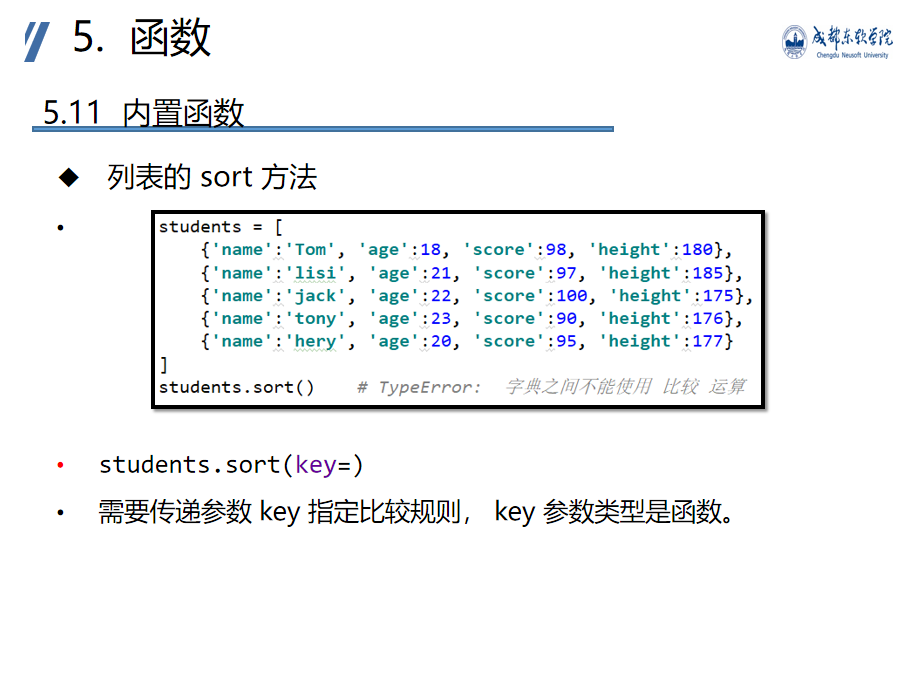


Syntax: filter(function. Iterable)
Function: a function used for filtering. In the filter, it will automatically pass the elements in iterable to function. Then judge whether you want to keep this data according to the return or False of function
iterable: iteratable object

Supplement:
isinstance(object, classinfo) determines whether the instance is of this type
object is a variable
classinfo is a type (tuple,dict,int,float)

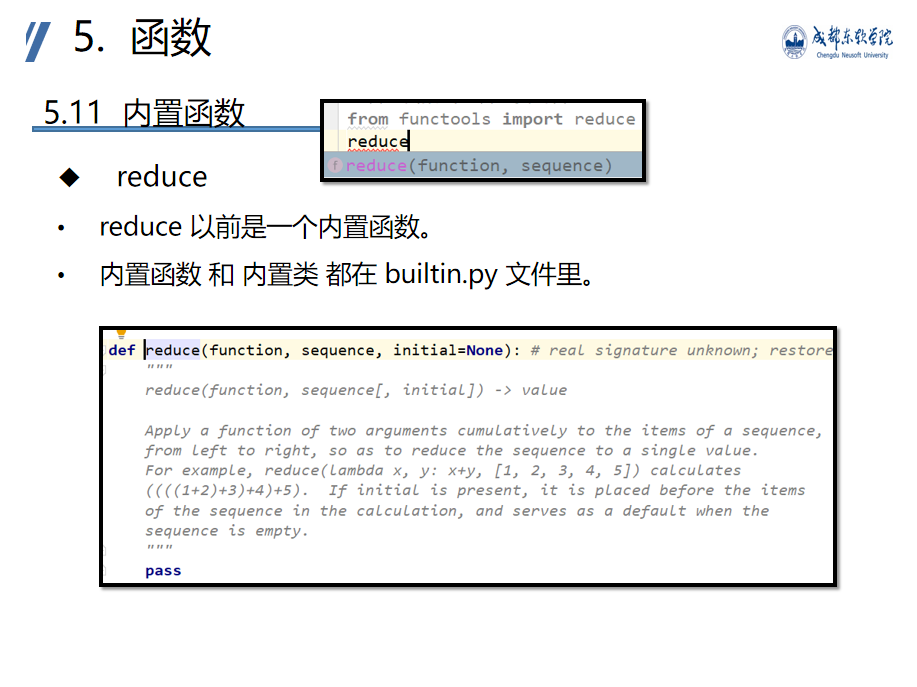


from functools import reduce list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] value = reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, list1) print(value) # 28 = 1+2+3+4+5+6+7



Example:
max() and min():
dict1 = {'Xiao Hong':20,'Xiao Ming':18,'Small fish':19,'light snow':22,'Xiaodong':17}
result = max(dict1.items(),key=lambda s:s[1])
print(result)
result = min(dict1.items(),key=lambda s:s[1])
print(result)