Python's operation of Excel requires the support of third-party libraries. If you want to be compatible with Excel files in xls format before Excel 2007, you can use third-party libraries xlrd and xlwt. The former is used to read Excel files and the latter is used to write Excel files. If you use a newer version of Excel, that is, Excel files in xlsx format, you can also use the openpyxl library.
Reading and writing Excel files
Read Excel file
For example, there is an Excel file named "Alibaba 2020 stock data. xls" in the resources folder under the current folder. If you want to read and display the contents of the file, you can complete it through the code shown below.
import xlrd
# Workbook -- > an Excel file -- > Workbook
wb = xlrd.open_workbook('resources/Alibaba stock data in 2020.xls')
# Get the names of all worksheets
print(wb.sheet_names())
# Get the specified worksheet -- > worksheet
# sheet = wb.sheet_by_name('stock data ')
sheet = wb.sheet_by_index(0)
# Gets the number of rows and columns of the form
print(sheet.nrows, sheet.ncols)
# Gets the specified row
print(sheet.row(0))
# Get the specified row. You can add two parameters to specify the column to column of the row
print(sheet.row_slice(0, start_colx=0, end_colx=3))
# Gets the specified column
print(sheet.col(4))
print(sheet.col_slice(1, start_rowx=2, end_rowx=4))
# Get cell data
cell = sheet.cell(2, 2)
print(type(cell))
print(cell.value)
# Traverse the entire form
print(f'Transaction date\t\t\t Highest price\t minimum price\t Opening price\t Closing price\t Turnover\t\t Adjust closing price')
for row in range(1, sheet.nrows):
for col in range(sheet.ncols):
value = sheet.cell(row, col).value
if col == 0:
# Process the time and date into six tuples, and then take the month, year and day
# year, month, day, *_ = xlrd.xldate_as_tuple(value, 0)
# print(f'{year} year {month: 0 > 2D} month {day: 0 > 2D}', end='\t')
# Get the time date object and format the date
curr_date = xlrd.xldate_as_datetime(value, 0)
print(curr_date.strftime('%Y year%m month%d day'), end='\t')
elif col == 5:
print(f'{int(value):<10d}', end='\t')
else:
print(f'{value:.2f}', end='\t')
print()
There is an Excel file named "Alibaba 2020 stock data. xlsx" under the resources folder under the current folder. If you want to read and display the contents of the file, you can complete it through the code shown below.
import datetime
import openpyxl
# Load a workbook -- > Workbook
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook('resources/Alibaba stock data in 2020.xlsx')
print(type(wb))
# Gets the name of the worksheet
print(wb.sheetnames)
# Get worksheet
sheet = wb.worksheets[0]
print(type(sheet))
# Get the number of form columns and rows
print(sheet.max_row, sheet.max_column)
# Dimension of cell
print(sheet.dimensions)
# Take the value of the cell
print(sheet.cell(3, 3).value)
print(sheet['C3'].value)
print(sheet['G255'].value)
# Loop through all cells
for row_ch in range(1, 256):
for col_ch in 'ABCDEFG':
value = sheet[f'{col_ch}{row_ch}'].value
if type(value) == datetime.datetime:
print(value.strftime('%Y year%m month%d day'), end='\t')
elif type(value) == int:
print(f'{value:<10d}', end='\t')
elif type(value) == float:
print(f'{value:.4f}', end='\t')
else:
print(value, end='\t')
print()
# for row in range(2, sheet.max_row):
# for col in range(1, sheet.max_column + 1):
# value = sheet.cell(row, col).value
# if col == 1:
# print(value.strftime('%Y year% m month% d'), end='\t')
# elif col == 6:
# print(f'{value:<10d}', end='\t')
# else:
# print(f'{value:.4f}', end='\t')
# print()
# for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2):
# for cell in row:
# value = cell.value
# if type(value) == datetime.datetime:
# print(value.strftime('%Y year% m month% d'), end='\t')
# elif type(value) == int:
# print(f'{value:<10d}', end='\t')
# elif type(value) == float:
# print(f'{value:.4f}', end='\t')
# else:
# print(value, end='\t')
# print()
There are three ways to traverse all cells
Write Excel file
The following code implements the operation of writing the test scores of 5 students and 3 courses into Excel file (xls), and sets the style for the header.
import random
import xlwt
# Set style
header_style = xlwt.XFStyle()
header_pattern = xlwt.Pattern()
header_pattern.pattern = xlwt.Pattern.SOLID_PATTERN
# header_pattern.pattern_back_colour = xlwt.Style.colour_map['coral']
header_pattern.pattern_fore_colour = xlwt.Style.colour_map['aqua']
header_style.pattern = header_pattern
# Set font
header_font = xlwt.Font()
header_font.height = 20 * 22
header_font.bold = True
header_style.font = header_font
header_alignment = xlwt.Alignment()
# Vertical alignment
header_alignment.vert = xlwt.Alignment.VERT_CENTER
header_alignment.horz = xlwt.Alignment.HORZ_CENTER
header_style.alignment = header_alignment
# Step 1: create a workbook
wb = xlwt.Workbook()
# Step 2: add worksheet
sheet = wb.add_sheet('Final exam ') # type: xlwt.Worksheet
# Step 3: write data to the cell
titles = ('full name', 'language', 'mathematics', 'English')
for col_index, title in enumerate(titles):
sheet.write(0, col_index, title, header_style)
names = ('indigo plant', 'Xiao Hong', 'Xiaobai', 'Xiao Rong', 'Blue ')
for row_index, name in enumerate(names):
sheet.write(row_index + 1, 0, name)
for i in range(3):
sheet.write(row_index + 1, i + 1, random.randrange(50, 101))
# Step 4: save Workbook
wb.save('resources/Grade one class two examination result sheet.xls')
After running, open the file as follows:
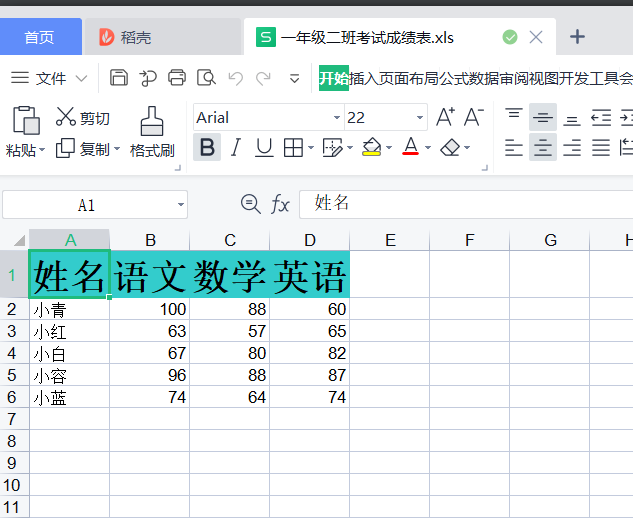
The following code implements the operation of writing the test scores of 5 students and 3 courses into Excel file (xlsx).
import random
import openpyxl
# Step 1: create a workbook
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
# Step 2: add worksheet (activate the created form)
sheet = wb.active
sheet.title = 'Final exam '
# Step 3: write data to the cell
titles = ('full name', 'language', 'mathematics', 'English')
for col_index, title in enumerate(titles):
sheet.cell(1, col_index + 1, title)
names = ('indigo plant', 'Xiao Hong', 'Xiaobai', 'Xiao Rong', 'Blue ')
for row_index, name in enumerate(names):
sheet.cell(row_index + 2, 1, name)
for i in range(3):
sheet.cell(row_index + 2, i + 2, random.randrange(50, 101))
# Step 4: save Workbook
wb.save('resources/Grade one class two examination result sheet.xlsx')
Note: workbooks created with openpyxl library will automatically generate a form. You can activate the form directly or add a new form. When traversing, the row index and column index start from 1.
For Excel files in xlsx format, add style codes as follows:
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.styles import Alignment, Font, Border, Side
alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center')
side = Side(color='ff7f50', style='mediumDashed')
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook('resources/Grade one class two examination result sheet.xlsx')
sheet = wb.worksheets[0]
# Change column width
sheet.column_dimensions['E'].width = 120
# Career change height
sheet.row_dimensions[1].height = 30
sheet['E1'] = 'average'
sheet.cell(1, 5).font = Font(size=18, bold=True, color='ff1493', name='HYj1gf')
sheet.cell(1, 5).alignment = alignment
sheet.cell(1, 5).border = Border(left=side, top=side, right=side, bottom=side)
for i in range(2, 7):
sheet[f'E{i}'] = f'=average(B{i}:D{i})'
sheet.cell(i, 5).font = Font(size=12, color='4169e1', italic=True)
sheet.cell(i, 5).alignment = alignment
wb.save('resources/Statistical table of examination results.xlsx')
The effects are as follows:
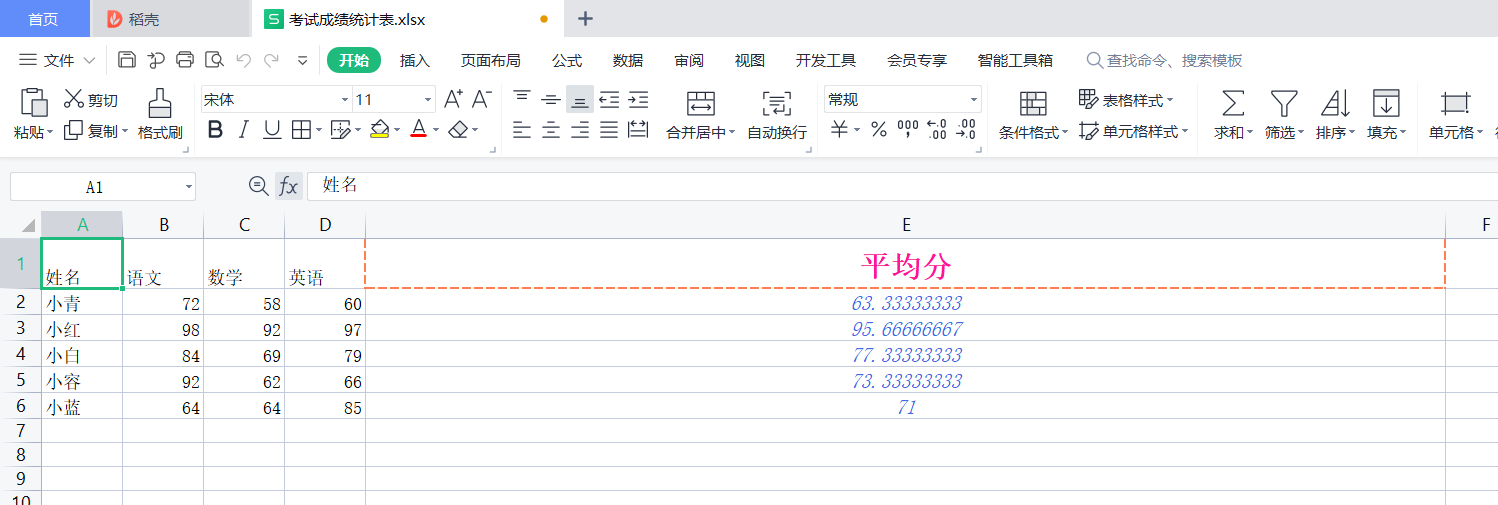
Formula calculation
Open the previously written "grade 1, class 2 examination result sheet. xls" file, calculate everyone's average score and fill in the last column.
You can use the Formula of Excel to calculate. We can first use xlrd to read the excel folder, and then use the copy function provided by a third-party library named xlutils to convert the read excel file into a Workbook object for writing. When calling the write method, we can write a Formula object into the cell.
import xlwt
import xlrd
from xlutils.copy import copy
wb1 = xlrd.open_workbook('resources/Grade one class two examination result sheet.xls')
wb2 = copy(wb1)
sheet = wb2.get_sheet(0)
sheet.write(0, 4, 'average')
for row_index in range(1, 6):
sheet.write(row_index, 4, xlwt.Formula(f'average(B{row_index + 1}:D{row_index + 1})'))
wb2.save('resources/Grade one class two examination result sheet.xls')